Food Web Worksheets High School Answers
Food web worksheets are an essential tool for high school students studying ecology and the interconnectedness of living organisms in an ecosystem. These worksheets provide a structured way for students to grasp the concept of a food web, identify its components, and understand the relationships between various organisms within a specific habitat or ecosystem. With the help of these worksheets, high school students can strengthen their understanding of this important ecological concept and improve their ability to analyze and interpret intricate webs of energy flow.
Table of Images 👆
- Food Web Pyramid Worksheet
- Food Web Worksheets High School
- Biology Food Web Worksheet for High School
- Chain Food Animal Habitat Worksheets
- Food Chain Worksheet and Answers
- Food Chains and Webs Worksheets
- Food Web Worksheet
- Desert Food Web Worksheet
- High School Food Chain Worksheet
- Amazon Rainforest Food Web Activity
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
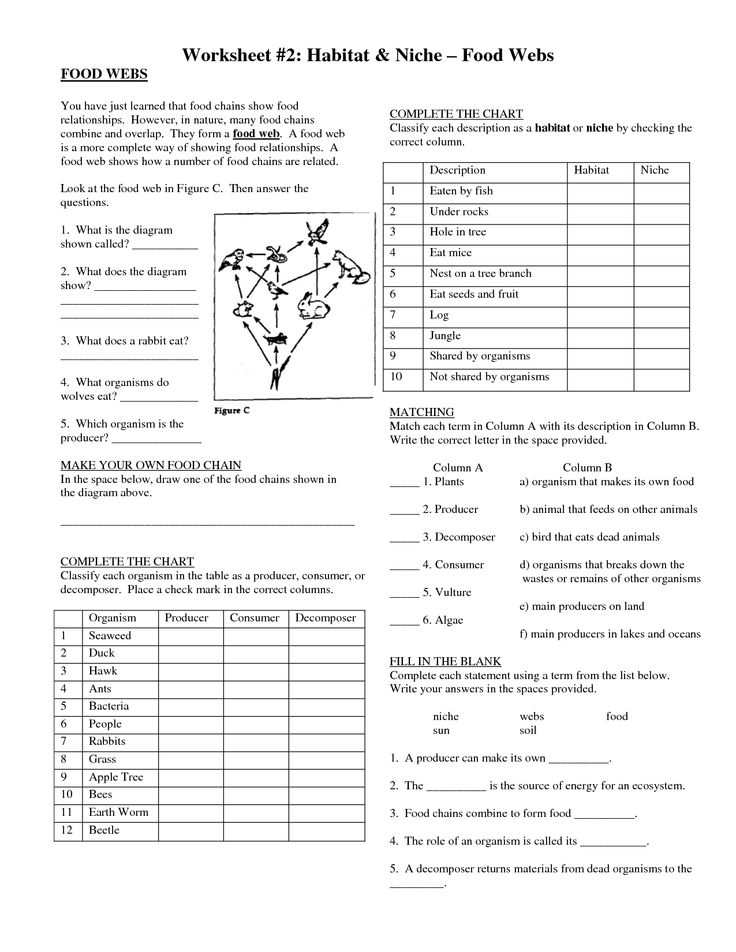
What is a food web?
A food web is a diagram that illustrates the interconnected feeding relationships between different organisms in an ecosystem. It shows how energy and nutrients flow through the ecosystem as organisms consume and are consumed by one another, illustrating the complex interactions that exist in nature.
What are the different trophic levels in a food web?
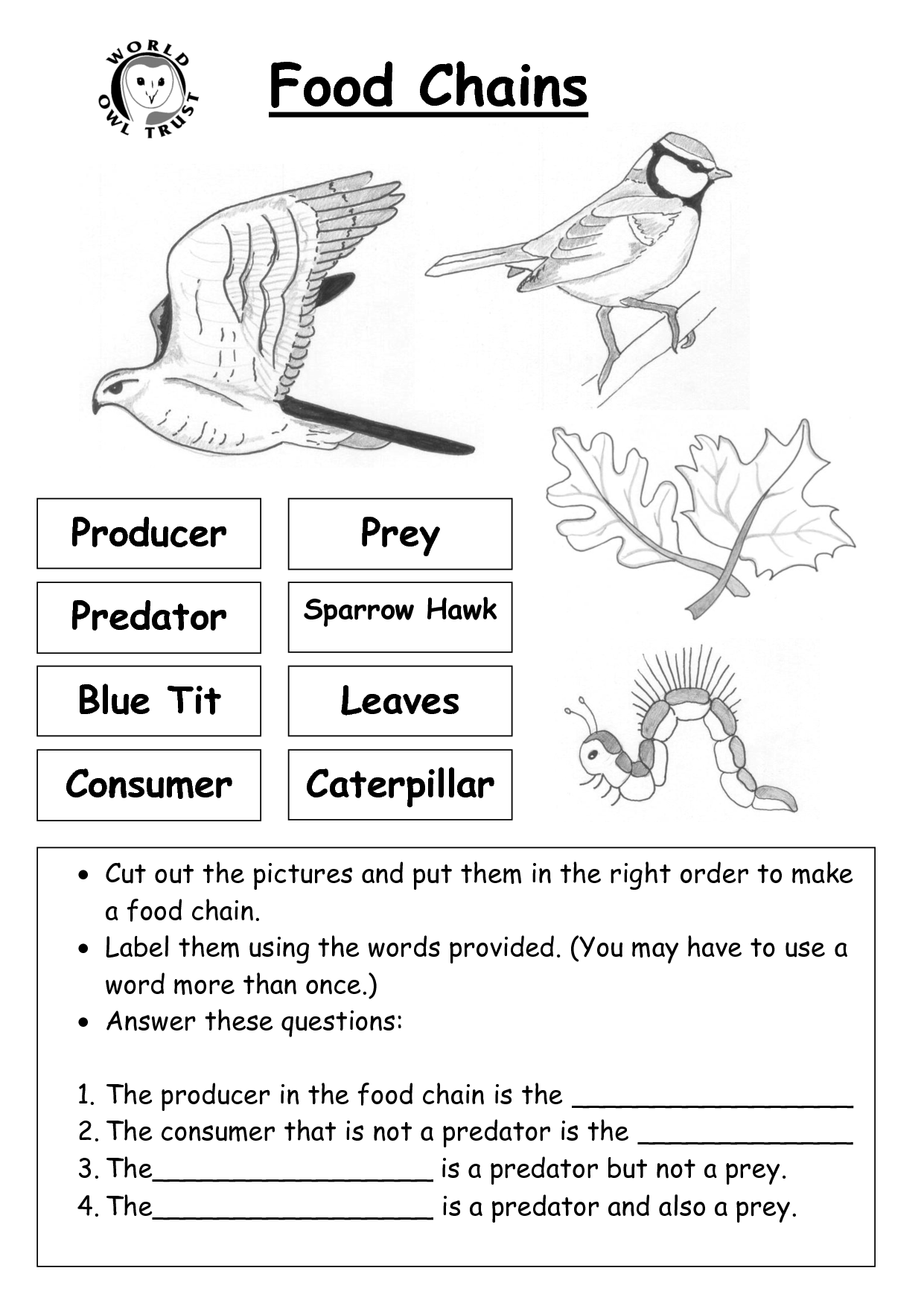
The different trophic levels in a food web are producers (plants, algae), primary consumers (herbivores that eat producers), secondary consumers (carnivores that eat primary consumers), tertiary consumers (carnivores that eat secondary consumers), and decomposers (organisms that break down dead organisms and waste into nutrients for producers).
How do producers obtain their energy?
Producers obtain their energy through a process called photosynthesis, where they convert sunlight into chemical energy by using water and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen. This energy is then used by the producers to carry out their metabolic processes and is ultimately transferred to consumers in the ecosystem through the food chain.
What are primary consumers and give an example?
Primary consumers are organisms that consume producers (plants) as their main food source in an ecosystem. They are herbivores that directly eat plants for energy. An example of a primary consumer is a rabbit that feeds on grass in a grassland ecosystem.
Describe the role of decomposers in a food web.
Decomposers play a crucial role in a food web by breaking down dead plant and animal matter into simpler organic materials like nutrients, which are then recycled back into the ecosystem. They help to clean up and recycle waste, releasing essential elements like nitrogen and phosphorus from decaying matter to be used again by producers such as plants. Ultimately, decomposers contribute to the overall health and sustainability of the ecosystem by ensuring that nutrients are continuously recycled and made available for the next generation of organisms.
What is an apex predator and provide an example?
An apex predator is a predator that is at the top of the food chain and has no natural predators of its own. These predators play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by controlling the populations of other species. An example of an apex predator is the orca, also known as the killer whale. Orcas are at the top of the marine food chain and are known to hunt a wide variety of prey, including fish, seals, and even other whales.
Explain the concept of energy flow in a food web.
Energy flow in a food web refers to the transfer of energy between different organisms in an ecosystem. In a food web, energy is passed from one organism to another through feeding relationships. Producers, such as plants, obtain energy from the sun through photosynthesis and are consumed by primary consumers, which are then eaten by secondary consumers, and so on. As energy is transferred through each trophic level, some energy is lost as heat, waste, and respiration, resulting in a decrease in available energy at higher trophic levels. This flow of energy is essential for sustaining life in an ecosystem and maintaining the balance of the food web.
How does the removal of a species impact the rest of the food web?
The removal of a species can have far-reaching impacts on the rest of the food web. Each species is interconnected with others through various relationships such as predator-prey dynamics, competition, and symbiosis. If a species is removed, it can disrupt the balance of the ecosystem, leading to cascading effects on other species. For example, if a predator is removed, it can result in an increase in the population of its prey species, which in turn can lead to a decrease in the populations of the prey's own prey species. This can have domino effects throughout the food web, ultimately altering the structure and functioning of the entire ecosystem.
Discuss the importance of biodiversity in a food web.
Biodiversity in a food web is crucial as it ensures the stability and resilience of the ecosystem. A diverse range of species ensures that there are various types of organisms to balance the predator-prey relationships and nutrient cycles. This diversity also increases the chances of some species adapting to changes in the environment, such as the introduction of new predators or fluctuations in food availability. Without biodiversity, the food web would be vulnerable to disruptions, leading to imbalances that could potentially destabilize the entire ecosystem. Ultimately, biodiversity in a food web is essential for maintaining a healthy and thriving ecosystem.
How can human activities disrupt or alter food webs?
Human activities can disrupt or alter food webs in various ways, such as overfishing leading to imbalances in predator-prey relationships, pollution from agriculture or industry affecting the health of species in the food web, habitat destruction fragmenting ecosystems and reducing biodiversity, and introducing invasive species that outcompete or prey on native species. These disruptions can have cascading effects on the entire food web, leading to population declines, shifts in species abundance, and ultimately destabilizing the ecosystem.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments