Ecosystem Worksheets for Middle School
Middle school students can explore the diverse and fascinating world of ecosystems with the help of engaging worksheets. These carefully designed resources provide a structured approach to learning about different types of ecosystems, the organisms that inhabit them, and the intricate relationships between living and non-living components.
Table of Images 👆
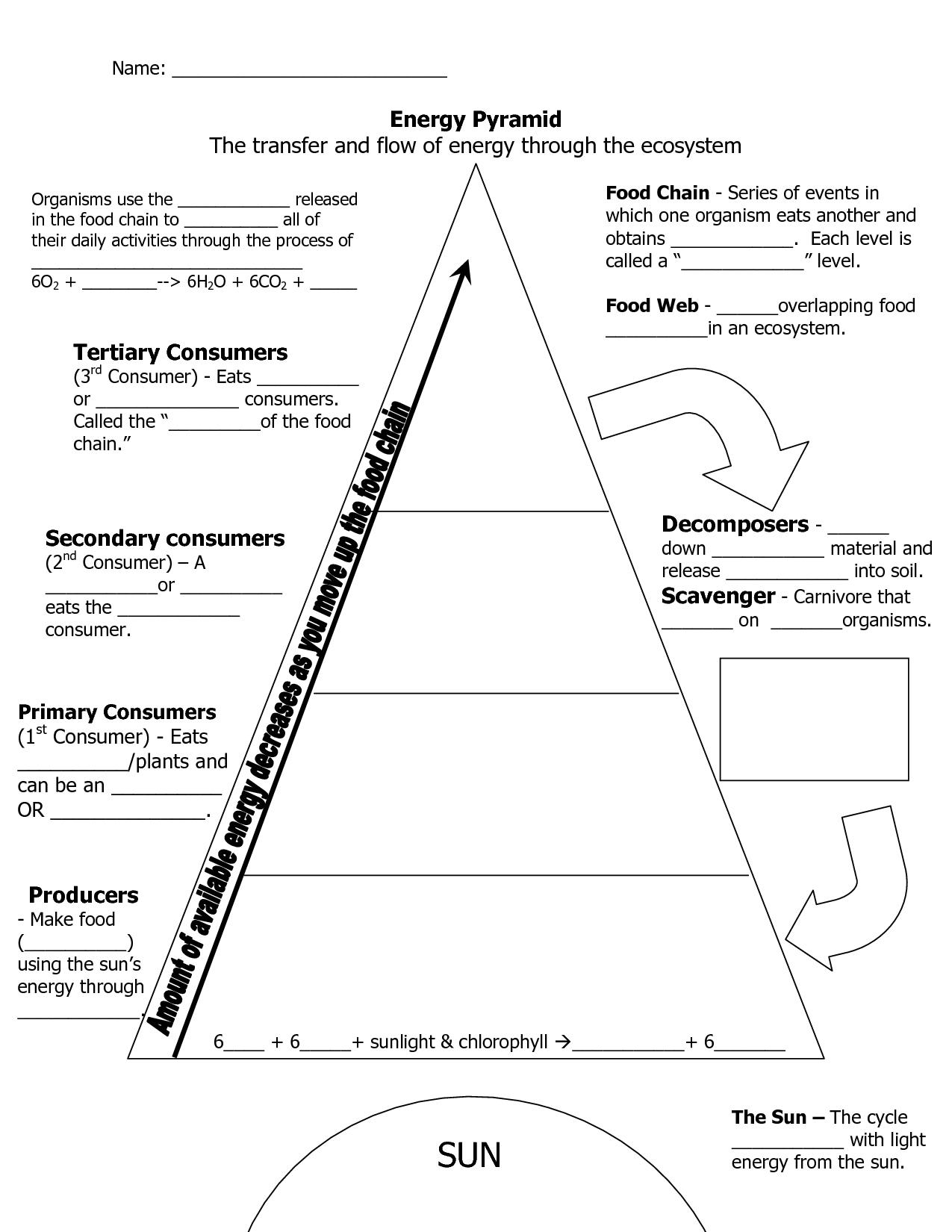
- Food Web Pyramid Worksheet
- Food Chain Worksheets
- High School Ecosystem Food Chain Worksheet
- Ecological Succession Worksheet
- Marine Biology Worksheets High School
- Biome Worksheets High School
- Biome Worksheets 3rd Grade
- Ecosystem Crossword Puzzle Answers
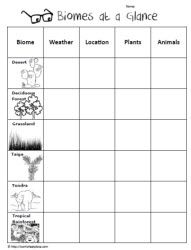
- Biome Organizer Chart Worksheet
- Ecosystems and Biomes Worksheets
- Food Chain Worksheet 3rd Grade
- Human Footprint Worksheet Answers
- Ecosystem Organization Pyramid Worksheet
- Biome Map Coloring Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
What is an ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms interacting with each other and their physical environment. It includes plants, animals, microorganisms, and the non-living components like water, soil, and sunlight. Ecosystems can be as small as a pond or as large as a forest, and they are essential for maintaining balance in nature and providing services that support life on Earth.
Explain the difference between a biotic and abiotic factor in an ecosystem.
Biotic factors are living components of an ecosystem, such as plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria, that interact with each other. In contrast, abiotic factors are non-living components, like sunlight, temperature, water, soil, and air, that also influence the ecosystem but do not involve living organisms. Both biotic and abiotic factors play crucial roles in shaping the dynamics and sustainability of an ecosystem.
Describe the role of producers in an ecosystem.
Producers play a critical role in an ecosystem by converting sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, which serves as the foundation of the food chain. They are typically plants or algae that provide food and oxygen for other organisms, such as herbivores and ultimately carnivores. Producers help maintain the balance of nutrients and energy within an ecosystem, supporting the survival and biodiversity of all other organisms.
How do consumers obtain their energy in an ecosystem?
Consumers obtain energy in an ecosystem by consuming other organisms. This can involve either directly consuming producers (plants and algae) or consuming other consumers (animals) that have consumed producers. Through this process of eating and being eaten, energy is transferred through the food chain within an ecosystem.
What is the significance of decomposers in an ecosystem?
Decomposers play a crucial role in an ecosystem by breaking down dead organisms and organic matter into simpler nutrients that can be used by other organisms. This process, known as decomposition, contributes to the recycling of essential nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus, making them available for primary producers such as plants to uptake and continue the food chain. Without decomposers, organic matter would accumulate, leading to a buildup of waste and nutrient deficiency in the ecosystem. Ultimately, decomposers help maintain ecosystem balance and sustainability by facilitating nutrient cycling and promoting overall ecosystem health and productivity.
Define the term "food chain" and provide an example.
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where each member serves as food for the next member in the chain. An example of a food chain is grass (producer) being consumed by a grasshopper (primary consumer), which in turn is eaten by a bird (secondary consumer), and finally, the bird is preyed upon by a hawk (tertiary consumer).
Explain the concept of a food web and provide an example.
A food web is a visual representation of interconnected food chains within an ecosystem, illustrating how different organisms in an ecosystem depend on each other for food. It shows the flow of energy and nutrients as various organisms eat and are eaten by others. For example, in a forest ecosystem, a food web could include trees being eaten by insects, which are then consumed by birds, which are in turn preyed upon by larger predators like owls or foxes. This interconnected network helps maintain balance and stability within the ecosystem.
Describe the process of photosynthesis and its importance in an ecosystem.
Photosynthesis is the biological process through which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen. This process occurs in chloroplasts, using the chlorophyll pigment to capture the sunlight energy and convert it into chemical energy. Photosynthesis is vital for ecosystems as it is the foundation of the food chain, providing organisms with energy and oxygen. It also helps regulate levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, contributing to the balance of gases crucial for supporting life on Earth.
What is a habitat and why is it important for organisms?
A habitat is the natural environment or home of an organism, including all biotic and abiotic factors that influence its life. Habitats provide organisms with shelter, food, water, and other essential resources necessary for survival and reproduction. They also offer protection from predators and provide opportunities for interactions within the ecosystem. Each organism is adapted to its specific habitat, and any changes in the habitat can impact the survival and population dynamics of the organisms living there. In essence, habitats are crucial for the well-being and success of organisms, as they provide the necessary conditions for life to thrive.
How do human activities impact ecosystems?
Human activities impact ecosystems in various ways, such as deforestation, pollution, overfishing, and urbanization. These activities can lead to habitat destruction, loss of biodiversity, air and water pollution, disruption of food chains, and climate change. Ultimately, human actions can result in negative consequences for ecosystems, including the destabilization of natural processes and the decline of ecosystem services that are essential for human well-being.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments