Earth Materials Worksheet
Are you an elementary school teacher searching for engaging and educational resources to teach your students about Earth materials? Look no further! Our Earth Materials Worksheet is designed specifically for young learners, providing them with a fun and interactive way to explore and understand the different types of materials found on our planet. Whether you are discussing rocks, minerals, soil, or other natural resources, this worksheet offers a comprehensive introduction to this fascinating subject.
Table of Images 👆
- Free Earth Day Worksheets ESL
- Earth System Science Worksheet
- Free Printable Earth Day Coloring Sheets
- Glencoe Earth Science Worksheet Answers
- Earth Science Water Cycle Worksheets
- Man Made and Natural Resources Worksheets
- Critical Thinking Science Worksheets
- Earth Layers Lesson Plan
- Earth Day Kindergarten Activities Worksheets
- Inside Earth Layers Worksheet
- Day Earth Math Worksheets
- Earth Interior Worksheets Answers
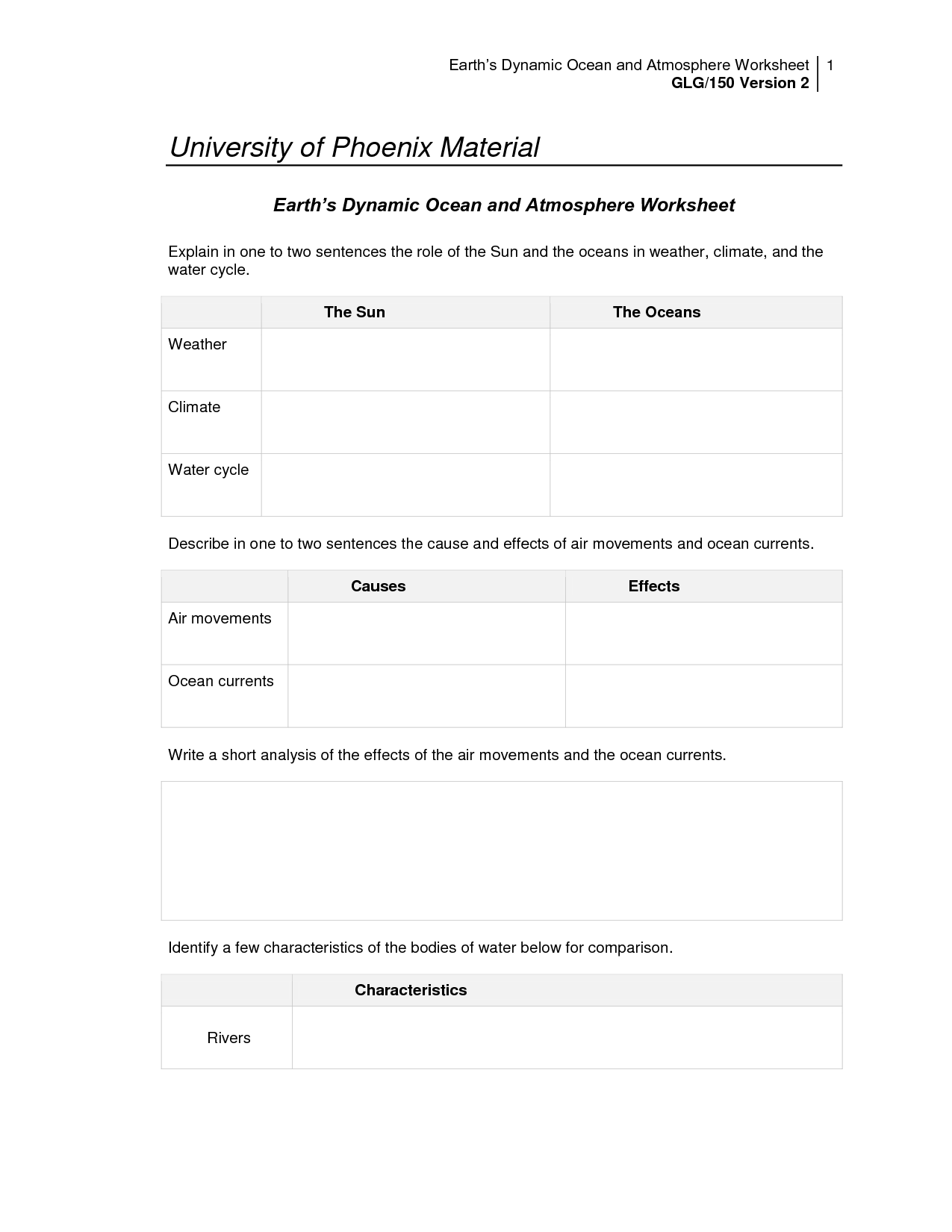
- Atmosphere and Oceans Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What are the three main types of rocks and how are they formed?
The three main types of rocks are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks form from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation and compression of sediments like mud, sand, and organic materials. Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing rocks are subjected to high temperatures and pressures, causing their mineral composition and texture to change without fully melting.
How are minerals different from rocks?
Minerals are naturally occurring inorganic substances with a specific chemical composition and crystal structure, while rocks are aggregates of minerals or organic materials. Rocks are composed of one or more minerals, and they can also contain non-mineral components like volcanic glass or organic material. In summary, minerals are the building blocks of rocks, and while rocks are made up of minerals, minerals can also exist on their own in nature.
What are the different layers of the Earth and what are they made of?
The Earth is composed of four main layers: the inner core, outer core, mantle, and crust. The inner core is mostly made of iron and nickel. The outer core is also made of iron and nickel, but it is in a liquid state. The mantle is composed of silicate rocks rich in magnesium and iron. The crust, the outermost layer, is primarily made of lighter rock materials like granite and basalt.
How is sedimentary rock formed?
Sedimentary rocks are formed through the deposition and solidification of sediment that is weathered and eroded from pre-existing rocks. This sediment can be carried by water, wind, or ice, and is eventually deposited in layers. Over time, these layers become compacted and cemented together, forming solid sedimentary rock. The most common types of sedimentary rocks are sandstone, limestone, and shale.
What is the process of metamorphism?
Metamorphism is the process in which rocks undergo changes in mineral composition, texture, or both due to changes in temperature, pressure, or presence of fluids. It occurs deep within the Earth's crust where rocks experience intense heat and pressure, causing the minerals within them to recrystallize to form new minerals and textures. Metamorphism can lead to the formation of new rocks such as marble from limestone or gneiss from granite, and these changes help us understand the geologic history of the Earth.
What are the characteristics of igneous rocks?
Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. They can be classified into two types: intrusive, which form underground and have larger crystal sizes due to slower cooling, and extrusive, which form on the Earth's surface and have smaller crystal sizes due to rapid cooling. Igneous rocks typically have a crystalline texture, are composed of mineral grains, and are often hard and resistant to weathering. They can vary in color, composition, and density, and are an important component of the Earth's crust.
How are minerals identified and categorized?
Minerals are identified and categorized based on their physical and chemical properties. Physical properties such as color, streak, luster, hardness, cleavage, and crystal form are used to help distinguish between different minerals. Chemical properties, such as composition and structure, are also important factors in identifying and categorizing minerals. Minerals can be classified into different groups based on their chemical composition, crystal structure, and other characteristics, helping to organize and understand the vast array of minerals found in nature.
What are the primary factors that contribute to soil formation?
The primary factors that contribute to soil formation include climate (temperature and precipitation), parent material (original rocks and minerals), organisms (plants and microorganisms), topography (slope and orientation), and time (the longer a soil has been forming, the more developed it becomes). These factors interact to determine the physical, chemical, and biological properties of the soil, shaping its characteristics and fertility.
How does erosion impact landforms and Earth's surface?
Erosion plays a significant role in shaping landforms and altering the Earth’s surface. It wears down surfaces through processes such as water, wind, and ice movement, resulting in the formation of valleys, canyons, cliffs, and beaches. Erosion helps in leveling mountains over time, carving out rivers and lakes, and reshaping coastlines. It also plays a part in transporting sediments from one place to another, contributing to the formation of new landforms. Overall, erosion has a transformative effect on the Earth's surface, continually changing landscapes and sculpting the environment.
What are some examples of renewable and non-renewable Earth materials?
Examples of renewable Earth materials include sunlight, wind, and biomass such as crops and trees. Non-renewable Earth materials include fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, as well as minerals such as gold, silver, and diamonds.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments