Gene and Chromosome Mutation Worksheet
Gene and chromosome mutation worksheets provide a valuable learning resource for biology students looking to deepen their understanding of genetics and inheritance. These worksheets are designed to provide practice and reinforcement of key concepts related to gene and chromosome mutations, making them an ideal tool for high school or college-level biology courses.
Table of Images 👆
- Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answer Key
- Gene and Chromosome Mutation Worksheet Answer
- DNA Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Gene Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Sickle Cell Anemia Mutation Worksheet Answers
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Vocabulary
- Chromosomal Mutations Worksheet
- Genetics Heredity Worksheets
- Gene Expression Worksheet Answers
- Chromosome Mutation Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is a gene mutation?
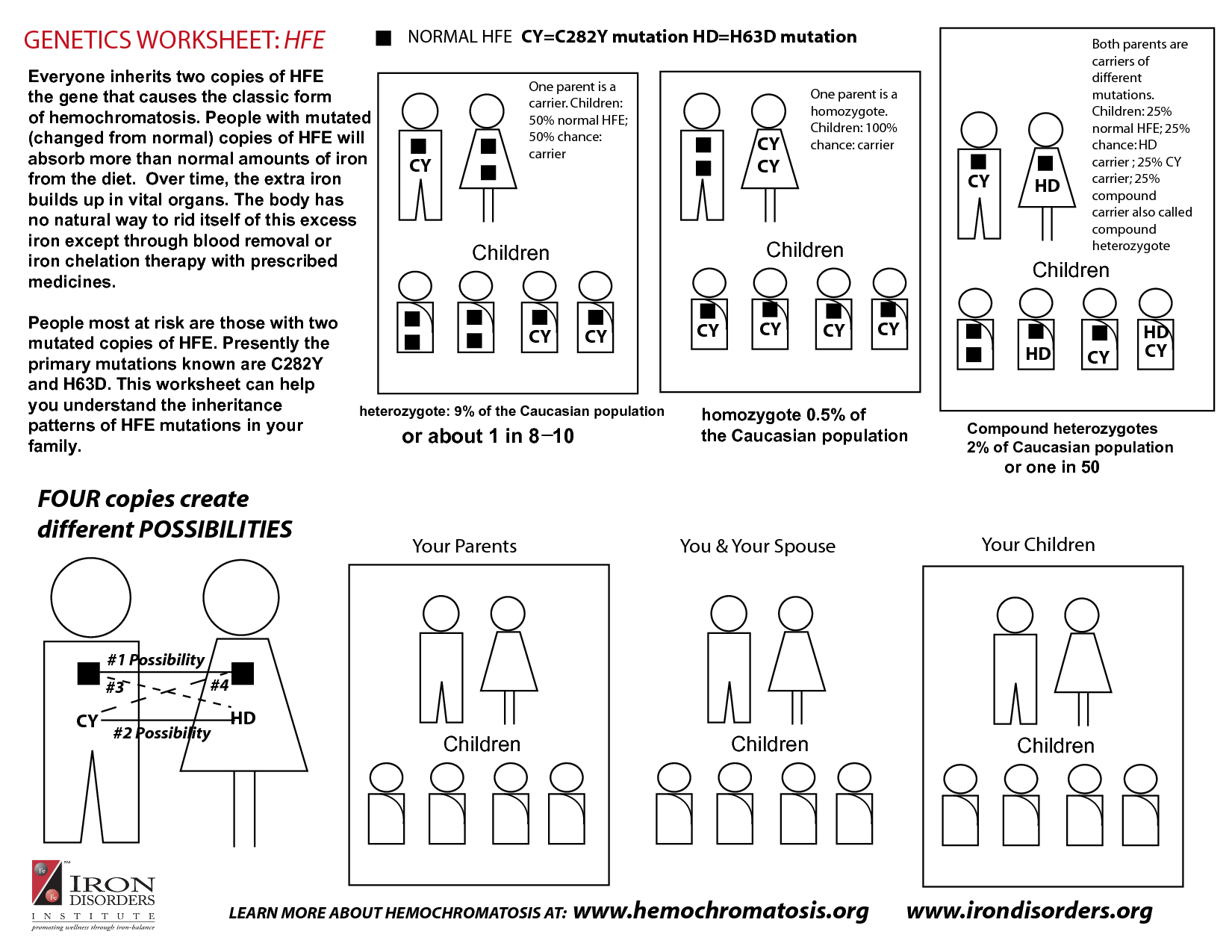
A gene mutation is a permanent alteration in the DNA sequence within a gene, which can result in a change in the gene's function or expression. Mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, such as errors during DNA replication, exposure to UV radiation, or chemical damage. Some mutations can be beneficial, leading to genetic diversity and evolution, while others can be harmful, causing genetic disorders or diseases.
How do gene mutations occur?
Gene mutations can occur through various mechanisms, including spontaneous errors during DNA replication, exposure to mutagenic agents such as chemicals or radiation, or through genetic recombination. These mutations can result in changes to the genetic code, leading to alterations in the proteins produced by the affected gene, potentially causing genetic disorders or contributing to the development of diseases such as cancer.
What are the types of gene mutations?
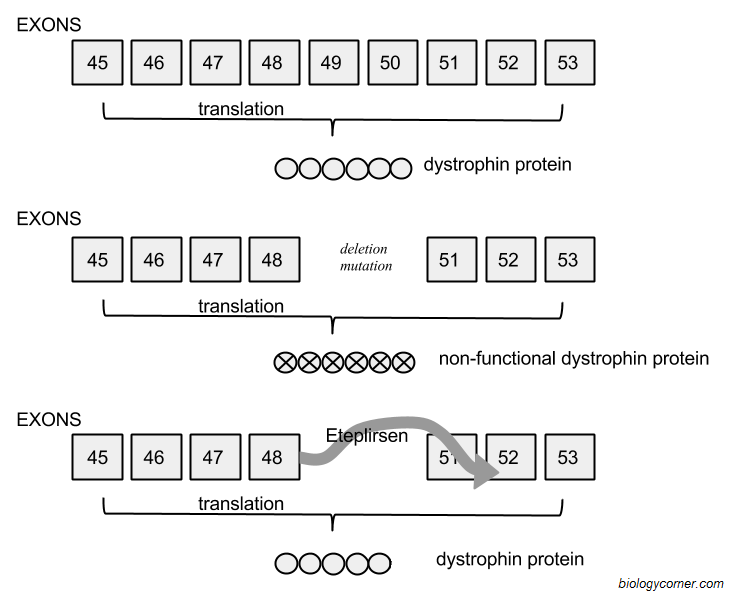
There are several types of gene mutations, including point mutations (such as substitutions, insertions, and deletions), chromosomal mutations (such as inversions, duplications, and translocations), and gross mutations (such as aneuploidy and polyploidy). These mutations can lead to various genetic disorders and diseases by altering the normal functioning of genes.
What are the consequences of gene mutations?
Gene mutations can lead to a variety of consequences, depending on the specific gene affected and the nature of the mutation. Some mutations can cause genetic disorders or diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia. Others can increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer. In some cases, gene mutations may have no noticeable effect. Additionally, mutations can sometimes be passed down to future generations, potentially affecting the health and well-being of offspring. Overall, gene mutations can result in a range of outcomes from mild to severe, with significant implications for an individual's health and genetic inheritance.
What is a chromosome mutation?
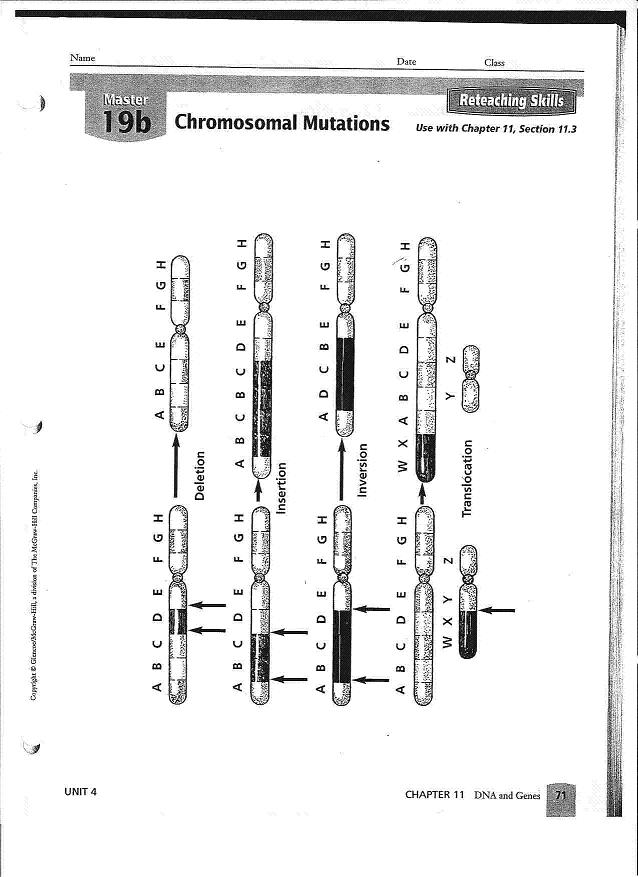
A chromosome mutation is a change in the structure or number of chromosomes in an organism's cells. These mutations can involve the deletion, duplication, inversion, or translocation of genetic material within a chromosome, or the gain or loss of entire chromosomes. Chromosome mutations can lead to genetic disorders, developmental abnormalities, or changes in an organism's physical characteristics.
How do chromosome mutations occur?
Chromosome mutations can occur through a variety of mechanisms such as errors during DNA replication, exposure to mutagenic agents like radiation or certain chemicals, or through genetic recombination during meiosis. These mutations may result in changes to the structure or number of chromosomes, leading to genetic disorders or abnormalities.
What are the types of chromosome mutations?
The types of chromosome mutations include deletions (loss of part of a chromosome), duplications (presence of extra copies of a part of a chromosome), inversions (reversing the direction of a part of a chromosome), translocations (movement of a segment of one chromosome to another chromosome), and aneuploidy (addition or loss of an entire chromosome). These mutations can lead to genetic disorders and can affect an individual's health and development.
What are the consequences of chromosome mutations?
Chromosome mutations can lead to a range of consequences, including genetic disorders, birth defects, developmental delays, and an increased risk of certain diseases such as cancer. These mutations can disrupt the normal functioning of an individual's cells, potentially affecting their growth, development, and overall health. Some chromosome mutations may also be incompatible with life, leading to miscarriages or stillbirths. Overall, chromosome mutations can have significant impacts on an individual's physical and/or cognitive well-being.
How do gene mutations differ from chromosome mutations?
Gene mutations are changes in the DNA sequence of a gene, which can alter the protein products that are created. On the other hand, chromosome mutations involve changes in the structure or number of chromosomes, which can result in larger-scale alterations in genetic material, such as deletions, duplications, inversions, or translocations. While gene mutations impact individual genes, chromosome mutations can affect multiple genes or larger regions of the genome.
Why is understanding gene and chromosome mutations important in studying genetics?
Understanding gene and chromosome mutations is crucial in studying genetics because they play a significant role in genetic variation, inherited diseases, and evolution. Mutations in genes can lead to changes in proteins, which can affect an individual's traits and susceptibility to diseases. Chromosome mutations, such as deletions or duplications, can also have profound effects on an organism's development and health. By studying these mutations, researchers can gain valuable insights into the mechanisms of inheritance, genetic disorders, and the evolutionary processes that shape the diversity of life on Earth.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments