Division Worksheets 2
Are you a teacher or a parent looking for division worksheets to help your students or children practice their division skills? Look no further! In this blog post, we will explore a variety of division worksheets that are perfect for honing your students' or children's understanding of this essential mathematical operation.
Table of Images 👆
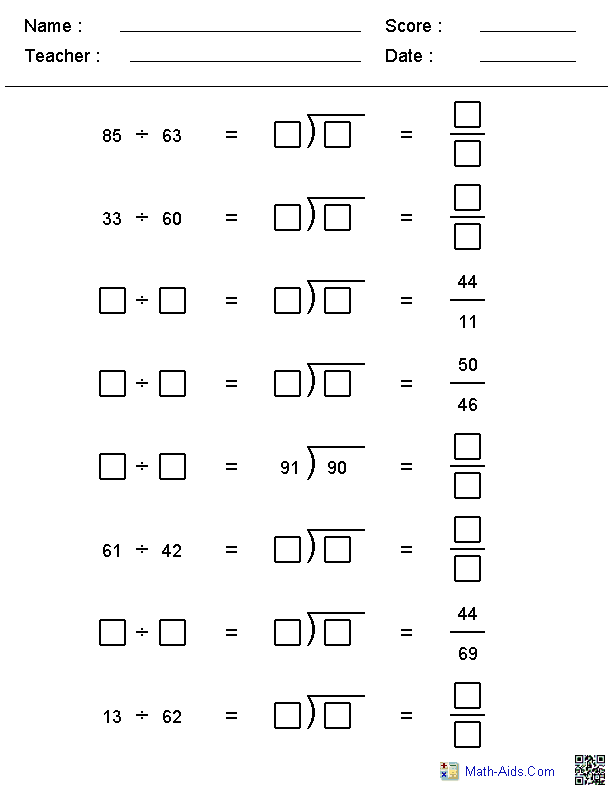
- 2-Digit Divisor Long Division Worksheets
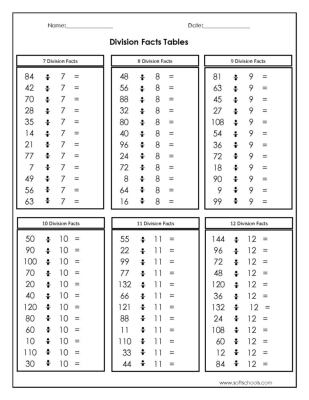
- Division Table Worksheets 1 12
- Printable Division Worksheets 4th Grade Math
- Long Division Worksheets
- Free Printable Division Worksheets 4th Grade
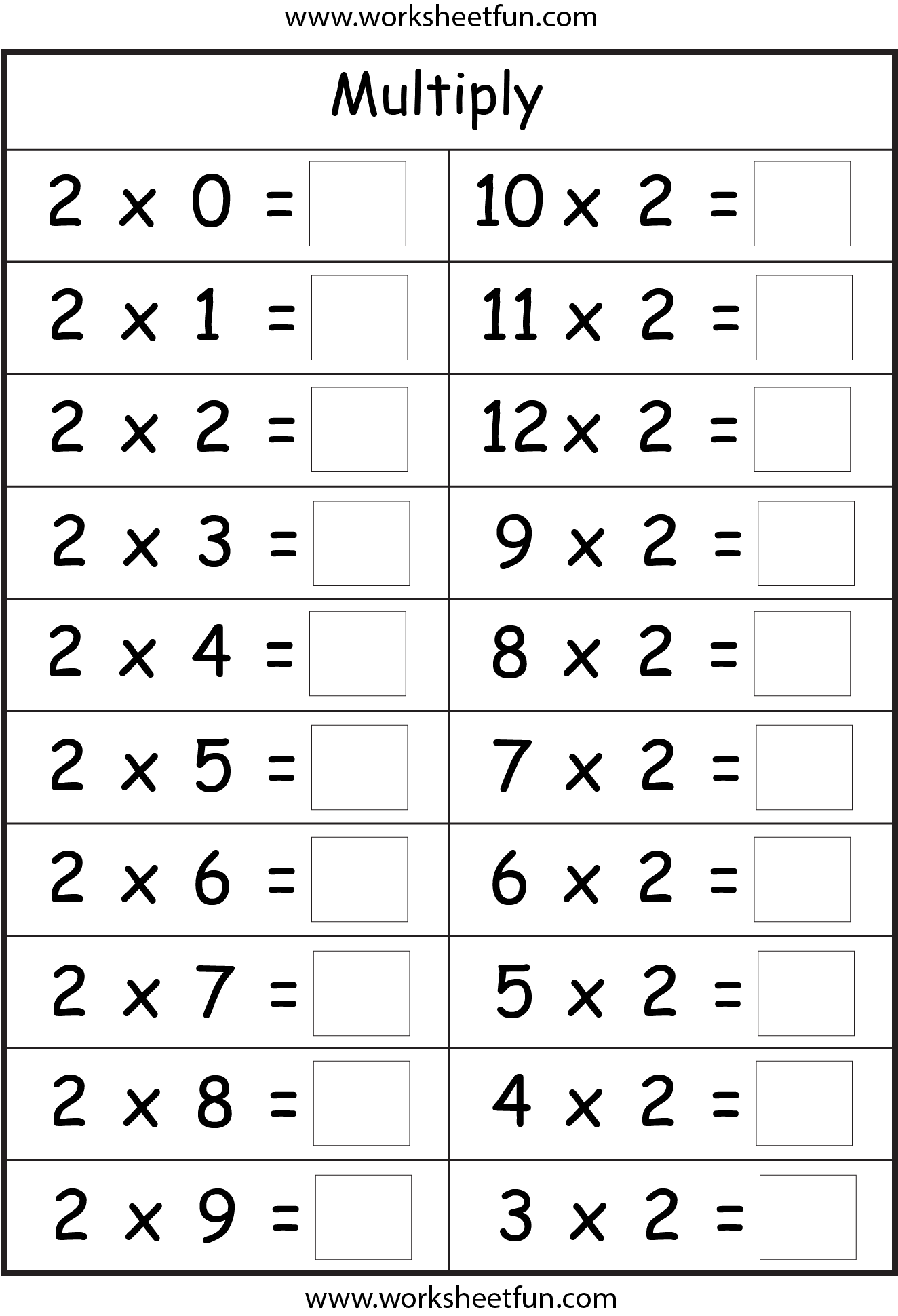
- 2 3 4 5 Multiplication Facts Worksheet
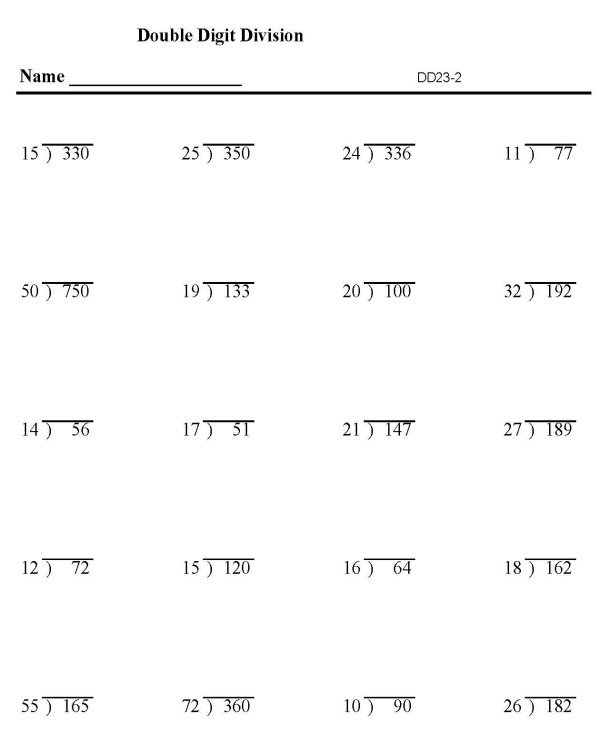
- Two-Digit Division Worksheets
- 8th Grade Math Worksheets Geometry
- Number Lines with Decimals Worksheets
- Adding and Subtracting Integers Worksheet
- 7th Grade Math Worksheets
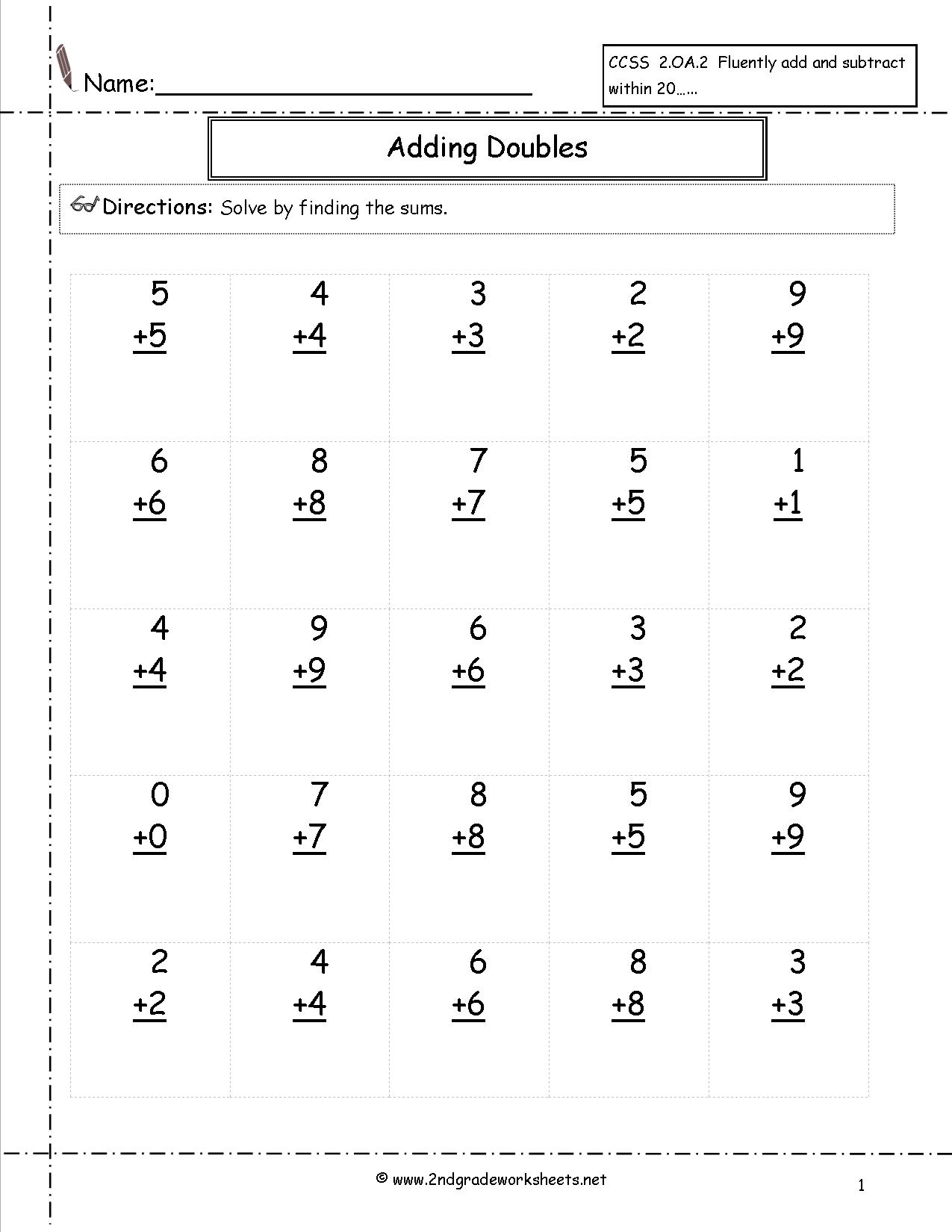
- Single Digit Addition Worksheets
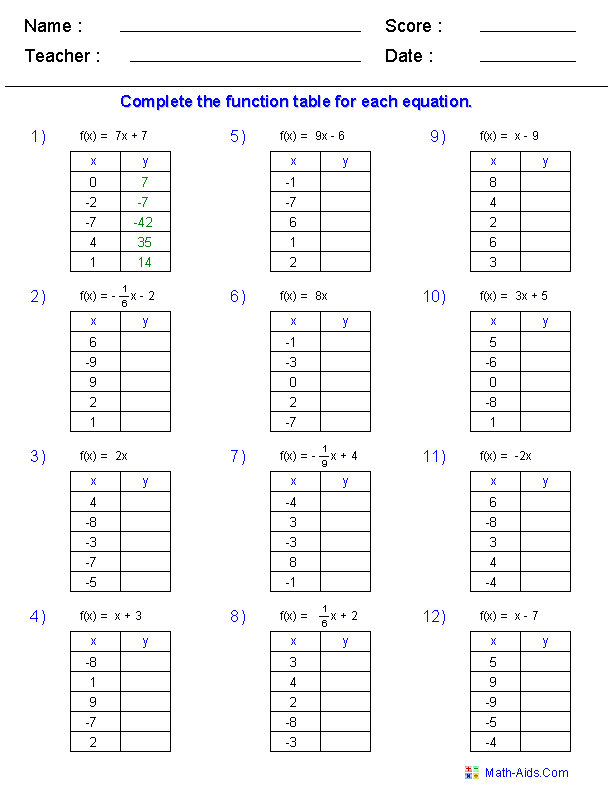
- Function Tables Worksheets
- 8th Grade Math Problems Worksheets
- Math Addition Worksheets 2nd Grade
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
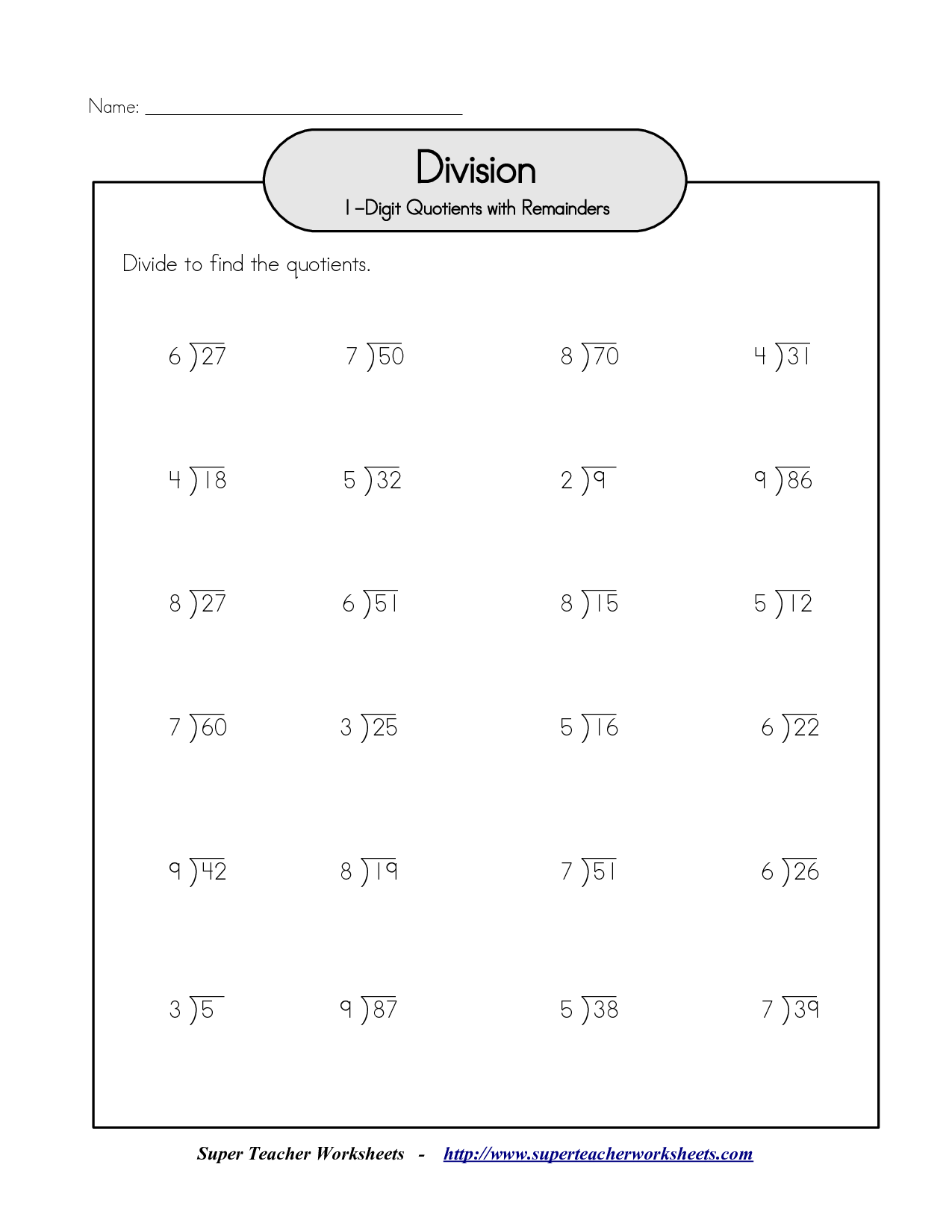
What is division?
Division is an arithmetic operation that involves splitting a number into equal parts or groups. It is the process of determining how many times one number is contained within another number, resulting in a quotient. The division process involves dividing a dividend by a divisor to obtain a quotient or a result.
How is division different from multiplication?
Division is the inverse operation of multiplication, where the total quantity is divided into equal parts. In multiplication, the total quantity is added repeatedly to itself a certain number of times, while in division, the total quantity is split into equal parts to determine the quantity in each part. Division is essentially sharing or distributing a total amount, whereas multiplication is combining or scaling a quantity by a certain factor.
What is the dividend in a division equation?
The dividend in a division equation is the number that is being divided by another number, known as the divisor, to get the quotient. It is the total quantity that is being divided into equal parts to determine how many of those parts can be allocated to each divisor.
What is the divisor in a division equation?
The divisor in a division equation is the number by which another number (the dividend) is divided to give a quotient. It is the number that indicates how many times the dividend will be divided to achieve the quotient.
How is the quotient calculated in division?
The quotient in division is calculated by dividing the dividend by the divisor. It represents the number of times the divisor can be subtracted from the dividend without producing a negative result, or in other words, how many times one number can be divided by another.
What is a remainder in division?
A remainder in division is the amount that is left over when one number is divided by another, which does not result in a whole number. It is the difference between the dividend (the number being divided) and the product of the quotient (the whole number result of the division) and the divisor (the number the dividend is being divided by).
What is a whole number quotient?
A whole number quotient is the result of dividing one whole number by another whole number, where the answer is a whole number without any remainder. In other words, the whole number quotient is the number you get when you divide integers that evenly divide without any remainder.
How do you divide a decimal number?
To divide a decimal number, you can treat it as you would a whole number division problem, but with decimals included. Align the decimal points of the divisor and the dividend, and perform the division as usual. If needed, add zeros to the right of the decimal point in the dividend. After solving the division problem, bring down any remaining decimal places from the dividend to the quotient.
What is the concept of long division?
Long division is a method used in mathematics to divide a large number (dividend) by a smaller number (divisor) to find the quotient and possibly the remainder. It involves a series of steps where the divisor is divided into the most significant digits of the dividend, then multiplication and subtraction are used to determine the next digit of the quotient until the entire dividend is divided. This process is repeated until there are no more digits to bring down, enabling the division to be completed and the quotient obtained.
How can division be used in real-life situations?
Division can be used in real-life situations such as splitting a bill among a group of friends, calculating the average score of a sports team, determining the cost per unit of a product when buying in bulk, or allocating resources such as time or money based on different proportions or ratios.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.







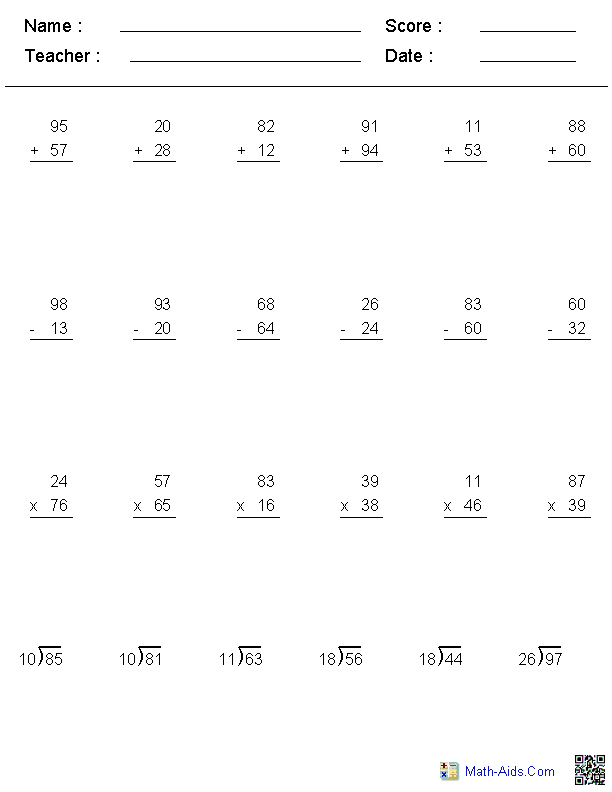















Comments