Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet Answers
The Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet provides a hands-on activity for students to learn and understand the structure and function of the cell membrane. This worksheet is designed for biology students who are studying cell biology and are looking to reinforce their understanding of the cell membrane as an important entity in cell functioning.
Table of Images 👆
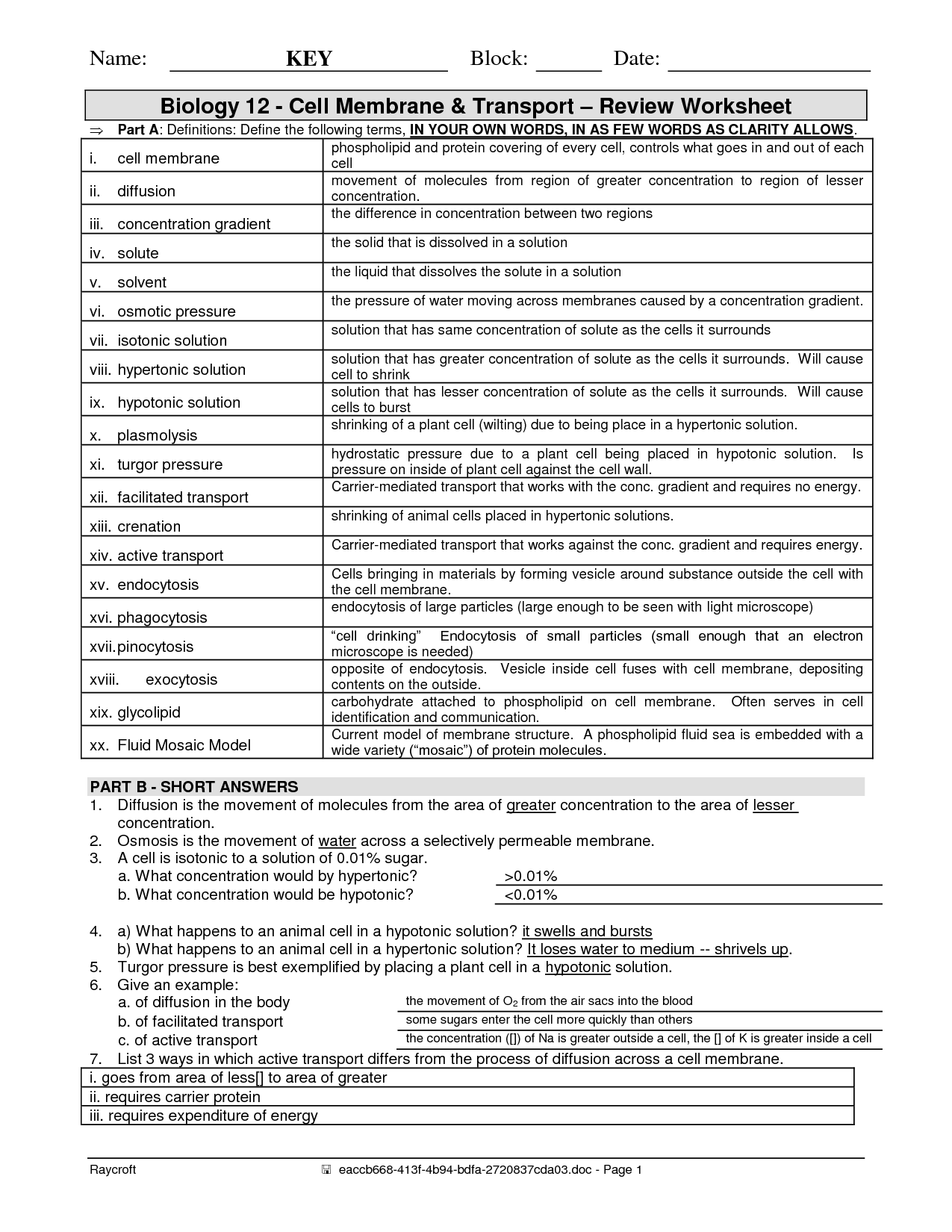
- Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Membrane Worksheet Answer Key
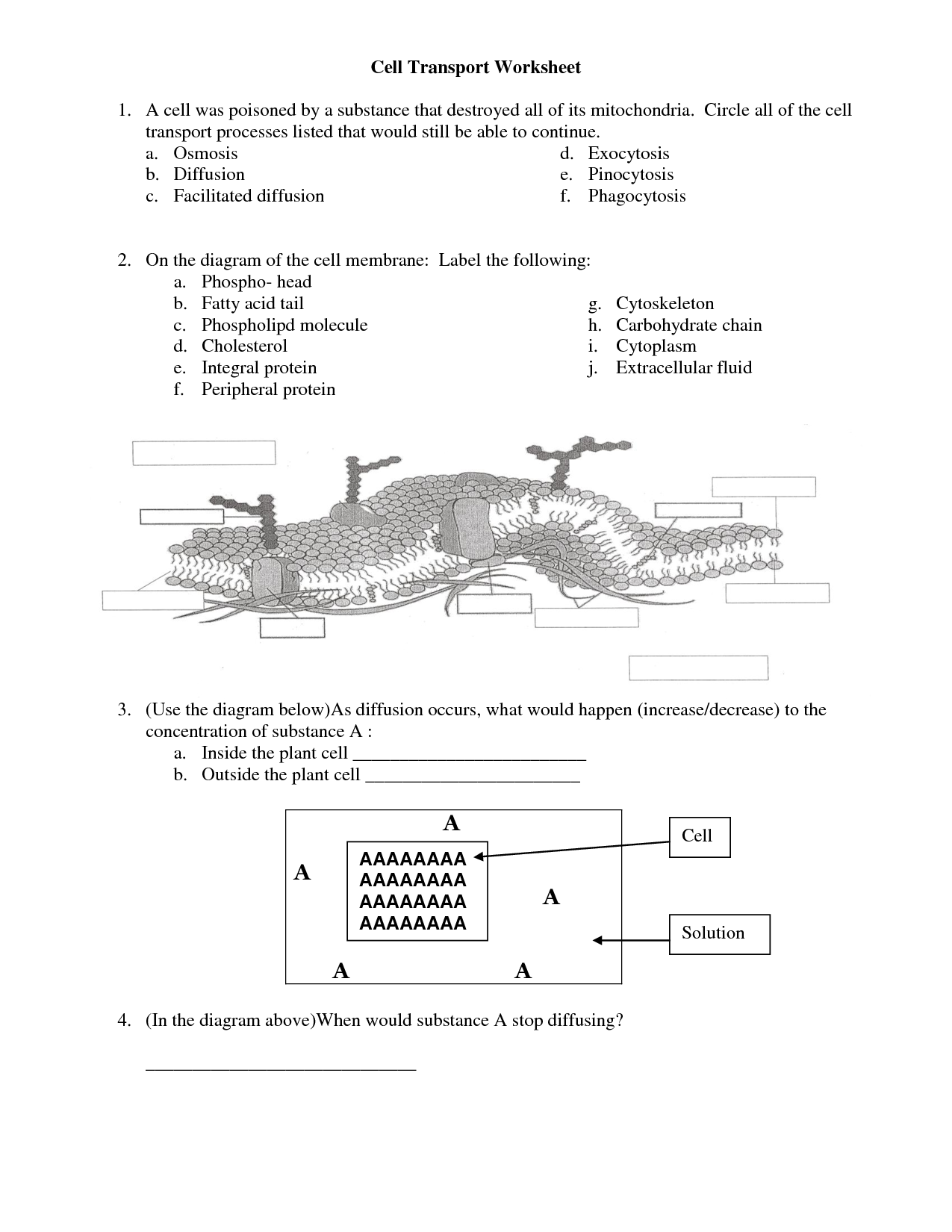
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key Review
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Membrane Transport Worksheet
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key
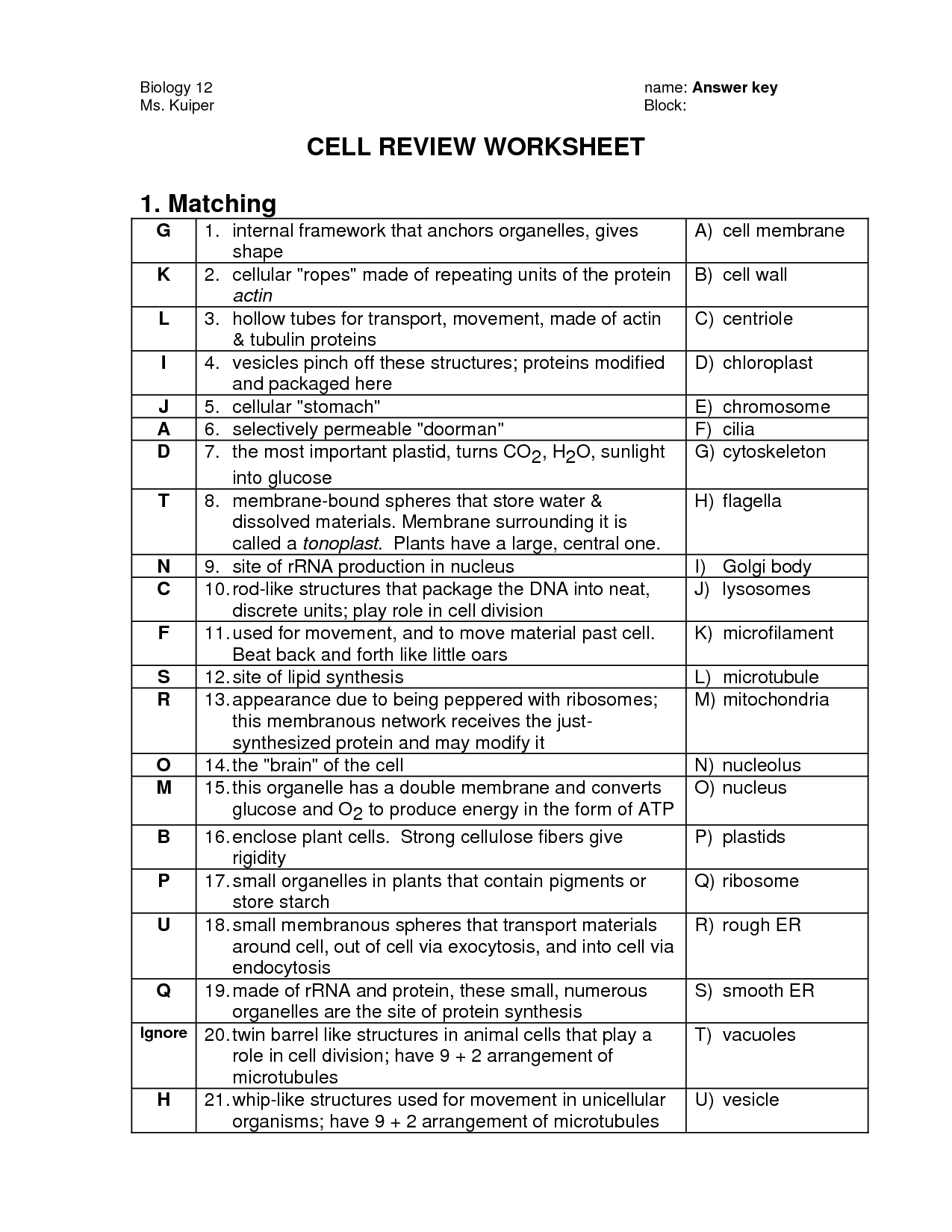
- Cell City Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Membrane and Transport Worksheet Answers
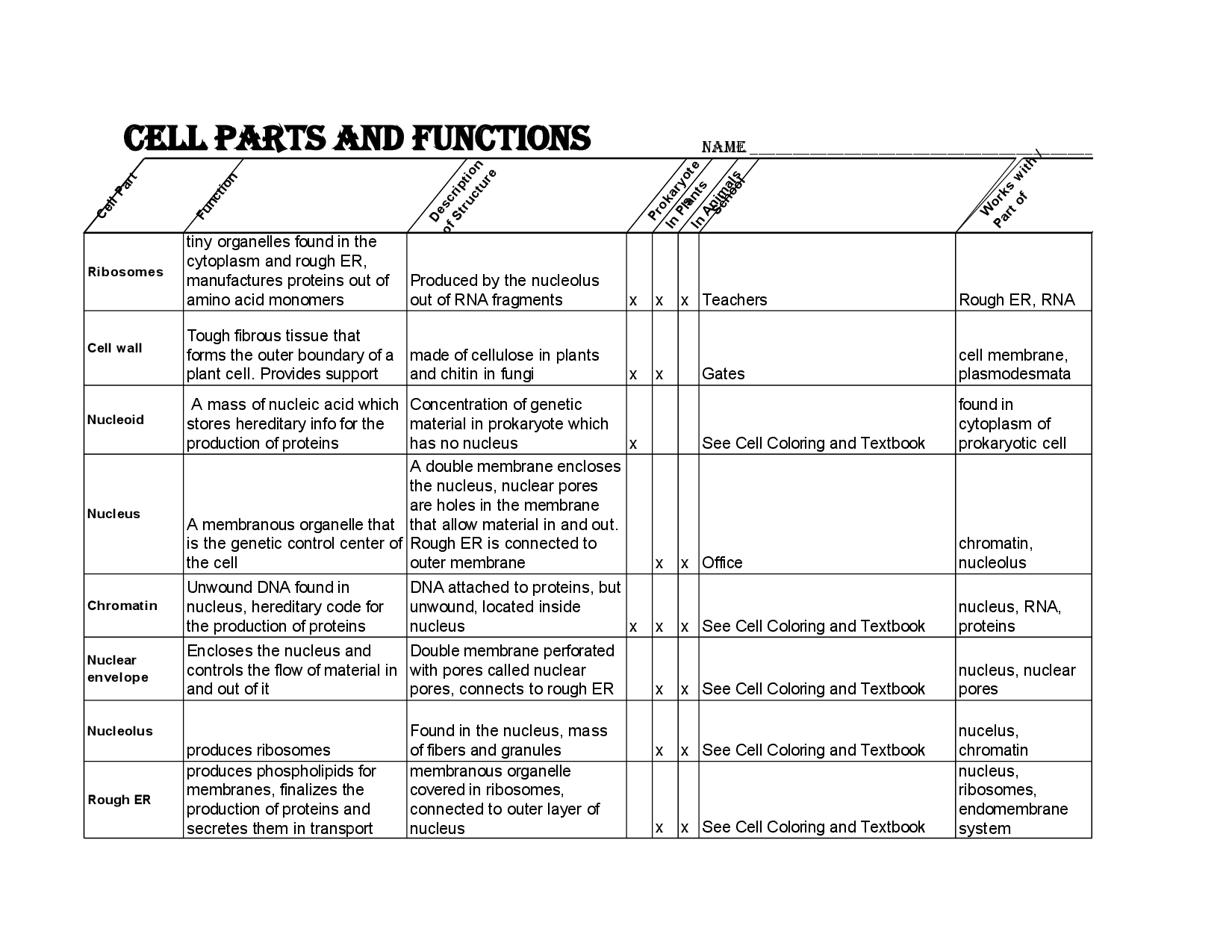
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the main function of the cell membrane?
The main function of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell, acting as a barrier that controls the flow of ions, nutrients, and waste products to maintain cellular homeostasis and protect the cell's internal environment.
What is the composition of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is primarily composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. The phospholipid bilayer forms the basic structure of the membrane, with proteins and cholesterol embedded within or attached to the lipid layer. Carbohydrates are also present on the outer surface of the membrane, often attached to proteins or lipids, playing a role in cell recognition and signaling.
How does the cell membrane regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell?
The cell membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell through a process known as selective permeability. The lipid bilayer of the cell membrane acts as a barrier that only allows certain molecules and ions to pass through. Specific proteins embedded in the membrane, such as channel proteins and carrier proteins, facilitate the transport of substances by either allowing them to pass through pores or actively transporting them across the membrane. This selective permeability ensures that essential molecules enter the cell while waste products and other harmful substances are kept out, maintaining the cell's internal environment and overall function.
What are the different types of proteins found in the cell membrane?
The different types of proteins found in the cell membrane include integral proteins, which are embedded within the lipid bilayer, and peripheral proteins, which are located on the inner or outer surface of the membrane. Integral proteins can be further classified as transmembrane proteins that span the entire membrane, and lipid-anchored proteins that are attached to the membrane through lipid molecules. Additionally, there are receptor proteins that help in communication with the external environment, channel proteins that facilitate the transport of molecules across the membrane, and enzyme proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions at the membrane surface. These proteins work together to maintain the structure and function of the cell membrane.
How does the cell membrane maintain homeostasis?
The cell membrane maintains homeostasis by selectively allowing substances to enter and leave the cell through the process of passive and active transport. It also helps to regulate the concentration of ions and molecules inside the cell, control cell signaling, and participate in cell-cell recognition. Additionally, the cell membrane can adjust its fluidity and composition to respond to changes in the external environment, thereby helping to maintain the internal balance necessary for proper cellular function.
How does the cell membrane recognize and respond to external signals?
The cell membrane recognizes and responds to external signals through its proteins, such as receptors, that are embedded within the lipid bilayer. When an external signal molecule binds to a specific receptor on the cell membrane surface, it triggers a series of events that activate signaling pathways within the cell. These pathways can lead to changes in the cell's behavior, such as altering gene expression, triggering cellular responses, or initiating cell division. Overall, the cell membrane's ability to recognize and respond to external signals is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and coordinating appropriate responses to changes in the cell's environment.
What role does cholesterol play in the structure and function of the cell membrane?
Cholesterol plays a crucial role in the structure and function of the cell membrane by maintaining its fluidity and stability. It helps prevent the membrane from becoming too rigid or too permeable by interacting with the phospholipid molecules. Additionally, cholesterol is involved in the organization of lipid rafts, which are important for signaling and membrane protein trafficking within the cell. Overall, cholesterol is essential for maintaining the integrity and functionality of the cell membrane.
How do cells attach to neighboring cells or extracellular matrix through the cell membrane?
Cells attach to neighboring cells or the extracellular matrix through various cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) present on the cell membrane. CAMs, such as integrins, cadherins, and selectins, facilitate cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions by binding to specific ligands or molecules on the surface of adjacent cells or the extracellular matrix. These interactions are crucial for processes such as cell signaling, tissue formation, immune response, and maintaining cell structure and function.
How does the cell membrane contribute to cell adhesion and communication?
The cell membrane contributes to cell adhesion by containing specialized proteins like cadherins and integrins that help cells stick together and interact with each other. Additionally, the cell membrane also contains receptor proteins that allow cells to communicate with their environment by binding to signaling molecules and transmitting information into the cell to regulate various cellular processes. In this way, the cell membrane plays a crucial role in facilitating cell adhesion and communication, which are essential for proper cell function and coordination within tissues and organs.
What happens when the integrity of the cell membrane is compromised?
When the integrity of the cell membrane is compromised, the cell becomes vulnerable to damage and can no longer regulate what substances enter and exit the cell properly. This can lead to a loss of important cellular components, disruption of essential cellular functions, and potentially cell death. The compromised cell membrane also makes the cell more susceptible to infections and other harmful external factors.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments