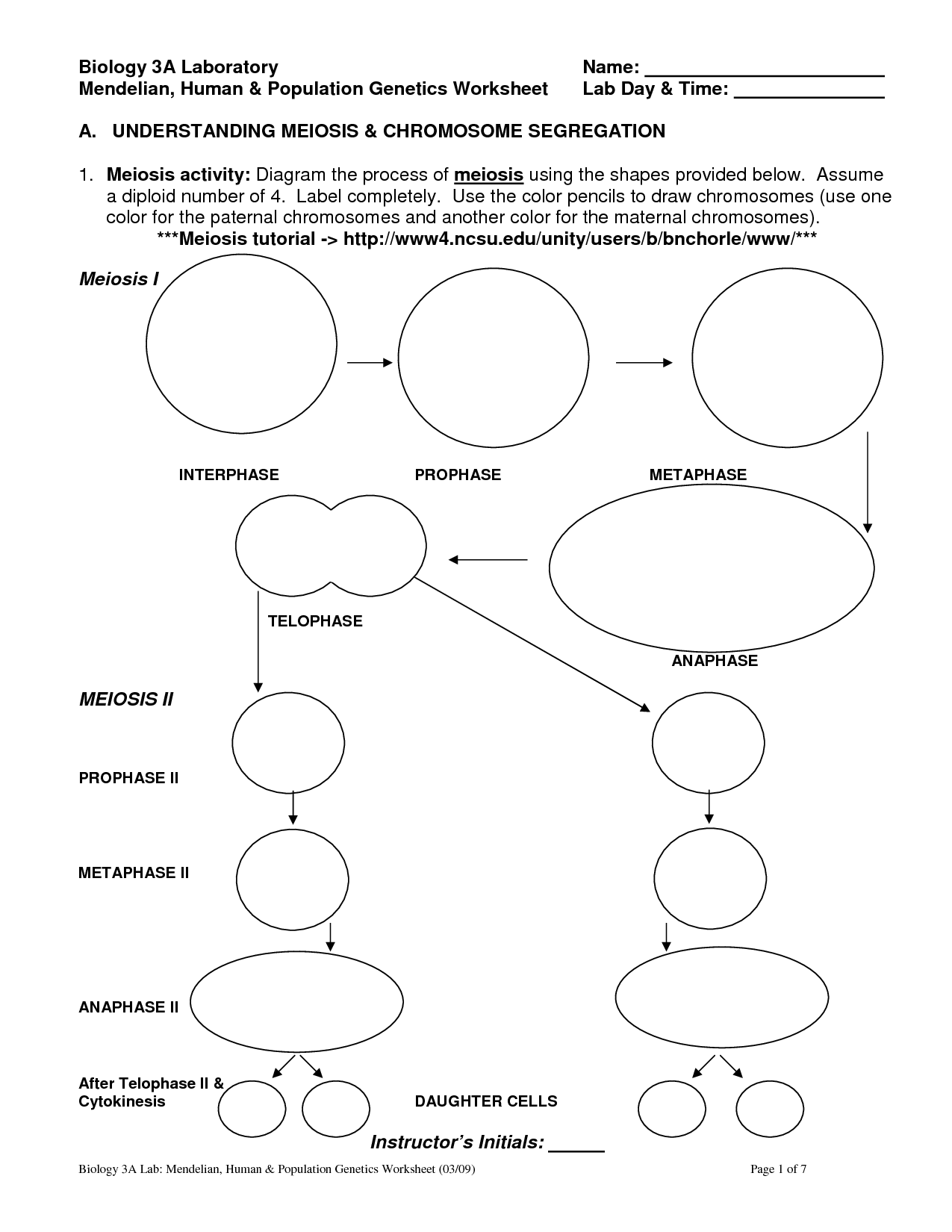
Chromosome Diagram Worksheet
A chromosome diagram worksheet is a valuable tool for students learning about genetics and biology. This worksheet provides a visual representation of the entity and subject of chromosomes, allowing students to better understand their structure and function. By completing this worksheet, students can deepen their understanding of genetics and improve their ability to analyze and interpret genetic information.
Table of Images 👆
- Chromosome Diagram
- Function Mapping Diagram Worksheet
- Coloring Pages Chromosome Structure
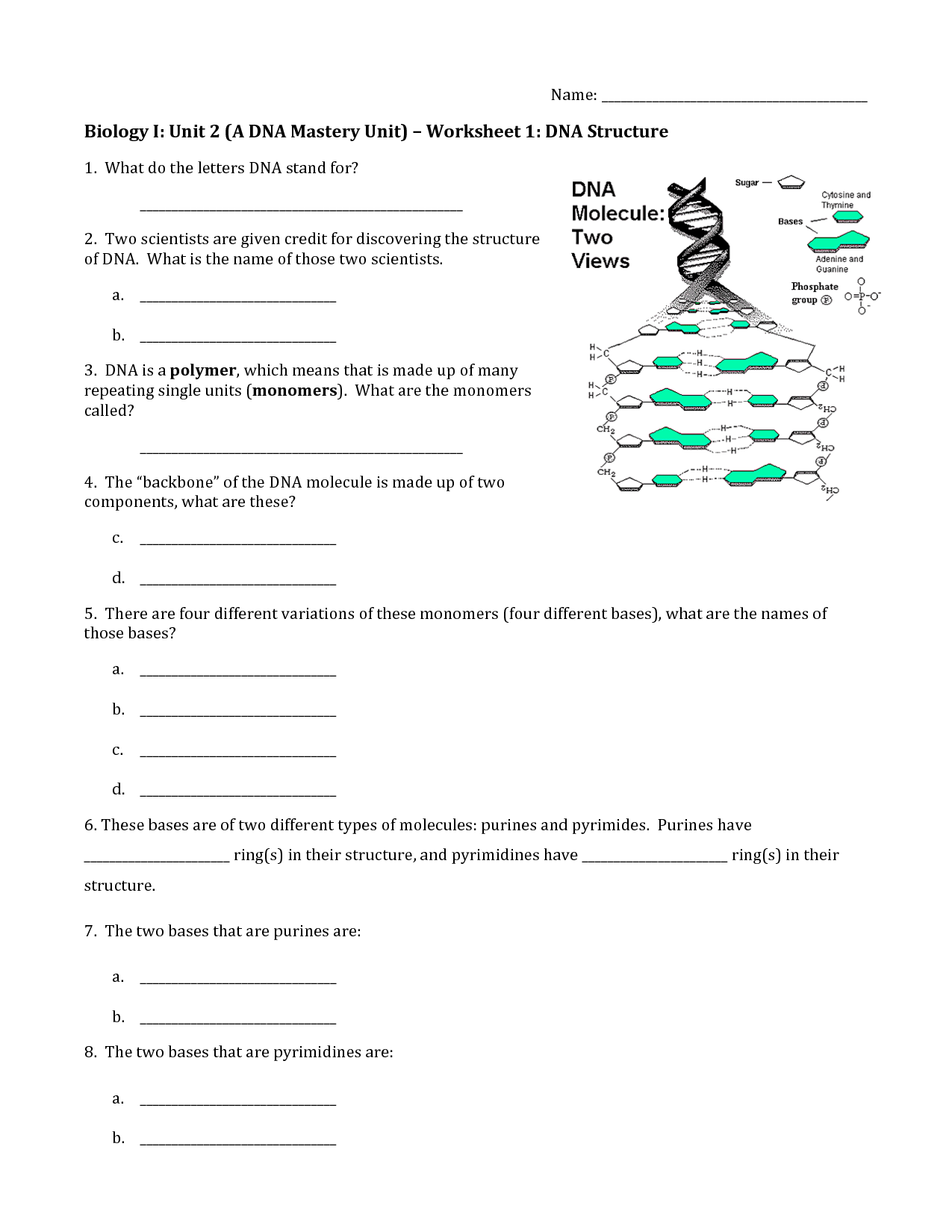
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answers
- Chromosome Structure Worksheet
- Meiosis Coloring Worksheet
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet
- Chromosomes Cell Division Worksheet
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
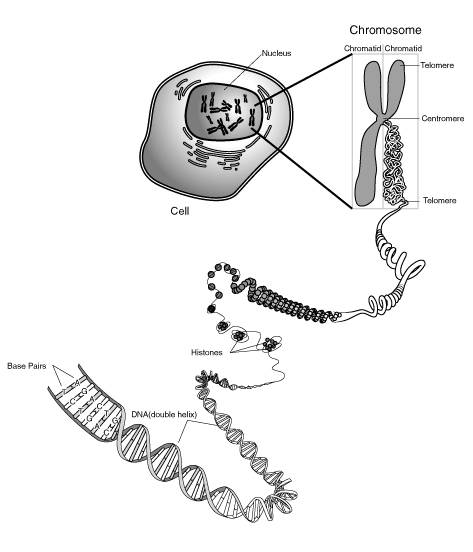
What is a chromosome?
A chromosome is a thread-like structure made of DNA and proteins that carry genetic information in the form of genes. Chromosomes are located in the nucleus of a cell and are passed from parents to offspring, determining traits such as eye color, height, and other characteristics. Humans typically have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with one set inherited from each parent.
What is the structure of a chromosome?
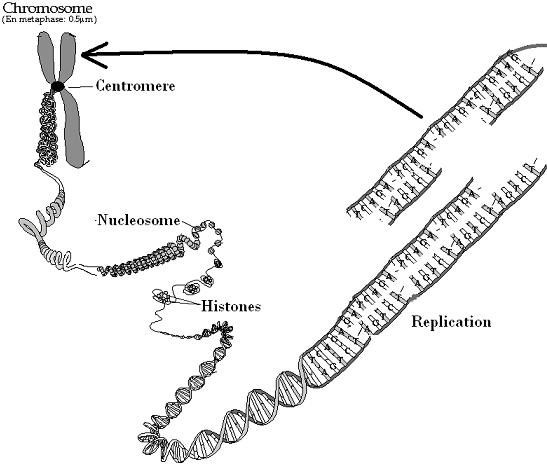
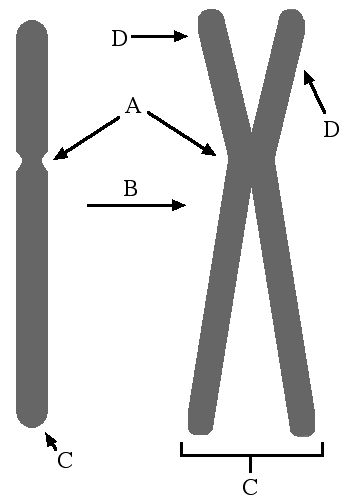
A chromosome is a long, thread-like structure made up of DNA and proteins. It consists of two sister chromatids connected at a centralized region called the centromere. Chromosomes are organized in pairs, with one inherited from each parent, and play a crucial role in carrying genetic information and ensuring proper cell division and replication.
What are the different parts of a chromosome?
A chromosome is made up of DNA molecules, histone proteins, and other associated proteins. The DNA molecules contain the genetic information, while histone proteins help in packing the DNA into a compact structure. Other associated proteins play roles in gene regulation, DNA replication, and other chromosomal functions. The different parts of a chromosome work together to ensure the proper functioning and organization of genetic material within the cell.
How many chromosomes are present in a human cell?
A human cell typically contains 46 chromosomes, with 23 pairs of chromosomes - one set inherited from each parent. This consists of 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes (XX for females and XY for males).
What is the function of a centromere?
A centromere is a region on a chromosome where two sister chromatids are held together, and it plays a critical role in ensuring proper chromosome segregation during cell division. It helps to organize and distribute the chromosomes to daughter cells by attaching to the spindle fibers that pull the chromosomes apart during cell division. Additionally, the centromere is vital for the stability of chromosomes and helps to prevent chromosome breakage.
What is the role of telomeres in a chromosome?
Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences located at the ends of chromosomes that serve to protect the genetic material from deterioration and prevent the loss of important genetic information during cell division. They also play a crucial role in maintaining the stability and integrity of chromosomes. Additionally, telomeres help to regulate the lifespan of cells and are associated with aging and diseases related to cell division, such as cancer.
What are sister chromatids?
Sister chromatids are two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome that are joined at the centromere. This means that they have the same DNA sequence and genes, as they are produced through the process of DNA replication during the S phase of the cell cycle. Sister chromatids are held together until they are separated during cell division, either during mitosis to produce two identical daughter cells or during meiosis to produce gametes with half the number of chromosomes.
How do homologous chromosomes differ from each other?
Homologous chromosomes are similar in length, gene position, and centromere location, but they differ in the specific alleles they carry. Each homologous chromosome comes from a different parent and may carry different versions of genes, which can result in variations in traits.
What is the difference between autosomes and sex chromosomes?
Autosomes are the non-sex chromosomes found in both males and females, and they determine an individual's hereditary characteristics besides sex determination. On the other hand, sex chromosomes determine an individual's sex, with females having two X chromosomes (XX) and males having one X and one Y chromosome (XY). This distinction between autosomes and sex chromosomes is fundamental in genetics and reproductive biology.
What is the significance of karyotyping in analyzing chromosomes?
Karyotyping is significant in analyzing chromosomes as it allows for the visualization of an individual's entire set of chromosomes, providing information about their number, size, and structure. This technique can help identify genetic disorders, chromosomal abnormalities, and mutations by comparing the individual's karyotype to a normal reference. Karyotyping is commonly used in prenatal testing, cancer diagnosis, and research to study chromosomal anomalies and understand their implications on an individual's health and development.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments