Codon Worksheet Answer Key
If you're a science teacher or a student studying genetics, you'll definitely appreciate having a reliable codon worksheet answer key at your disposal. With this handy reference tool, you can easily test your knowledge and understanding of DNA coding, RNA transcription, and protein synthesis. Whether you're reviewing for an exam or simply hoping to deepen your understanding of this complex subject, a codon worksheet answer key can be an invaluable resource.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- DNA Codon Chart Worksheet
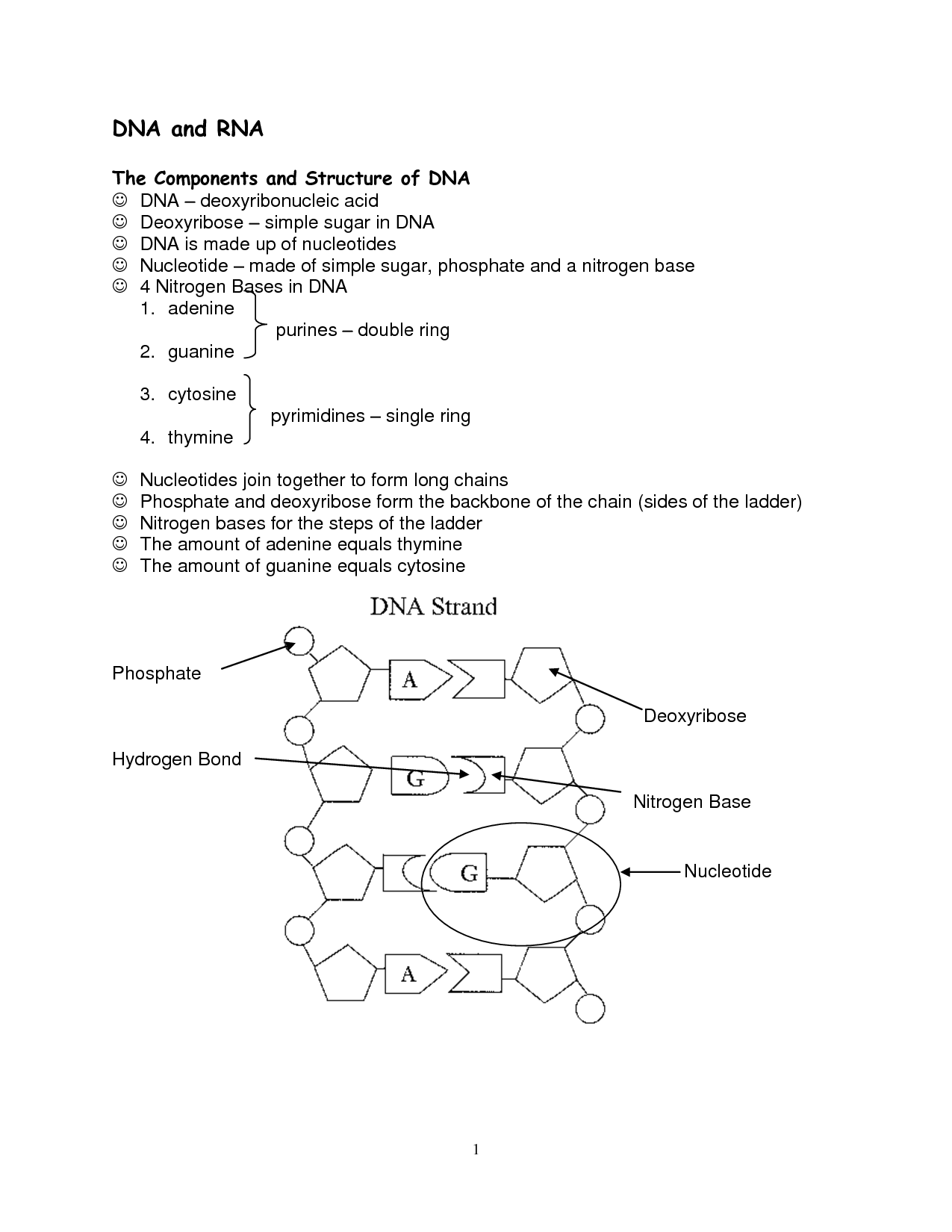
- DNA and RNA Structure Worksheet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Aerobic Respiration Worksheet Answer Key
- mRNA Codon Chart Worksheet
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
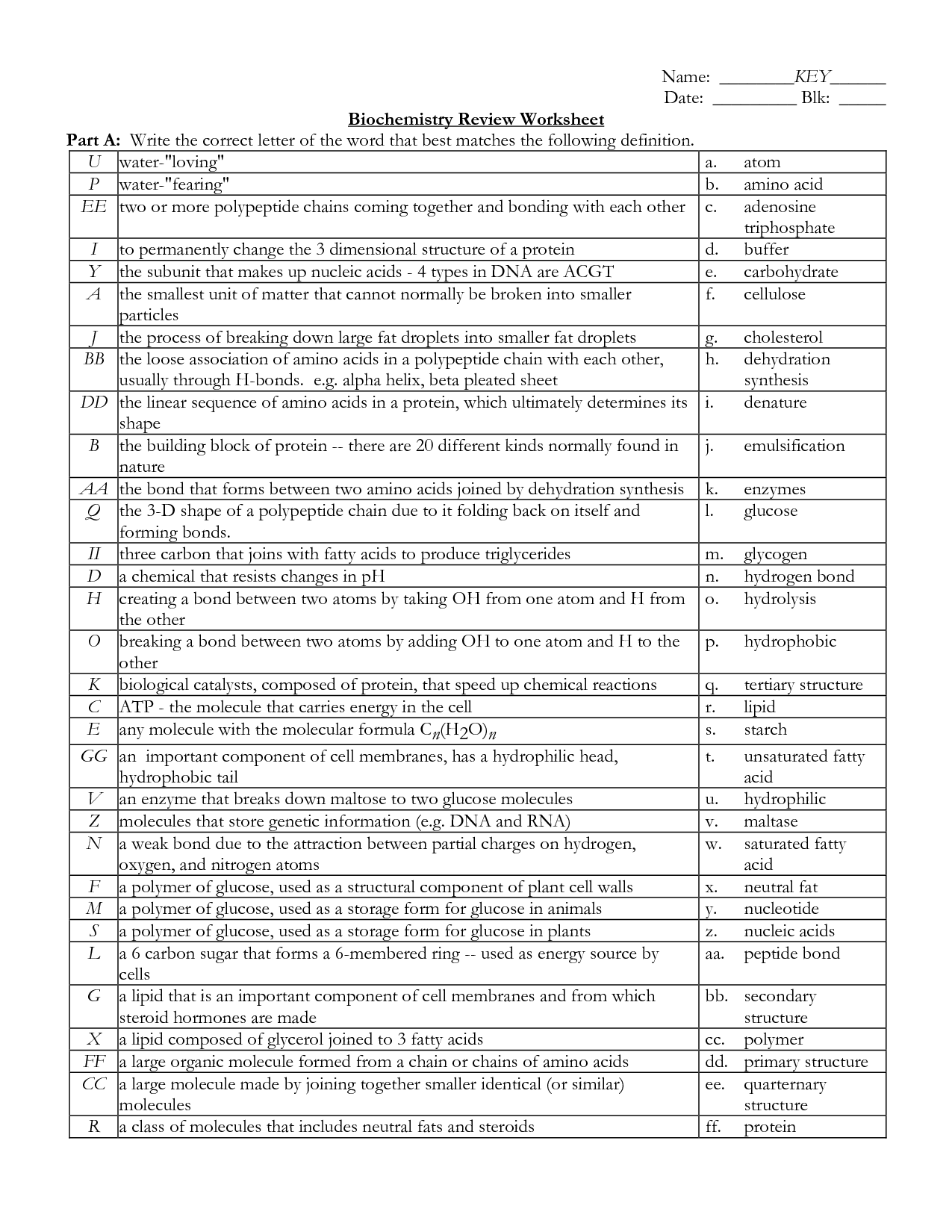
- Biochemistry Review Worksheet
- Codon Practice Worksheet Answers
- Amino Acid Codon Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure Worksheet High School
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
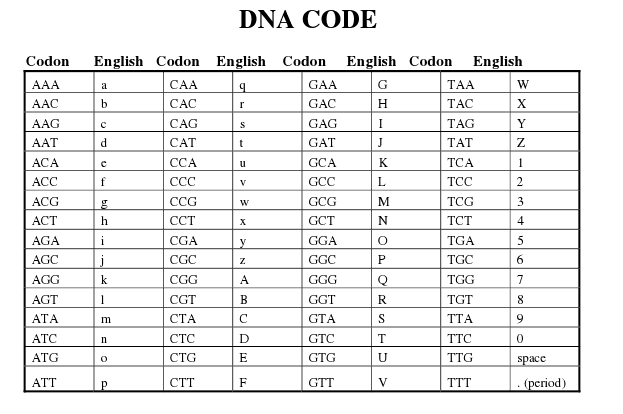
What is a codon?
A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides in mRNA that corresponds to a specific amino acid or signals the start or stop of protein synthesis during translation in the cell.
How many letters are in a codon?
A codon consists of three nucleotides, which translates to three letters.
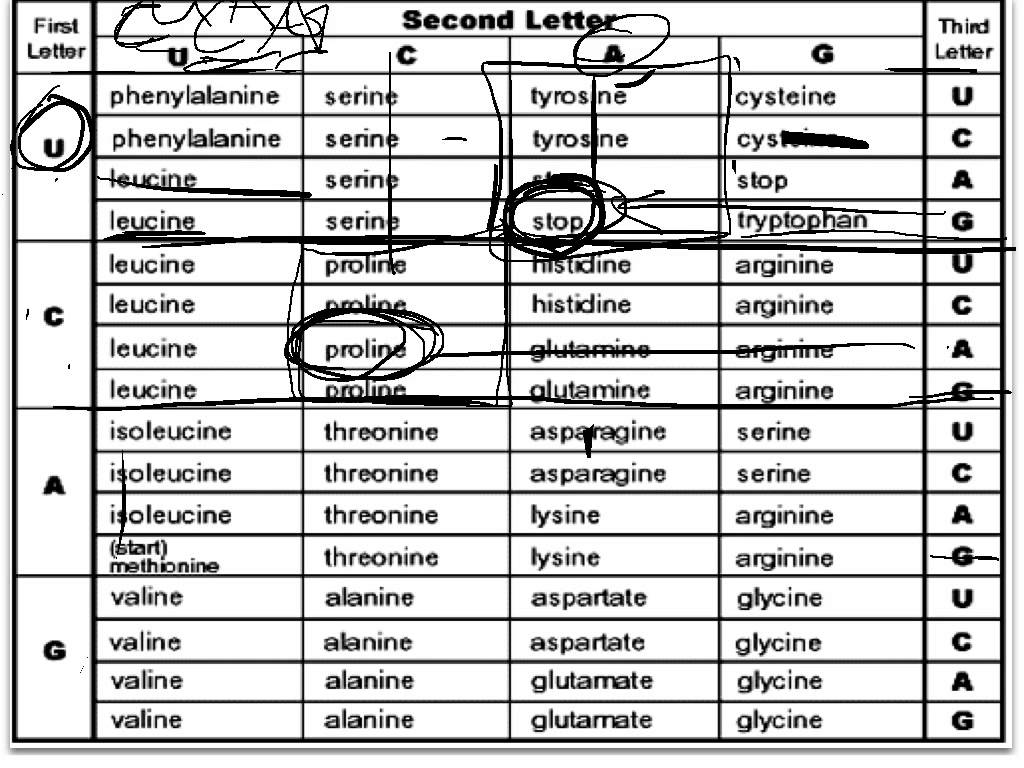
What is the function of a start codon?
The function of a start codon is to indicate the beginning of a protein-coding sequence in messenger RNA (mRNA) during protein synthesis. It signals the ribosome to initiate translation and start assembling the corresponding amino acids to form a protein. The most common start codon in eukaryotes is AUG, which codes for the amino acid methionine.
How many different start codons are there?
There is only one start codon, AUG, which codes for the amino acid methionine and signifies the beginning of protein translation in mRNA sequences.
What is the purpose of a stop codon?
The purpose of a stop codon is to signal the end of protein synthesis during translation in the process of gene expression. When a stop codon is reached on the mRNA strand, the ribosome recognizes it and releases the newly synthesized protein, completing the protein synthesis process by directing the ribosome to stop building the protein chain.
How many different stop codons are there?
There are three different stop codons in the genetic code: UAA, UAG, and UGA. These codons signal the termination of translation during protein synthesis.
Can multiple codons code for the same amino acid?
Yes, multiple codons can code for the same amino acid. This redundancy in the genetic code is known as degeneracy. For example, the amino acid leucine is coded for by six different codons: UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, and CUG. This redundancy helps to protect against errors in DNA replication or mutation, as a change in one codon might not necessarily alter the amino acid sequence produced.
What is the role of tRNA in translation?
tRNA, or transfer RNA, plays a crucial role in translation by bringing amino acids to the ribosome based on the codons in the mRNA. Each tRNA molecule carries a specific amino acid and has an anticodon that can bind to the complementary mRNA codon during protein synthesis. This allows the ribosome to read the mRNA sequence and build a polypeptide chain by joining the amino acids that tRNAs deliver, ultimately creating a functional protein.
How does a ribosome recognize the start codon?
A ribosome recognizes the start codon, which is typically AUG in eukaryotes, by using the initiator tRNA bearing the amino acid methionine. This tRNA is specific for recognizing and binding to the start codon and is associated with the initiation factor proteins that help position the ribosome at the correct location on the mRNA molecule. The ribosome then scans along the mRNA until it identifies the start codon, at which point translation can begin.
What happens if a mutation occurs in a codon sequence?
If a mutation occurs in a codon sequence, it can result in a change to the amino acid that the codon codes for. This can lead to a different protein being produced during translation, which may affect the function of the protein and potentially cause changes or abnormalities in the organism. Mutations in codon sequences can have a wide range of consequences depending on the specific change that occurs and its impact on protein structure and function.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments