Cell Cycle Review Worksheet
Are you struggling to grasp the different phases and processes of the cell cycle? Look no further! This Cell Cycle Review Worksheet is designed to help students at the high school or introductory college level better understand the entity and subject of the cell cycle.
Table of Images 👆
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle Review Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- The 12 Cell Review Worksheet Answers Biology
- Cancer and Cell Cycle Worksheet
- Virtual Cell Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Division and Reproduction Worksheet
- Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Worksheet
- Cell Division Mitosis Worksheet and Answers
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Cellular Respiration Review Worksheet Answers
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key
- The Cell Cycle and Cancer Virtual Lab Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cancer Cell Cycle Worksheet and Answers
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
What is the cell cycle?
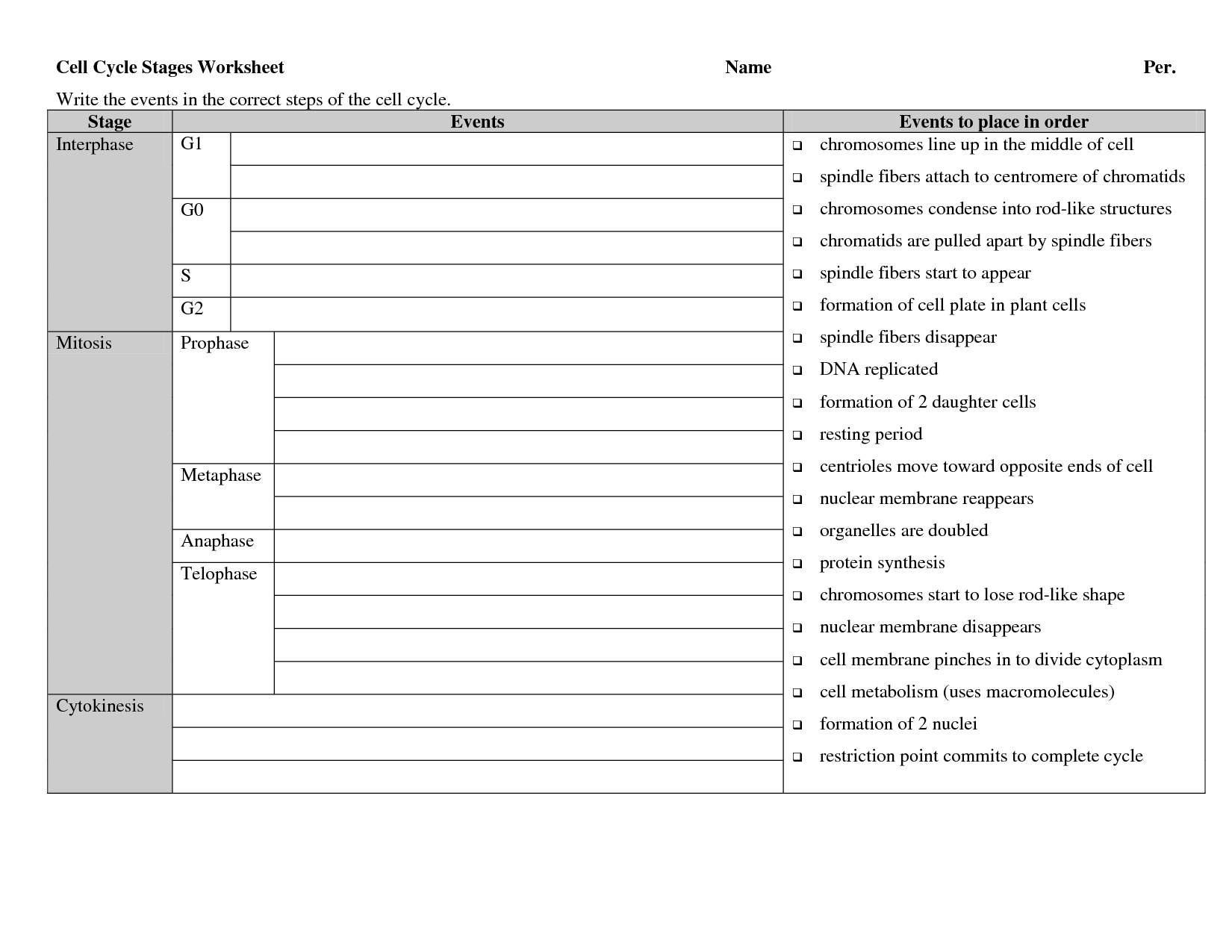
The cell cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication. It consists of interphase (G1, S, and G2 phases), where the cell grows and replicates its DNA, followed by mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase), where the duplicated DNA is segregated into two daughter cells. The cell cycle ensures the accurate duplication and distribution of genetic material, allowing for growth, development, and repair of tissues.
What are the phases of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle consists of interphase, which includes G1 phase (cell growth), S phase (DNA replication), and G2 phase (preparation for cell division), followed by the mitotic phase, which includes mitosis (nuclear division) and cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division).
What is the purpose of the G1 phase?
The purpose of the G1 phase is for the cell to grow in size, synthesize proteins, and carry out its normal functions. During this phase, the cell prepares for DNA replication in the following phase of the cell cycle. Additionally, the G1 phase allows the cell to assess its environment and ensure that conditions are favorable for it to proceed through the cell cycle.
What happens during the S phase?
During the S phase of the cell cycle, DNA replication takes place. This process involves the duplication of the cell's entire genome, ensuring that each daughter cell resulting from cell division receives a complete and identical set of genetic information. The S phase is a critical step in preparing for cell division and is essential for the accurate transmission of genetic material to new cells.
What is the function of the G2 phase?
The primary function of the G2 phase in the cell cycle is to allow the cell to prepare for mitosis (cell division) by ensuring that all DNA replication from the S phase is completed accurately and any DNA damage is repaired. This phase also allows the cell to check for DNA errors and carry out any necessary corrections before proceeding to mitosis, thus ensuring the proper segregation of genetic material during cell division.
What is the role of mitosis in the cell cycle?
The role of mitosis in the cell cycle is to ensure the accurate division and distribution of the genetic material (chromosomes) to two daughter cells. This process is crucial for growth, development, and tissue repair in multicellular organisms, as it produces genetically identical daughter cells that are essential for maintaining the proper function and structure of tissues and organs.
What are the four stages of mitosis?
The four stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the nuclear membrane breaks down, chromosomes condense, and the spindle fibers begin to form. In metaphase, the chromosomes line up at the center of the cell. Anaphase involves the separation of sister chromatids, which are then pulled to opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers. Finally, in telophase, the nuclear membrane reforms, chromosomes decondense, and two daughter cells start to form.
What happens during prophase?
During prophase, the first stage of mitosis, the nuclear envelope breaks down, chromosomes condense and become visible, and the mitotic spindle begins to form. Additionally, the centrosomes move to opposite poles of the cell, while the spindle fibers attach to the kinetochores of the chromosomes. This stage is crucial for the organization and preparation of the cell for cell division.
What occurs during metaphase?
During metaphase, the chromosomes align along the metaphase plate in the center of the cell. The spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of the sister chromatids, facilitating their movement and ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes during cell division.
What happens during cytokinesis?
During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm of a cell divides into two separate daughter cells after the process of mitosis is completed. This division is facilitated by the formation of a cleavage furrow in animal cells or a cell plate in plant cells, which ultimately leads to the physical separation of the two daughter cells. This final stage of the cell cycle ensures that each daughter cell receives its portion of the organelles and other cellular components to become fully functional individual cells.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments