Electrical Circuits Worksheets
Are you a student or teacher looking for a practical and engaging way to reinforce your understanding of electrical circuits? Look no further than our collection of electrical circuits worksheets. These worksheets are designed to assist students in mastering key concepts related to circuits, such as Ohm's law, series and parallel circuits, and electrical components. With a variety of exercises and activities, these worksheets make learning about electrical circuits easy and enjoyable.
Table of Images 👆
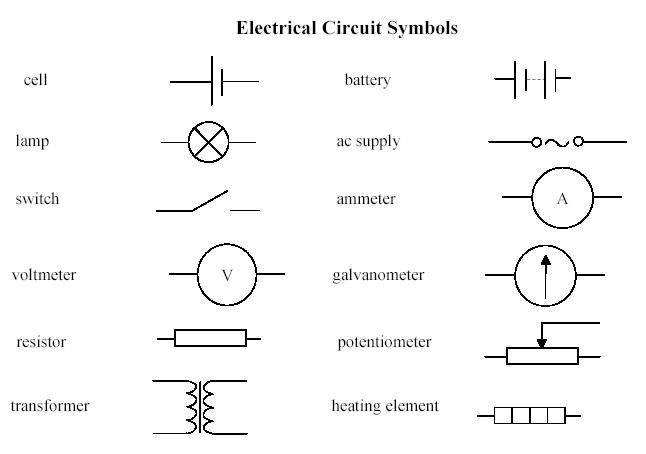
- Electrical Circuit Symbols
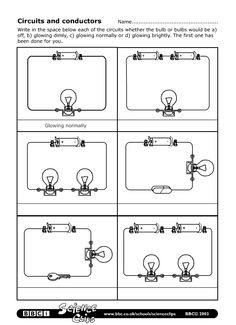
- Conductors and Insulators Worksheet 4th
- Series Parallel Circuit Worksheet
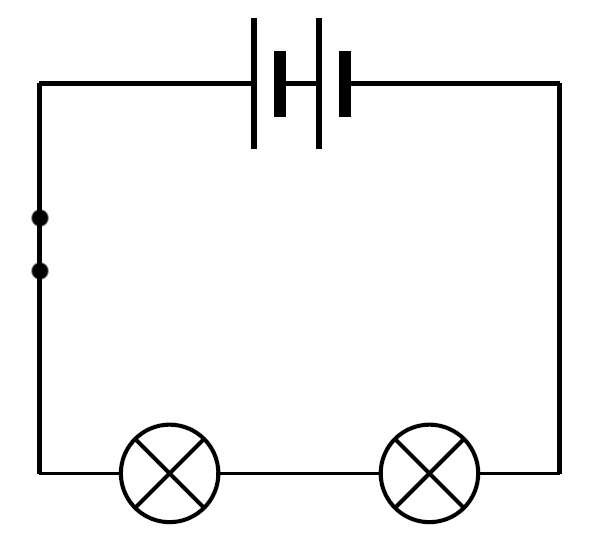
- Series Circuit Diagram
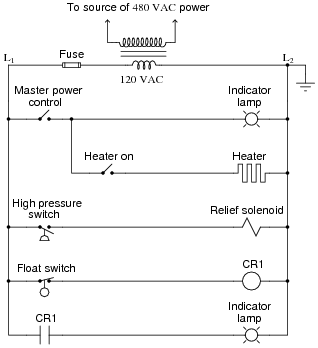
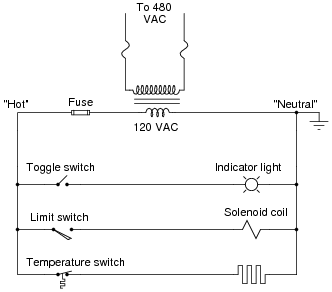
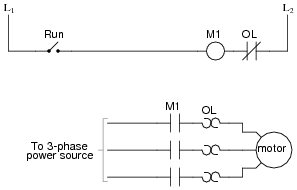
- Relay Ladder Logic Diagram
- Switch Ladder Diagram Symbols
- Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheets
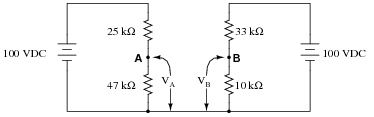
- Voltage Divider Circuit
- The Thermal Overload Heater Symbol for Protection
- Electricity Circuit Worksheets 4th Grade
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is a circuit?
A circuit is a closed loop or path through which electricity flows, typically consisting of an energy source, wires, electrical components such as resistors and capacitors, and a load that uses the electricity. It is designed to allow the flow of electric current to power devices and perform specific functions based on the configuration of the components within the circuit.
What is the purpose of a switch in a circuit?
The purpose of a switch in a circuit is to open or close the circuit, allowing or interrupting the flow of electric current. Switches are used to control the flow of electricity in a circuit, turning devices on and off or changing the direction of current flow. They provide a means for users to easily control the operation of electrical appliances and devices.
What are the main components of a circuit?
The main components of a circuit are a power source (such as a battery or a power supply), conductive materials (such as wires or traces on a printed circuit board), electronic components (such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, and transistors), a load (such as a light bulb or a motor), and a switch (to control the flow of electricity within the circuit).
How does a series circuit differ from a parallel circuit?
In a series circuit, components are connected in a single path, so the same current flows through each component one after the other. If one component breaks, the whole circuit is interrupted. In a parallel circuit, components are connected in multiple paths, allowing for different currents to flow through each branch independently. If one component breaks, the other branches can still function.
What is the role of a resistor in a circuit?
A resistor in a circuit is used to limit the flow of electrical current, thereby controlling the amount of voltage and current in the circuit. It is commonly used to adjust signal levels, protect components from high currents, and divide voltages in a circuit. Resistor values are measured in ohms and they are crucial components in various electrical and electronic devices to ensure proper functioning and prevent damage.
How does a capacitor store and release electrical energy?
A capacitor stores electrical energy by accumulating opposite charges on its two conductive plates separated by an insulating material, creating an electric field between the plates. When connected to a circuit, the capacitor releases stored energy by discharging the opposite charges, allowing the flow of current as the electric field collapses. This process enables capacitors to temporarily store and release electrical energy in a quick and efficient manner, making them essential components in various electronic devices and circuits.
What is the difference between AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current)?
The main difference between AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) is the direction in which the electric current flows. In AC, the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction, while in DC, the electric charge flows in one direction continuously. AC is commonly used in household appliances and power distribution systems, while DC is often used in electronics and batteries. Additionally, AC can easily be converted to different voltages using transformers, whereas DC is typically more stable over long distances.
How does a diode control the flow of electric current?
A diode controls the flow of electric current by allowing current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. When the diode is forward-biased, meaning the voltage across the diode allows current to flow easily, the diode conducts electricity. Conversely, when the diode is reverse-biased, it acts as an insulator, preventing current from flowing in the wrong direction. This behavior is due to the way a diode is constructed, with a semiconductor material that creates a barrier that only allows current to flow under certain conditions.
How does a transformer work in an electrical circuit?
A transformer consists of two coils of wire, usually wound around an iron core. When an alternating current flows through the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field in the core. This changing magnetic field induces an alternating current in the secondary coil through electromagnetic induction, allowing for the voltage to be either stepped up or stepped down depending on the number of turns in each coil. In this way, a transformer enables efficient transfer of electrical energy from one circuit to another at different voltage levels without loss of power.
What safety precautions should be taken when working with electrical circuits?
When working with electrical circuits, here are some important safety precautions to follow: always turn off power before working on circuits, use insulated tools, wear appropriate personal protective equipment such as gloves and goggles, work in a dry environment, avoid using damaged equipment, never overload circuits, and ensure proper grounding. It is also important to ensure that you have the knowledge and training to work on electrical circuits safely to prevent injury or damage.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments