Carbohydrates Practice Worksheets
Carbohydrates practice worksheets are a valuable resource for students seeking to strengthen their understanding of this essential macronutrient. Designed to cater to the needs of biology or health science students, these worksheets provide an in-depth exploration of carbohydrates and their impact on the human body.
Table of Images 👆
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- Nomenclature Worksheet 2 Answer Key
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- Definition Figurative Language Worksheets
- Ketone and Aldehyde Synthesis Problems
- Worksheets Answer Key
- Enzyme Practice Worksheet Answer Key
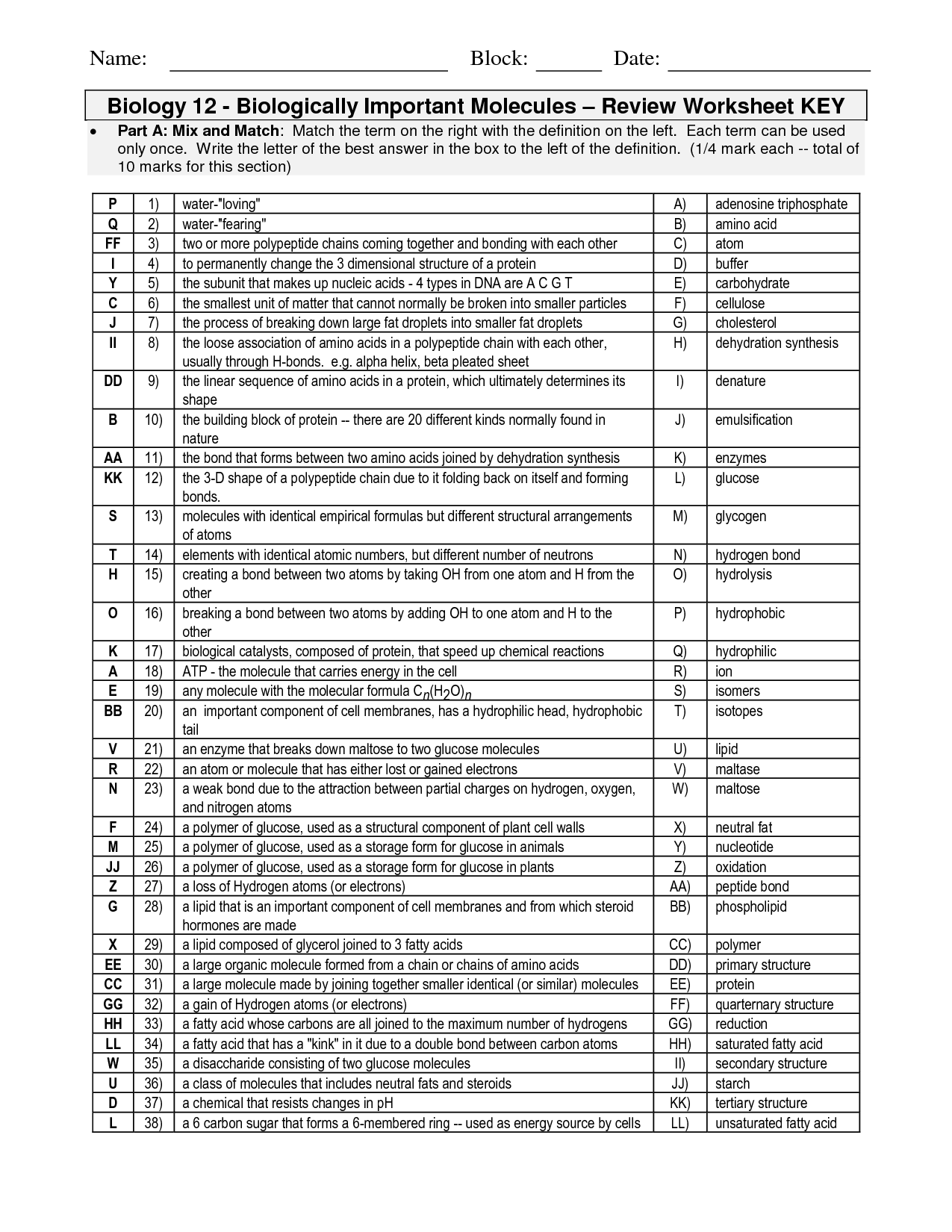
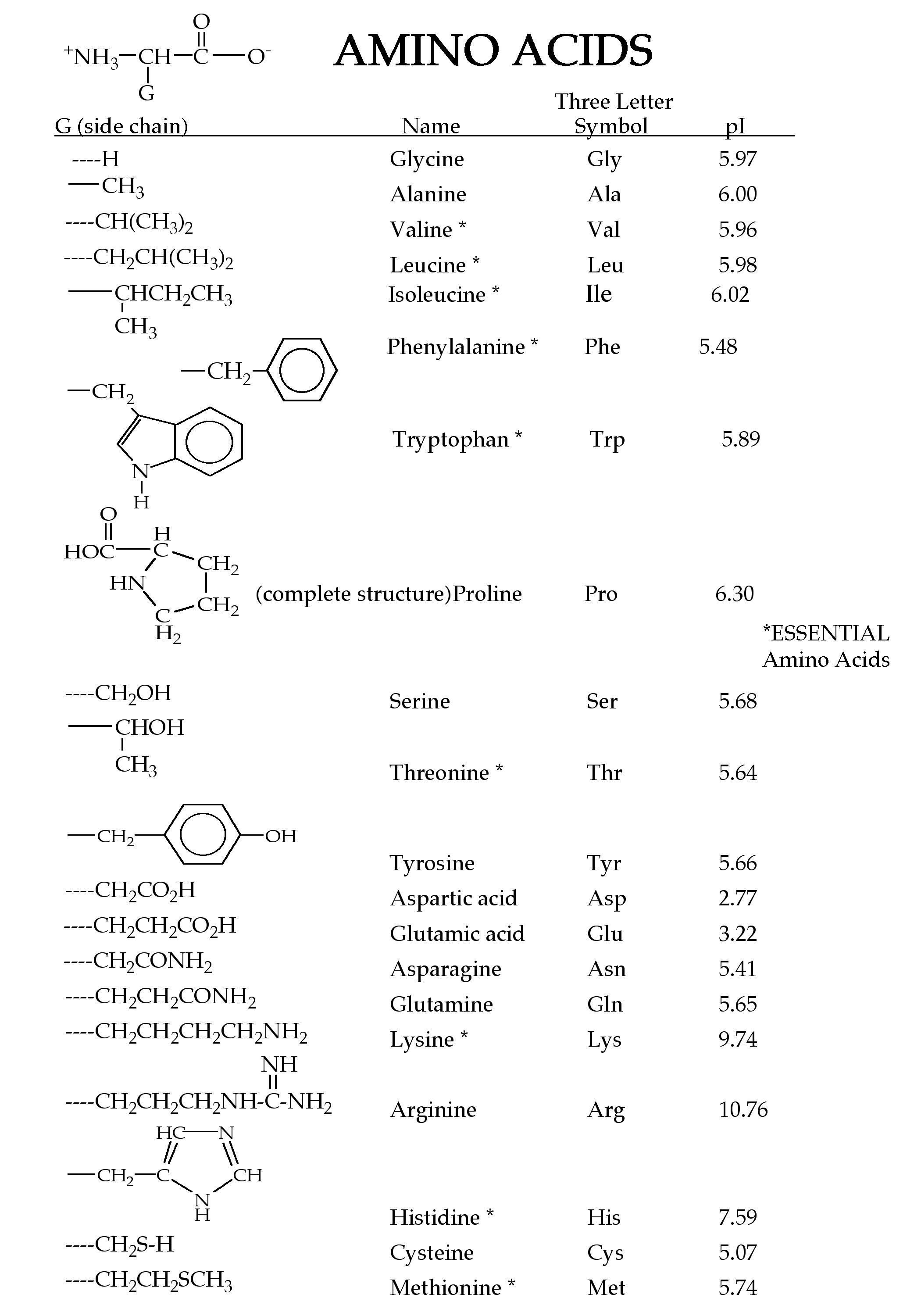
- Amino Acid Worksheet
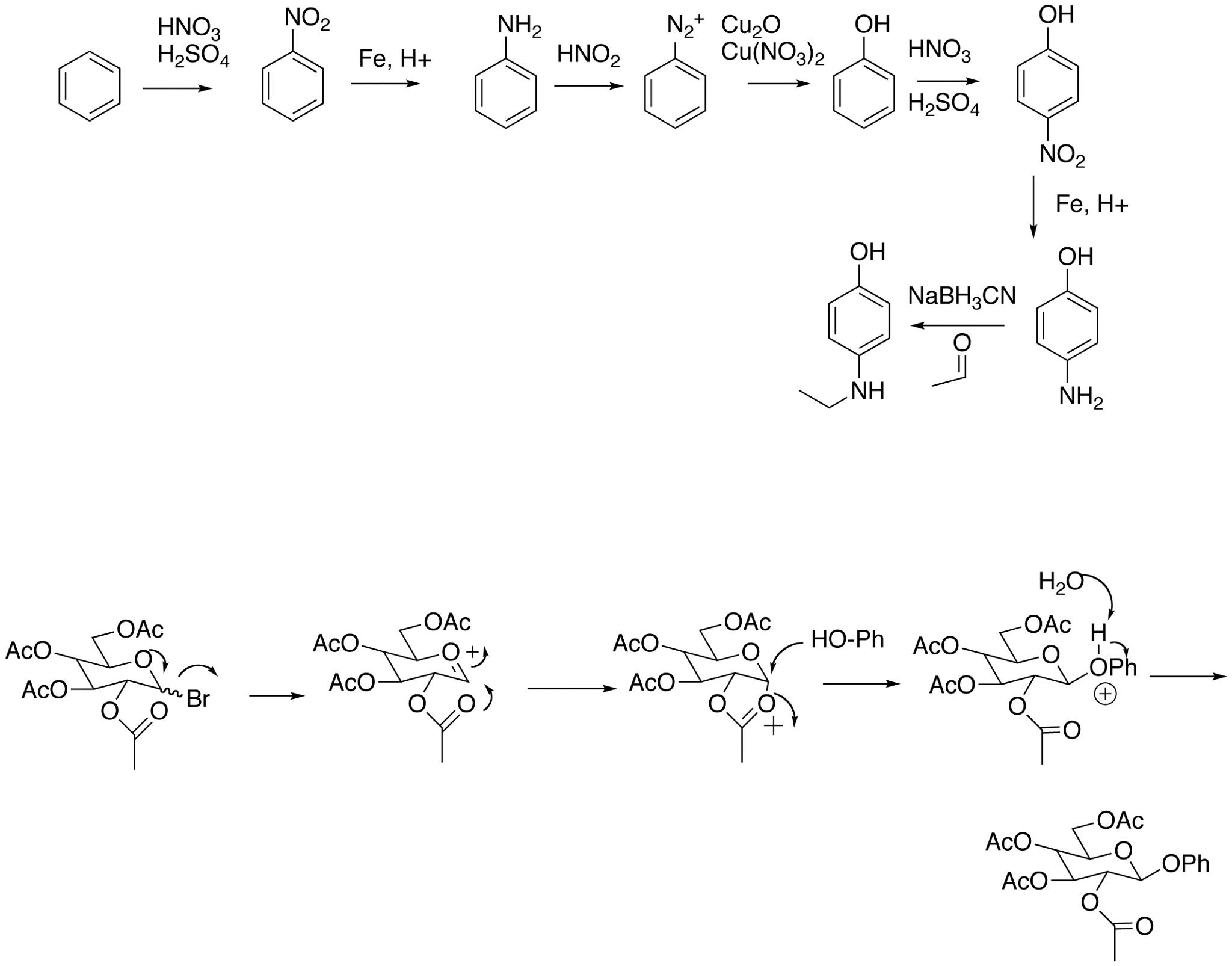
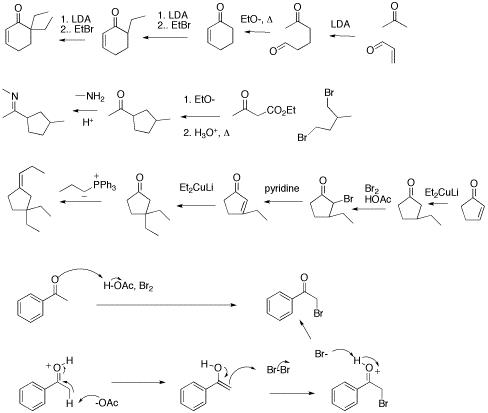
- Reaction Mechanism Practice Problems
- Molecules of Life Worksheet Answers Key
- Worksheet Reaction Rates Answer Key
- Free Math Printable Worksheets Divisibility Rules
- Carbohydrates Biology
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
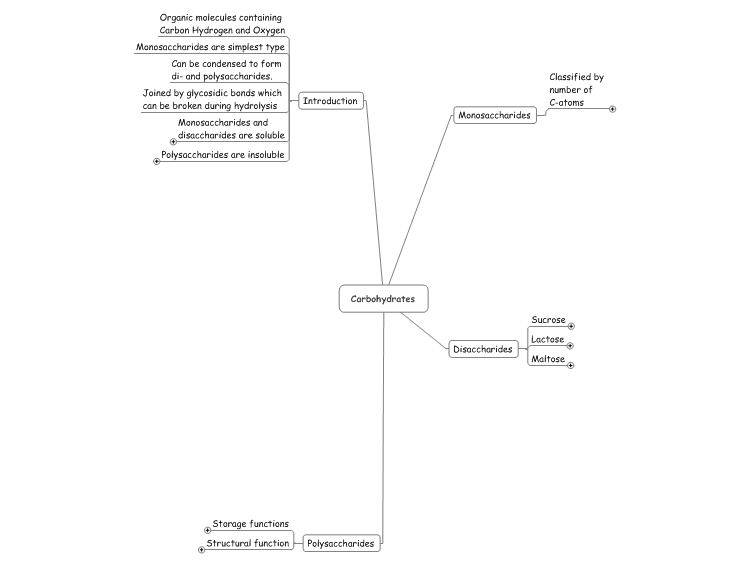
What are carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are macronutrients found in food that provide the main source of energy for the body. They can be simple carbohydrates like sugars found in fruits or complex carbohydrates like starches found in grains. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is used by cells for energy production and fueling various bodily functions.
What is the primary function of carbohydrates in the body?
Carbohydrates are the body's main source of energy. When consumed, they are broken down into glucose, which is then used by cells to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy source for the body. Carbohydrates also play a crucial role in providing fuel for the brain and nervous system, as well as supporting various biological processes such as protein synthesis and immune function.
What are the three main types of carbohydrates?
The three main types of carbohydrates are sugars, starches, and fiber. Sugars include simple carbohydrates like glucose and fructose, starches are complex carbohydrates found in foods like grains and potatoes, and fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest but is important for digestive health.
Describe the structure of a monosaccharide.
A monosaccharide is a simple sugar molecule that consists of a single carbohydrate unit. It has a basic structure formula of (CH2O)n where n is equal to or greater than three. Monosaccharides have a central carbon atom with a carbonyl group (either an aldehyde or a ketone group) and multiple hydroxyl groups attached to the carbon atom. This results in a molecule that is typically a ring or linear structure. Common examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
What is the difference between a simple carbohydrate and a complex carbohydrate?
Simple carbohydrates, also known as simple sugars, are made up of one or two sugar molecules that are quickly digested and absorbed by the body, leading to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. In contrast, complex carbohydrates are made up of multiple sugar molecules linked together, requiring more time and energy to break down and resulting in a slower, more sustained release of energy. This difference in digestion and absorption rates leads to simple carbohydrates often being referred to as "bad" carbs with minimal nutritional value, while complex carbohydrates are considered "good" carbs due to their fiber content and more sustained energy release.
Give an example of a food that contains simple carbohydrates.
A good example of a food that contains simple carbohydrates is honey. Honey is a natural sweetener that is high in simple sugars such as glucose and fructose, making it a quick source of energy for the body.
Give an example of a food that contains complex carbohydrates.
One example of a food that contains complex carbohydrates is oatmeal. Oatmeal is a whole grain that is rich in fiber and provides sustained energy due to its complex carbohydrate content. It is a popular and nutritious breakfast choice that can be easily customized with various toppings such as fruits, nuts, and seeds to create a balanced meal.
What is the role of carbohydrates in providing energy?
Carbohydrates serve as the body's primary source of energy. When consumed, they are broken down into glucose, which is then used by the body's cells to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main form of energy that powers cellular processes. Without an adequate supply of carbohydrates, the body may resort to breaking down proteins and fats for energy, which can have negative effects on overall health.
How does the body break down and digest carbohydrates?
When you consume carbohydrates, they are broken down in the mouth through the action of salivary amylase. In the stomach, carbohydrates are further broken down by stomach acid, and then the bulk of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the small intestine with the help of pancreatic amylase. The resulting smaller sugar molecules are then absorbed through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream to be used for energy or stored in the liver and muscles.
What is the recommended daily intake of carbohydrates for the average adult?
The recommended daily intake of carbohydrates for the average adult is about 45-65% of total daily calories. This typically translates to 225-325 grams of carbohydrates for a 2,000 calorie diet. However, individual carbohydrate needs can vary based on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and overall health goals. It's important to choose complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes to meet your daily carbohydrate needs for optimal health and energy levels.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments