Decoding DNA Worksheet
The decoding DNA worksheet is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the process involved in unraveling the genetic code. Whether you are a student studying biology or a science enthusiast interested in delving deeper into the world of genetics, this worksheet offers a clear and concise breakdown of the essential concepts and techniques used in decoding DNA.
Table of Images 👆
- 3rd Grade Word Worksheets
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Reading Comprehension Worksheets
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- DNA and Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- 2nd Grade Decoding Worksheets
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet
- Worksheet DNA mRNA Amino Acid
- 6th Grade Thanksgiving Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
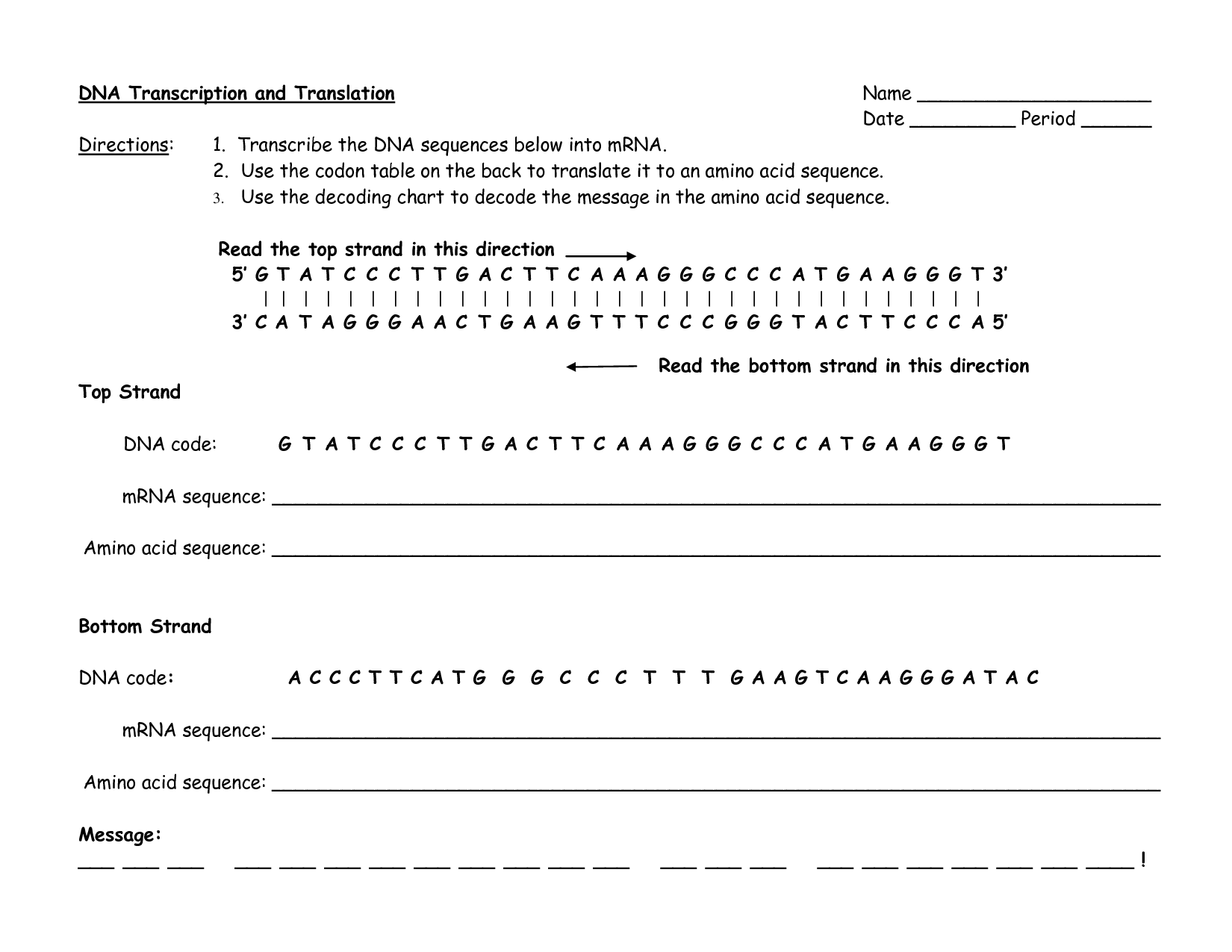
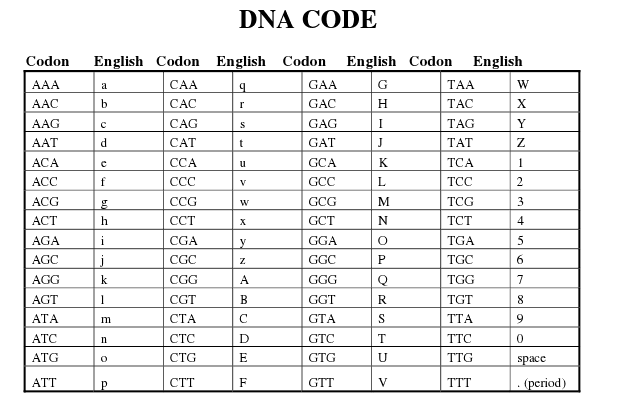
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the purpose of decoding DNA?
The purpose of decoding DNA is to understand the genetic code that determines the characteristics and functions of an organism. By decoding DNA, scientists can identify specific genes, mutations, and genetic variations related to diseases, traits, or evolutionary relationships. This knowledge can lead to advancements in medicine, agriculture, forensics, and evolutionary studies, ultimately improving our understanding of life and enabling the development of targeted therapies and personalized treatments.
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA?
The four nitrogenous bases found in DNA are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). These bases are paired up in specific combinations to form the rungs of the DNA double helix, where adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine.
How is DNA organized in a eukaryotic cell?
DNA in a eukaryotic cell is organized into multiple linear chromosomes located in the nucleus. Each chromosome contains a tightly wound complex of DNA and proteins called chromatin. During cell division, the chromatin condenses further into visible structures known as chromosomes to allow for accurate segregation of genetic material. Additionally, eukaryotic cells also contain DNA in organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts, where it is organized differently compared to nuclear DNA.
What is the role of DNA polymerase in DNA replication?
DNA polymerase is responsible for catalyzing the formation of new DNA strands during DNA replication. It adds nucleotides to the growing DNA chain, using the existing template strand as a guide. DNA polymerase also possesses proofreading capabilities, allowing it to correct errors that may arise during replication. This enzyme plays a critical role in ensuring the accurate and faithful duplication of genetic information.
How does transcription differ from replication?
Transcription is the process of transcribing DNA into RNA, while replication is the process of duplicating DNA. In transcription, only a single strand of DNA is used to produce a complementary RNA strand, which carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes for protein synthesis. In contrast, during replication, the entire DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules. This leads to the formation of two identical daughter cells during cell division.
What is the function of messenger RNA (mRNA)?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries genetic information from the DNA in the cell nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis. In other words, mRNA transcribes the genetic code from the DNA and delivers it to the ribosomes so that proteins can be produced according to the instructions encoded in the DNA.
What is a codon and what does it represent?
A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides in mRNA that corresponds to a specific amino acid or signals the end of protein synthesis. Codons represent the basic unit of genetic code in protein synthesis, determining the sequence of amino acids that are assembled into a protein.
How does the process of translation convert mRNA into a protein?
During translation, the mRNA molecule is decoded by ribosomes in the cytoplasm to synthesize a specific protein. Ribosomes match transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to the codons of the mRNA, with each tRNA carrying a specific amino acid that corresponds to the codon sequence. As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, it reads each codon and brings in the appropriate tRNA that carries the correct amino acid. These amino acids are then joined together in a specific sequence dictated by the mRNA, ultimately forming a protein.
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
The central dogma of molecular biology is a framework that describes the flow of genetic information within a biological system. It states that genetic information is transcribed from DNA to RNA through the process of transcription, and then translated from RNA to protein through the process of translation. This fundamental principle governs how genetic information is stored, expressed, and utilized within living organisms.
How does the knowledge of DNA decoding impact fields such as medicine and forensics?
The knowledge of DNA decoding has revolutionized fields such as medicine and forensics by allowing for more precise diagnoses, personalized treatments, and identification methods. In medicine, understanding DNA decoding has enabled the development of targeted therapies for genetic diseases, cancer treatments, and predictive testing for hereditary conditions. In forensics, DNA decoding plays a crucial role in identifying individuals, solving crimes, and establishing paternity with a high degree of accuracy. Overall, the knowledge of DNA decoding has significantly advanced these fields by providing invaluable insights into human health and identification.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments