Food Chain vs Food Web Worksheet
Understanding the intricacies of ecological relationships can be a challenging task. However, with the help of worksheets, learning about the food chain and food web becomes an engaging and enlightening experience. Whether you are a curious student or a dedicated teacher looking for a resource to effectively teach this topic, a food chain vs food web worksheet is the ideal tool to enhance your understanding of the entities and subjects involved in these ecological systems.
Table of Images 👆
- Food Chains and Webs Worksheets
- Food Web Worksheet
- Food Web Pyramid Worksheet
- Food Chain Worksheets
- Food Chains and Webs Worksheets
- Food Chain Activity
- Food Chain Worksheets
- Worksheets On Food Chains
- Food Web Worksheets High School
- Wetland Food Web Worksheet
- Blank Food Web Worksheets
- Food Chains and Webs Worksheets
- Food Chains and Webs Worksheets
- Desert Food Web Worksheet
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
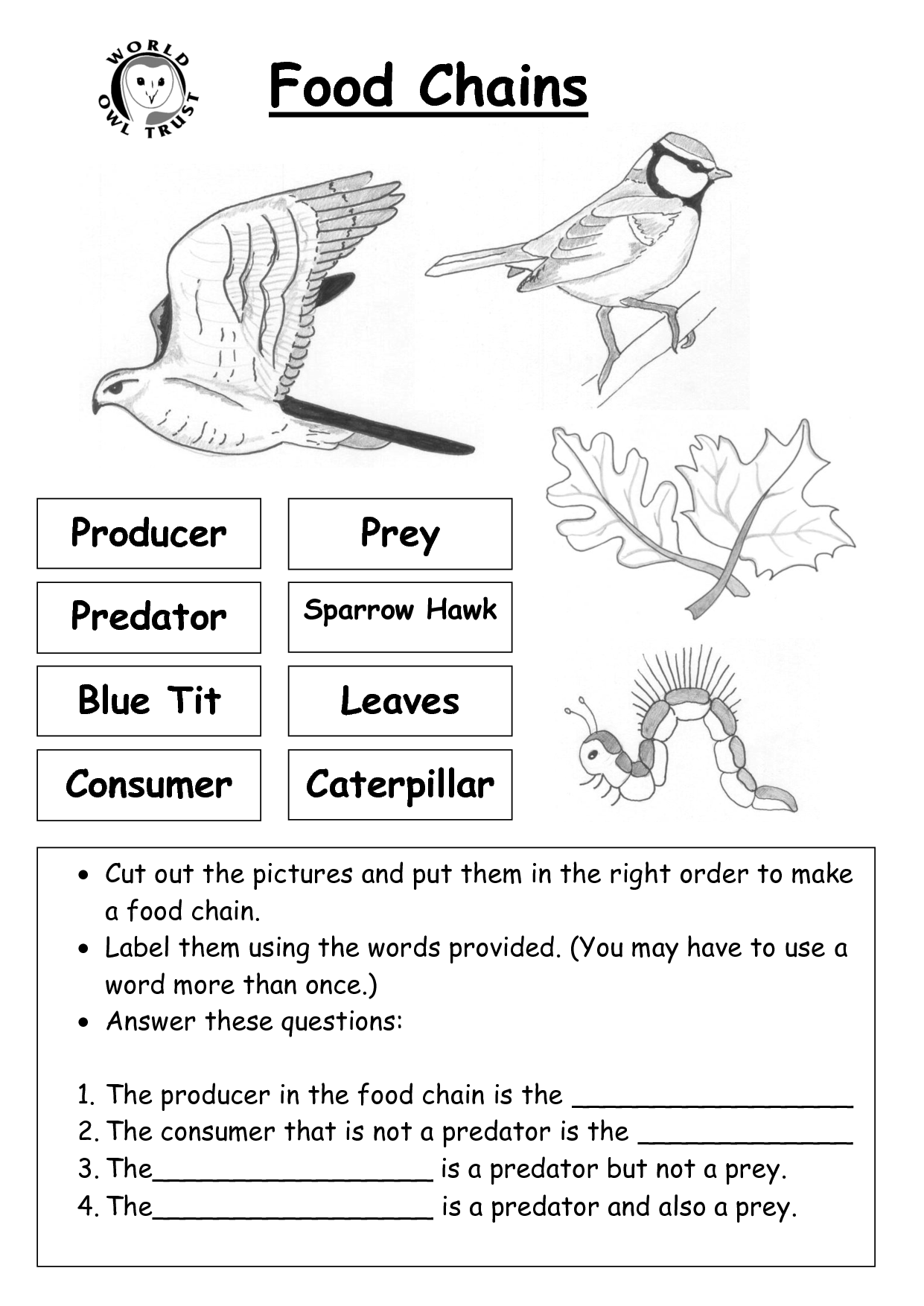
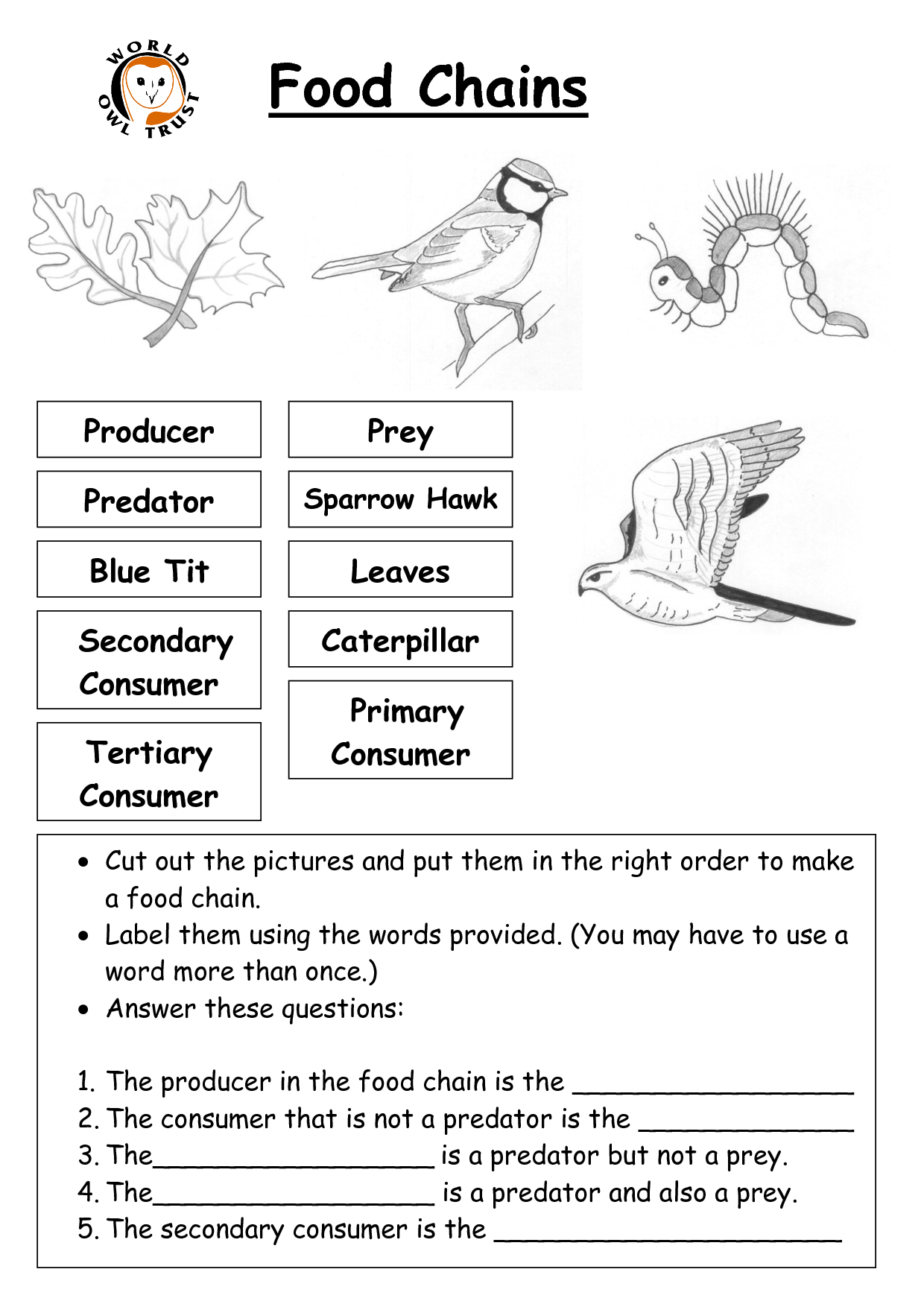
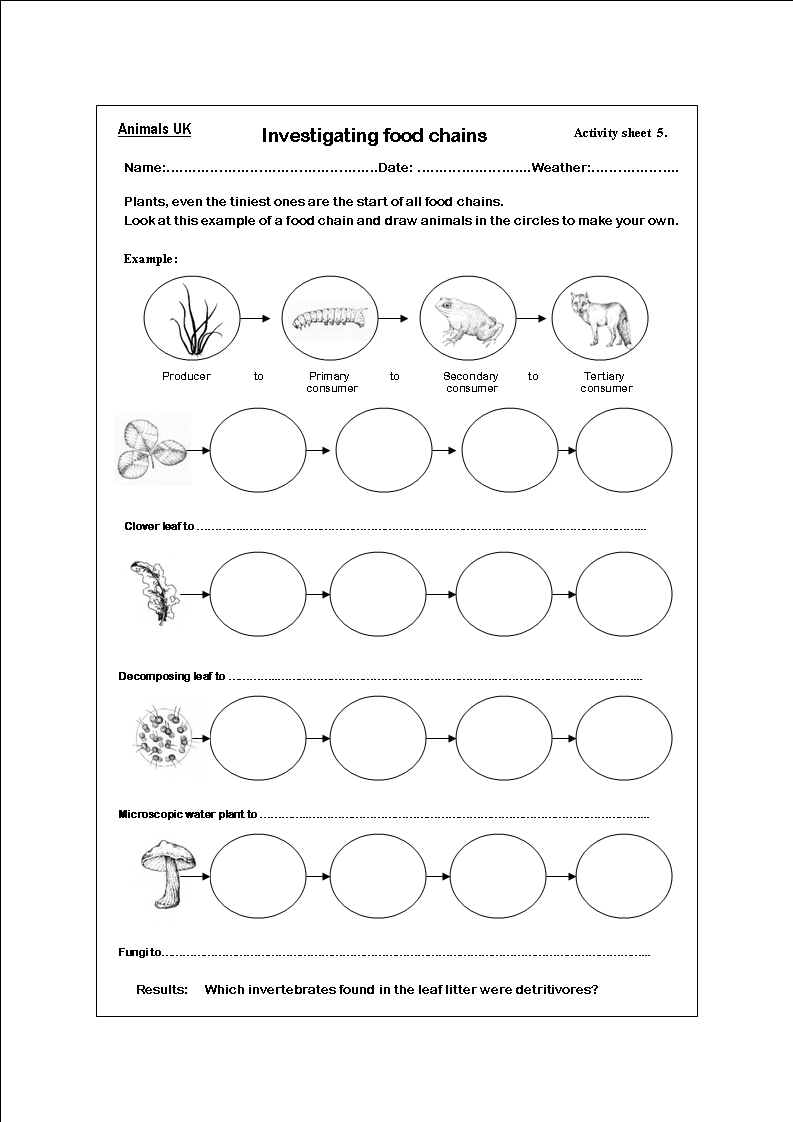
What is a food chain?
A food chain is a linear sequence showing the flow of energy and nutrients in an ecosystem, where each member of a community serves as a source of food for the next. It starts with a producer (plants), followed by primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores), and so on, depicting the transfer of energy and nutrients from one organism to another.
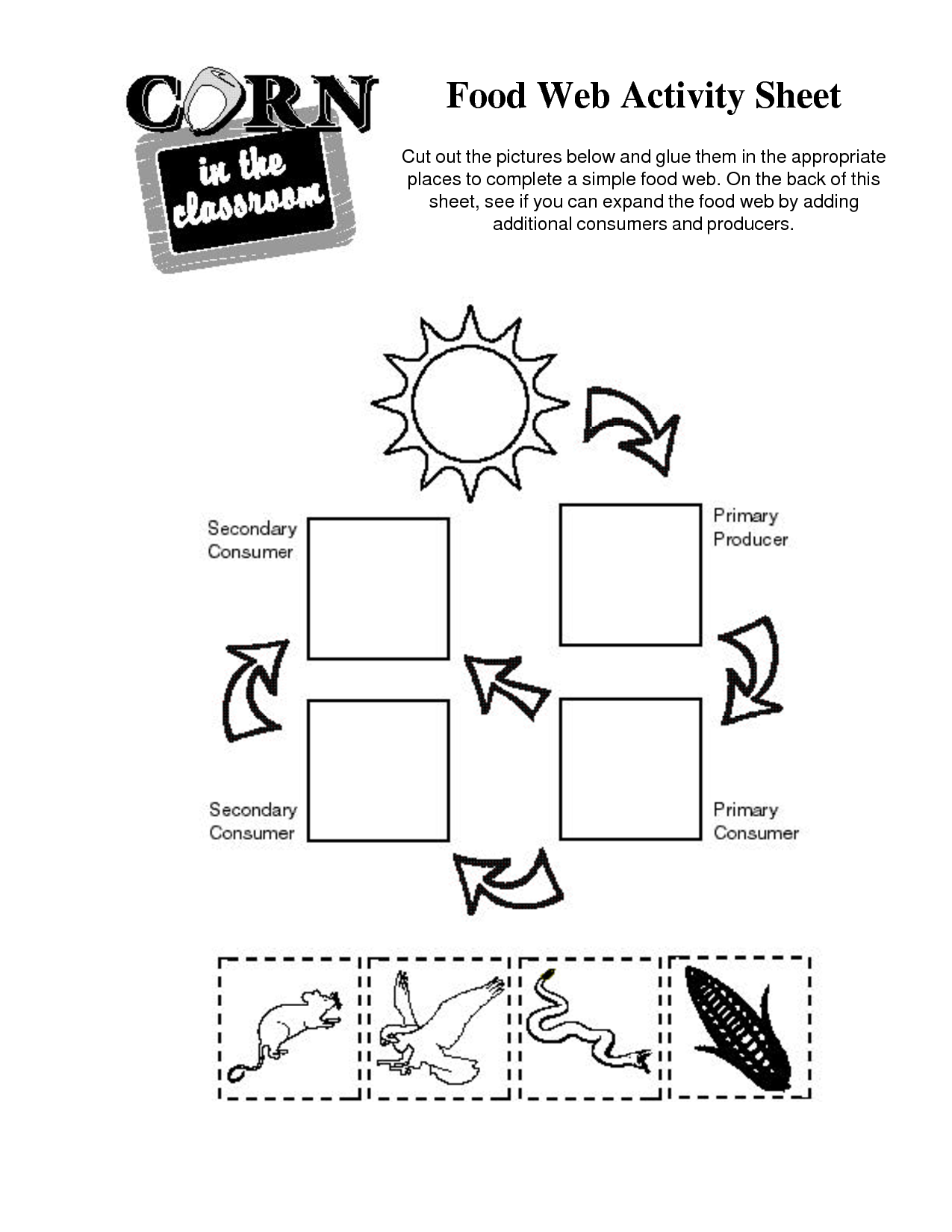
What is a food web?
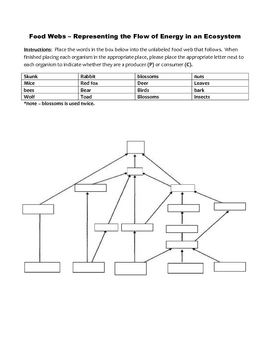
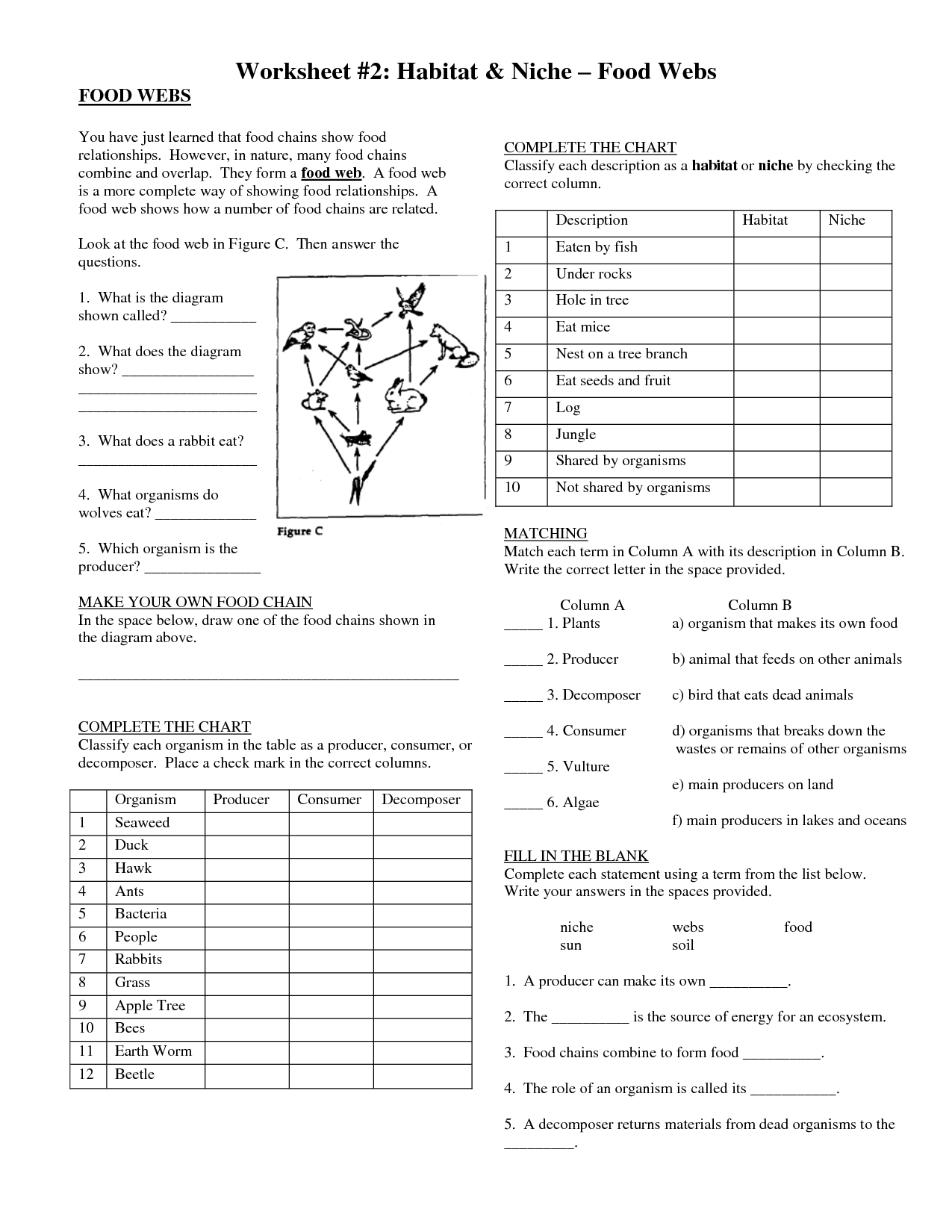
A food web is a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains that show the flow of energy and nutrients through an ecosystem. It illustrates the transfer of energy from one organism to another as they consume each other for food, ultimately depicting the complex connections and relationships between different organisms within a specific habitat.
How does a food chain differ from a food web?
A food chain is a linear progression of organisms consuming each other in a specific order, showing a single path of energy flow in an ecosystem. In contrast, a food web is a system of interconnected food chains, illustrating all the possible feeding relationships among different organisms in an ecosystem. Essentially, a food chain represents a single pathway of energy transfer, while a food web shows the complexity and interconnectedness of energy flow in an ecosystem involving multiple organisms and their interactions.
Define a producer in a food chain or food web.
A producer in a food chain or food web is an organism, typically a plant or algae, that is capable of creating its own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Producers are the foundation of the food chain/web as they convert energy from the sun or other sources into organic compounds that can be used by other organisms for energy.
What role do consumers play in a food chain or food web?
Consumers play a crucial role in a food chain or food web as they are organisms that obtain their energy by consuming other organisms. They help regulate the population size of other species in the ecosystem by feeding on producers (plants) or other consumers. Consumers transfer energy and nutrients through the food chain, aiding in the flow of energy from one trophic level to another. Their feeding interactions are essential for maintaining the balance and stability of ecosystems.
Explain the concept of a primary consumer.
A primary consumer is an organism in an ecosystem that feeds directly on producers, such as plants, algae, or phytoplankton. These organisms are herbivores, which means they consume autotrophic organisms to obtain energy and nutrients for their own growth and survival. Primary consumers play a crucial role in energy transfer within food chains and food webs, as they are the first level of consumers above the producers and serve as a primary food source for secondary consumers.
Define a secondary consumer and provide an example.
A secondary consumer is an organism that primarily feeds on primary consumers. An example of a secondary consumer is a snake that eats mice and other small mammals.
What is the significance of decomposers in a food chain or food web?
Decomposers play a crucial role in a food chain or food web by breaking down dead organic matter such as plant and animal waste into simpler compounds like nutrients. This process releases these nutrients back into the ecosystem, allowing them to be recycled and reused by producers, thus maintaining the balance and productivity of the entire ecosystem. Without decomposers, organic matter would accumulate, and nutrients would be locked away, leading to ecosystem degradation and reduced overall biodiversity.
Describe the relationship between energy transfer and trophic levels in a food chain or food web.
Energy transfer in a food chain or food web follows the 10% rule, where only about 10% of the energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next level as organisms are consumed. This means that energy decreases as it moves up the trophic levels, with most of the energy being lost as heat during metabolic processes. As a result, higher trophic levels, like apex predators, have less energy available to them compared to primary producers at the base of the food chain. This relationship is crucial for understanding the flow of energy and nutrients within ecosystems.
Discuss the importance of maintaining balance in a food chain or food web ecosystem.
Maintaining balance in a food chain or food web ecosystem is crucial for the overall health and stability of the ecosystem. Each organism plays a specific role in the food chain, and disruptions in this balance can have ripple effects throughout the ecosystem. For instance, overpopulation of a certain species can lead to overconsumption of resources and can lead to the decline of other species. On the other hand, the decline of a predator species can result in an increase in prey population, which can then lead to resource depletion or ecological imbalance. Therefore, it is essential to preserve the balance in a food chain or food web ecosystem to ensure the sustainability and health of the entire ecosystem.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments