Energy Pyramid Worksheet Answer Key
Are you a science teacher in search of a comprehensive energy pyramid worksheet answer key? Look no further. In this blog post, we will provide you with a detailed answer key for energy pyramid worksheets, designed specifically for middle school students. Whether you are teaching a lesson on food chains and energy flow or reviewing ecological concepts, this answer key will be an invaluable resource to assess your students' understanding of the topic. Let's dive in and explore the world of energy pyramids!
Table of Images 👆
- Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key
- Ecological Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Food Web Pyramid Worksheet
- Blank Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key
- Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answers
- Ecological Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Photosynthesis Biology Answer Key POGIL
- Blank Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Biomass Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Food Web Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Ecosystem Worksheet Answer Key
- Food Pyramid Worksheets
- Energy Flow through Ecosystem Worksheet Answers
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Types of Energy Worksheet PDF
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
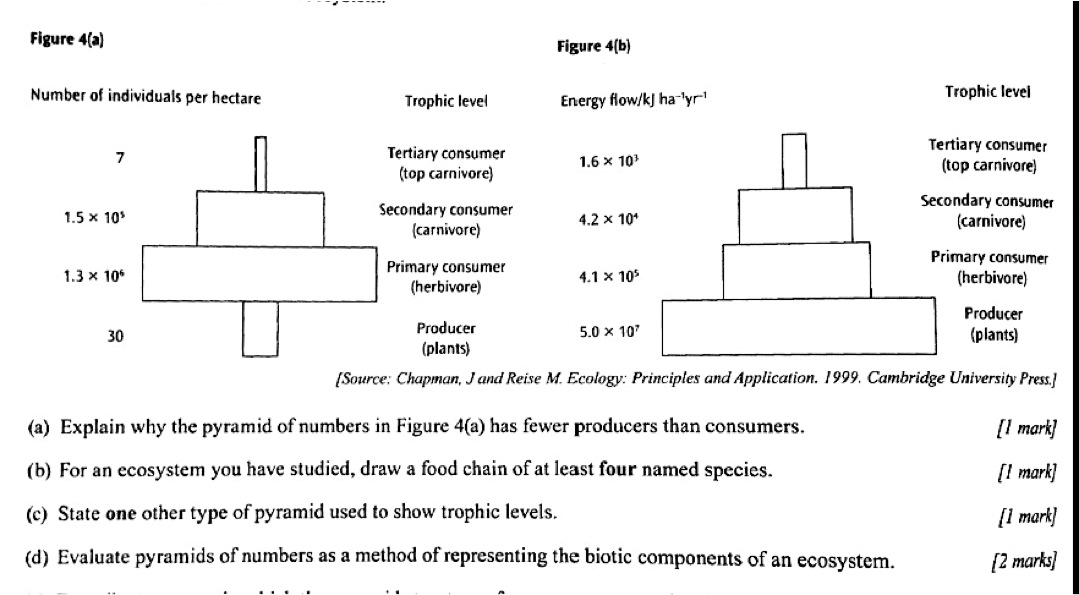
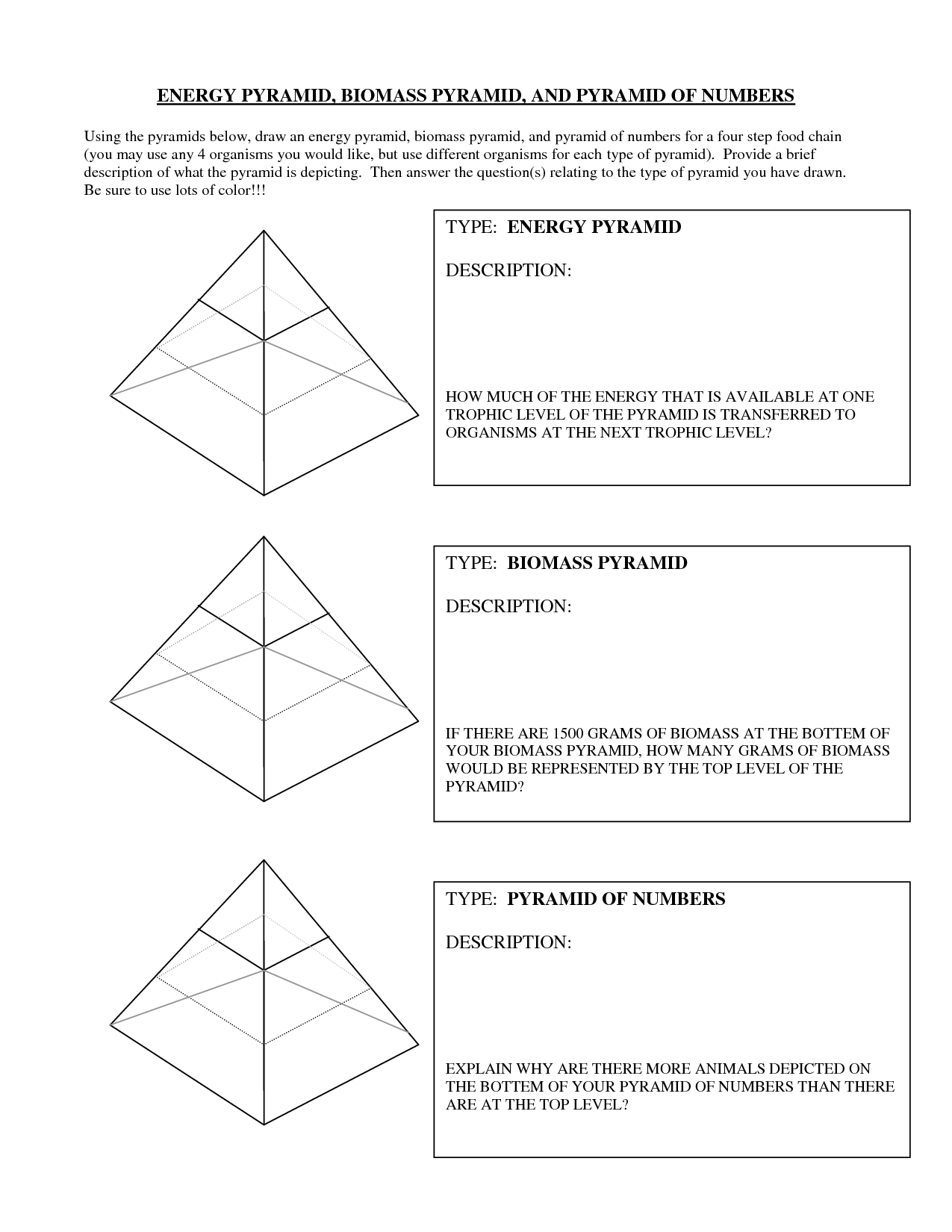
What is an energy pyramid?
An energy pyramid is a graphical representation of the trophic levels within an ecosystem, showing the flow of energy from one level to the next. It illustrates how energy is transferred and loss as it moves from producers (plants) to primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores), and so on. The pyramid typically narrows at the top to reflect the decreasing energy available at each successive trophic level due to metabolic losses and heat production.
Why is the shape of an energy pyramid important?
The shape of an energy pyramid is important because it visually represents the flow of energy through an ecosystem, showcasing the decreasing energy levels at each trophic level. It illustrates the concept of energy transfer and helps to understand the efficiency of energy transfer within an ecosystem, highlighting how energy is lost as it moves up the food chain. This shape is a crucial tool for ecologists to study the dynamics of energy flow and the relationships between different organisms in an ecosystem.
What does the base of an energy pyramid represent?
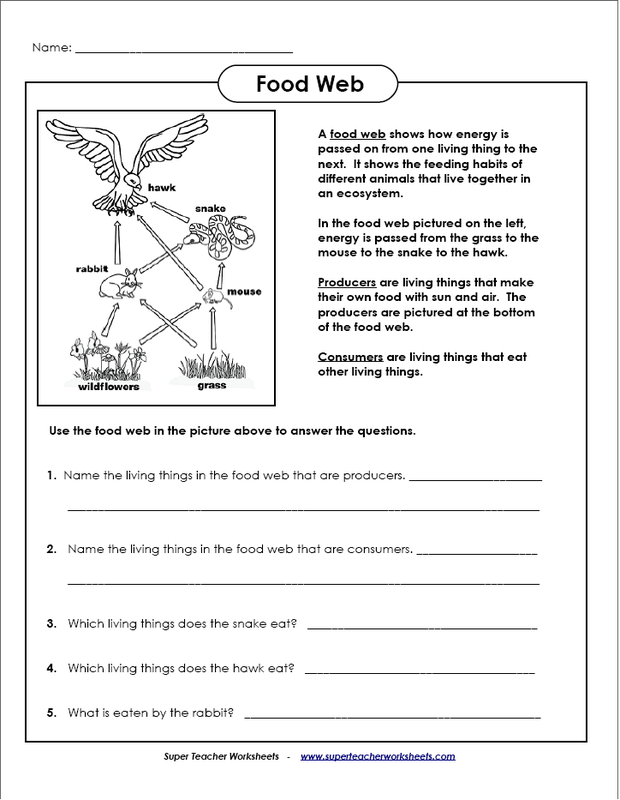
The base of an energy pyramid represents the primary producers or autotrophic organisms, such as plants, algae, and some bacteria, that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. They form the foundation of the energy pyramid by generating food and energy for all other levels of consumers.
What type of organisms are found at the base of an energy pyramid?
Primary producers, such as plants and algae, are typically found at the base of an energy pyramid. These organisms are able to capture energy from the sun through photosynthesis and form the foundation of the food chain by converting this energy into organic matter that other organisms can consume and use for growth and energy.
What happens to the energy as it moves up the energy pyramid?
As energy moves up the energy pyramid, it decreases. This is because energy is lost at each trophic level through metabolic processes, heat production, and waste production. Each higher trophic level receives less energy than the level below it, resulting in a decrease in available energy as it moves up the pyramid.
What is a producer in an energy pyramid?
A producer in an energy pyramid is an organism, typically a plant or algae, that produces energy through photosynthesis. These organisms are located at the base of the energy pyramid because they are able to convert sunlight into chemical energy, which is then passed on to consumers in higher trophic levels through the food chain.
Give an example of a producer in an energy pyramid.
In an energy pyramid, an example of a producer would be plants such as grasses, trees, or algae that are capable of converting sunlight into energy through the process of photosynthesis. These plants serve as the foundation of the pyramid by synthesizing organic compounds from inorganic substances and providing energy to the organisms at higher trophic levels.
What is a consumer in an energy pyramid?
A consumer in an energy pyramid is an organism that obtains energy by consuming other living organisms. Consumers are categorized into different levels based on their position in the food chain, with primary consumers feeding on producers, secondary consumers feeding on primary consumers, and so on. They play a crucial role in transferring energy through the ecosystem by feeding on lower trophic levels and being a source of energy for higher trophic levels.
Give an example of a consumer in an energy pyramid.
An example of a consumer in an energy pyramid is a snake that feeds on mice and insects. The snake is considered a secondary consumer as it consumes primary consumers such as mice and insects, which in turn feed on producers like plants. This hierarchy represents the flow of energy within an ecosystem, with each level relying on the one below for energy and nutrients.
How does the energy pyramid illustrate the flow of energy through an ecosystem?
The energy pyramid illustrates the flow of energy through an ecosystem by showing how energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next. At the base of the pyramid are the primary producers, such as plants, that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. The energy then moves up the pyramid as it is consumed by herbivores, then carnivores, and finally top predators. As energy is transferred between trophic levels, some energy is lost as heat, resulting in fewer organisms at higher trophic levels. This pyramid shape visually represents how energy becomes less available as it moves up the food chain in an ecosystem.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments