Forces at Worksheet
Worksheets are a valuable tool for educators and students alike, as they provide a structured approach to learning and allow for practice and reinforcement of key concepts. Designed to cater to a specific subject or topic, worksheets serve as an entity that guides individuals in their educational journey. With a focus on organization and comprehension, worksheets offer a clear and concise format for suitable target audiences seeking a hands-on approach to learning.
Table of Images 👆
- Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Worksheet Answers
- Science Force and Motion Worksheets
- Force and Acceleration Worksheet Answers
- Force and Motion Worksheets 5th Grade
- Science Worksheets Force
- Forces Worksheets Middle School
- Friction Force Worksheet
- Force and Gravity Worksheet
- Friction Force Worksheet
- Impulsive Force Model Worksheet 2 Answers
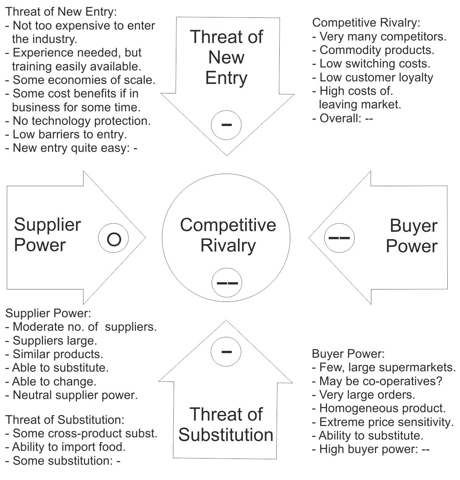
- Porters Five Forces Analysis
- Speed Word Problems Worksheet
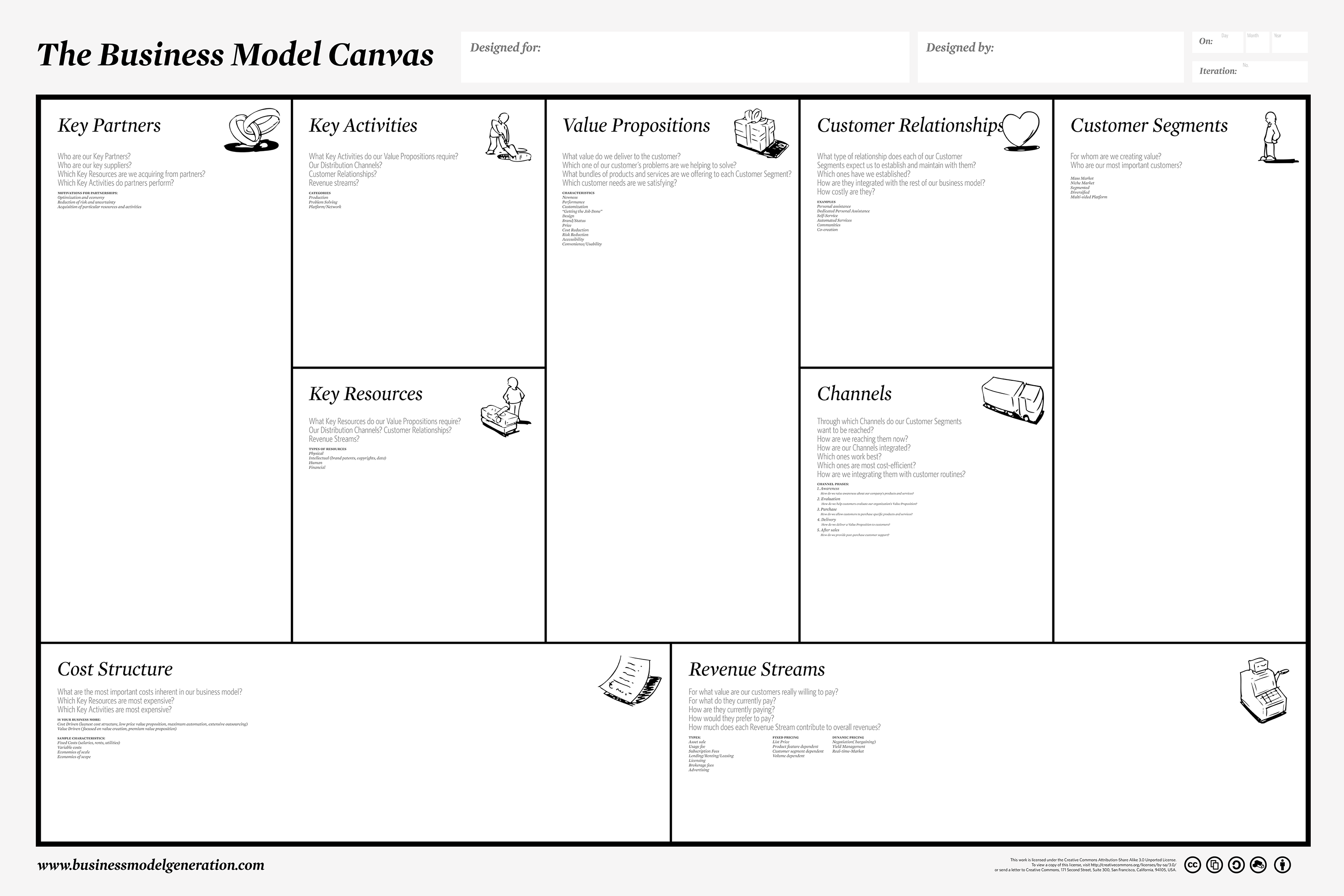
- Business Model Canvas Template
- Long and Short-Term Goals Essay Examples
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is a force?
A force is a push or pull that can cause an object to move, change direction, or deform. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction, and is typically measured in units such as newtons (N). Forces can be exerted through direct contact (contact force) or from a distance without physical touch (field force), such as gravity or electromagnetic forces.
What is the SI unit of force?
The SI unit of force is the newton (N).
Describe the difference between contact forces and non-contact forces.
Contact forces require physical contact between objects to occur, such as friction, tension, or normal forces. On the other hand, non-contact forces act even when objects are not in contact, like gravity, magnetic forces, or electrostatic forces. Contact forces involve direct interaction between objects, while non-contact forces can act over a distance without physical touch or direct contact.
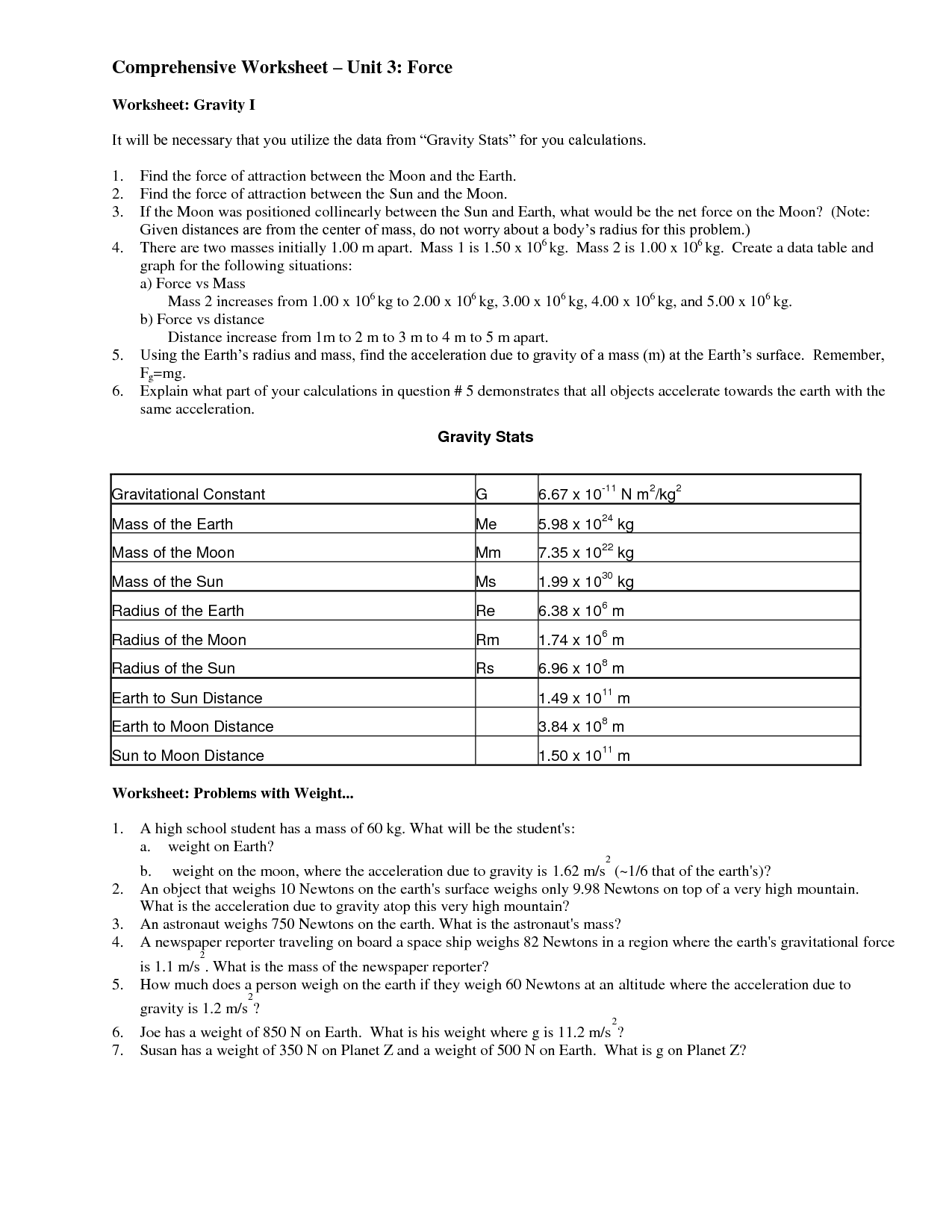
What is gravitational force? Give an example.
Gravitational force is the attractive force that exists between two masses due to their mass and distance from each other. An example of gravitational force is the force that keeps Earth in orbit around the Sun. The gravitational force between the two objects keeps them moving in their respective orbits.
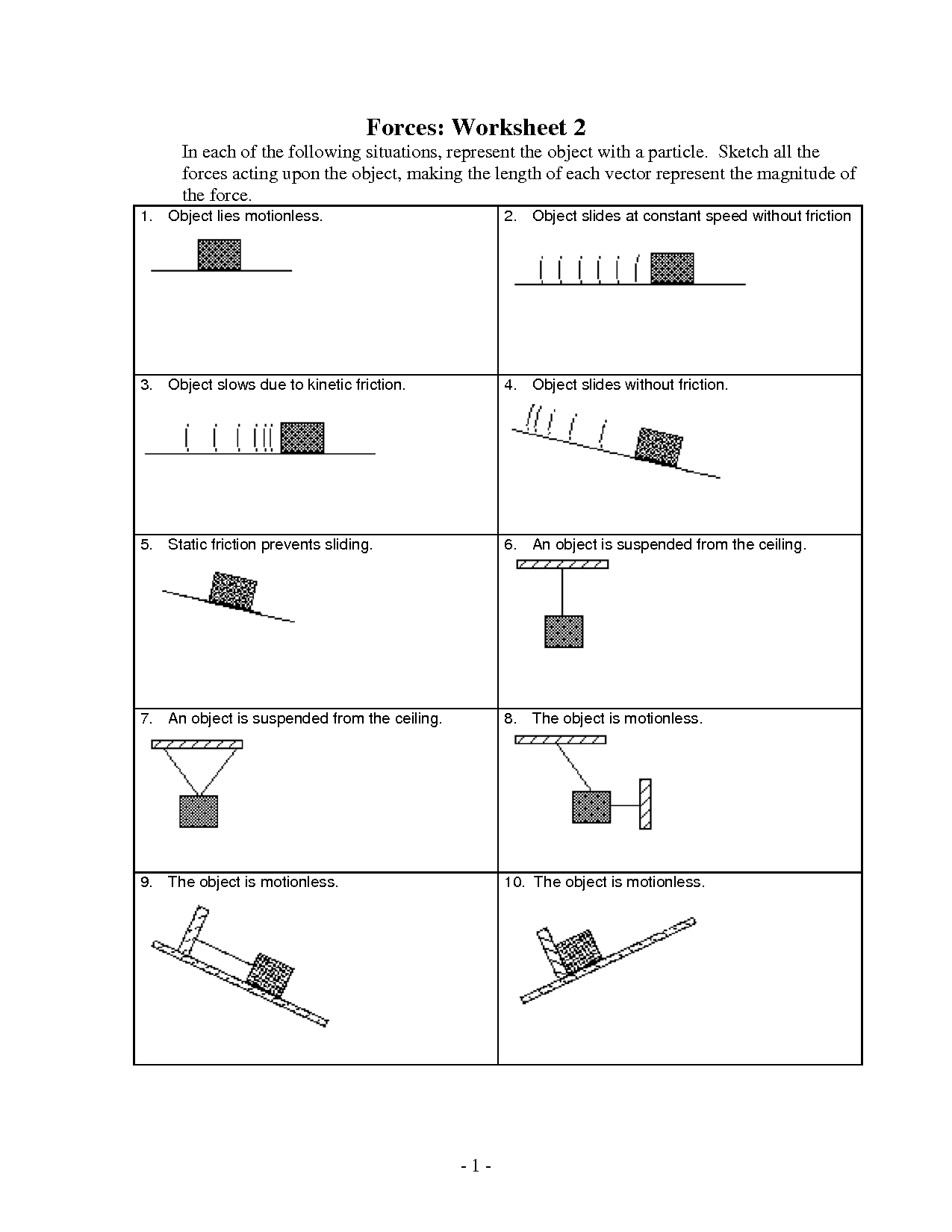
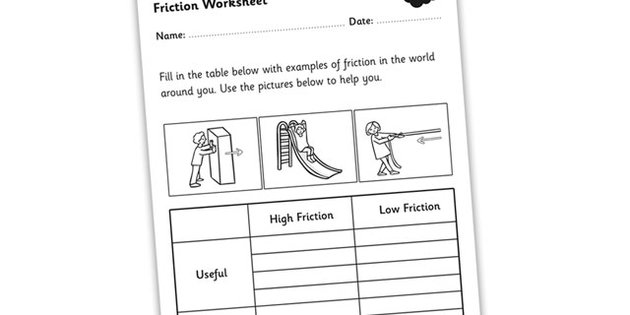
Explain the concept of frictional force.
Frictional force is the force that opposes the relative motion or tendency of such motion between two surfaces in contact. It arises due to the roughness of surfaces and the interactions between molecules at the contact point. Frictional force can act in the direction parallel to the surface of contact, either opposing the motion of an object (static friction) or resisting the motion of an object already in motion (kinetic friction). This force is essential for everyday life as it helps us walk, grip objects, and prevents slipping.
Describe the force of tension with an example.
Tension is a force that is transmitted through a string, rope, or cable when it is pulled tight. For example, when you pull a rope in a game of tug-of-war, the tension force in the rope opposes the force you are applying to it. This tension force can be measured by the amount of force exerted on either end of the rope to keep it taut.
What is the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces?
Balanced forces occur when two equal forces act on an object in opposite directions, resulting in no change in the object's motion. On the other hand, unbalanced forces occur when two unequal forces act on an object in opposite directions, causing a change in the object's motion, such as acceleration or deceleration. Balanced forces result in a state of equilibrium, while unbalanced forces lead to a state of motion or change in motion.
Explain the concept of applied force.
An applied force is a force that is exerted on an object by a person or another object. It is a push or pull that one object applies to another to cause it to move or change in some way. Applied forces can be used to accelerate an object, change its direction, or deform it. The magnitude and direction of the applied force determine how the object will respond, following the laws of motion as described by Newton.
Define the term normal force and provide an example.
The normal force is the force exerted by a surface perpendicular to an object in contact with it. This force prevents the object from falling through the surface due to gravity and is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the force the object exerts on the surface. For example, when a book is placed on a table, the normal force exerted by the table on the book counteracts the gravitational force pulling the book downward, keeping it in place.
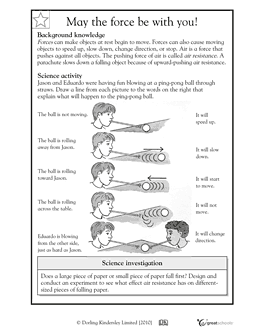
Describe the force of air resistance with an example.
Air resistance is the force that opposes the motion of an object moving through the air. This force increases as the speed of the object increases and is proportional to the surface area of the object. For example, when a skydiver jumps out of a plane, the force of air resistance increases as they pick up speed due to gravity pulling them down. The skydiver needs to overcome this force to reach terminal velocity, where the force of air resistance equals the force of gravity, allowing them to fall at a constant speed.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments