Genetics and Meiosis Worksheet
Genetics and meiosis are complex concepts that can sometimes be challenging to understand. If you're a student or educator looking for a useful resource to reinforce your knowledge on these topics, a genetics and meiosis worksheet can be incredibly beneficial. Created specifically for students studying genetics or biology, these worksheets provide a comprehensive review of key concepts and allow you to practice your understanding through a variety of engaging exercises.
Table of Images 👆
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Study Guide Answers Chapter 10 Mendel and Meiosis
- Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Answers
- Chromosomes and Meiosis Reinforcement Worksheet Answers
- Mendelian Genetics Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Biology Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Sickle Cell Anemia Mutation Worksheet Answers
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Vocabulary
- Meiosis Coloring Worksheet
- Meiosis vs Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- AP Biology Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- 11 4 Meiosis Worksheet Answers
- Meiosis Matching Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is genetics?
Genetics is the branch of biology that studies genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms. It involves the study of how traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes, which are segments of DNA that encode specific traits. Genetics plays a crucial role in understanding inherited traits, genetic disorders, evolutionary processes, and the development of new medical treatments.
What is meiosis?
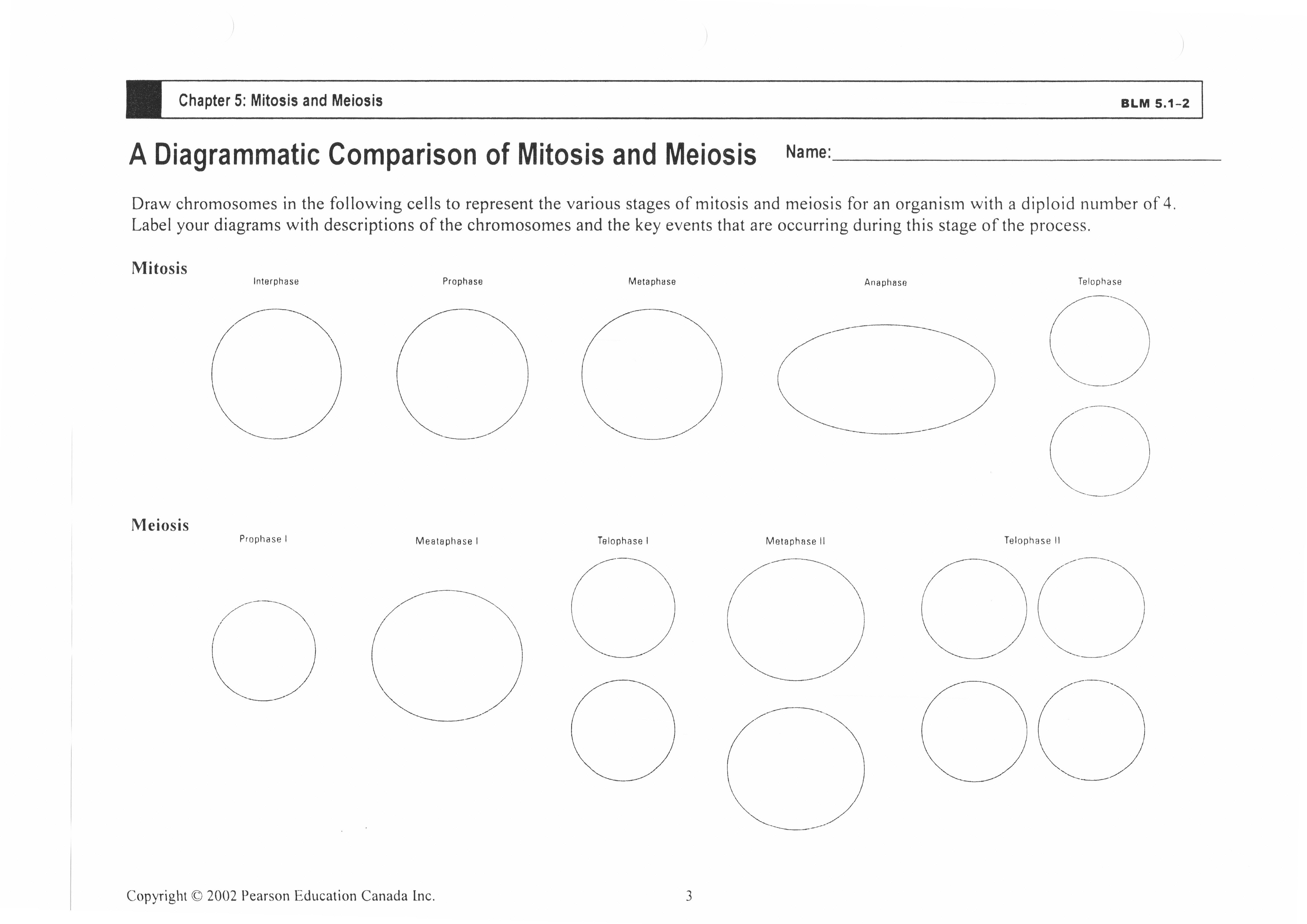
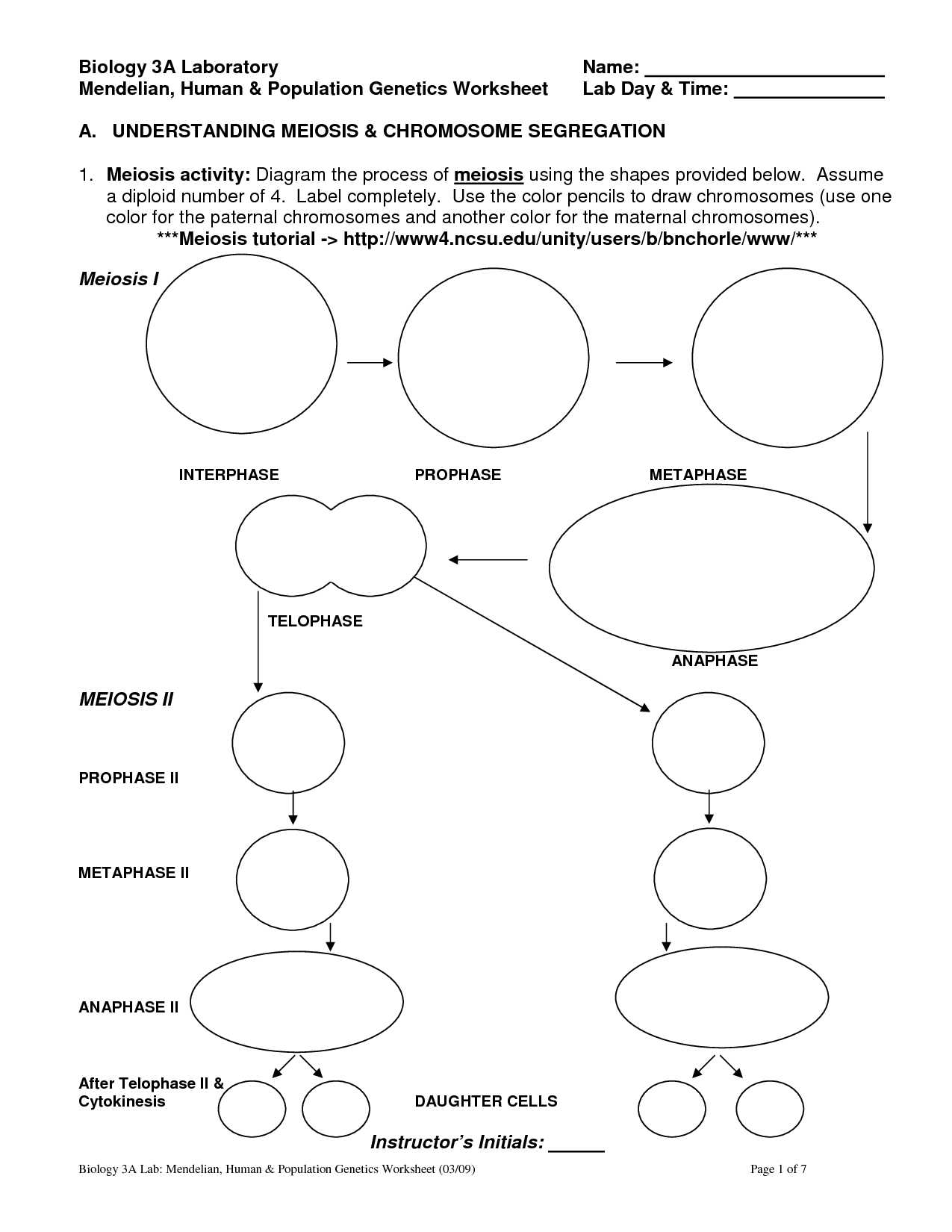
Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms, resulting in the production of haploid gametes (sex cells) with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This process involves two rounds of division, meiosis I and meiosis II, which produce four daughter cells that are genetically distinct from each other and the original parent cell. Meiosis plays a crucial role in genetic variation and maintaining the chromosome number across generations.
What is the purpose of meiosis in sexual reproduction?
The purpose of meiosis in sexual reproduction is to generate genetically diverse gametes (sperm and eggs) with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This ensures that when two gametes fuse during fertilization, the resulting zygote has the full complement of chromosomes and genetic variation necessary for survival and adaptation in changing environments.
How does meiosis differ from mitosis?
Meiosis differs from mitosis in that meiosis involves two rounds of cell division resulting in four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while mitosis involves a single round of cell division resulting in two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Additionally, meiosis is responsible for the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells) for sexual reproduction, while mitosis is responsible for growth, development, and tissue repair in multicellular organisms.
What are homologous chromosomes?
Homologous chromosomes are a pair of chromosomes that contain the same genes but may have different versions of those genes. They are inherited from each parent and are structurally similar, with the same size, shape, and gene positions. Homologous chromosomes play a crucial role in genetic inheritance and are involved in processes such as crossing over during meiosis, leading to genetic diversity in offspring.
What is the significance of crossing over in meiosis?
Crossing over in meiosis is significant because it results in the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes, leading to genetic diversity. This process shuffles genetic information, creating new combinations of alleles on chromosomes that are passed down to offspring. Ultimately, crossing over increases variation within a population, which is crucial for evolution as it produces individuals with unique genetic characteristics and adaptations that may be advantageous for survival and reproduction.
Explain the process of independent assortment in meiosis.
Independent assortment is the process in which homologous chromosomes randomly line up in metaphase I of meiosis, leading to different combinations of alleles being passed on to offspring. This random alignment results in a unique combination of maternal and paternal chromosomes in each gamete, increasing genetic diversity by creating different combinations of alleles that may be passed on to the next generation. Additionally, the random assortment of chromosomes leads to different genetic traits being inherited independently of each other, contributing further to genetic variation within a population.
What is a haploid cell?
A haploid cell is a type of cell that contains a single set of chromosomes, which means it has half the number of chromosomes found in a diploid cell. In humans, haploid cells are typically found in sex cells (sperm and egg cells) and are produced through the process of meiosis. When haploid sex cells combine during fertilization, they form a diploid zygote that will develop into a new organism.
How do gametes form in meiosis?
Gametes form in meiosis through a process that involves two rounds of cell division (meiosis I and meiosis II) resulting in the formation of four genetically unique haploid cells. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over, leading to genetic recombination. The chromosomes then separate into two different cells. In meiosis II, the sister chromatids of each chromosome are separated, resulting in the formation of four daughter cells, each containing only one set of chromosomes. These daughter cells are the gametes, which are haploid and genetically diverse due to the crossing over event that occurred during meiosis I.
What are some potential genetic variations that can occur through meiosis?
Some potential genetic variations that can occur through meiosis include genetic recombination (crossing over) between homologous chromosomes, independent assortment of chromosomes during metaphase I, and random fertilization of gametes during sexual reproduction. These processes result in the creation of genetically diverse offspring with unique combinations of alleles inherited from the parents.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments