DNA Model Worksheet
Are you a science teacher searching for a valuable tool to help your students grasp the intricate structure of DNA? If so, this DNA Model Worksheet may be just what you need. This worksheet is designed to engage students with hands-on learning, allowing them to construct their own DNA models and gain a deeper understanding of this essential subject.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Model Cut Out Worksheets
- Labeled DNA Model Worksheet
- The Double Helix DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- DNA Coloring Page for Kids
- DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- The DNA Double Helix Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Paper Model Activity
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- Worksheets DNA Coloring Page
- DNA Molecule Label Worksheet
- DNA Paper Model Activity
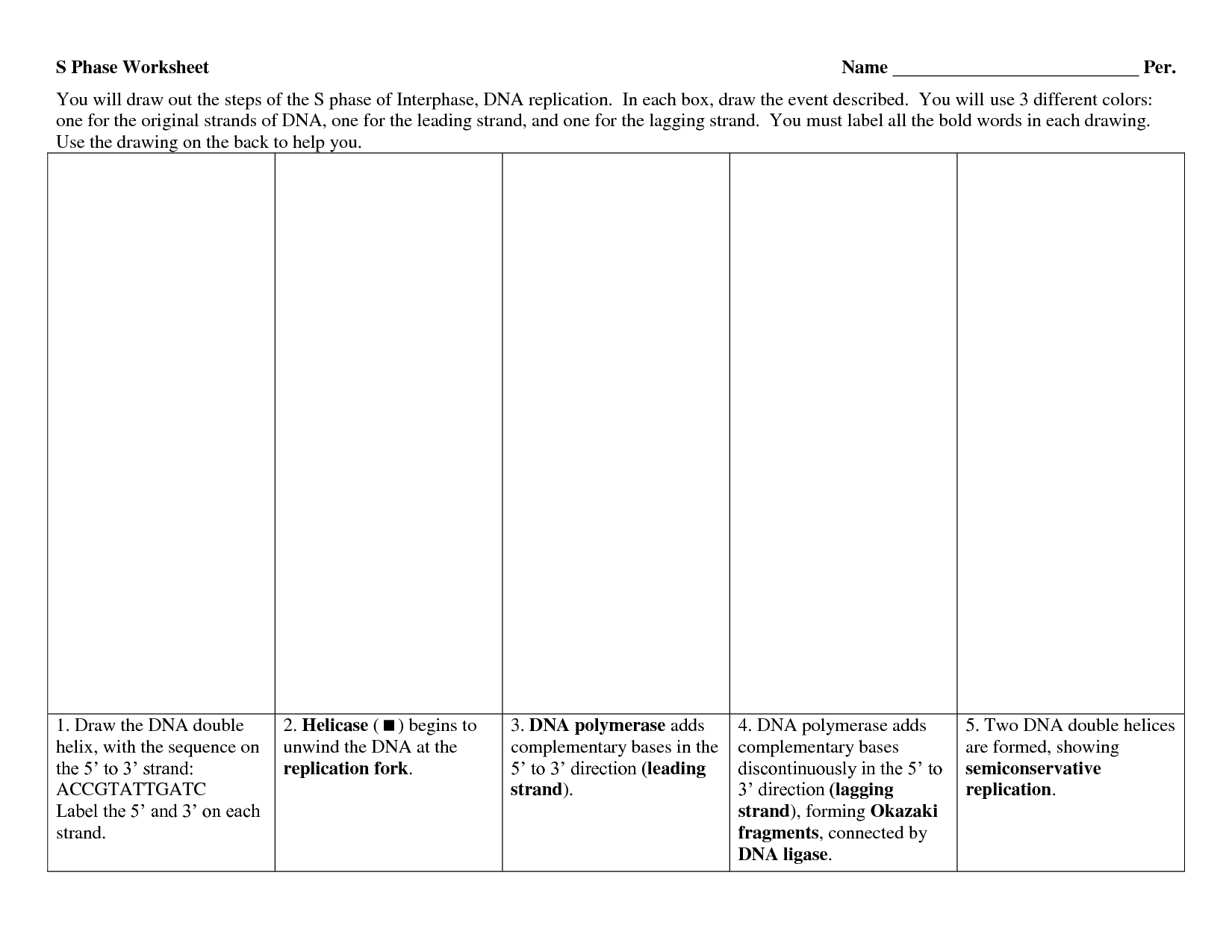
- DNA Replication Worksheet
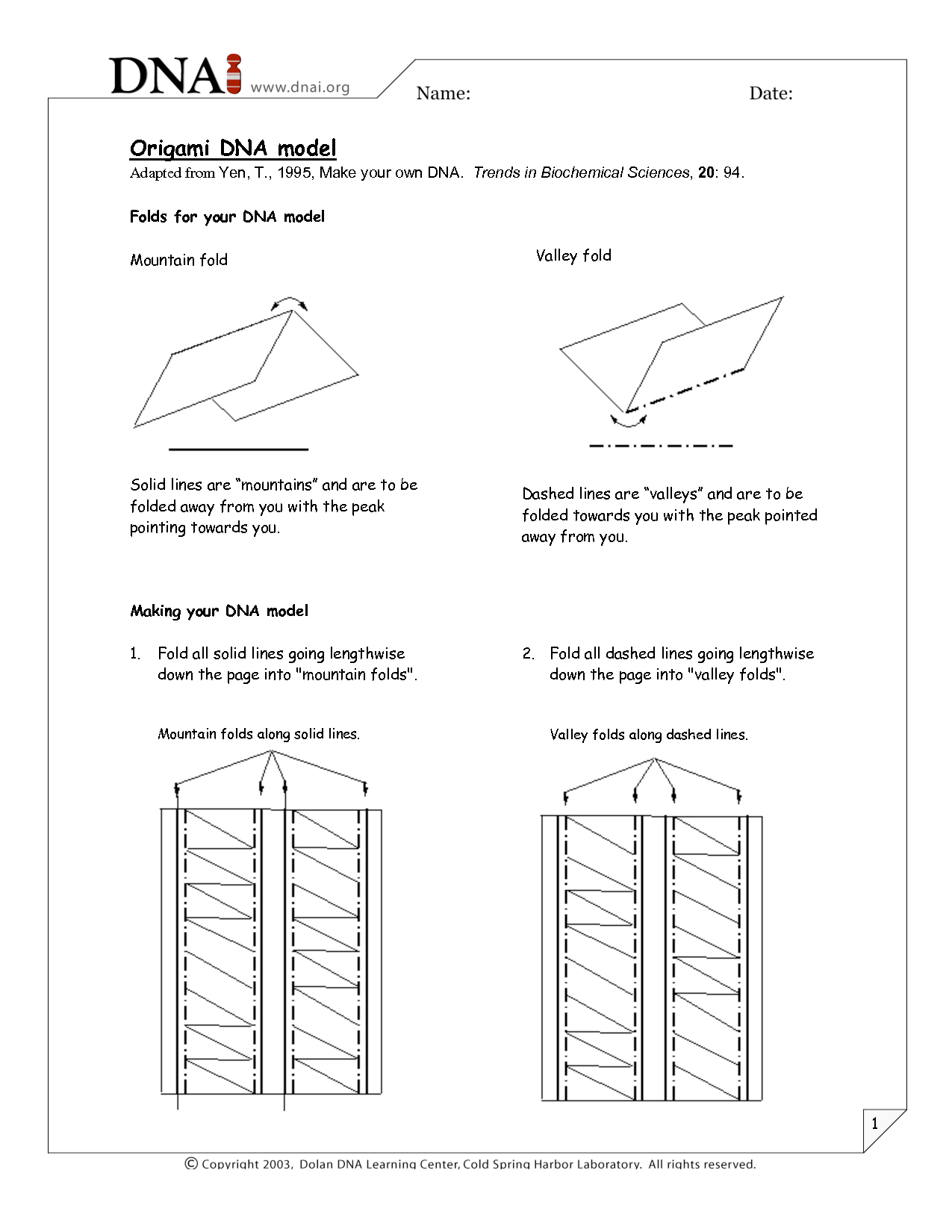
- Origami DNA Model Template
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
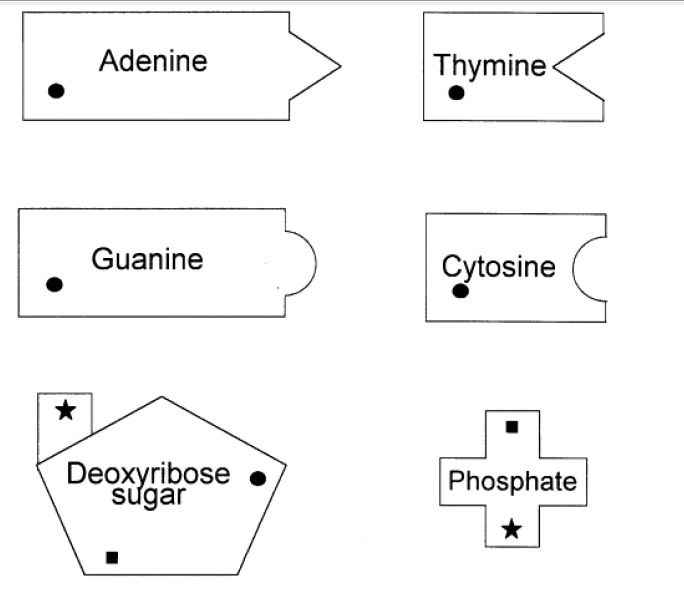
What is DNA made up of?
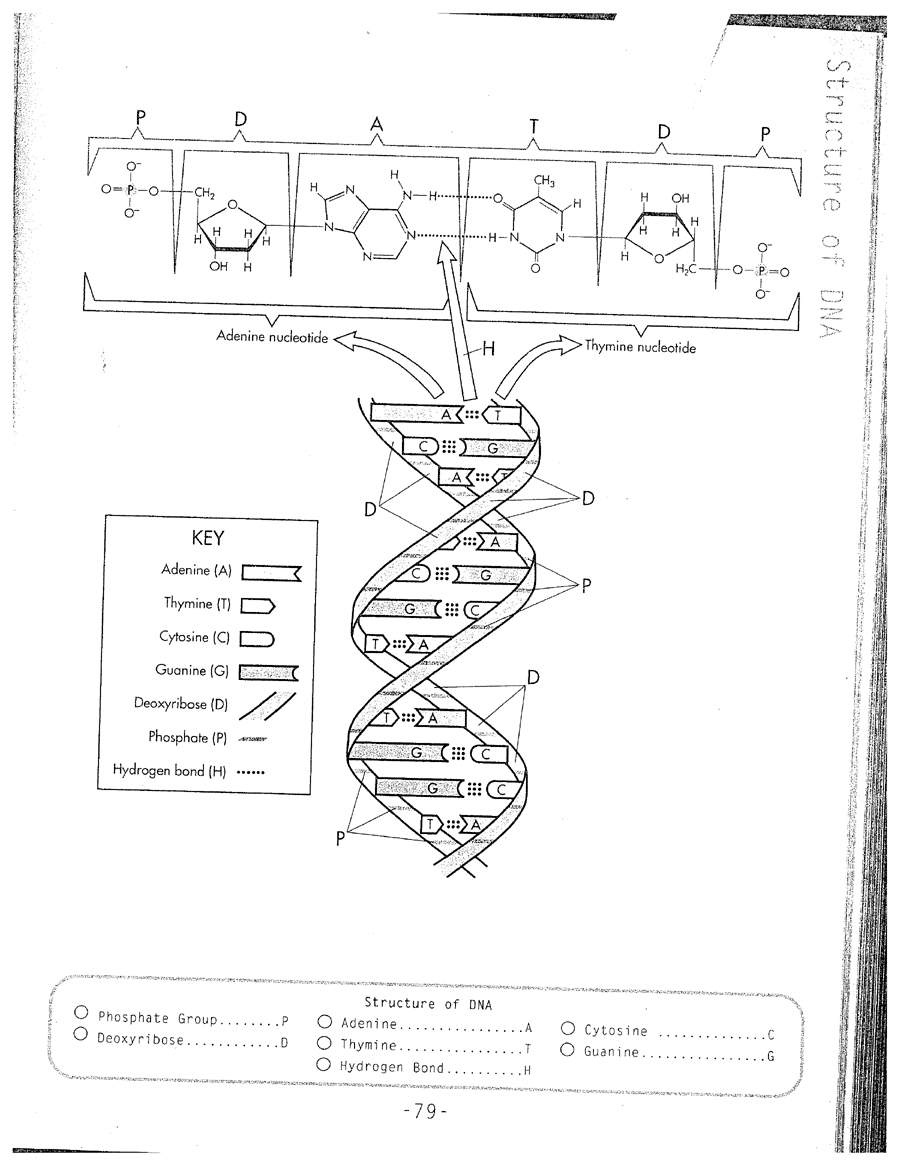
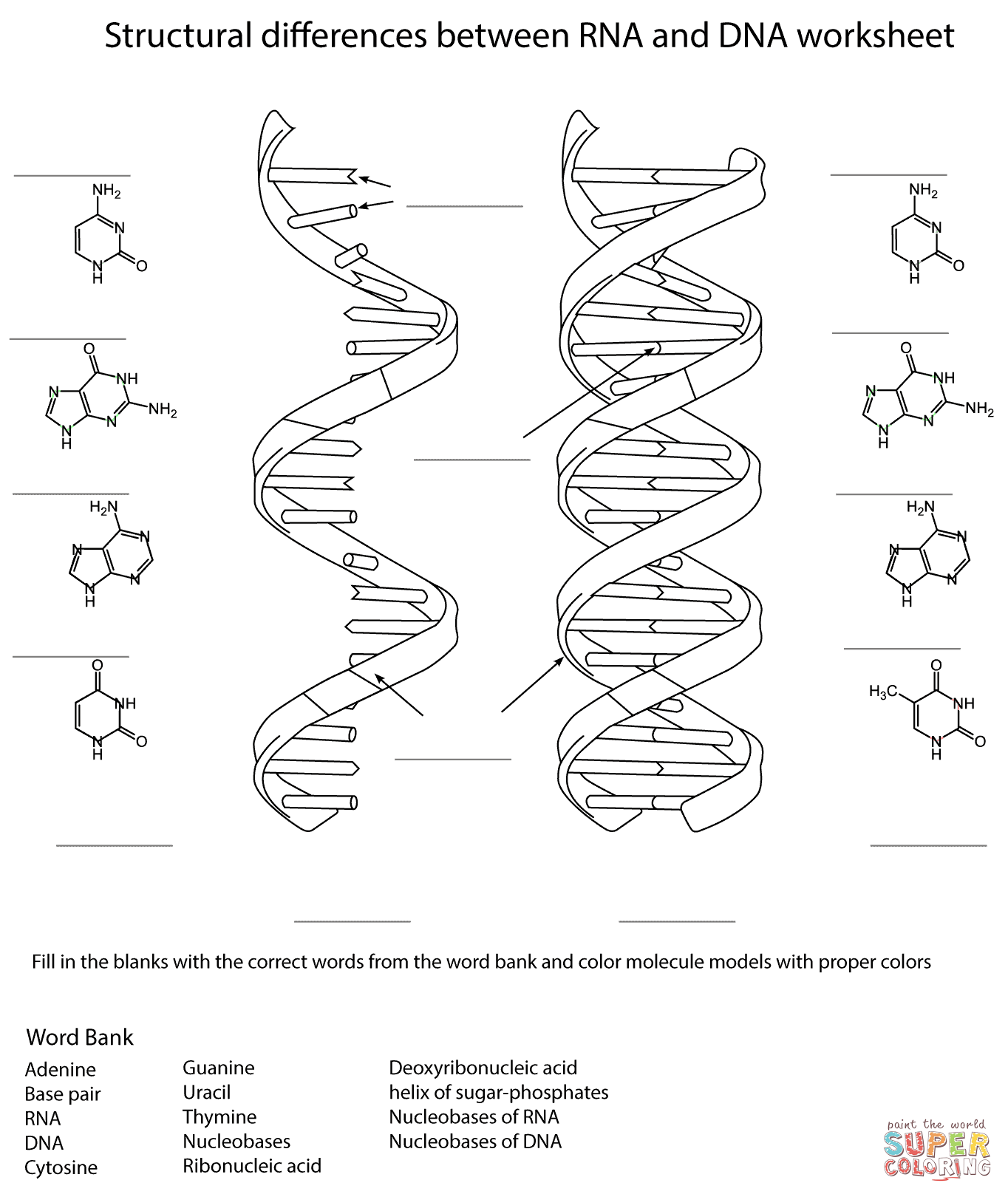
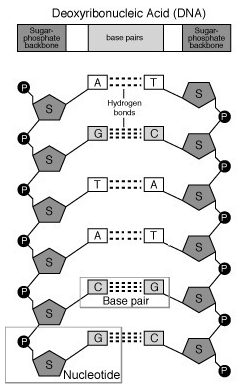
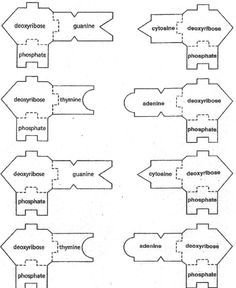
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine). These nucleotides are arranged in a double-helix structure, with the nitrogenous bases pairing specifically (adenine with thymine, and cytosine with guanine) to form the genetic code that determines the characteristics of living organisms.
What are the four bases found in DNA?
The four bases found in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases pair up with each other in a specific manner - A with T and C with G - forming the building blocks of the DNA double helix structure.
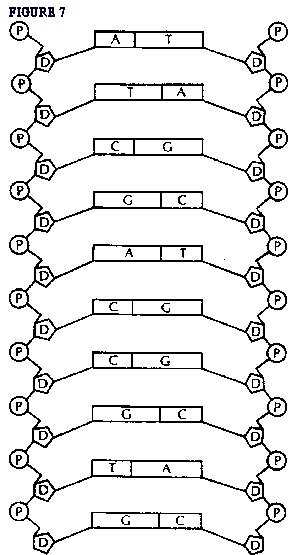
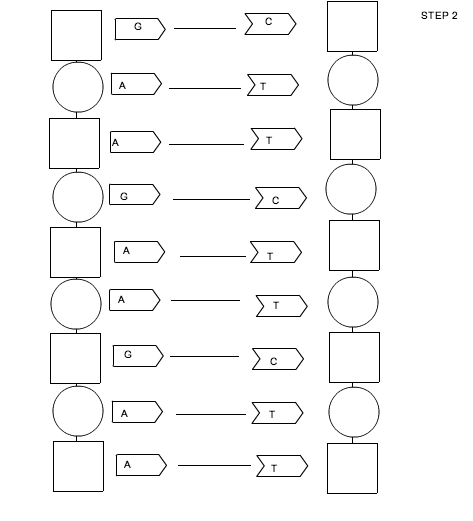
How do the bases pair up in DNA?
The bases pair up in DNA through hydrogen bonds: adenine pairs with thymine, and guanine pairs with cytosine. This complementary base pairing allows DNA to effectively store and transmit genetic information through the precise ordering of these base pairs along the double helix structure of the DNA molecule.
What is the purpose of the sugar-phosphate backbone in DNA?
The sugar-phosphate backbone in DNA serves to provide structural support and stability to the molecule. It also helps to protect the nitrogenous bases in the interior of the double helix, ensuring the genetic information encoded in the sequence of bases is preserved and can be accurately copied during DNA replication. Additionally, the backbone plays a role in maintaining the overall shape and integrity of the DNA molecule, crucial for its function in storing and transmitting genetic information.
What is the shape of the DNA double helix?
The DNA double helix has a twisted ladder-like structure, consisting of two strands coiled around each other in a spiral shape. The sugar-phosphate backbones of the strands form the sides of the ladder, while the nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) form the rungs, connecting the two strands together through hydrogen bonds.
What is the role of DNA replication?
The role of DNA replication is to make a copy of the DNA molecule, ensuring the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. It is a vital process in all living organisms as it allows for accurate duplication of the genetic material, enabling cell division and growth, as well as repair and maintenance of damaged DNA.
What is a gene and what does it encode?
A gene is a specific sequence of DNA that contains the instructions for making a particular protein or RNA molecule. It encodes the genetic information necessary for the synthesis of these molecules, which play essential roles in various cellular processes and functions within an organism.
How does DNA control the production of proteins in cells?
DNA controls the production of proteins in cells through a process called protein synthesis. It starts with the DNA in the cell's nucleus being transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. The mRNA then travels to the ribosomes, where transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring amino acids to the ribosomes based on the mRNA sequence. The ribosomes then read the mRNA code in groups of three nucleotides called codons and assemble amino acids into a protein according to the instructions encoded in the DNA. This process ensures that the correct proteins are produced in the cells.
What is the significance of genetic mutations in DNA?
Genetic mutations in DNA are significant as they contribute to the diversity and evolution of species, drive genetic diseases, and can impact traits such as susceptibility to diseases, physical characteristics, and behavior. While some mutations may be harmful, others can be beneficial and provide a foundation for natural selection to act upon, leading to adaptation and survival of species in changing environments. Tracking and studying mutations also play a crucial role in fields like medicine, forensics, and evolutionary biology.
How does DNA contribute to inheritance and genetic variation?
DNA is the molecule that contains the genetic information passed down from parents to offspring, determining their physical traits and characteristics. Through processes like replication, transcription, and translation, DNA is responsible for the transmission of genetic material across generations. Inheritable traits are carried in specific regions of DNA called genes, which can be inherited from both parents and contribute to the genetic variation seen within populations. Mutations, genetic recombination during meiosis, and the random assortment of chromosomes during fertilization can further increase genetic diversity, playing a crucial role in evolution and adaptation.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments