Cell Membrane Labeling Worksheet
The Cell Membrane Labeling Worksheet is a useful tool designed to help biology students better understand the intricate details of a cell's outer boundary. This worksheet is ideal for high school or college-level learners who are studying cellular anatomy and function. Through a series of labeled diagrams and accompanying questions, students can engage with the subject matter and enhance their understanding of key cellular structures.
Table of Images 👆
- Cell Membrane Diagram Worksheet
- Cell Membrane Diagram Labeled
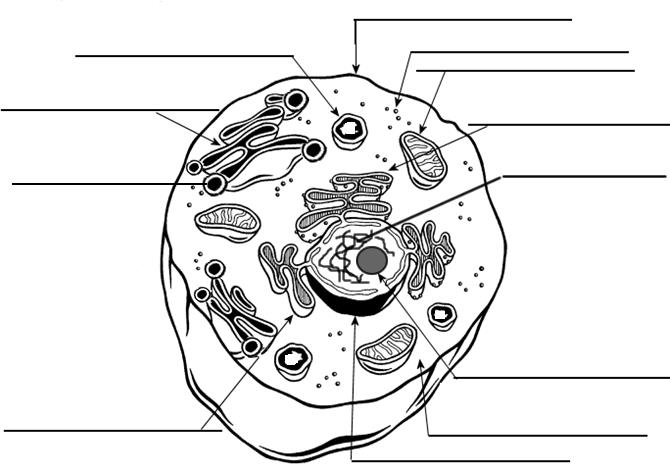
- Cell Organelle Labeling Worksheet
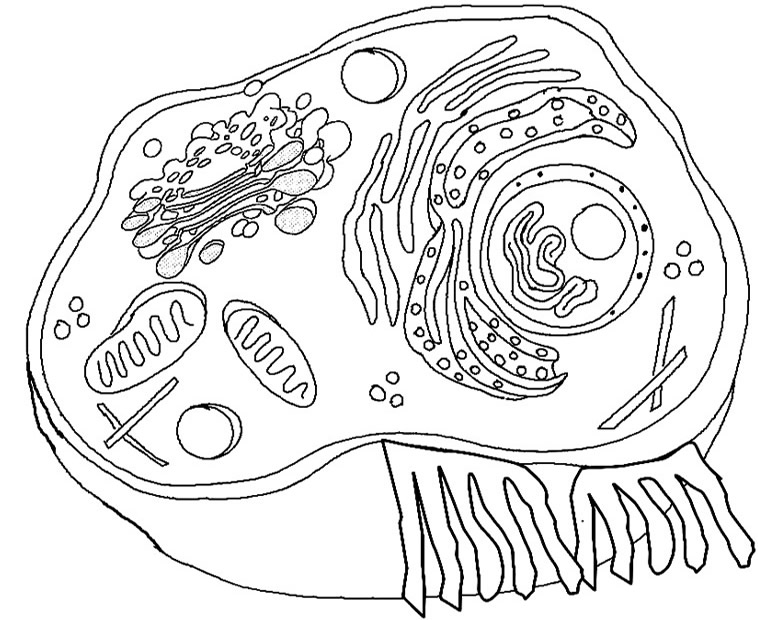
- Animal Cell Coloring Answers
- Unlabeled Animal Cell Diagram Worksheet
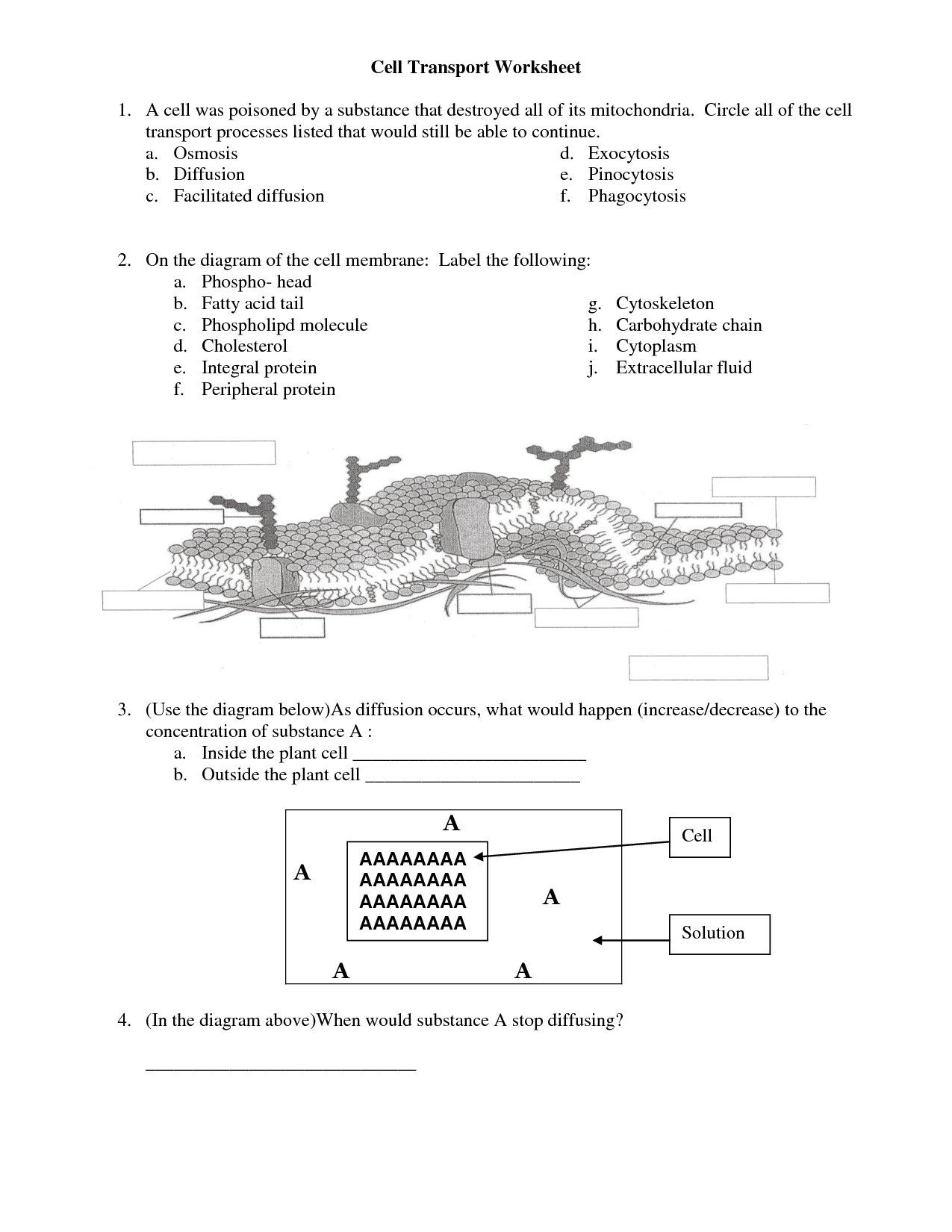
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Membrane Diagram Worksheet
- Cell Organelles Coloring
- Labeled Animal Cell Worksheet
- Prokaryotic Cell Coloring Page
- Biology Cell Worksheets
- Cell Diagram Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the main function of the cell membrane?
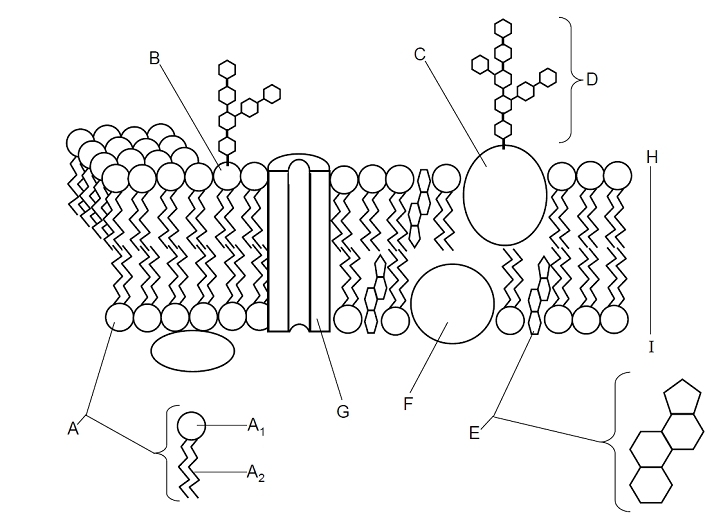
The main function of the cell membrane is to regulate the passage of substances in and out of the cell, allowing nutrients to enter and waste products to exit while also maintaining the cell's internal environment and protecting it from external threats. Additionally, the cell membrane plays a key role in cell signaling and communication with other cells.
Name two types of molecules that make up the cell membrane.
Two types of molecules that make up the cell membrane are phospholipids and proteins.
What is the significance of phospholipids in the cell membrane structure?
Phospholipids play a crucial role in the cell membrane structure by forming a phospholipid bilayer, which is a semi-permeable barrier that encloses and protects the contents of the cell while also regulating the movement of molecules in and out of the cell. The hydrophobic tails of phospholipids provide a stable structure, while the hydrophilic heads interact with water inside and outside of the cell. This unique arrangement allows the cell membrane to maintain its integrity and selective permeability, essential for cellular functions such as transport, signaling, and maintaining homeostasis.
What is the role of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
Cholesterol plays a vital role in the cell membrane by helping to maintain its fluidity and stability. It regulates the rigidity of the membrane, keeping it from becoming too stiff or too fluid, which affects the permeability of the membrane to various molecules and ions. Cholesterol also helps to prevent the packing of fatty acid tails in the phospholipid bilayer, enhancing the structural integrity of the membrane. Overall, cholesterol is crucial for maintaining the proper structure and function of the cell membrane.
How do integral proteins contribute to the cell membrane's function?
Integral proteins in the cell membrane contribute to its function by facilitating the transport of molecules across the membrane, acting as channels or carriers. They also play roles in cell signaling and cell-cell recognition by binding to specific ligands or other cells. Additionally, integral proteins help maintain the cell membrane's structure and stability, participating in cell adhesion and support. Overall, integral proteins are essential components of the cell membrane that enable various important cellular processes to occur.
What is the purpose of peripheral proteins in the cell membrane?
Peripheral proteins in the cell membrane primarily serve roles in cell signaling, transport, and structural support. They can facilitate cell communication, serve as enzymes for specific cellular processes, and help in anchoring the membrane to the cytoskeleton. Additionally, they can regulate the membrane's fluidity and participate in the transport of molecules across the membrane. Overall, peripheral proteins play crucial roles in maintaining the functions and integrity of the cell membrane.
Describe the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane.
The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the cell membrane as a fluid phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The phospholipid bilayer is fluid, allowing for lateral movement of lipids and proteins within the membrane. Proteins are interspersed throughout the membrane, with some extending across the bilayer (integral proteins) and others loosely attached to the surface (peripheral proteins). This model emphasizes the dynamic and diverse nature of the cell membrane, with proteins serving various functions such as transport, signaling, and cell recognition.
How does the cell membrane maintain its selective permeability?
The cell membrane maintains its selective permeability through the presence of various proteins and channels that regulate the passage of molecules in and out of the cell. These proteins and channels act as gatekeepers, allowing only certain substances to pass through while blocking others. Additionally, the lipid bilayer structure of the cell membrane controls the diffusion of hydrophobic molecules through the membrane, contributing to its selectively permeable nature. This selective permeability is crucial for regulating the internal environment of the cell and ensuring proper functioning and survival.
Explain the process of active transport across the cell membrane.
Active transport is a mechanism that moves molecules across the cell membrane against their concentration gradient, requiring energy in the form of ATP. This transport process involves specific protein pumps embedded in the membrane that actively move molecules such as ions and small molecules from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. As ATP is hydrolyzed, the pump changes shape, allowing the molecule to bind to it and then be transported across the membrane. This process is essential for maintaining cell homeostasis and for functions like nutrient uptake, waste removal, and signal transduction.
How do cells communicate with each other through the cell membrane?
Cells communicate with each other through the cell membrane by using various signaling molecules such as hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth factors. These signaling molecules bind to specific receptors on the cell membrane, triggering a cascade of molecular events that ultimately lead to a cellular response. This process allows cells to coordinate their activities and respond to changes in their environment.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments