DNA Codons Worksheet
Are you a biology student or an enthusiast looking to strengthen your understanding of DNA codons? Look no further! In this blog post, we will introduce you to a helpful tool known as the DNA Codons Worksheet. Designed to enhance your knowledge of genetic codes, this worksheet will provide you with the opportunity to practice deciphering the essential building blocks of life – DNA codons. Whether you're preparing for an exam or simply seeking to deepen your understanding of the subject, this worksheet will serve as an invaluable resource for you.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Genetic Code Chart Worksheet
- mRNA Codon Chart Worksheet
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- Amino Acid Codon Chart Worksheets
- DNA Structure Worksheet High School
- DNA Codon Chart Worksheet
- Transcription Worksheet DNA mRNA Amino Acid
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA RNA Structure Worksheet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
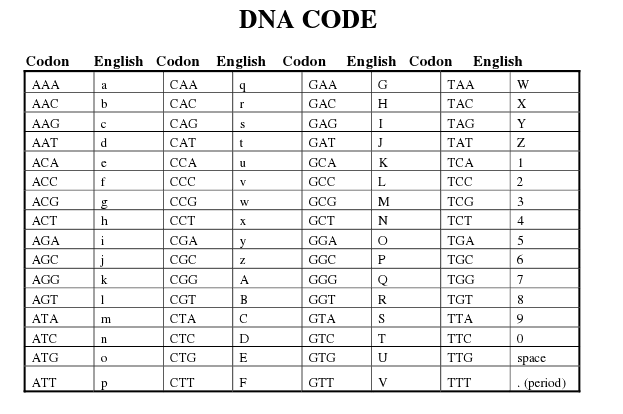
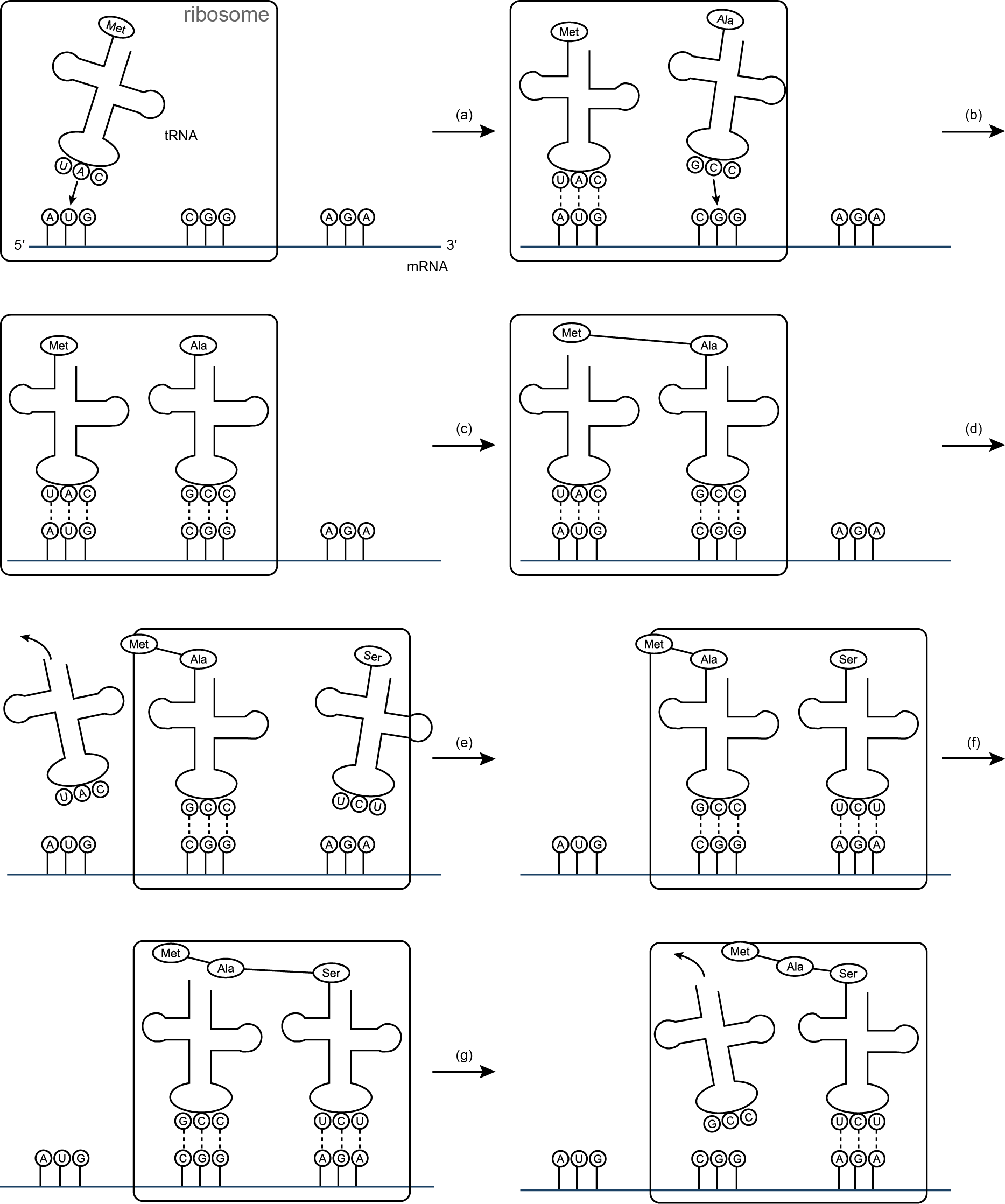
What is a DNA codon?
A DNA codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on the DNA molecule that encodes a specific amino acid or a signal for the initiation or termination of protein synthesis. It is an essential component of the genetic code used by cells to translate the information in DNA into proteins that carry out various functions in the body.
How many nucleotides make up a codon?
A codon consists of three nucleotides.
What is the role of a codon in protein synthesis?
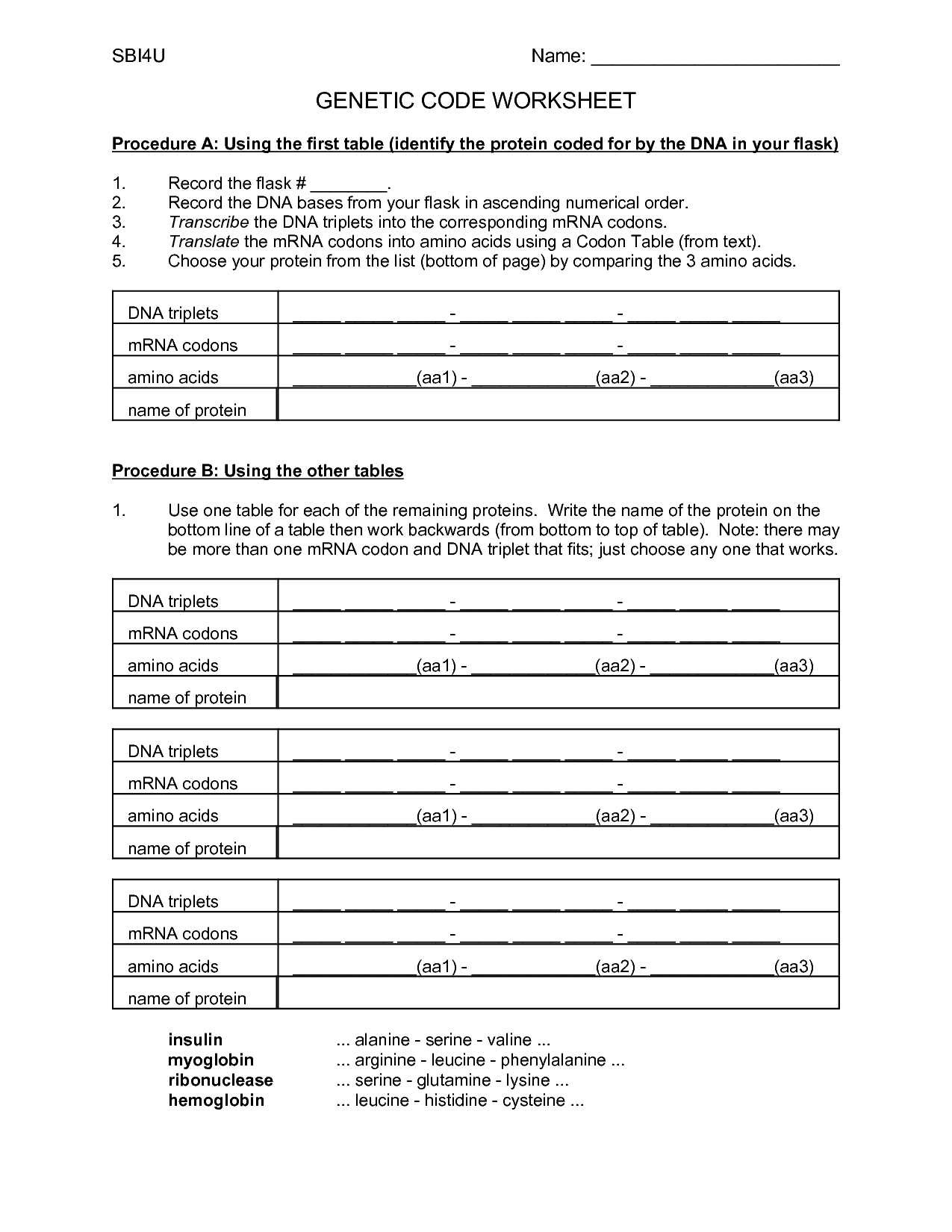
A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule that codes for a specific amino acid during protein synthesis. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, acting as a sort of "genetic code" that determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein. This process occurs during translation, where transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring the corresponding amino acids to the ribosome based on the codon sequence on the mRNA, ultimately leading to the synthesis of a specific protein.
How many different codons are possible in the DNA code?
There are 64 different codons possible in the DNA code. This is because there are 4 different nucleotides (adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine) in DNA, and each codon is made up of a sequence of three nucleotides. With 4 possible choices for each position and three positions in a codon, the total number of possible combinations is 4^3, which equals 64.
How is the genetic code universal?
The genetic code is considered universal because the same set of codons (three DNA or RNA nucleotides that specify a particular amino acid) is used in virtually all organisms on Earth to translate genetic information into proteins. This means that the same codon will code for the same amino acid across different species, highlighting the shared evolutionary history of life on our planet and demonstrating the fundamental unity of all living organisms at the molecular level.
What is the start codon and its function?
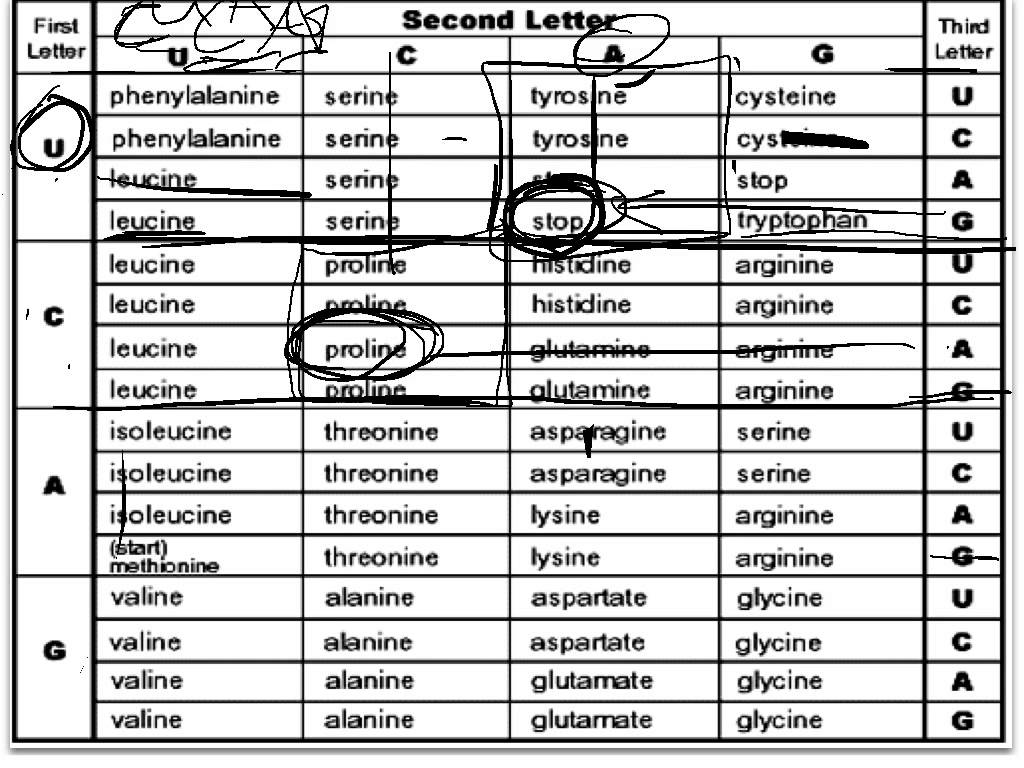
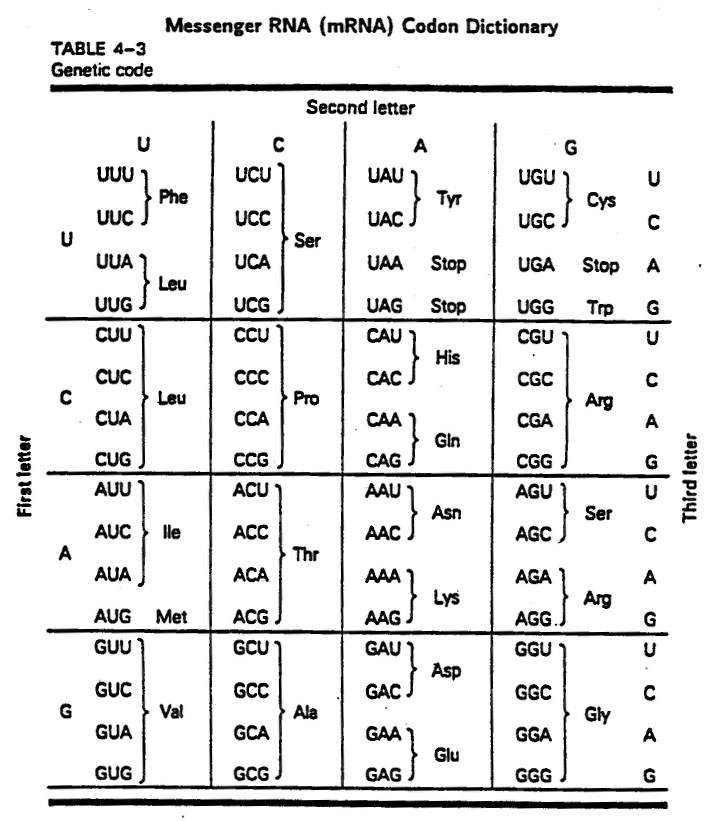
The start codon is AUG, which codes for the amino acid methionine in most organisms. It serves as the initiation signal for protein synthesis, indicating the beginning of the protein coding sequence on mRNA. The ribosome recognizes the start codon and initiates translation, ensuring that the correct reading frame is maintained for the synthesis of the protein.
How many stop codons are there, and what do they indicate?
There are three stop codons in the genetic code: UAA, UAG, and UGA. These codons signal the termination of protein synthesis during translation, indicating to the ribosome to stop adding amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain. This results in the release of the completed protein from the ribosome.
Can a single codon code for multiple amino acids?
No, a single codon codes for only one amino acid. Each codon in the genetic code corresponds to a specific amino acid, ensuring accurate and precise protein synthesis during translation.
What is the significance of the redundancy in the genetic code?
The redundancy in the genetic code, where multiple codons can code for the same amino acid, provides a level of robustness and error tolerance to the genetic information. This redundancy helps to mitigate the effects of mutations by allowing some changes in the DNA sequence without altering the final protein that is produced. It also aids in the efficiency of protein synthesis by providing flexibility in the coding process. Overall, the redundancy in the genetic code is crucial for ensuring the accurate translation of genetic information into functional proteins.
How do mutations in codons affect protein production?
Mutations in codons can affect protein production by introducing changes in the sequence of mRNA, leading to alterations in the amino acid sequence of the protein produced. These changes can result in a different protein being synthesized, a non-functional protein being produced, or a protein with altered functions. Depending on the type of mutation (silent, missense, nonsense, frameshift), the impact on protein production can vary, ultimately affecting the structure, function, and stability of the protein.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments