Ecological Succession Worksheet
Ecological succession worksheets are an essential resource for educators and students seeking to understand the intricate relationships between different species and their environments. By providing a comprehensive overview of the subject, these worksheets allow students to grasp the concept of ecological succession, the process that describes how an ecosystem changes over time. Designed with the needs of biology, ecology, or environmental science students in mind, these worksheets offer a practical and engaging way to explore this important ecological concept.
Table of Images 👆
- Ecological Succession Worksheet Answers
- Biology Ecological Succession Pond Worksheet
- Ecological Succession Worksheet Answer Key
- Following Directions Activity Worksheet
- Ecological Succession Worksheet Answer Key
- Primary and Secondary Succession Worksheet
- Primary and Secondary Succession Worksheet
- Ecological Succession Worksheet Answers
- Ecological Succession Worksheet Answer Key
- Ecological Succession Worksheet Answer Key
- Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism Worksheet
- Energy Pyramid Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
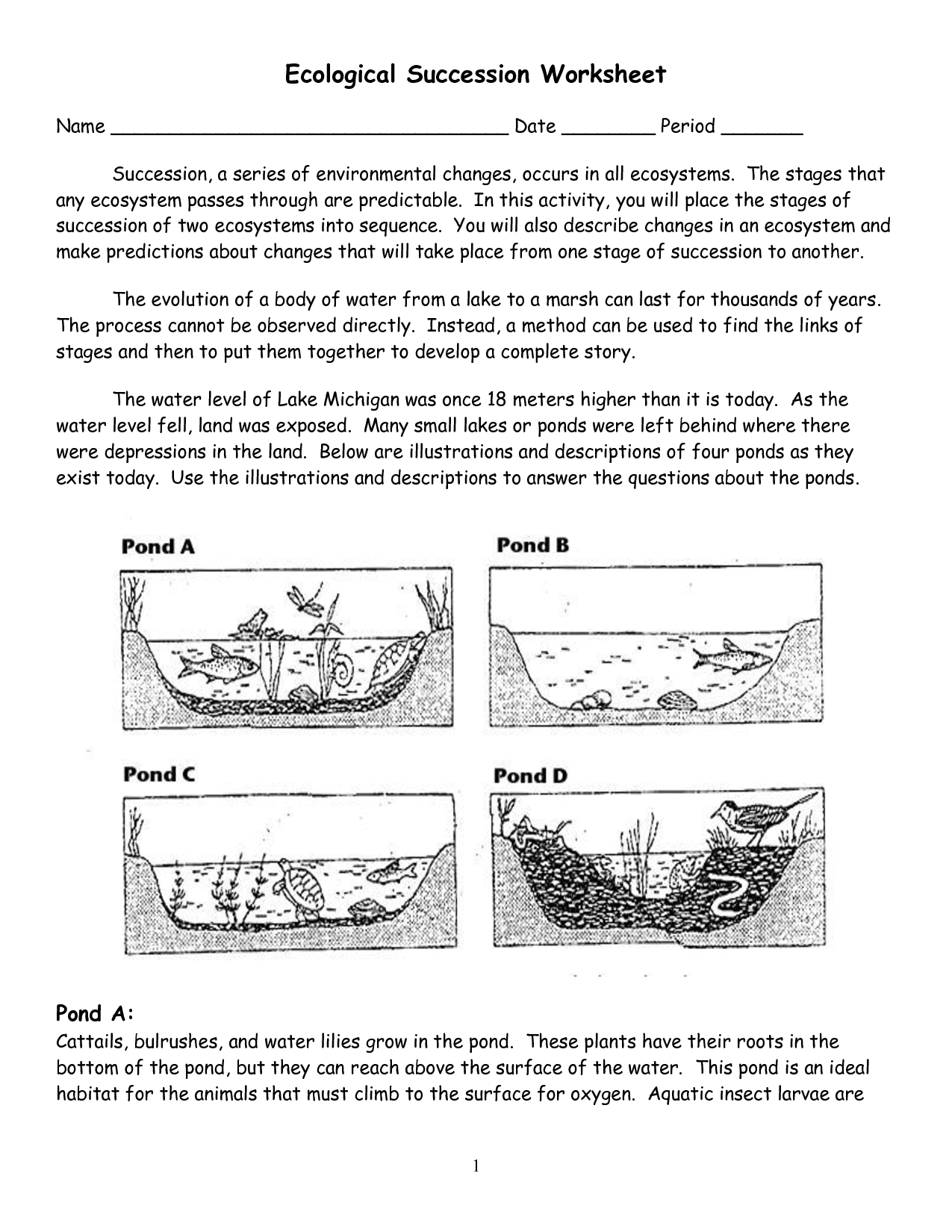
What is ecological succession?
Ecological succession is the process by which an ecological community gradually changes and develops over time, typically following a disturbance such as a fire, flood, or human intervention. This process involves a series of predictable changes in the species composition and structure of the community, leading to the establishment of more complex and stable ecosystems. Succession can be classified as primary, occurring in areas without any previous ecosystem, or secondary, occurring in areas where an existing ecosystem has been disturbed or destroyed.
What are the two main types of ecological succession?
The two main types of ecological succession are primary succession and secondary succession. Primary succession occurs in areas where no soil is present, typically starting from bare rock, and involves the gradual development of a community of organisms over time. In contrast, secondary succession occurs in areas where soil is already present, typically following a disturbance such as a fire or flood, and involves the reestablishment of a community of organisms that existed before the disturbance.
What is the difference between primary and secondary succession?
Primary succession occurs in newly formed or barren landscapes where no soil is present, while secondary succession occurs in areas where soil is already present but has been disturbed or destroyed, such as after a wildfire or logging. Primary succession starts with the colonization of pioneer species like lichens and mosses, while secondary succession begins with the regrowth of existing plants from seeds or roots left behind. Both processes ultimately lead to the development of a stable and diverse ecosystem over time, but the starting conditions and initial steps differ between primary and secondary succession.
How does primary succession start?
Primary succession starts with the colonization of barren land by pioneer species such as algae, lichens, and mosses. These organisms can survive in harsh environmental conditions and begin to break down rocks and create some soil. As they die and decompose, they add organic matter to the soil, which allows more complex plants like grasses and shrubs to gradually establish. Over time, the soil becomes more developed, facilitating the growth of trees and other larger plants, leading to a mature and stable ecosystem.
What are the pioneer species in primary succession?
Pioneer species in primary succession are typically lichens and mosses that are able to colonize bare rock or soil, breaking it down and creating organic matter that helps facilitate the growth of other plants. These species are well adapted to harsh environmental conditions and play a crucial role in initiating the process of succession by creating a more hospitable environment for other plants to establish and grow.
What is the role of mosses and lichens in primary succession?
Mosses and lichens play a crucial role in primary succession by being among the first pioneer species to colonize barren environments. These organisms are able to grow on rock surfaces and begin the process of breaking them down, helping to form soil that can support the growth of other plant species. By stabilizing and enriching the soil, mosses and lichens create conditions that enable the establishment of more complex plant communities over time, ultimately leading to the development of a diverse and stable ecosystem.
How do pioneer species prepare the environment for other plant species?
Pioneer species prepare the environment for other plant species by breaking down rocks and soil through their roots and releasing organic matter through their decomposition, which enriches the soil and makes it more suitable for other plant species to grow. They also improve soil structure and increase nutrient availability, which helps create a more hospitable environment for a wider diversity of plants to establish and thrive. By paving the way and initiating ecological succession, pioneer species play a crucial role in transforming barren landscapes into diverse and flourishing ecosystems.
How does secondary succession start?
Secondary succession begins with the colonization of organisms in an area that has been cleared of previous vegetation due to disturbances like fires, human activities, or severe weather events. Pioneer species such as grasses and weeds are the first to establish in the newly available environment, gradually creating suitable conditions for more complex plant species to grow. Over time, the community of organisms evolves, leading to the development of a stable and diverse ecosystem.
What are some examples of disturbances that can trigger secondary succession?
Some examples of disturbances that can trigger secondary succession include wildfires, severe storms, logging activities, volcanic eruptions, and mining activities. These disturbances can cause significant damage to an ecosystem, leading to the loss of vegetation and disruption of the soil structure, which then allows for new species to gradually recolonize and establish themselves in the area, ultimately leading to the process of secondary succession.
How does an ecosystem change as it goes through succession?
An ecosystem changes as it goes through succession by transitioning from a simple, barren landscape to a more complex and diverse environment over time. Initially, pioneer species colonize the area and create soil, paving the way for more complex plant communities to establish. As different plant species grow and compete for resources, the ecosystem becomes more diverse, attracting a variety of animals and forming intricate food webs. Ultimately, a mature and stable ecosystem emerges with a balance of species and interactions, resulting in increased biodiversity and ecological resilience.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments