Bohr Diagram Worksheet
For pupils studying chemistry or physics, Bohr diagram worksheets can help them visualize and understand the structure of atoms. Learners can practice drawing accurate Bohr diagrams, which show the arrangement of electrons in an atom's energy levels, by utilizing these worksheets. This engaging and participatory method not only improves their knowledge and comprehension but also helps to reinforce basic atomic structure ideas. Bohr diagram worksheets, whether as an object or subject, are a wonderful resource for both instructors and students.
Table of Images 👆
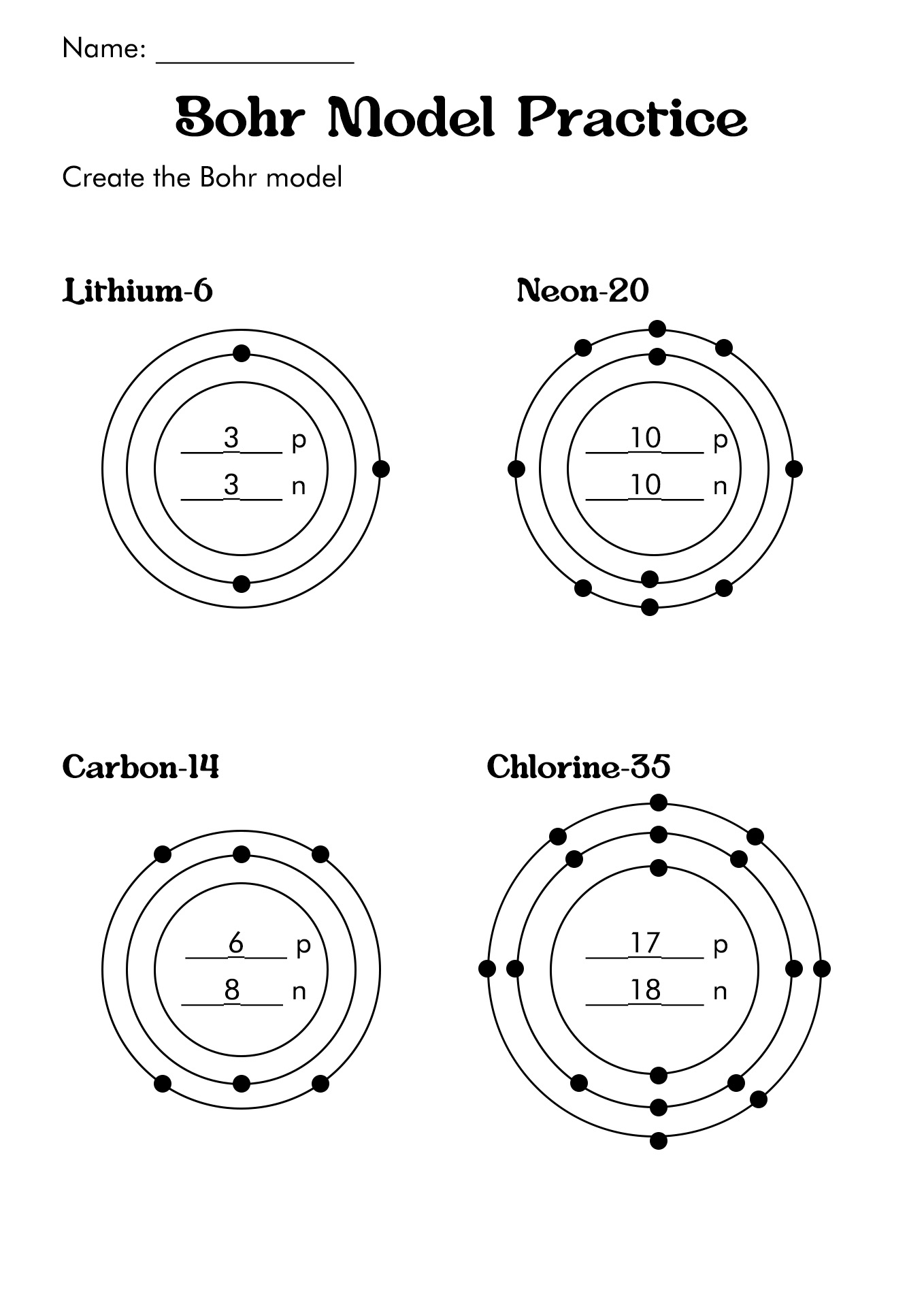
- Bohr Model Worksheet Answers
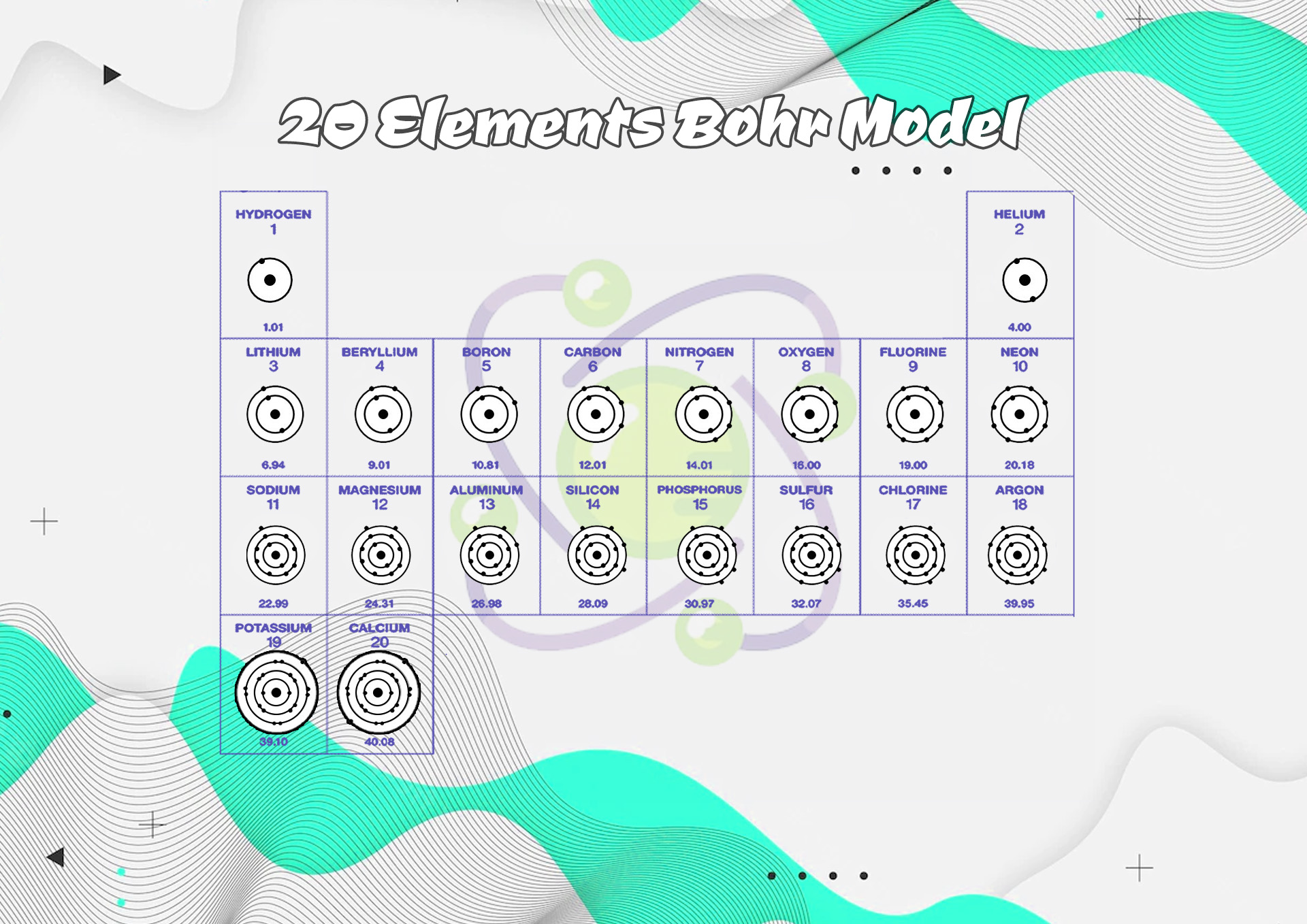
- Diagram of the First 20 Elements Bohr Model
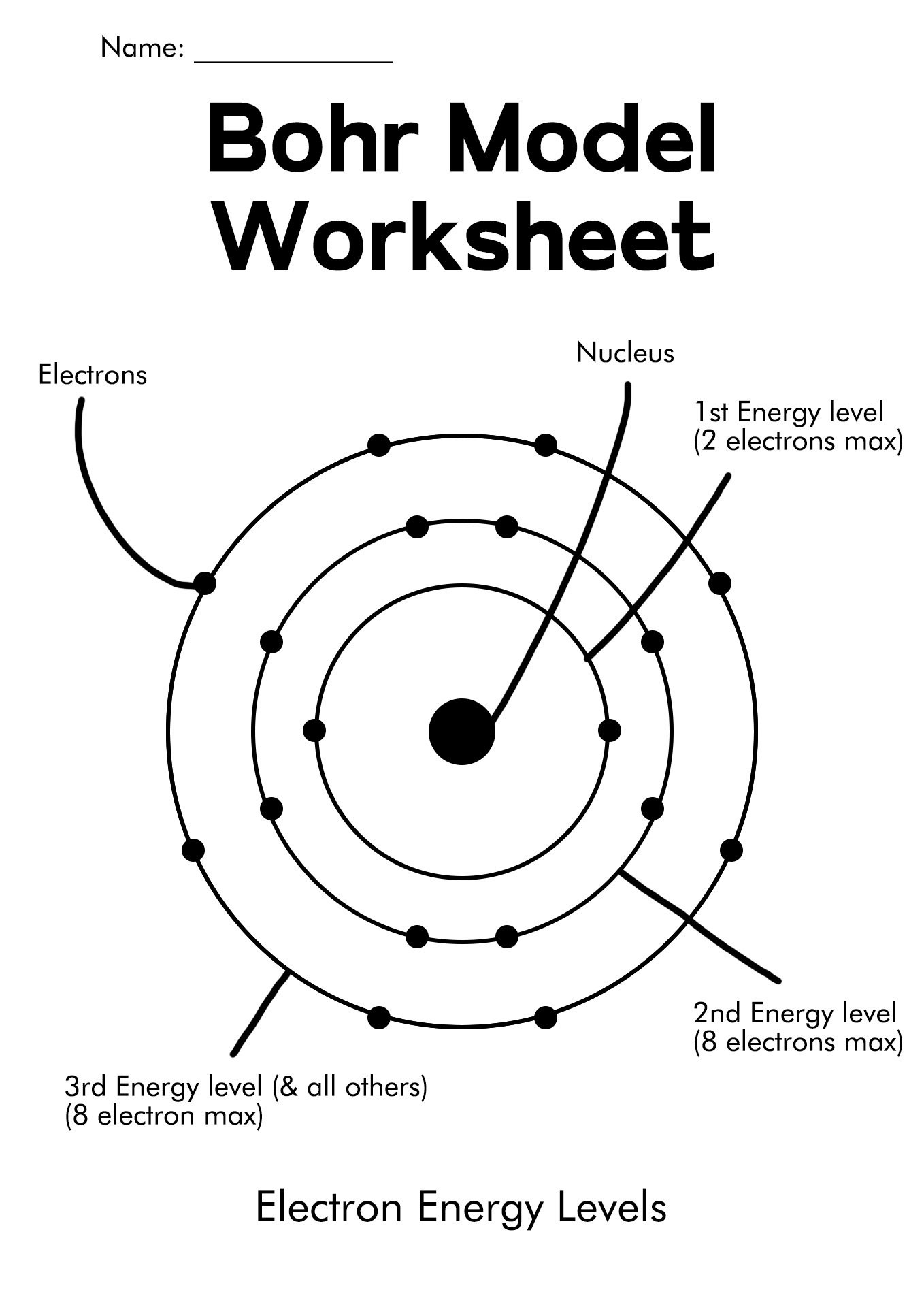
- Blank Bohr Model Worksheet
- Rutherford-Bohr Diagram Worksheet
- Bohr Atomic Models Worksheet Answers
- Periodic Table First 20 Elements
- Bohr Diagrams First 18 Elements
- Bohr Model Diagrams Worksheet
- Rutherford-Bohr Diagram Worksheet
- Lewis Dot and Bohr Model Worksheet
- Bohr Diagrams First 18 Elements
- Bohr Diagrams First 20 Elements
- Diagram of the First 20 Elements Bohr Model
- Diagram of the First 20 Elements Bohr Model
- Bohr Atomic Model Worksheet
- Lewis Dot and Bohr Model Worksheet
- Atomic Structure Bohr Model Worksheet
- Bohr Model of the Atom Worksheet Answers
- Diverging Lens Ray Diagram Worksheet

Understanding atomic structure is crucial for students, and our Bohr Diagram Worksheet can provide valuable assistance in their learning process.
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
The Bohr diagram evolved from a comparable model developed by J. J. Thomson and Ernest Rutherford. The Bohr model raises difficult concerns for scientists and philosophers alike, and it remains a watershed moment in scientific thought.
What is the Bohr Diagram?
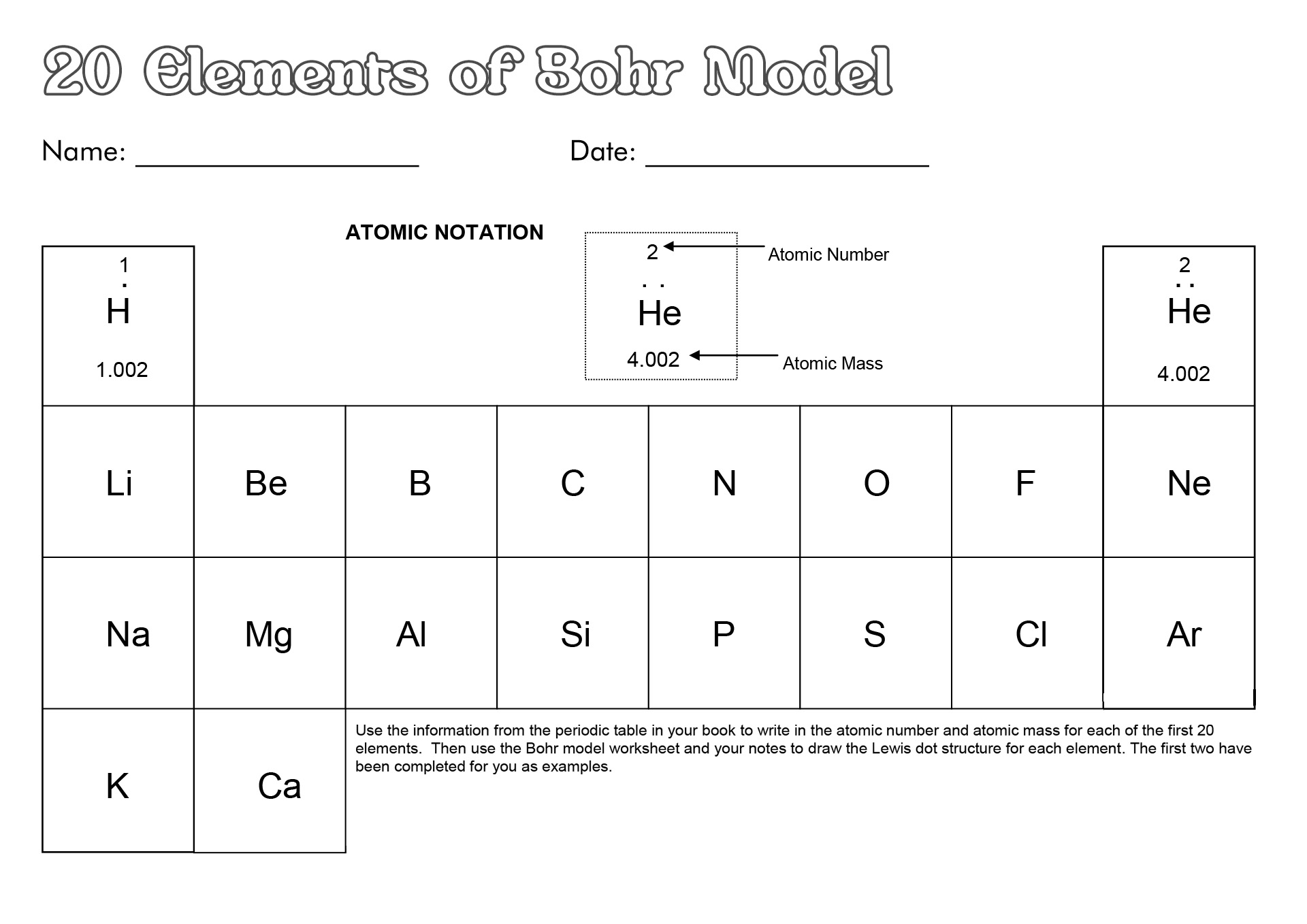
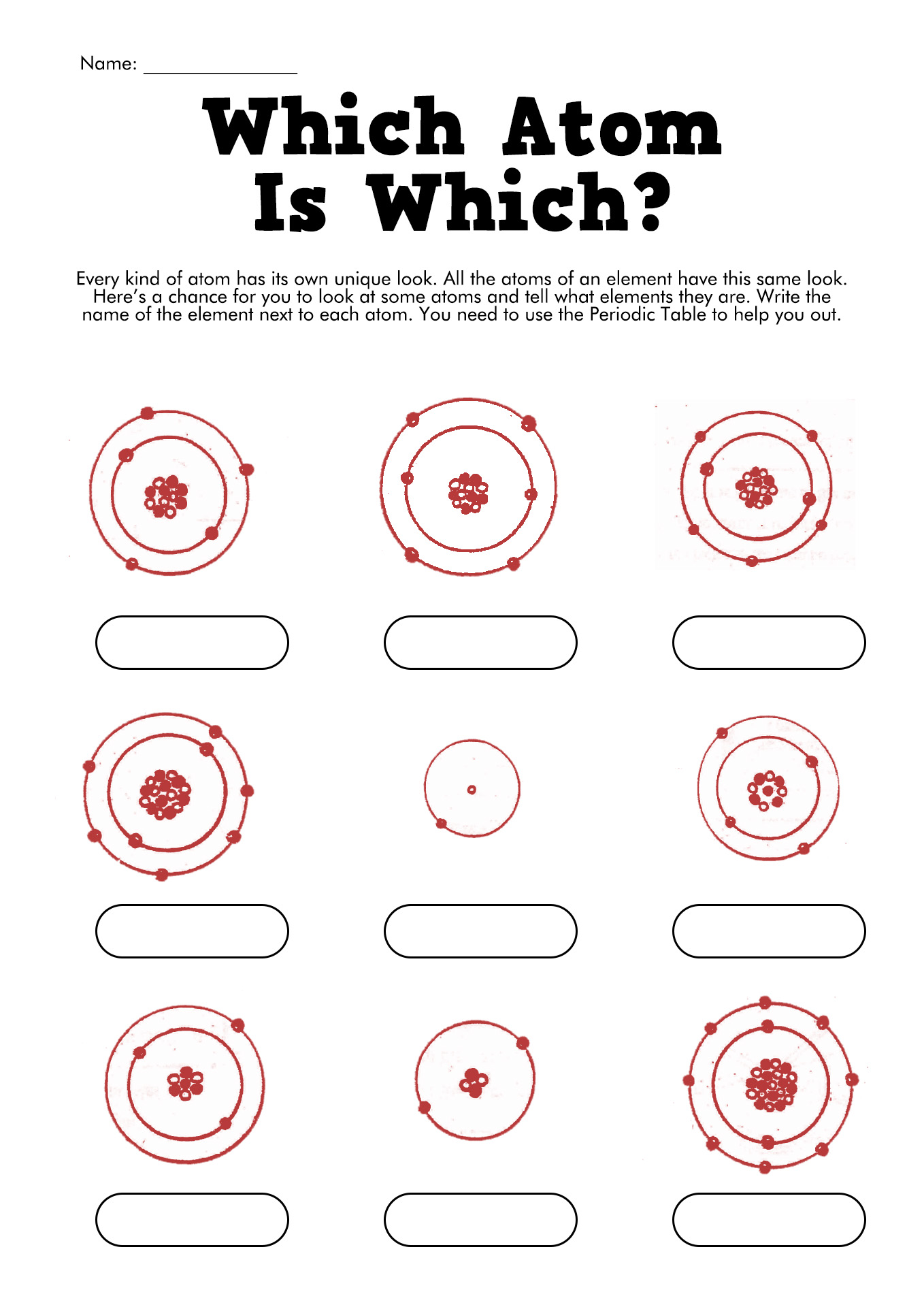
The Bohr diagram, also known as the Bohr model, is an ancient model of a hydrogen atom. Niel Bohr presented this idea as a center of a nucleus that contains protons and neutrons while an electron is in shells orbiting them. There is a correlation between the number of protons in an element, the atomic number that distinguishes one component from another, and the number of electrons it has.
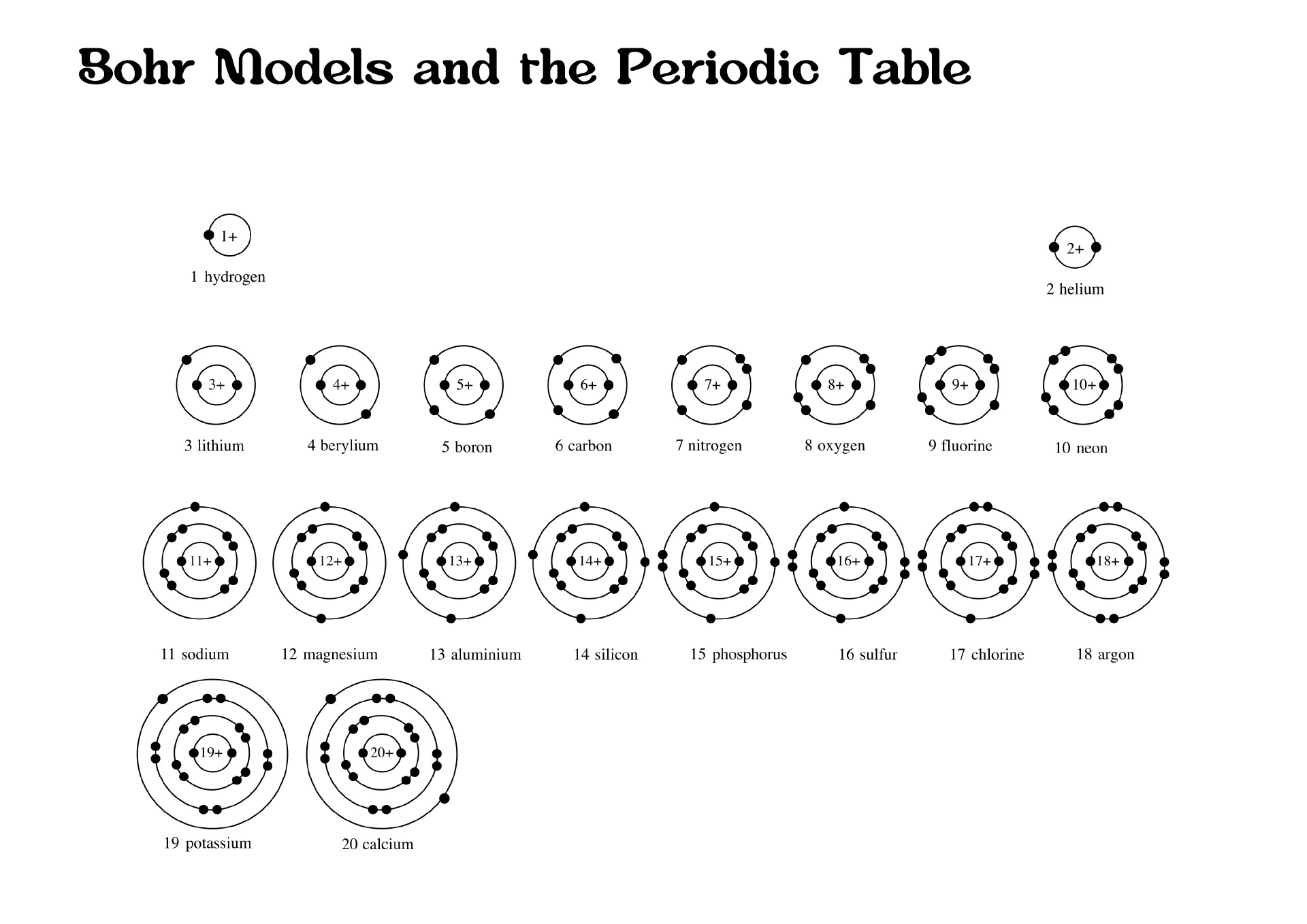
In all electrically neutral atoms, the number of electrons is the same as the number of protons. When the electrical is neutral, each element has as many electrons as its atomic number. In 1913 the initial diagram of the atom was developed by a Danish scientist, Niels Bohr.
The Bohr model depicts an atom as a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons, with electrons in circular orbits at a certain distance from the crux. The Bohr diagram shows that electrons orbit the nucleus much like planets orbit the sun. In the Bohr model, electrons move in circles over different shells depending on their element.
What is Ionization?
Ionization is the process by which electrically neutral atoms or molecules are transformed into charged atoms or molecules (ions) by gaining or losing electrons. Ionization is one of the main ways that radiation transfers its energy to matter. In chemistry, ionization happens in the liquid emulsion.
Impact ionization occurs when an electric current passes through a gas at low pressure. When the current-forming electrons have enough energy (the ionization energy varies from material to material), they push other electrons out of neutral gas molecules, creating ion pairs consisting of the generated positive ions and the separated negative electrons.
When some electrons attach to neutral gas molecules, they form negative ions. Intermolecular collisions at high temperatures can ionize the gas. Ionization generally occurs when particles of sufficient or radiant energy pass through a gas, liquid, or solid. High-energy neutral particles such as neutrons and neutrinos are more penetrating and cause less ionization.
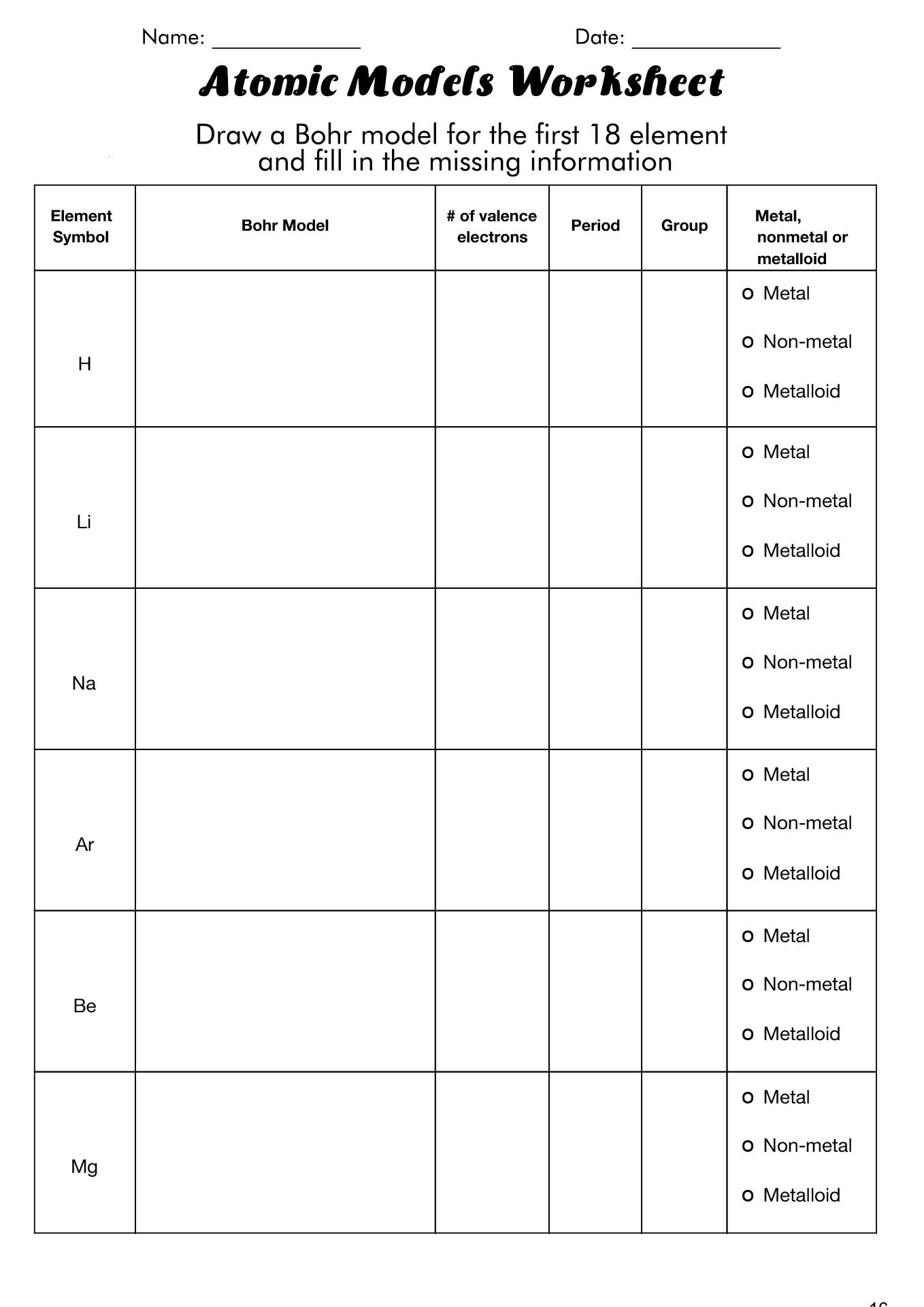
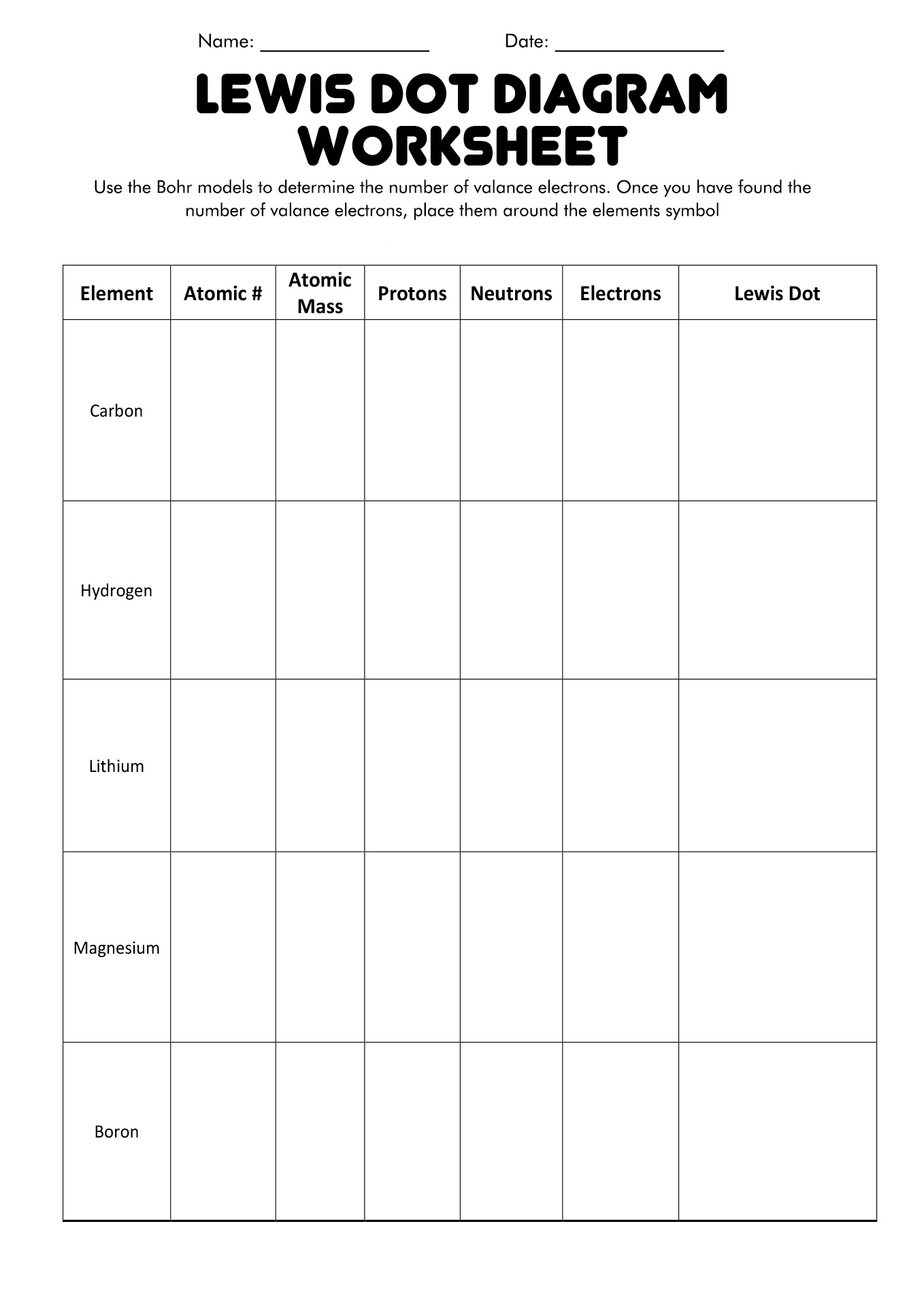
What are Valence Electrons?
Valence electrons are the electrons that hang around in an atom's outermost shell. Think of them as the cool kids in the atomic neighborhood. These electrons have the opportunity to participate significantly in chemical reactions and bonding.
An element's chemical characteristics are determined by its valence electron count, and elements with comparable valence electron counts typically exhibit similar behaviors. The way the elements interact with each other seems to be influenced by their own tiny clique.
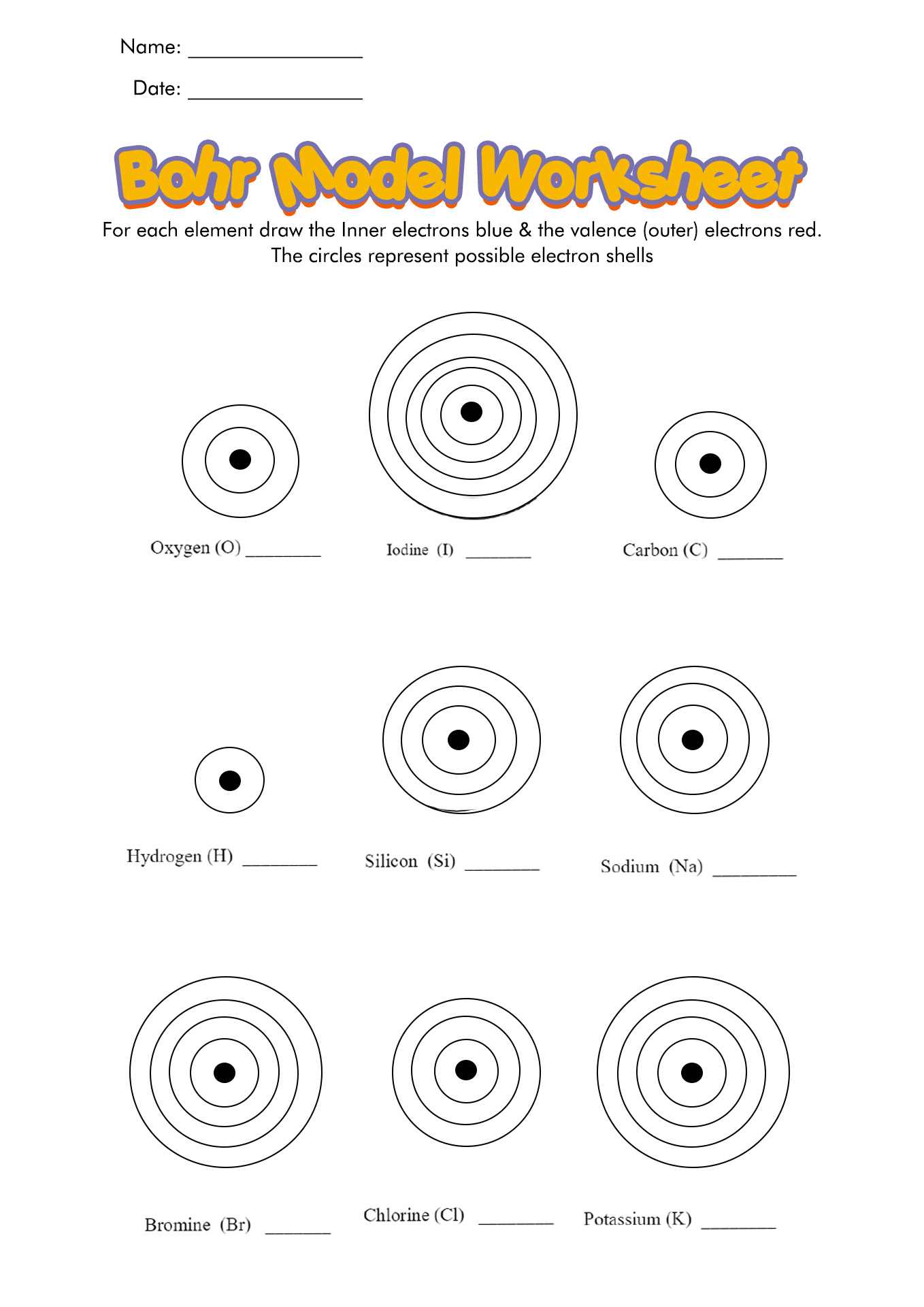
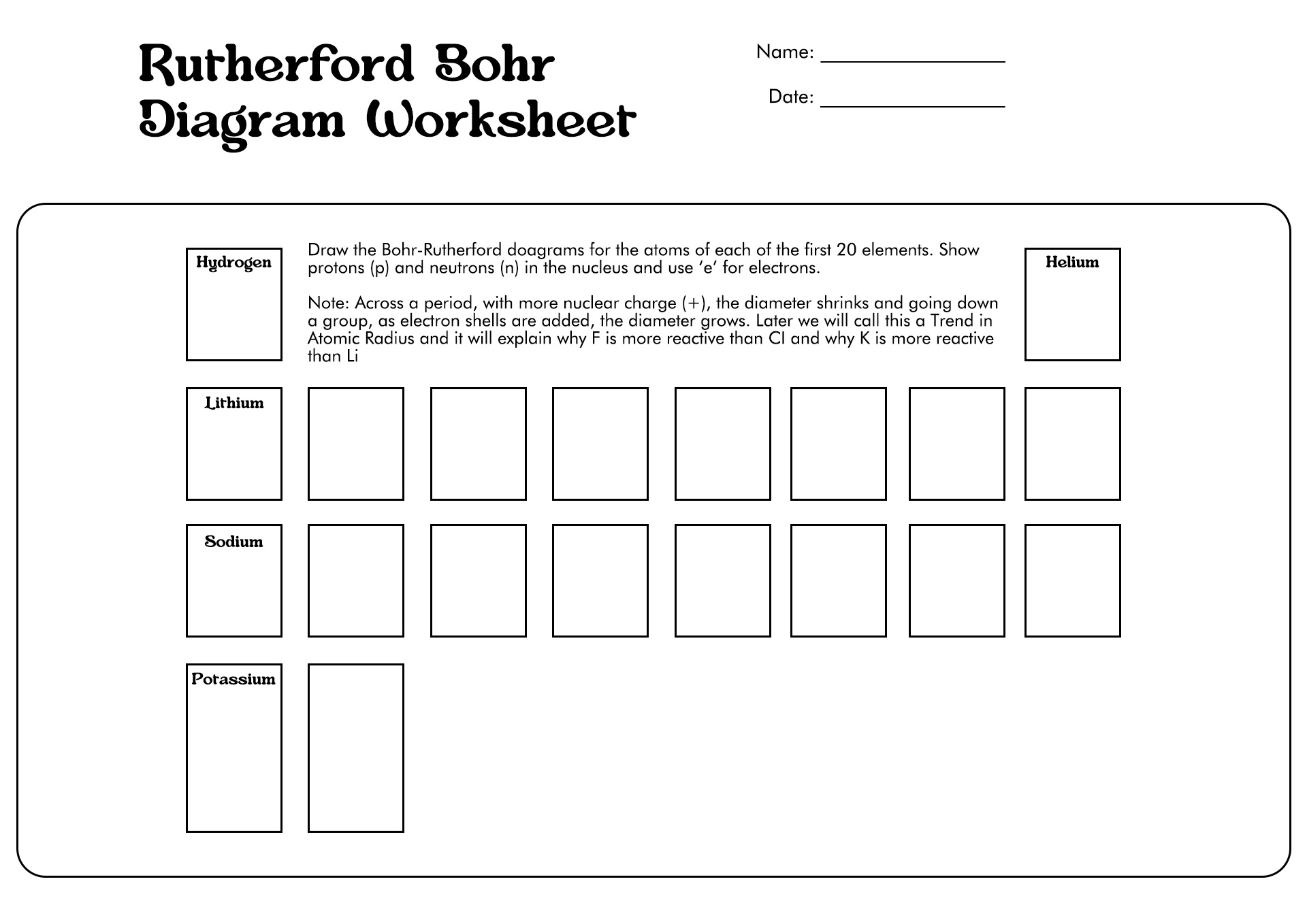
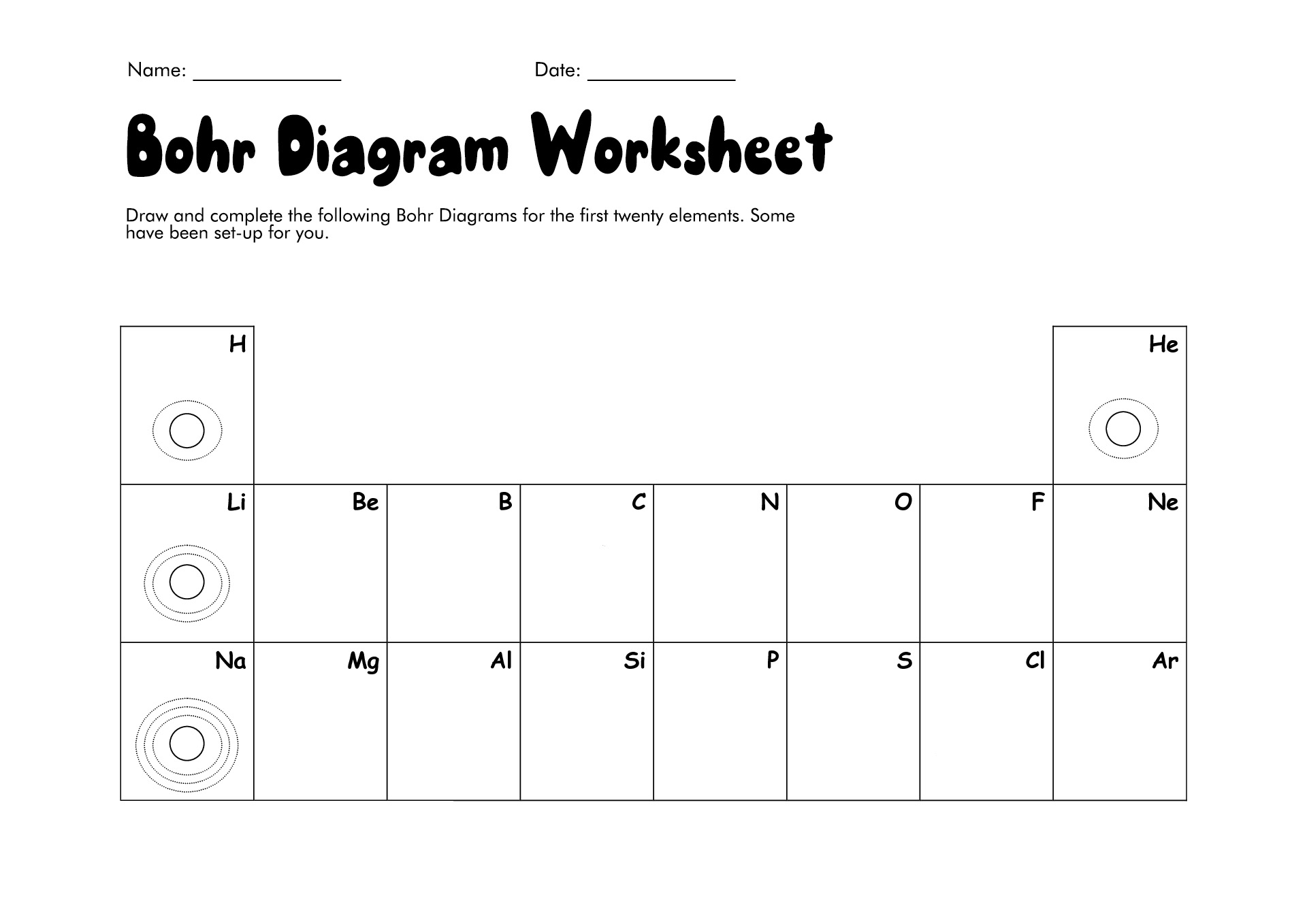
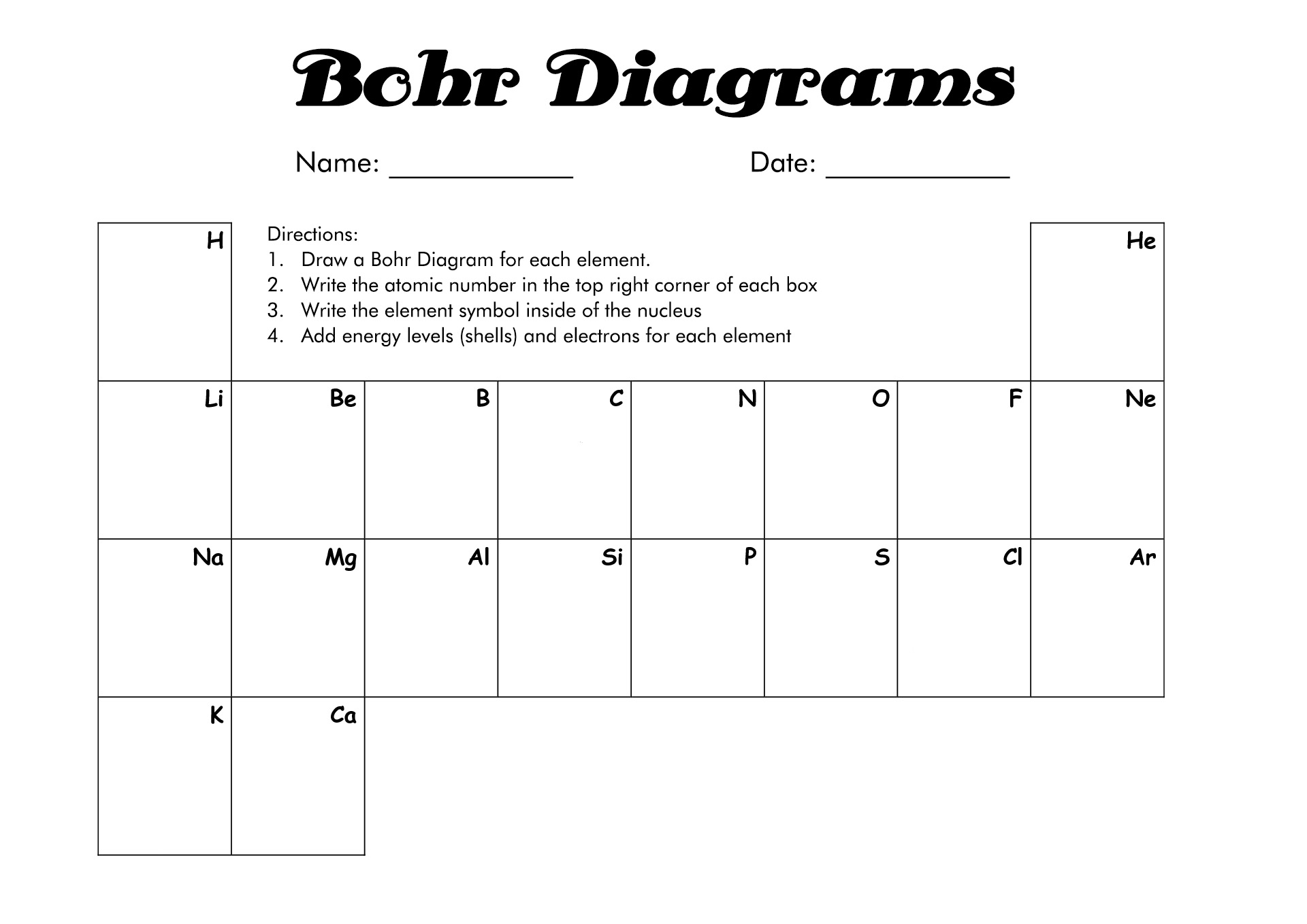
How to Draw the Bohr Diagram?
A Bohr diagram or Bohr-Rutherford diagram is a visual representation of electrons orbiting an atomic nucleus. The diagram uses various types of shells, such as K, L, M, N, and more. These shells hold a certain number of electrons, with the electron shells closest to the nucleus having lower energy and the electron shells furthest from the center having higher power.
To learn how to make the diagram, use our Bohr Diagram Worksheets. Below are the steps to draw the Bohr Model:
- Start by making the center.
- Put the number of neutrons and protons in the center.
- Make the initial power level.
- Pair the electrons and put them in the power level.
- Upkeep on the number of electrons in each position.
What are the Assumptions in the Bohr Model?
The importance of the Bohr model is to predict the allowed energy levels of the hydrogen atom. But that contradicts the fact that orbiting electrons do not radiate power. Learn more about this diagram through our Bohr Diagram Worksheets. Below are the assumptions of the Bohr diagram:
- Electrons in atoms rotate around the nucleus in circular orbits.
- Electrons in calm orbits do not let any power.
- When an electron drops to the lower point, the proton of the energy is similar to the power differences.
How to Use the Bohr Diagram Worksheet?
Understand the basic idea that electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels, with each level representing the maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated. Use the periodic table as a reference, keeping in mind that an energy level is represented by each row.
Learn the common element Bohr diagrams by heart because they are the basis for understanding other diagrams. To improve visualization, practice drawing the diagrams and group elements together because they frequently have similar electron configurations.
Use mnemonic devices to help you recall the orbital filling order; for a more practical approach, think about using interactive learning resources or simulations. Enjoy the process of solving the complex chemistry puzzle as you go step by step, paying attention to one element at a time.
The Bohr diagram, created in 1913 by the Danish scientist Niels Bohr, shows electrons in circular orbits around a central nucleus that contains protons and neutrons. It helps to explain bonding, ionization, and chemical reactions. It also helps to clarify the energy levels of hydrogen atoms. Therefore, these Bohr Diagram Worksheets can be applied by science teachers or tutors for their science enthusiast student to sharpen their physics knowledge.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments