DNA Fingerprinting Biology Worksheet Answer
If you are a biology student or teacher seeking a comprehensive and informative DNA fingerprinting worksheet answer, you have come to the right place. This blog post will provide an introduction to DNA fingerprinting, discuss its importance in various fields, and offer a detailed answer key to a biology worksheet centered around this topic.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Fingerprinting Activity Worksheet
- DNA Fingerprinting Paternity Test
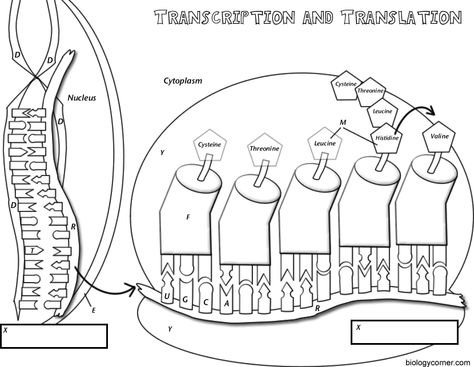
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- On Protein Synthesis DNA and RNA Worksheet Answers
- DNA Technology Worksheet Answers
- DNA RNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
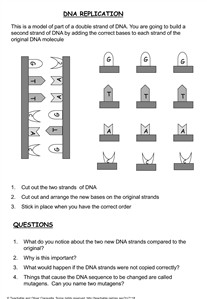
- DNA and Replication Worksheet
- DNA Fingerprint Worksheet
- Pedigree Worksheet and Answer Key
- DNA Fingerprinting Worksheet
- Restriction Mapping Problems AP Biology
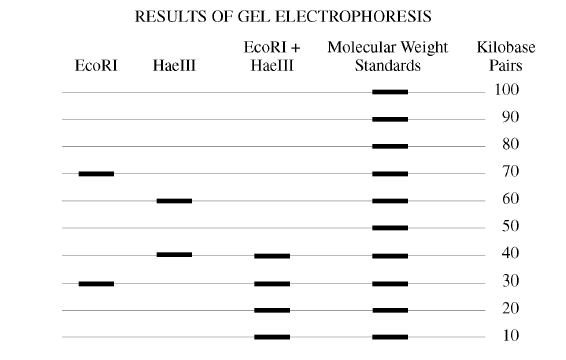
- DNA Gel Electrophoresis Worksheet
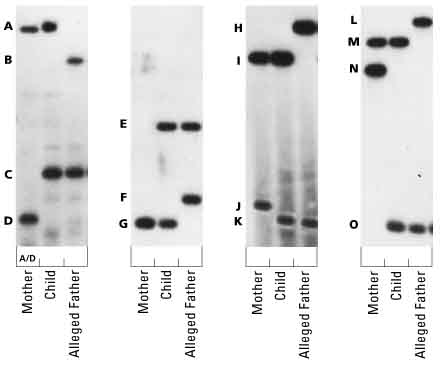
- DNA Gel Electrophoresis Paternity Test
- Student Exploration Gizmo Photosynthesis Lab Answer Key
More Biology Worksheets
Free Printable Biology WorksheetsCollege Biology Worksheets
7th Grade Biology Worksheets
Biology Macromolecules Worksheets and Answers
Karyotype Worksheet Answers Biology
What is DNA fingerprinting?
DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on unique patterns in their DNA. It involves analyzing specific regions of an individual's DNA, typically using molecular biology techniques like polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and gel electrophoresis. The resulting pattern of DNA fragments is then compared to other samples to determine genetic relatedness, paternity/maternity testing, or criminal investigations. DNA fingerprinting is highly accurate and has numerous applications in forensics, paternity testing, and medical research.
How is DNA extracted for analysis in DNA fingerprinting?
In DNA fingerprinting, DNA is typically extracted from cells using a process that involves breaking open the cell membrane to release the DNA, followed by purification to remove proteins and other contaminants. The most common method used is the organic extraction method, where a series of chemical solutions are used to break down the cell and isolate the DNA. Once the DNA is extracted, it can be analyzed and compared for genetic similarities and differences, forming the basis of DNA fingerprinting.
What are restriction enzymes and how are they used in DNA fingerprinting?
Restriction enzymes are proteins that cut DNA at specific sequences, creating DNA fragments. In DNA fingerprinting, restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA samples at specific sites, resulting in different fragment sizes. These fragments are then separated based on size using a technique like gel electrophoresis to create a unique pattern or "fingerprint" for each individual. By comparing the DNA fingerprints from different individuals, similarities and differences can be identified, allowing for identification or relationship testing in fields such as forensics and paternity testing.
How are DNA fragments separated in gel electrophoresis?
DNA fragments are separated in gel electrophoresis based on their size, where a sample containing DNA fragments is loaded into a gel matrix and subjected to an electric field. The negatively charged DNA molecules move towards the positive electrode, with smaller fragments traveling faster and farther through the gel than larger fragments due to the obstacles presented by the gel matrix. As a result, the DNA fragments get separated according to their sizes, allowing for analysis and comparison of fragment lengths.
What are DNA probes and why are they important in DNA fingerprinting?
DNA probes are short, single-stranded DNA sequences that are complementary to specific target sequences within an individual's DNA. In DNA fingerprinting, these probes are crucial as they bind to the unique regions of an individual's DNA, allowing scientists to identify and analyze those regions. This is essential for comparing DNA samples from different individuals and establishing genetic relationships, such as in forensic investigations or paternity testing. The specificity of DNA probes ensures accurate and reliable results in identifying individuals based on their genetic information.
What is the purpose of hybridization in DNA fingerprinting?
The purpose of hybridization in DNA fingerprinting is to identify specific DNA sequences by allowing single-stranded DNA probes to bind to complementary sequences in a sample. This technique helps to detect genetic variations or similarities between individuals based on their unique DNA profiles, which can be used for various applications such as paternity testing, forensic analysis, and genetic research.
How is autoradiography used to visualize DNA fragments in gel electrophoresis?
Autoradiography is used to visualize DNA fragments in gel electrophoresis by incorporating radioactive nucleotides into the DNA samples prior to electrophoresis. After electrophoresis, the gel is dried and exposed to X-ray film or a phosphorimager screen. The radioactive DNA fragments emit energy that exposes the film or screen, creating an image of the separated DNA bands. This allows for the visualization and analysis of the DNA fragments based on their size and migration distance in the gel.
What is the significance of the number and size of DNA fragments in a DNA fingerprint?
The number and size of DNA fragments in a DNA fingerprint are significant because they determine the uniqueness and variability of an individual's DNA profile. The fragments represent specific regions of DNA that vary between individuals due to genetic differences. By analyzing the number and size of these fragments, scientists can create a unique pattern that serves as a genetic identifier for an individual, making DNA fingerprinting a valuable tool for forensic investigations, paternity testing, and other applications requiring accurate identification based on genetic information.
How is DNA fingerprinting used in forensic science?
DNA fingerprinting, also known as DNA profiling, is a technique used in forensic science to identify individuals by analyzing unique patterns in their DNA. This technique is commonly used in criminal investigations to match DNA samples found at crime scenes to individuals or rule out suspects. By comparing DNA profiles from crime scene evidence with those of suspects or with DNA databases, forensic scientists can provide crucial evidence in identifying perpetrators or exonerating the innocent. DNA fingerprinting has revolutionized forensic investigations by providing highly accurate and reliable identification of individuals, making it a powerful tool in solving crimes and delivering justice.
What are some ethical considerations when using DNA fingerprinting?
Some ethical considerations when using DNA fingerprinting include ensuring informed consent from individuals whose DNA is being analyzed, protecting the privacy and confidentiality of individuals' genetic information, avoiding discrimination based on genetic information, and considering the potential societal implications of using DNA fingerprinting, such as in legal cases or for ancestry testing. It is important to establish clear guidelines for the storage and sharing of genetic data to ensure that it is used responsibly and ethically.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments