Calculating Energy Worksheet
Energy is a fundamental concept in science that allows us to understand and quantify different forms of power and activity. For those seeking an engaging and comprehensive resource to practice and enhance their energy calculation skills, this worksheet is designed to provide just that. Ideal for students studying physics or anyone interested in learning more about energy, this worksheet offers a diverse range of questions and exercises to strengthen comprehension and mastery of this vital topic.
Table of Images 👆
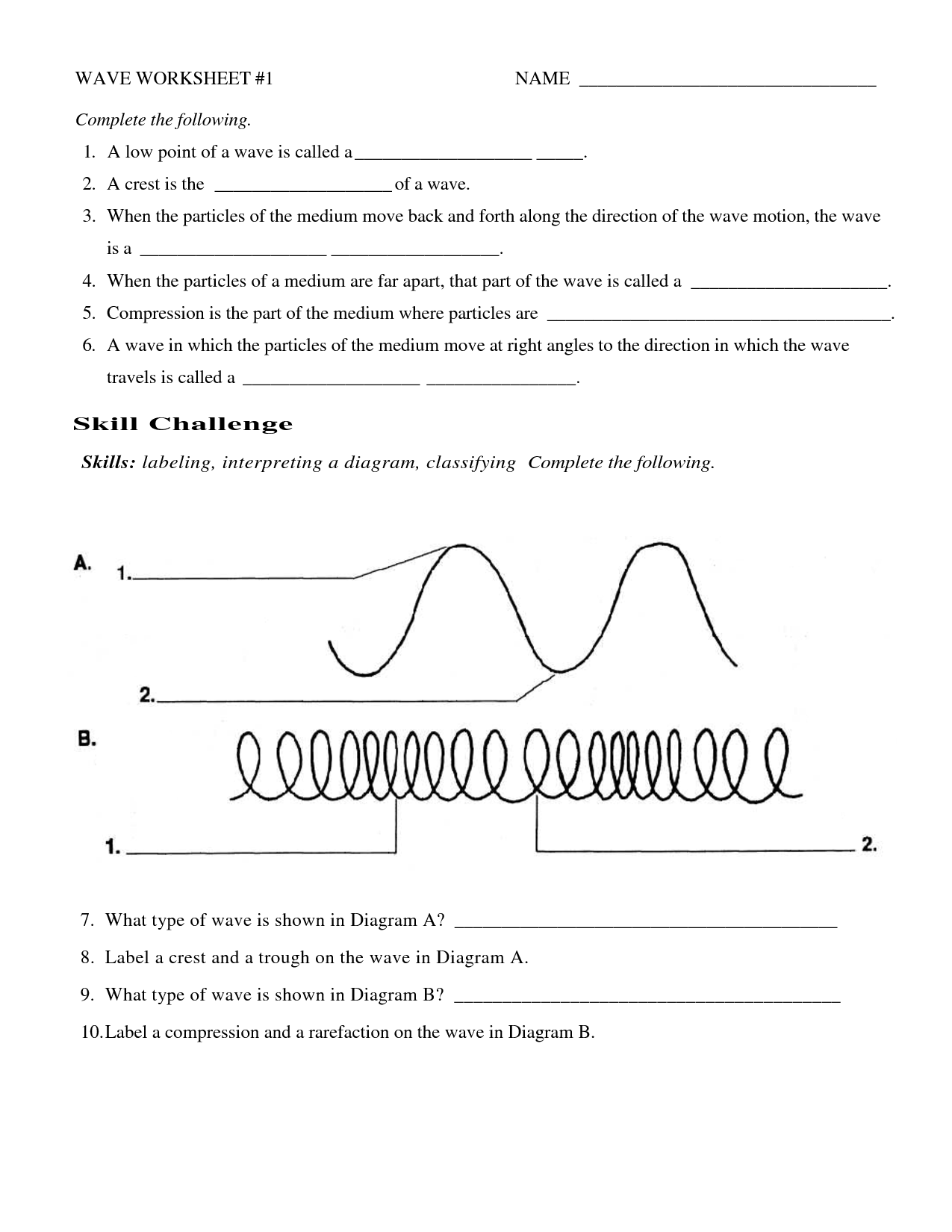
- Labeling Waves Worksheet Answer Key
- Calculating Work Worksheet Physics
- Potential Energy Worksheets
- Stoichiometry Worksheet Answers
- Finance Controller Cover Letter
- Potential and Kinetic Energy Examples
- Bond Length and Bond Energy Table
- Physical and Chemical Changes Study Guide
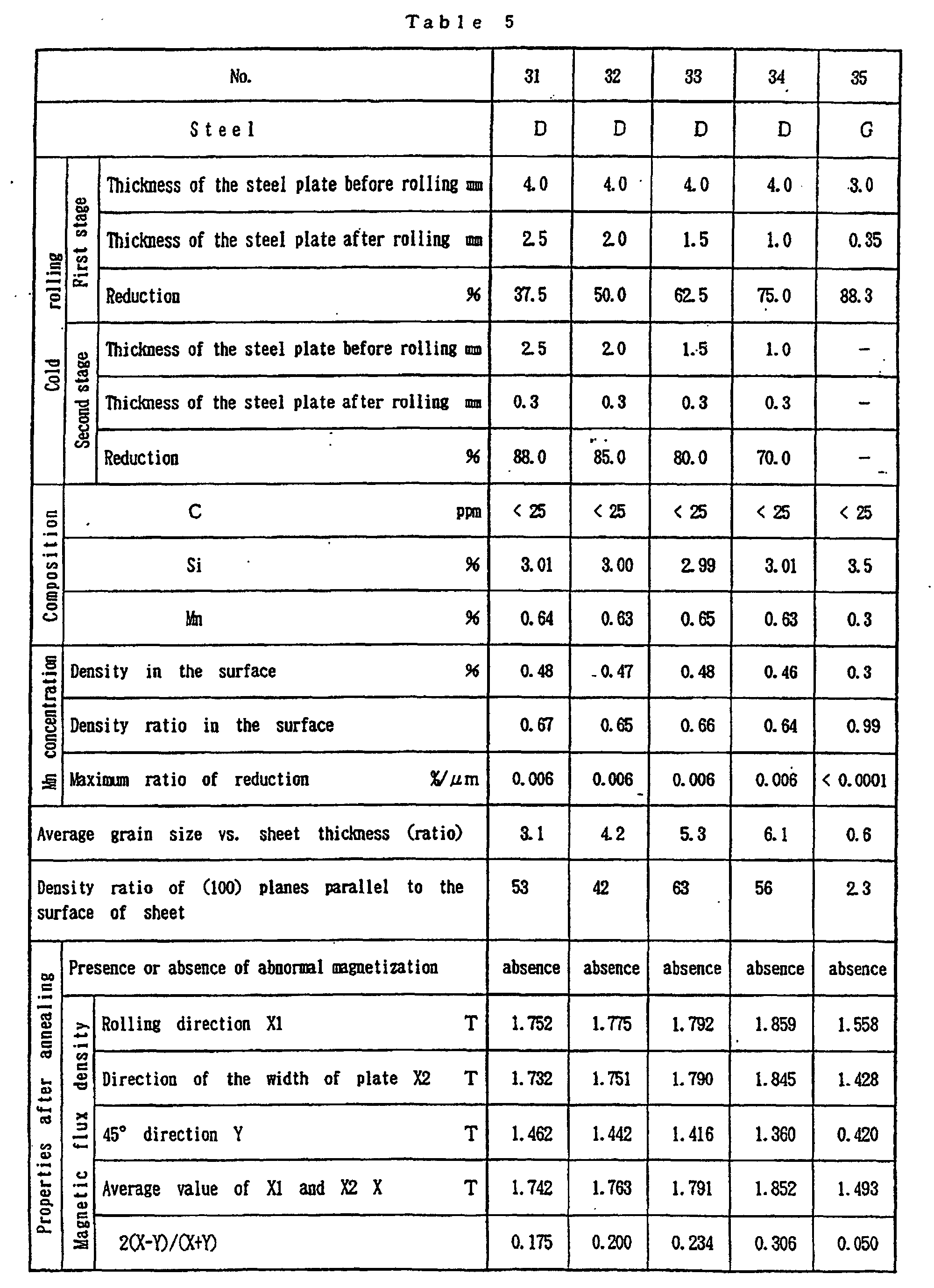
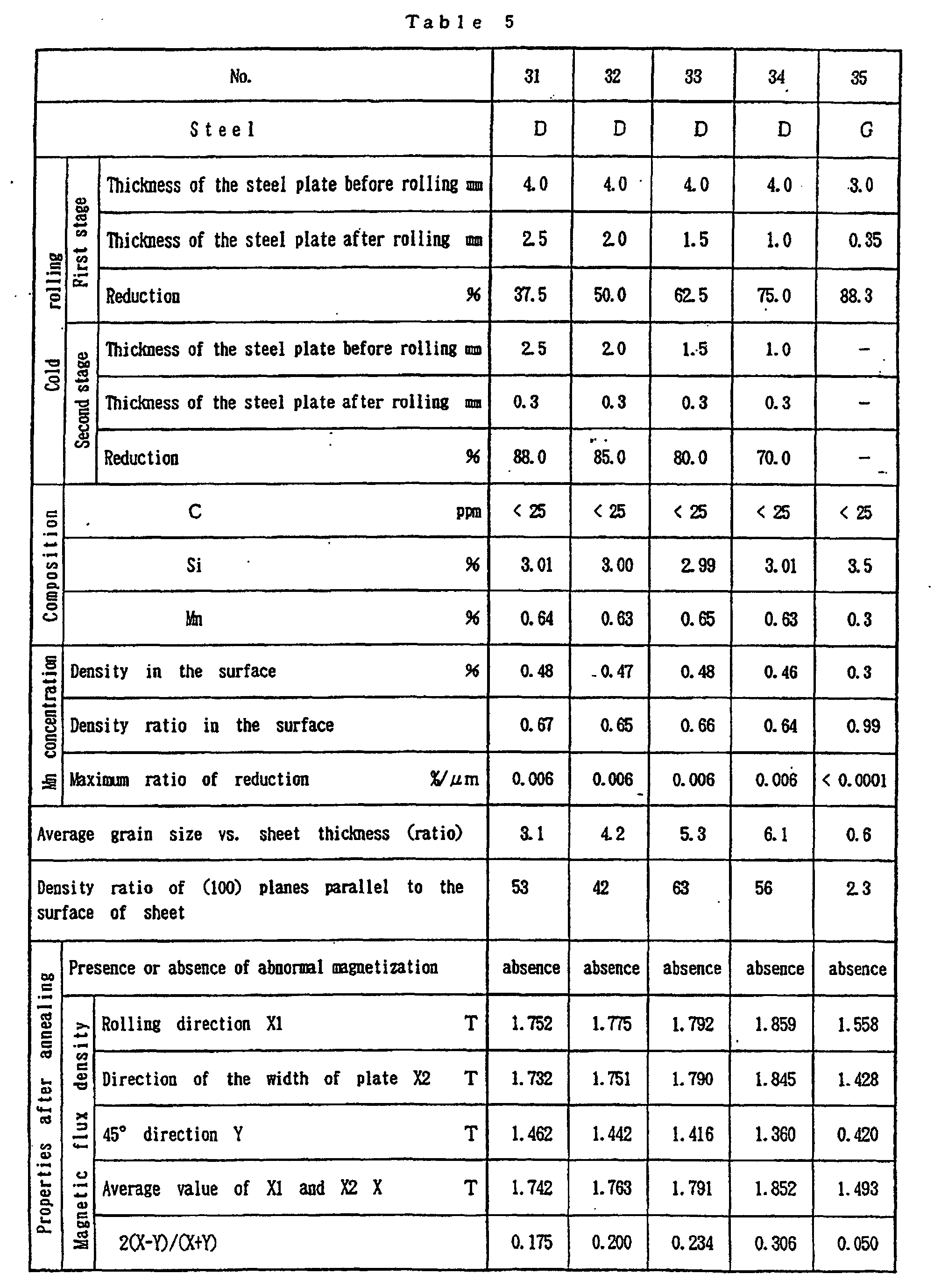
- Sheet Metal Density Chart
- Sheet Metal Density Chart
- Sheet Metal Density Chart
- Sheet Metal Density Chart
- Sheet Metal Density Chart
- Sheet Metal Density Chart
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Types of Energy Worksheet PDF
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
What is the formula to calculate kinetic energy?
The formula to calculate kinetic energy is KE = 0.5 * mass * velocity^2, where KE is the kinetic energy, mass is the mass of the object in motion, and velocity is the speed at which the object is moving.
How is potential energy calculated?
Potential energy is calculated using the formula: Potential energy = mass x gravity x height. In this formula, the mass of the object is multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity and the height at which the object is located to determine the potential energy stored in the object.
Explain the formula for calculating gravitational potential energy.
The formula for calculating gravitational potential energy is PE = mgh, where PE is the gravitational potential energy, m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the object above the reference point. This formula represents the energy stored in an object due to its position in a gravitational field, with the potential energy increasing as the object is raised to a higher height.
How do you calculate mechanical energy?
Mechanical energy is calculated as the sum of the potential energy and kinetic energy of an object. The formula for mechanical energy is ME = PE + KE, where ME is the mechanical energy, PE is the potential energy, and KE is the kinetic energy. Potential energy is calculated using the formula PE = mgh, where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the object above a reference point. Kinetic energy is calculated as KE = 0.5mv^2, where m is the mass of the object, and v is the velocity of the object. By adding these two components together, you can determine the total mechanical energy of an object.
What is the equation for calculating thermal energy?
The equation for calculating thermal energy is Q = mcΔT, where Q represents thermal energy, m is the mass of the object, c is the specific heat capacity of the material, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
Describe the formula for calculating electrical energy.
The formula for calculating electrical energy is E = P × t, where E represents the electrical energy in kilowatt-hours (kWh), P represents the power in kilowatts (kW), and t represents the time in hours. This formula is commonly used to determine the amount of electricity consumed by an electrical device or system over a specific period of time.
How is nuclear energy calculated?
Nuclear energy is calculated by determining the amount of energy released during nuclear reactions, such as fission or fusion. This energy is typically measured in terms of joules or electron volts. The calculation involves factors such as the mass defect (the difference in mass between the reactants and products), the speed of the reaction, and the efficiency of energy conversion. The formula E=mc^2, proposed by Albert Einstein, is often used to calculate the energy released in nuclear reactions, where E represents energy, m is mass, and c is the speed of light.
Explain the formula for calculating chemical energy.
The chemical energy of a substance can be calculated using the formula: \( E = mc\Delta T \), where E is the energy, m is the mass of the substance, c is the specific heat capacity of the substance, and ΔT is the change in temperature. This formula helps to determine the amount of energy stored within a substance due to the arrangement of its atoms and molecules.
What is the equation for calculating elastic potential energy?
The equation for calculating elastic potential energy is given by E = 1/2 * k * x^2, where E is the elastic potential energy, k is the spring constant, and x is the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position.
Describe the formula for calculating sound energy.
The formula for calculating sound energy is E = 0.5 * A^2 * ρ * c * S, where E is the sound energy, A is the amplitude of the sound wave, ρ is the density of the medium through which the sound is traveling, c is the speed of sound in that medium, and S is the cross-sectional area through which the sound wave is passing.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments