Classifying Organisms Worksheet Kingdom
In biology, the classification of organisms is crucial for understanding the diverse world of living things. This Classifying Organisms Worksheet focuses on the Kingdom level of classification, providing an engaging way for students to explore and learn about the various kingdoms found in the natural world. With clear instructions and thought-provoking questions, this worksheet is designed to help students better grasp the concept of classification and enhance their knowledge of the subject.
Table of Images 👆
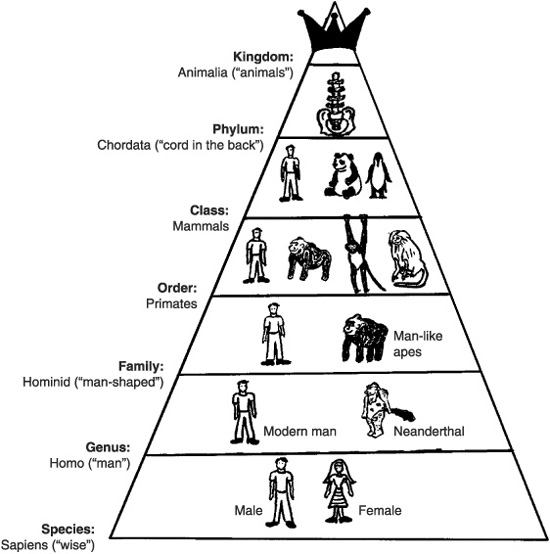
- Human Animal Kingdom Classification
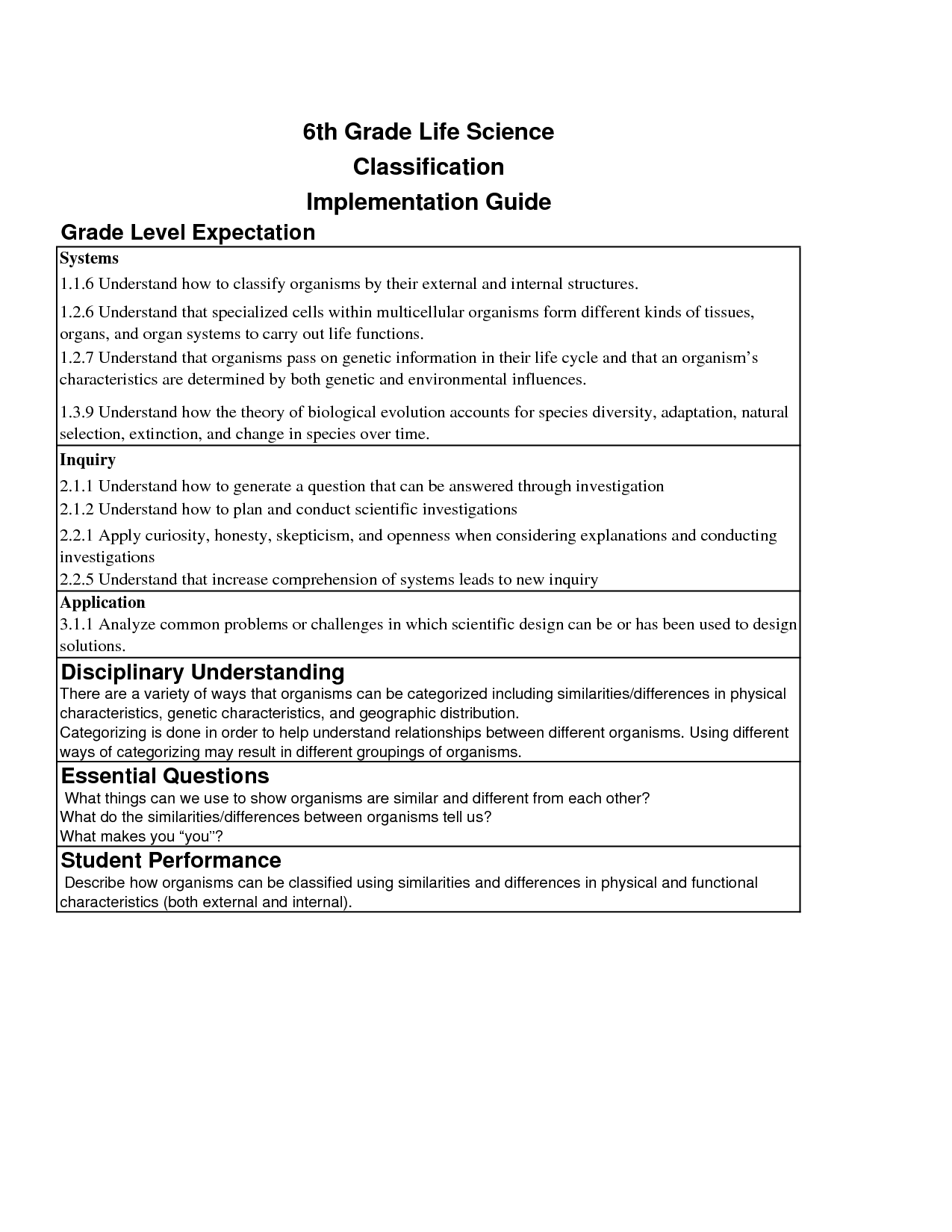
- Classification of Living Things Worksheets 6th Grade
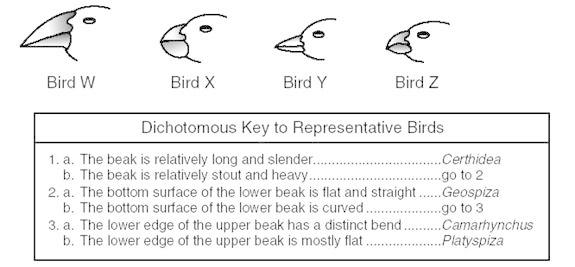
- Gram-negative Dichotomous Key
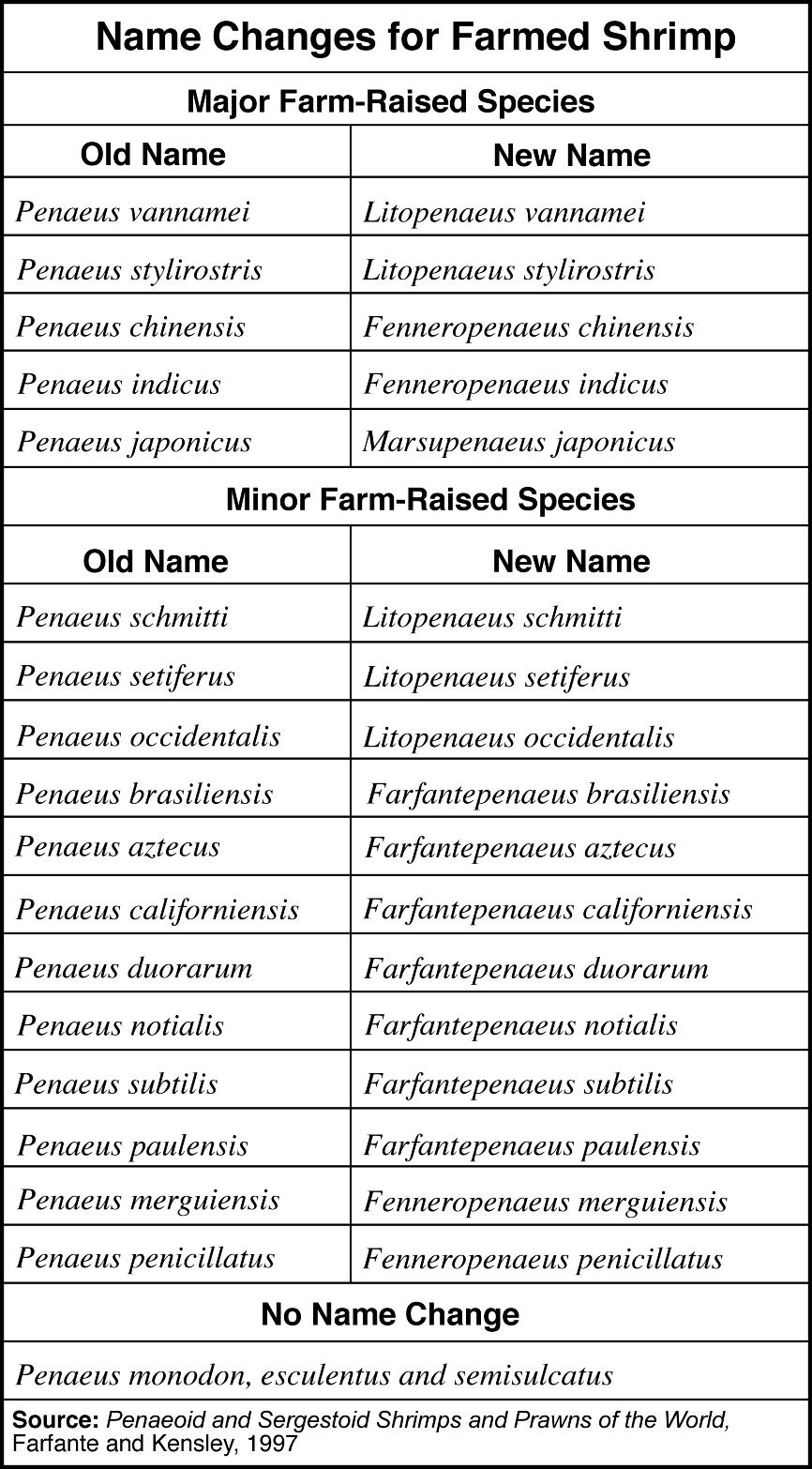
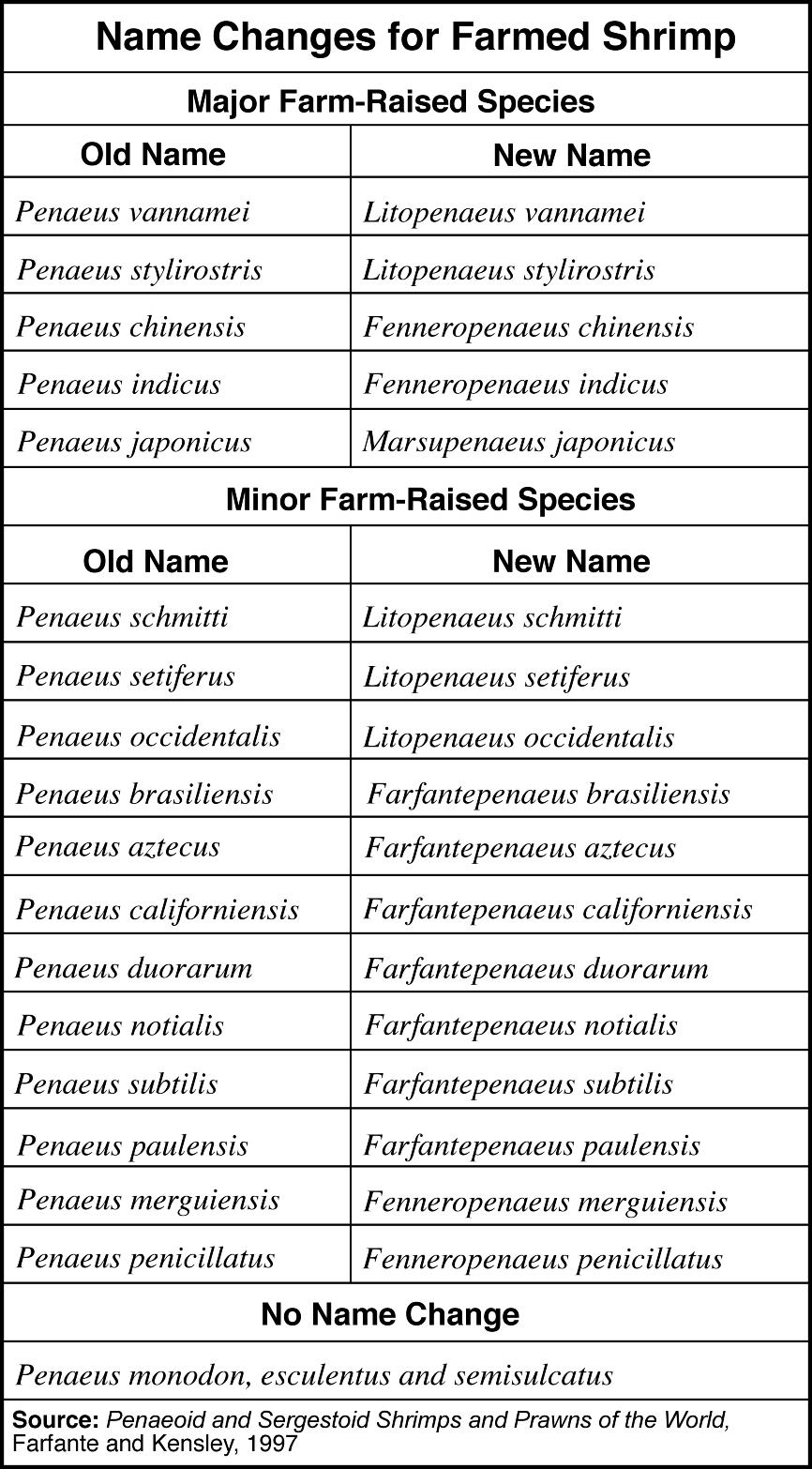
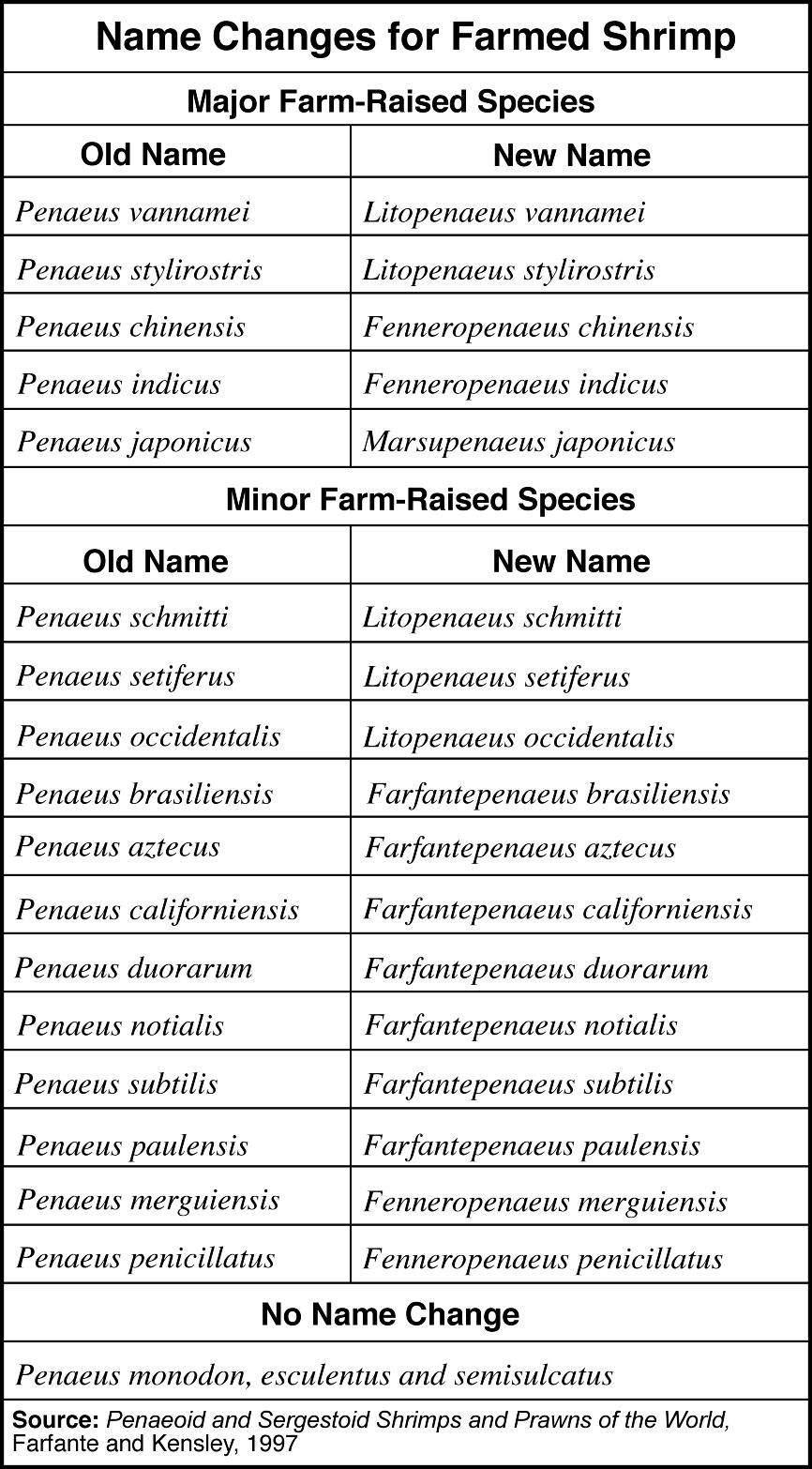
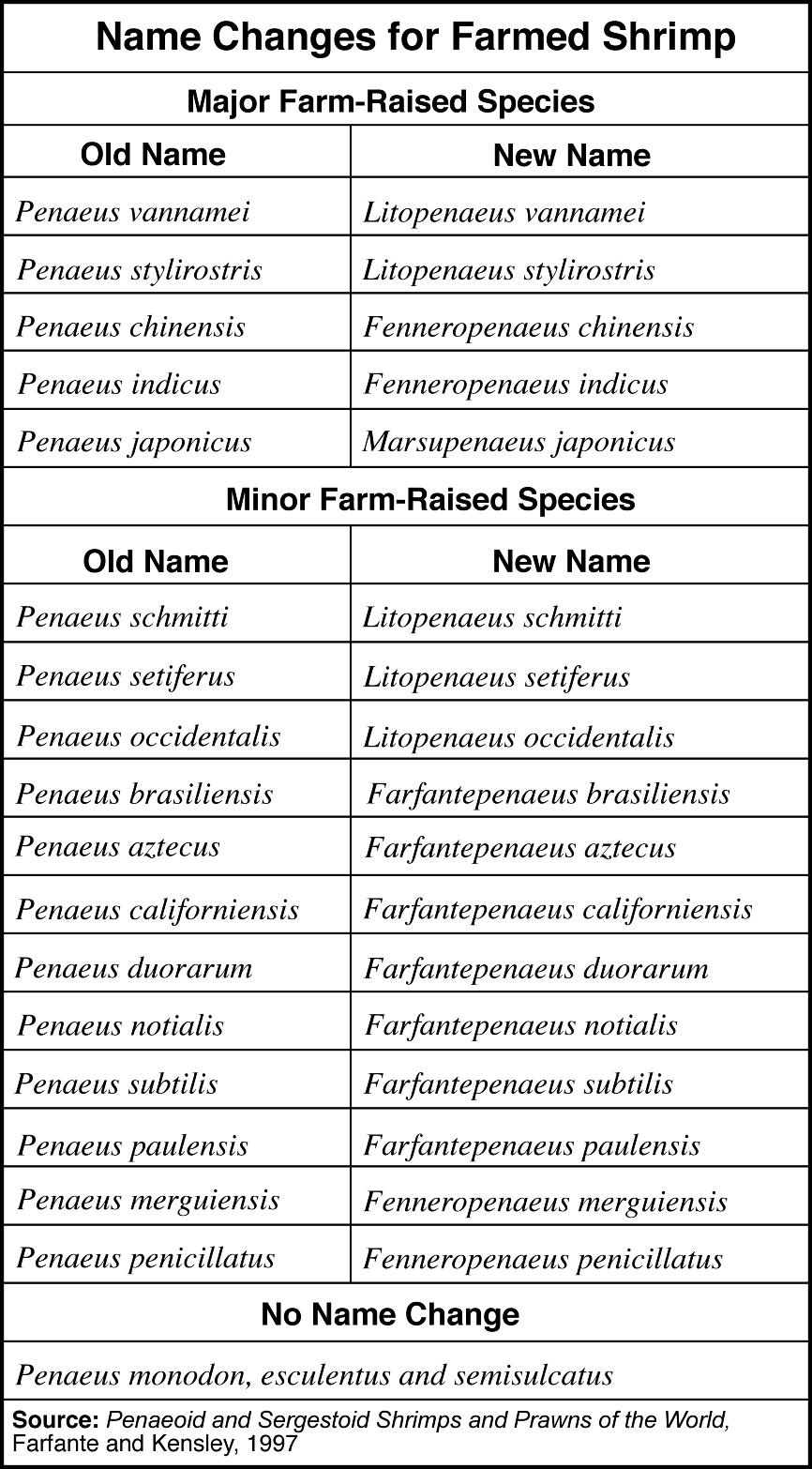
- Scientific Name Animal Species
- Scientific Name Animal Species
- Scientific Name Animal Species
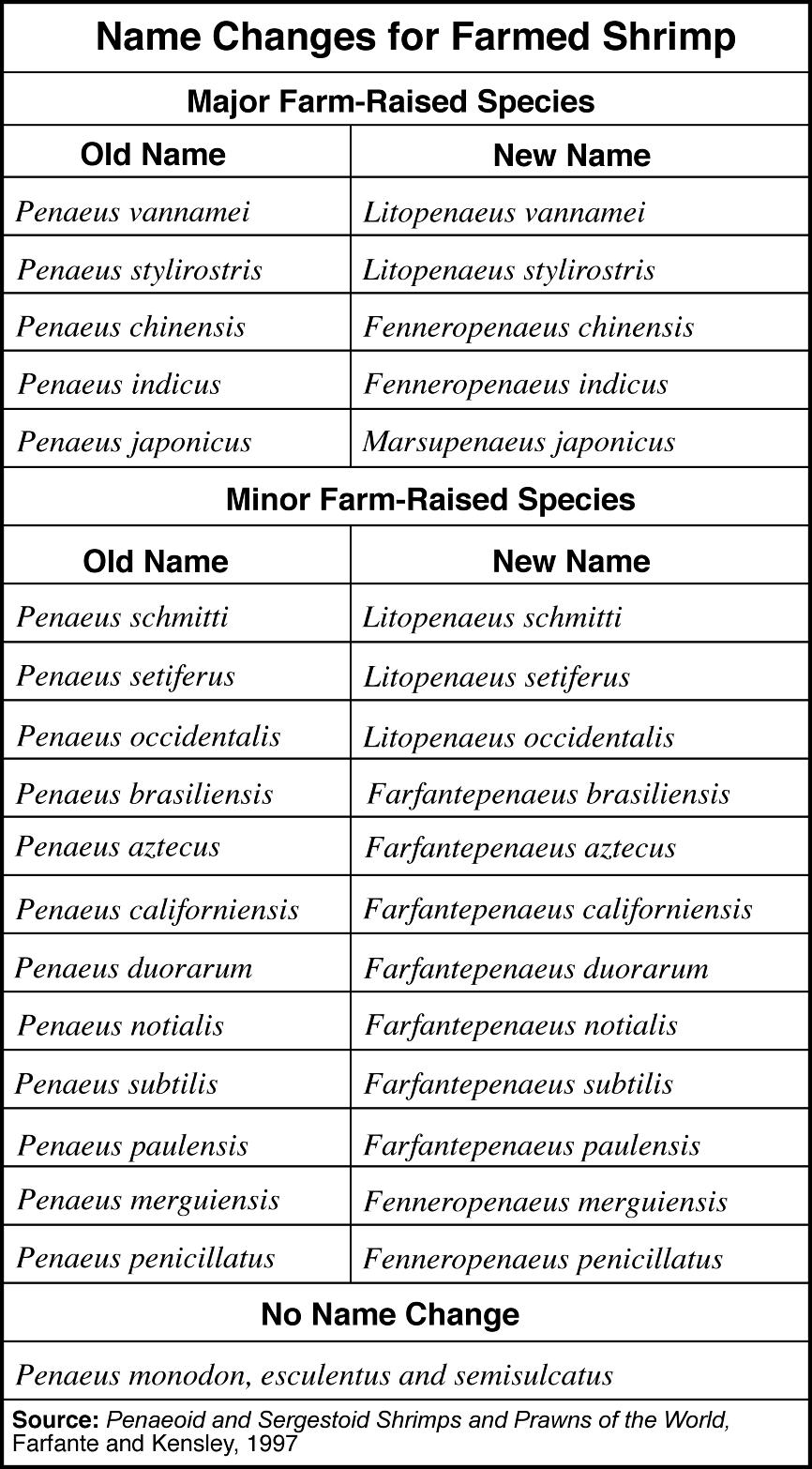
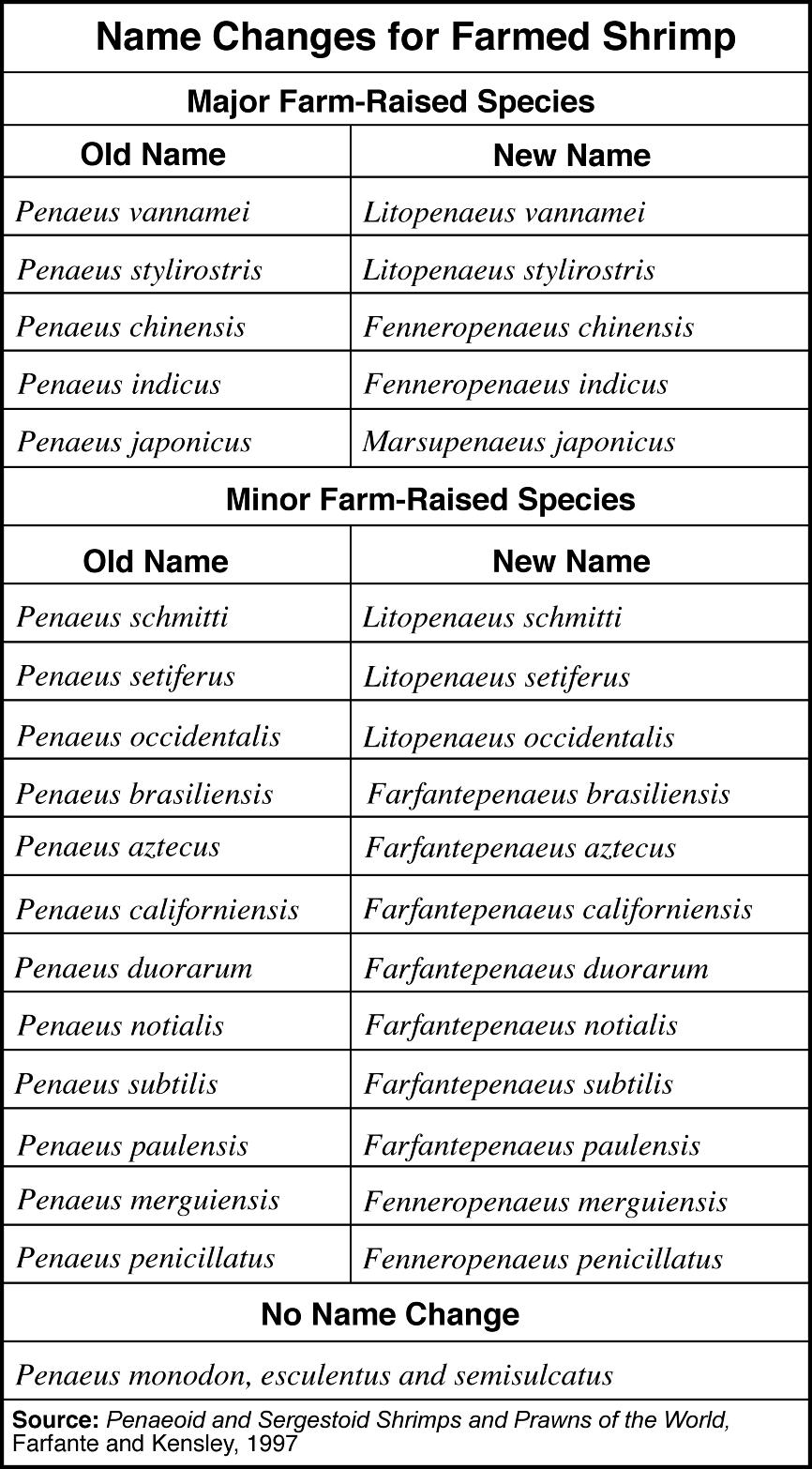
- Scientific Name Animal Species
- Scientific Name Animal Species
- Scientific Name Animal Species
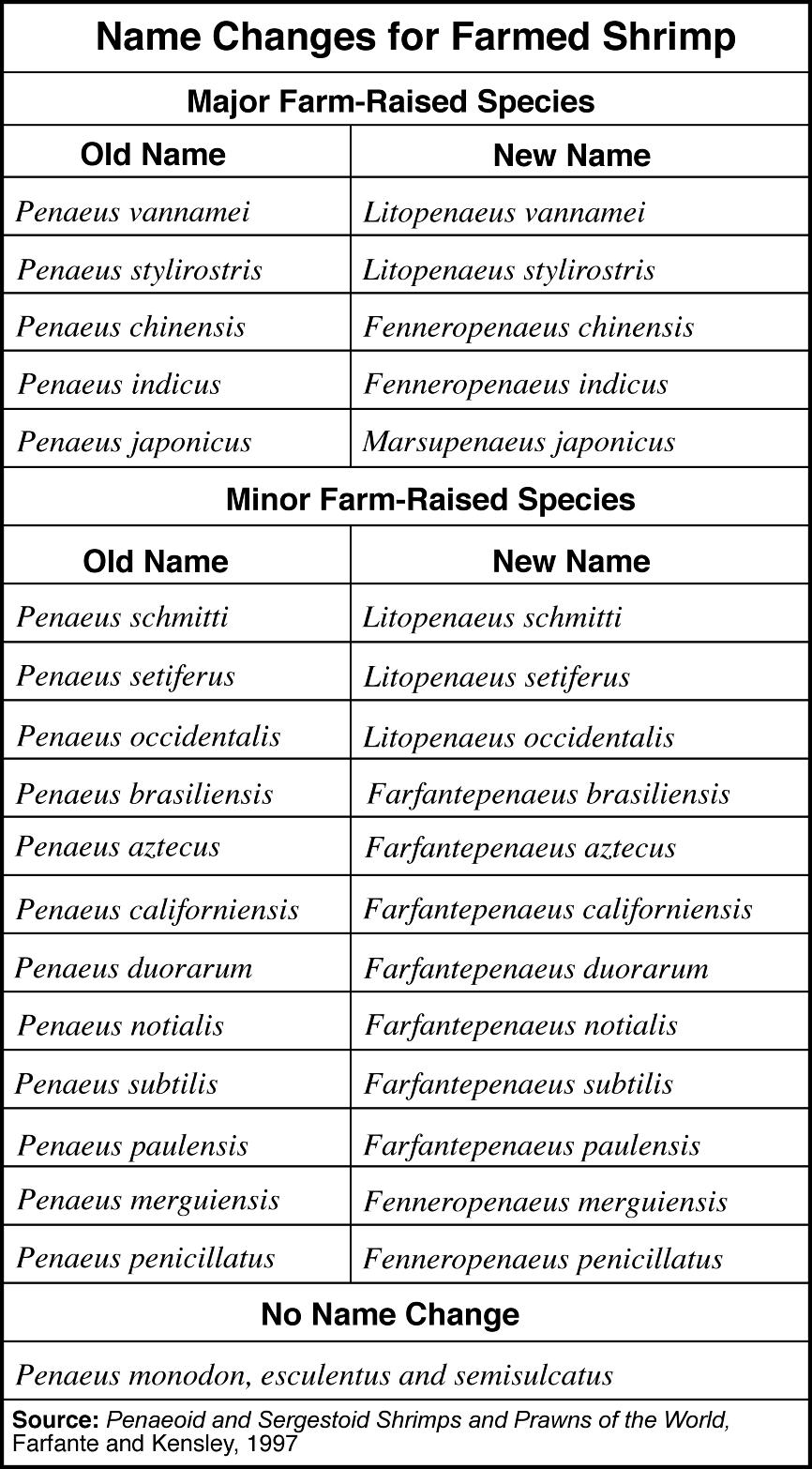
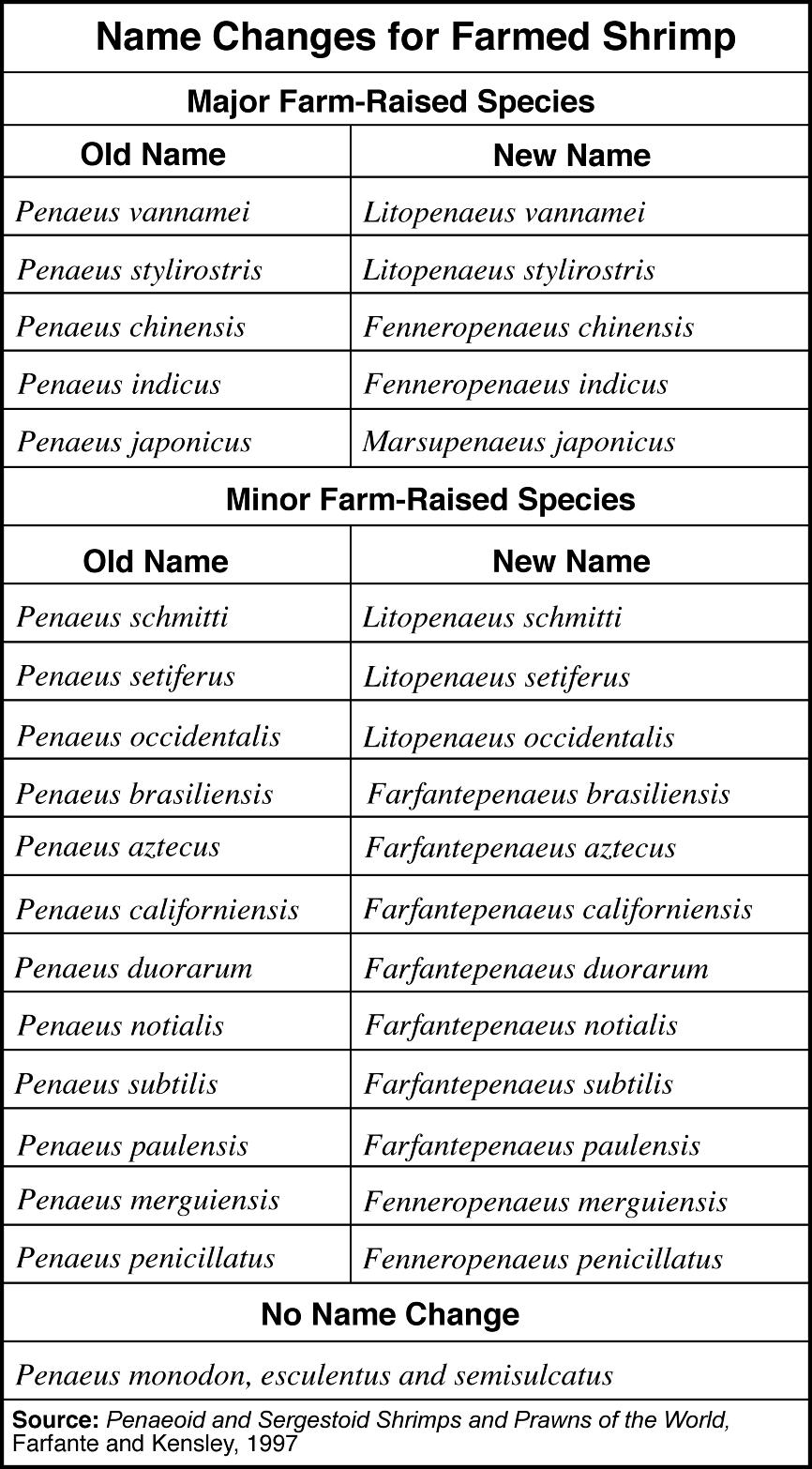
- Scientific Name Animal Species
- Scientific Name Animal Species
- Scientific Name Animal Species
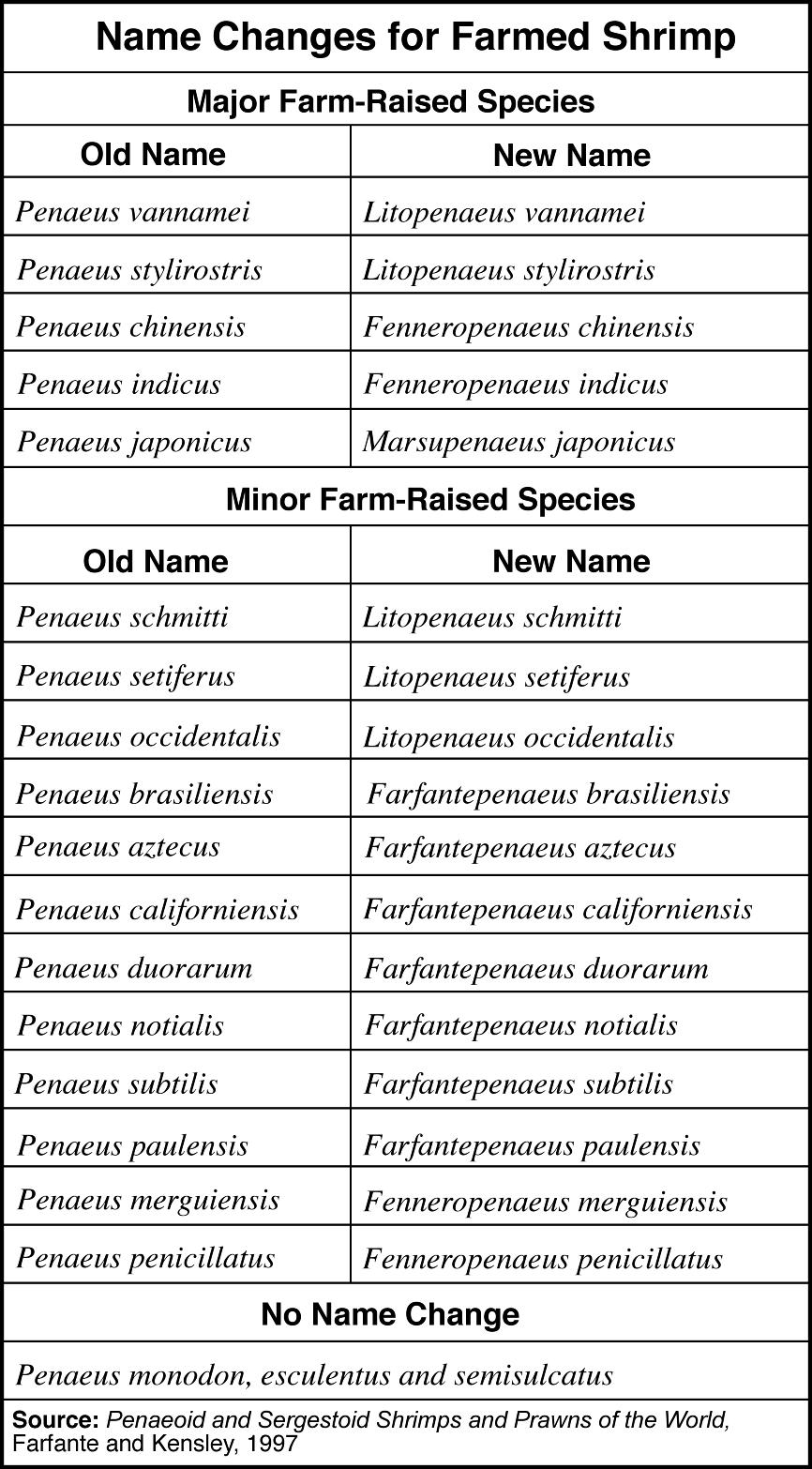
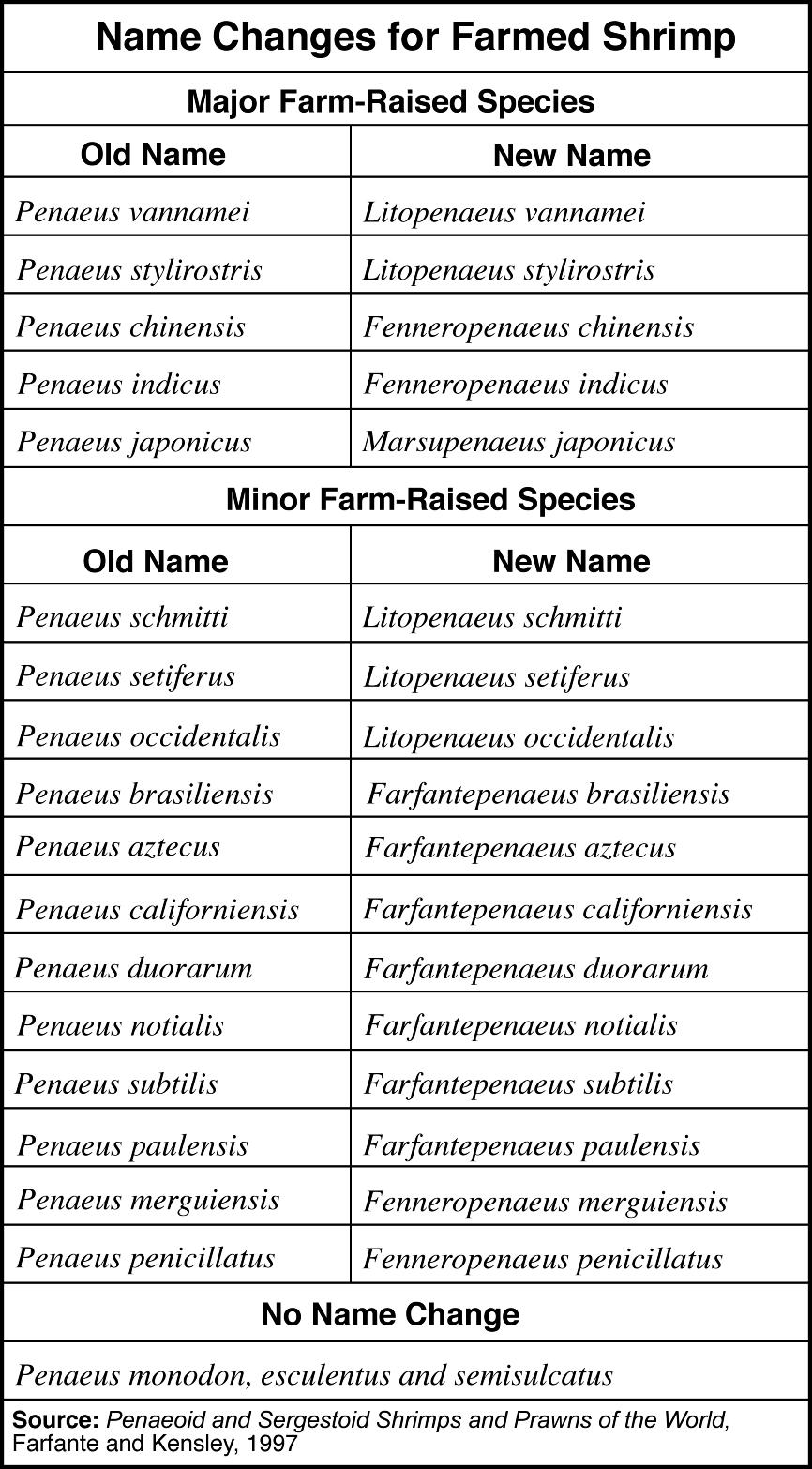
- Scientific Name Animal Species
- Scientific Name Animal Species
- Scientific Name Animal Species
- Scientific Name Animal Species
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is a kingdom?
A kingdom is a type of political entity ruled by a monarch, often referred to as a king or queen, with inheritable power and authority passed down through a royal family bloodline. In a kingdom, the monarch holds significant control over the government and the people within the borders of the kingdom.
How many kingdoms are there in the classification system?
There are currently six kingdoms in the classification system: Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, Archaea, and Bacteria.
What are the criteria used to classify organisms into different kingdoms?
Organisms are classified into different kingdoms based on a combination of criteria, including their cell type (prokaryotic or eukaryotic), cell structure, mode of nutrition (autotrophs or heterotrophs), reproduction methods, and other biochemical and genetic characteristics. This classification system aims to group organisms that share similar traits and evolutionary relationships, helping scientists understand the diversity and relationships among different species.
What are the characteristics of the Animalia kingdom?
The Animalia kingdom consists of multicellular organisms that are heterotrophic, meaning they cannot produce their own food and rely on consuming other organisms for nutrients. Animals also have the ability to move and possess specialized sensory organs for detecting their environment. Most animals have a well-defined body plan with different tissues and organs, and they reproduce sexually. Animals exhibit a wide range of shapes, sizes, and behaviors, making them one of the most diverse kingdoms in the biological classification system.
What are the characteristics of the Plantae kingdom?
The Plantae kingdom is characterized by organisms that are multicellular, photosynthetic, and have cell walls made of cellulose. They obtain energy through photosynthesis, use chlorophyll as a pigment for capturing light energy, and typically reproduce through seeds or spores. Plants range from small mosses to enormous trees, displaying a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and adaptations to different environments. They play a crucial role in ecosystems by producing oxygen, serving as food sources for other organisms, and stabilizing soil.
What are the characteristics of the Fungi kingdom?
The Fungi kingdom is characterized by organisms that are eukaryotic, mostly multicellular (some are unicellular), and heterotrophic. They obtain nutrients by secreting enzymes to break down organic matter in their environment. Fungi reproduce through the production of spores and have cell walls made of chitin. Many fungi play crucial roles in nutrient cycling and decomposition in ecosystems, while some can also cause diseases in plants and animals, making them important organisms in various ecological processes.
What are the characteristics of the Protista kingdom?
Protists are eukaryotic organisms that are typically unicellular but can also be multicellular. They are found in various habitats, including freshwater and marine environments. Protists have diverse morphological and biological characteristics, such as the presence of cilia, flagella, or pseudopods for movement, and some can photosynthesize like plants or consume organic matter like animals. The kingdom Protista is a diverse group that includes algae, protozoa, and slime molds, and they play important roles in various ecosystems as primary producers, consumers, and decomposers.
What are the characteristics of the Monera kingdom?
The Monera kingdom, also known as the prokaryotes, includes single-celled organisms like bacteria and archaea. They are unicellular, lack a true nucleus (having a nucleoid region instead), and lack membrane-bound organelles. Monera reproduce asexually through binary fission or other forms of asexual reproduction and are often found in diverse environments, displaying a wide range of metabolic capabilities such as photosynthesis and chemosynthesis. This kingdom plays crucial roles in various ecosystems, including nutrient recycling and symbiotic relationships with other organisms.
What are the characteristics of the Archaea (Archaeabacteria) kingdom?
Archaea, a domain separate from bacteria and eukaryotes, are single-celled microorganisms that have unique characteristics such as a distinct cell membrane composition, different ribosomal RNA structure, and the ability to live in extreme environments like hot springs, salt lakes, and deep-sea hydrothermal vents. They play a crucial role in various ecosystems and industries, showing great diversity in their metabolic pathways and adaptations to extreme conditions.
What are the characteristics of the Bacteria (Eubacteria) kingdom?
The Bacteria (Eubacteria) kingdom consists of unicellular organisms that lack a distinct nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, known as prokaryotes. They have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan and reproduce through binary fission. Bacteria can be diverse in shape, ranging from spheres (cocci) to rods (bacilli) to spirals. They can be found in various habitats, have diverse metabolic capabilities, and play critical roles in nutrient recycling, decomposition, and symbiotic relationships. Additionally, some bacteria can be pathogenic and cause diseases in plants, animals, and humans.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


















Comments