Carbohydrate Lipid and Worksheet
Worksheets are a valuable tool for students who are seeking a structured and organized way to practice and reinforce their understanding of carbohydrate and lipid molecules. These worksheets allow students to analyze and identify the key components of these biological entities, helping them gain a deeper understanding of their structure and function.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
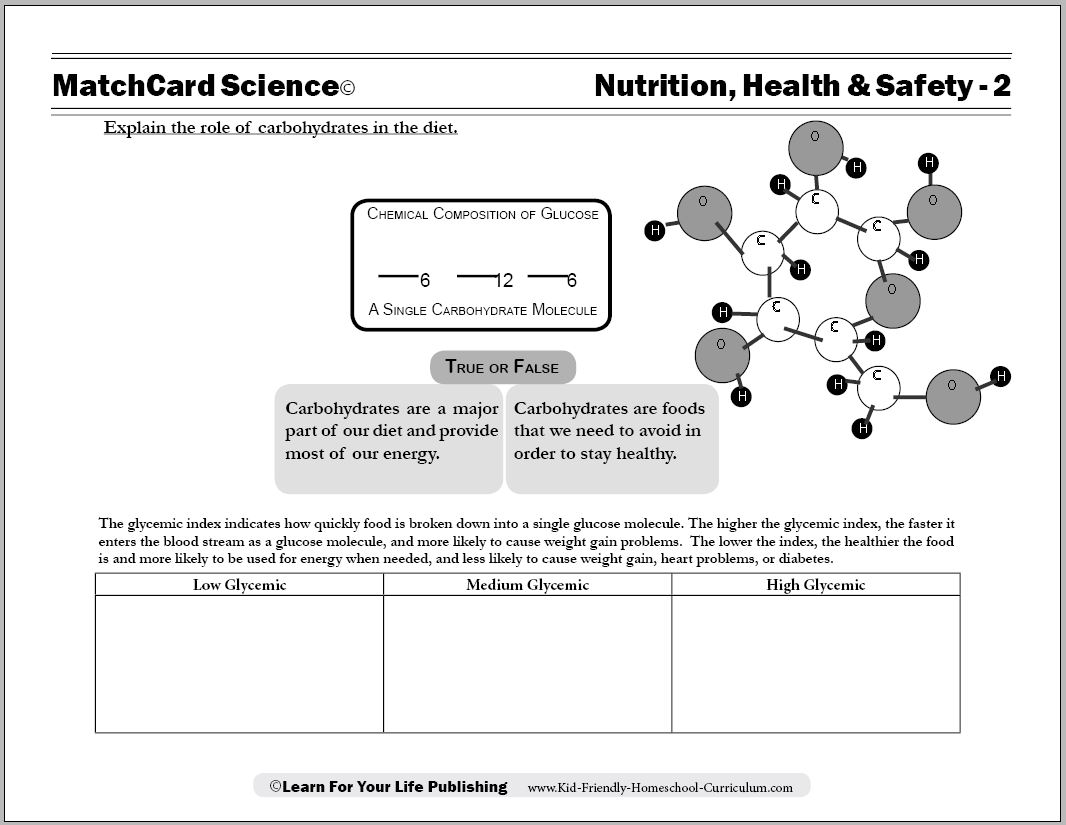
What is a carbohydrate?
A carbohydrate is a type of macronutrient that serves as a primary source of energy for the body. It is composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, and it can be found in foods such as bread, pasta, fruits, vegetables, and grains. Carbohydrates are classified into simple carbohydrates (sugars) and complex carbohydrates (starches and fiber), and they play a crucial role in providing fuel for the brain and muscles to function properly.
What are the main functions of carbohydrates in the body?
Carbohydrates serve as the primary source of energy for the body, providing fuel for the brain, muscles, and other vital organs. They also play a crucial role in biochemical processes such as cellular signaling and immune response. Additionally, carbohydrates are essential for maintaining digestive health, as dietary fiber helps promote healthy digestion and prevent constipation.
What are simple carbohydrates and give examples?
Simple carbohydrates are sugars that are quickly digested by the body, leading to a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. Examples of simple carbohydrates include glucose, fructose, sucrose (table sugar), lactose (milk sugar), and maltose (found in grains and some fruits). These sugars are often found in processed foods, sweets, candies, fruits, and dairy products.
What are complex carbohydrates and give examples?
Complex carbohydrates are sugars composed of long chains of molecules, which take longer to break down in the body and provide sustained energy. Examples include whole grains like wheat, oats, and barley, starchy vegetables like sweet potatoes and corn, legumes such as beans and lentils, and fiber-rich fruits like apples and berries.
What is the role of carbohydrates in energy production?
Carbohydrates are a primary source of energy for the body. When consumed, they are broken down into glucose, which is then converted into ATP (adenosine triphosphate) through a series of chemical reactions in the body's cells. ATP is the molecule that provides energy for various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, nerve conduction, and overall metabolic functions. Therefore, carbohydrates play a crucial role in providing the energy needed for the body to function properly.
What is a lipid?
A lipid is a diverse group of organic molecules that are insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents, such as alcohol or ether. They serve multiple functions in living organisms, including energy storage, cell membrane structure, and signaling molecules. Lipids include fats, oils, phospholipids, and steroids.
What are the main functions of lipids in the body?
Lipids in the body serve several important functions such as providing a concentrated source of energy, acting as structural components of cell membranes, aiding in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, serving as signaling molecules for various physiological processes, and helping with the insulation and protection of organs. Additionally, lipids are essential for hormone synthesis and play a role in maintaining cellular integrity and fluidity.
What are the different types of lipids?
The main types of lipids include triglycerides, phospholipids, sterols, and waxes. Triglycerides are the most common type of lipid and serve as a major energy source in the body. Phospholipids are key components of cell membranes and help regulate their structure and function. Sterols, such as cholesterol, are crucial for cell membrane integrity and hormone production. Waxes provide protective coatings for plants and animals, helping with waterproofing and insulation.
How are lipids digested and absorbed in the body?
Lipids are digested in the body through a process that involves emulsification by bile salts in the small intestine, followed by enzymatic breakdown by lipases into fatty acids and monoglycerides. These smaller lipid molecules are then absorbed through the intestinal lining into the bloodstream. Once absorbed, lipids are reassembled into triglycerides within the intestinal cells and packaged into chylomicrons for transport through the lymphatic system before entering the bloodstream for distribution to various tissues in the body.
What is a worksheet and how can it be used to study carbohydrates and lipids?
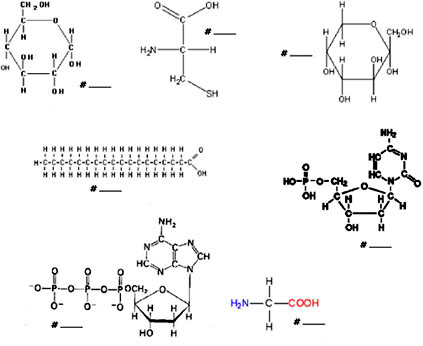
A worksheet is a tool or document used for organizing and conducting tasks, exercises, or studies related to a particular topic. In the context of studying carbohydrates and lipids, a worksheet can be designed to include questions, diagrams, charts, or tables that help students or researchers understand the structures, functions, classifications, and properties of carbohydrates and lipids. It can also be used to practice identifying different types of carbohydrates and lipids, studying their chemical compositions, reactions, and roles in biological systems, as well as comparing and contrasting their similarities and differences. By completing the activities on the worksheet, individuals can reinforce their knowledge, test their understanding, and improve their learning outcomes in the study of carbohydrates and lipids.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments