Earth Shadow Worksheet
The Earth Shadow worksheet is a helpful resource for students studying astronomy or those who have a keen interest in understanding celestial phenomena. This carefully crafted worksheet provides a comprehensive introduction to the concept of the Earth's shadow and its impact on various celestial events. The worksheet covers key topics such as lunar eclipses, solar eclipses, and the phases of the moon, making it an ideal tool for students and enthusiasts who wish to deepen their knowledge on this fascinating subject.
Table of Images 👆
- Light and Shadow Worksheet for 1st Grade
- Shadow Matching Worksheets
- Sun Worksheets 2nd Grade
- Shadow and Light Worksheets
- Shadow and Light Worksheets
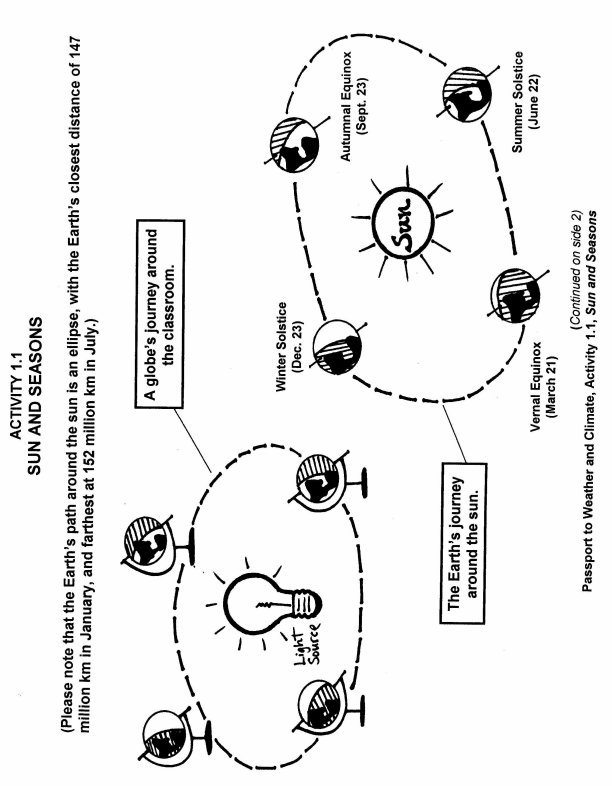
- Sun Earth and Seasons Worksheet
- Earth Coloring Pages Education
- Dinosaur Shadow Matching Worksheet
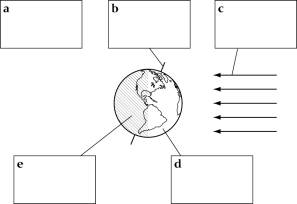
- Earth Spheres Worksheet
- Earth-Sun and Moon Worksheets
- Earth Rotation Day and Night Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What causes the Earth's shadow?
The Earth's shadow is caused by the planet blocking sunlight from reaching the portion of space directly behind it. This occurs during a lunar eclipse when the Earth is positioned between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon. The shadow is cone-shaped and consists of two parts: the darker, central umbra where all sunlight is blocked, and the lighter penumbra where only some sunlight is blocked.
Describe the shape of the Earth's shadow during a lunar eclipse.
During a lunar eclipse, the shape of the Earth's shadow on the moon appears as a curve that gradually covers the moon. As the eclipse progresses, the shadow moves across the face of the moon, creating a gradual darkening and then a reddish hue during totality known as the "blood moon." This shape is due to the Earth blocking the sunlight from reaching the moon and casting its shadow on the lunar surface.
How does the Earth's shadow impact the appearance of objects in space?
The Earth's shadow can impact the appearance of objects in space by causing eclipses. During a lunar eclipse, the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon and temporarily blocking its light. This gives the Moon a reddish hue, known as a blood moon. Similarly, during a solar eclipse, the Moon comes between the Earth and the Sun, casting a shadow on Earth and causing the Sun to be partially or totally obscured. These celestial events can dramatically alter the appearance of objects in space and provide unique viewing opportunities for scientists and enthusiasts alike.
Explain why the Earth's shadow is not visible during a solar eclipse.
The Earth's shadow is not visible during a solar eclipse because a solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, blocking the Sun's light from reaching the Earth. The Earth's shadow is cast in the opposite direction of the Sun, so during a solar eclipse, the Moon is blocking the Sun's light before it can reach the Earth, preventing the Earth's shadow from being visible.
Describe the different types of Earth shadows that occur during different times of the day.
During sunrise and sunset, Earth's shadow is most noticeable as a deep, elongated cone that stretches into the sky opposite to the direction of the sun. This is known as the "Belt of Venus" or the Earth's Shadow. As the day progresses, the Earth's shadow moves lower and becomes less distinct, eventually disappearing as the sun reaches its highest point in the sky around noon. At this time, the shadow lies directly beneath objects on the ground. Afternoon and evening bring about the reemergence of the Earth's shadow as the sun sets, creating a similar elongated cone but in the opposite direction from sunrise.
How does the Earth's shadow create the phenomena known as twilight?
Twilight occurs as a result of the Earth's shadow being cast into the atmosphere after sunset and before sunrise. The Earth's atmosphere scatters sunlight in all directions, causing the sky to continue to be illuminated even after the Sun has set or before it has risen. This scattering of light creates the various shades of colors seen during twilight, ranging from vibrant oranges and pinks to deeper purples and blues, as the Earth transitions between night and day.
Describe the motion of the Earth's shadow throughout the day.
The Earth's shadow changes throughout the day as the planet rotates on its axis, causing the shadow to move across the surface. In the morning, the shadow is longest and stretches westward as the Sun rises in the east. As the day progresses, the shadow shortens and moves eastward as the Sun moves higher in the sky. By midday, the shadow is at its shortest, directly beneath an object. In the afternoon, the shadow lengthens again, this time stretching towards the east as the Sun begins to set in the west. Ultimately, the Earth's rotation causes the shadow to shift from west to east, constantly changing in length and direction as the day progresses.
How does the Earth's shadow affect the length of daylight hours?
The Earth's shadow does not affect the length of daylight hours. Daylight hours are primarily determined by the rotation of the Earth on its axis and its orbit around the Sun. The Earth's shadow is mainly relevant during events such as lunar and solar eclipses, but it does not impact the overall length of daylight hours experienced on Earth.
Explain the concept of the umbra and penumbra in relation to the Earth's shadow.
The umbra refers to the central, darkest part of a shadow where all light is completely blocked, such as during a total solar eclipse when the Moon passes directly in front of the Sun. The penumbra is the outer part of the shadow where only some of the light source is blocked, creating a partial shadow that is less intense than the umbra. When Earth blocks sunlight from reaching the Moon, it creates a shadow that consists of both the darker umbra and the lighter penumbra regions, resulting in a lunar eclipse with varying degrees of darkness and visibility depending on the Moon's position within these shadow regions.
Describe how the Earth's shadow can be used to track the movement of celestial bodies.
The Earth's shadow can be used to track the movement of celestial bodies by observing how they pass through or are blocked by the shadow during events such as lunar and solar eclipses. When a celestial body moves through the Earth's shadow, its position and timing can be recorded to study its orbit and motion. This information can provide insights into the celestial body's path, speed, and relationship to other objects in space, aiding astronomers in understanding the mechanics of the solar system and beyond.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments