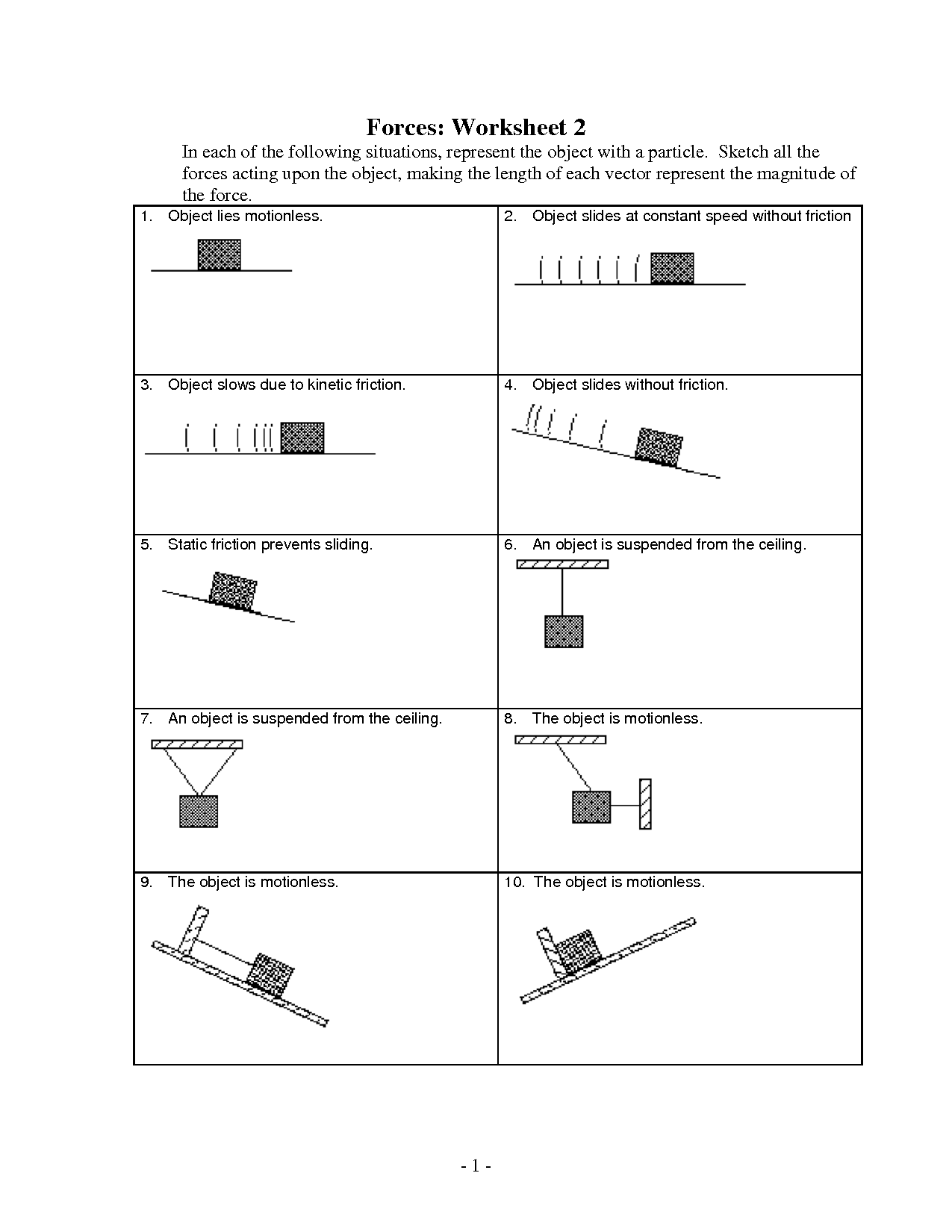
Force Diagrams Worksheet
Entity and subject, in the context of educational tools, are crucial factors to consider for teachers and students alike. When it comes to reinforcing learning and promoting critical thinking skills, worksheets have long been a staple in classrooms. With their structured format and diverse range of topics, worksheets provide a practical and efficient way for students to engage with course material and assess their understanding. Whether you are an educator seeking versatile resources or a student looking to strengthen your knowledge, worksheets can be a valuable tool for both teaching and learning.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
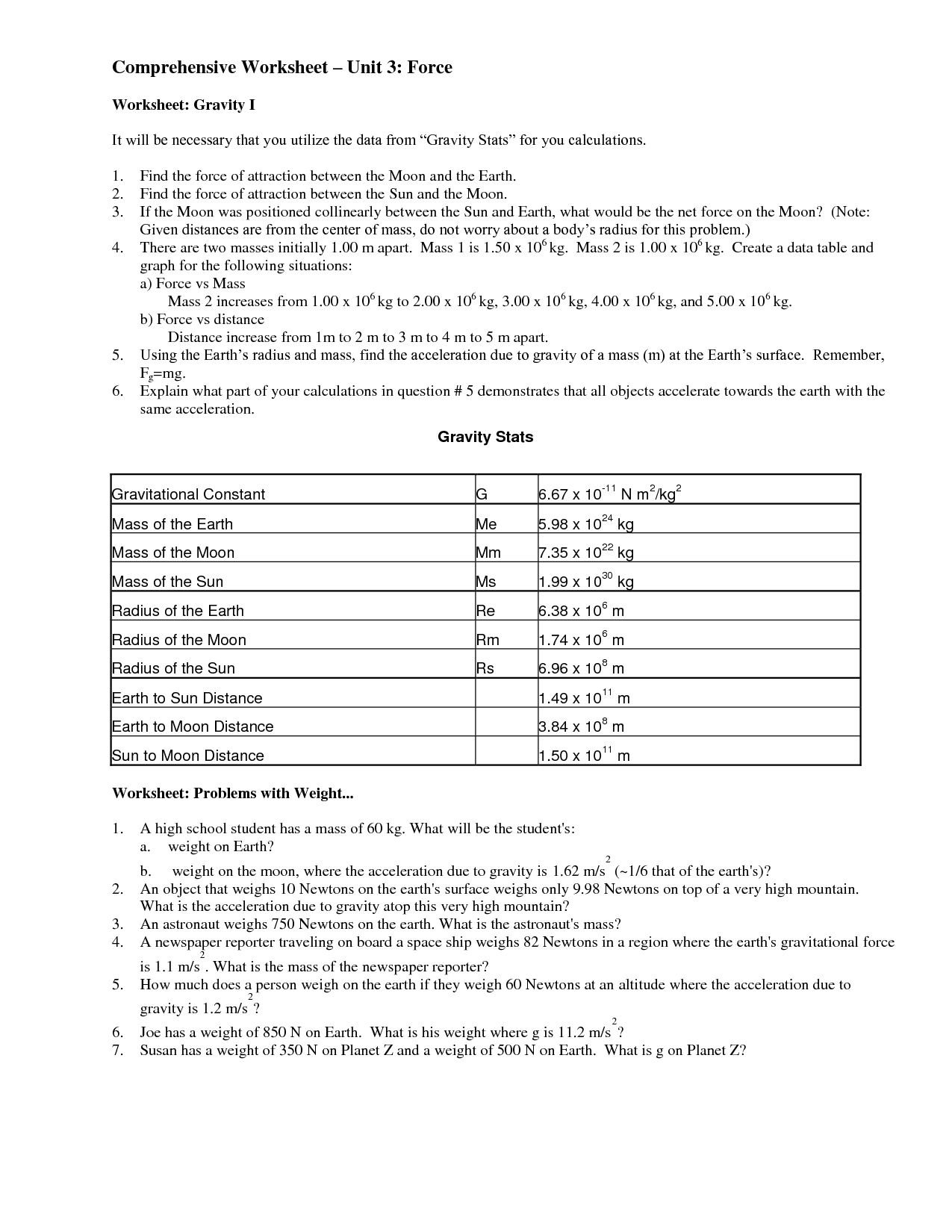
What is the purpose of a force diagram?
A force diagram, also known as a free-body diagram, is used to visually represent and analyze the forces acting on an object or a system. Its purpose is to help identify and understand the different forces at play, their directions, magnitudes, and interactions, enabling a clearer analysis of the forces involved in a given situation and aiding in the determination of the resultant force or motion of the object or system under consideration.
How are forces typically represented in force diagrams?
Forces are typically represented in force diagrams by arrows. The direction of the arrow indicates the direction in which the force is acting, while the length of the arrow represents the magnitude of the force. The forces are labeled with letters or symbols to indicate the type of force, such as gravity (Fg), normal force (Fn), tension (T), or friction (Ff). Additionally, force diagrams often include a coordinate system to help determine the net force acting on an object.
What is the difference between a balanced and unbalanced force diagram?
In a balanced force diagram, the forces acting on an object are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, resulting in no overall change in the object's motion. On the other hand, an unbalanced force diagram shows forces that are not equal and opposite, leading to a change in the object's motion, such as acceleration or deceleration. Balanced force diagrams represent a state of equilibrium, while unbalanced force diagrams illustrate a state of unbalance where there is a resulting movement or change in the object's motion.
How can the size of an arrow in a force diagram indicate the magnitude of a force?
The size of an arrow in a force diagram can indicate the magnitude of a force by following a scale where the length or thickness of the arrow is proportional to the strength of the force it represents. A longer or thicker arrow usually signifies a greater force magnitude, while a shorter or thinner arrow represents a lesser force magnitude. This visual representation allows for a quick and easy understanding of the relative strengths of different forces acting on an object in a given situation.
What does a force diagram show about the direction of each force?
A force diagram shows the direction of each force acting on an object by using arrows to represent the force vectors. The direction of the arrow indicates the direction of the force, with the length of the arrow typically representing the magnitude of the force. Each force arrow in a force diagram points in the direction that the force is acting on the object, helping to visually illustrate the forces at play in a given situation.
How can you determine the net force from a force diagram?
To determine the net force from a force diagram, you need to consider the magnitude and direction of all individual forces acting on an object. Add up all the forces in the same direction and subtract forces acting in the opposite direction. The net force is the vector sum of these forces, representing the overall force acting on the object. If the net force is non-zero, it will cause the object to accelerate in the direction of the net force according to Newton's second law of motion, F = ma.
How are forces shown in opposite directions represented in a force diagram?
Forces shown in opposite directions in a force diagram are typically represented by arrows pointing in the respective directions. The arrows will be of the same length and thickness to indicate equal magnitude, and they will point in opposite directions to denote opposite forces acting on an object. This representation helps visually illustrate the balance or equilibrium between the opposing forces.
What additional information can be included in a force diagram other than forces?
In addition to forces, a force diagram can include information like the direction of each force, the relative magnitude of each force compared to others, the point of application of each force, labels for each force to indicate the source or type of force, the angle of inclination of each force with respect to a reference axis, and any constraints or conditions that apply to the forces in the system. This additional information helps to provide a comprehensive visual representation of the forces acting on an object or system.
How are forces from different objects or sources represented in a force diagram?
Forces from different objects or sources are represented in a force diagram by drawing arrows. Each arrow represents a force acting on an object, with the length and direction of the arrow indicating the strength and direction of the force, respectively. The forces are labeled with names such as gravitational force, normal force, frictional force, tension, or applied force, depending on their origin and effect on the object. By including all the forces acting on the object in the diagram, one can analyze the net force and determine the resulting motion or equilibrium of the object.
How can force diagrams be used to analyze and predict the motion of objects?
Force diagrams can be used to analyze and predict the motion of objects by illustrating all the forces acting on the object and their directions. By summing up the forces in different directions (Newton's second law), one can determine the net force acting on the object. This net force will determine the acceleration of the object, which in turn can be used to predict its motion based on the object's mass. By examining force diagrams, one can understand how forces interact to cause motion and make predictions about an object's future movement.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments