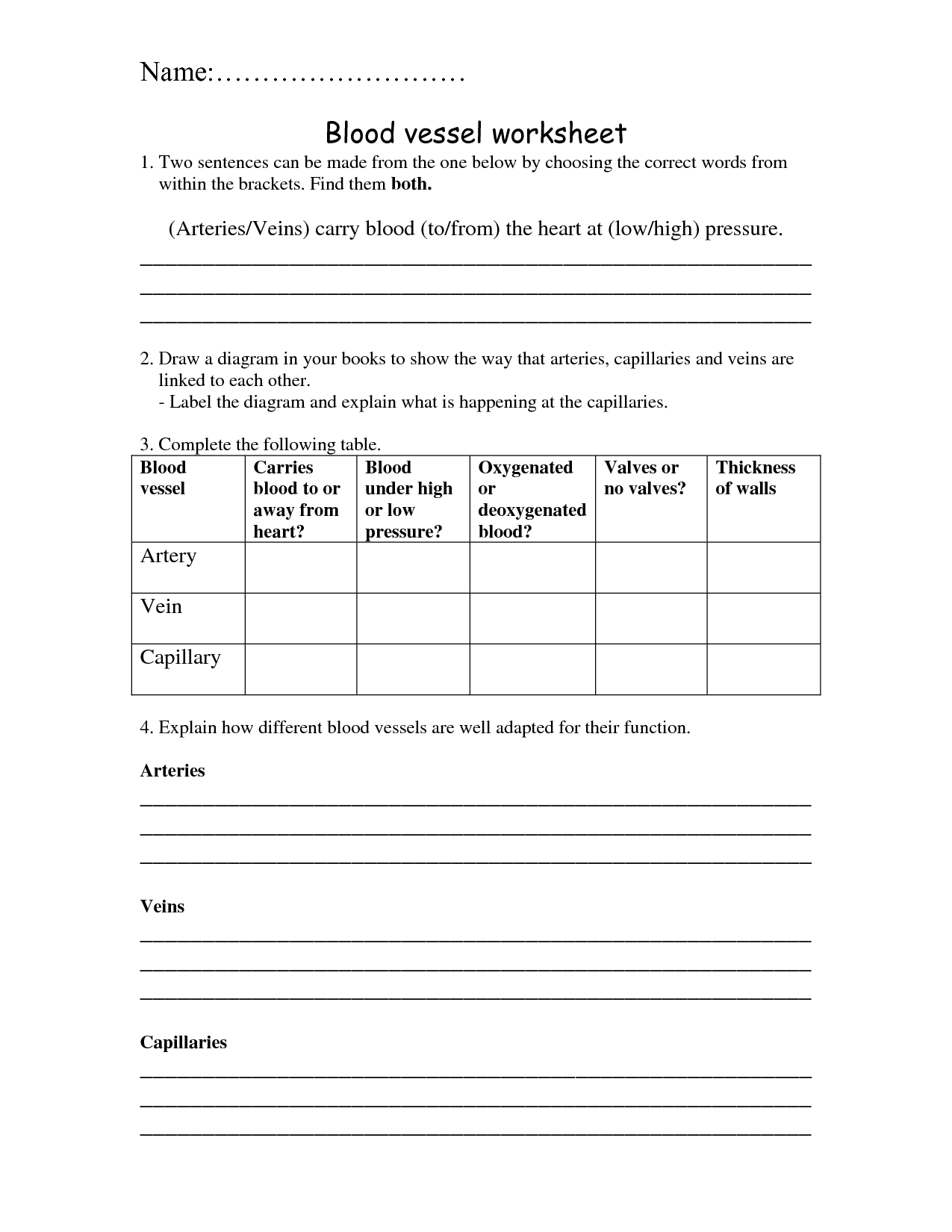
Blood Vessels Worksheet
Blood vessels are an essential component of our circulatory system, responsible for transporting blood throughout our bodies. If you're a student or educator looking for a reliable resource to reinforce your understanding of this complex topic, you've come to the right place. In this blog post, we will explore the benefits of utilizing worksheets to enhance your knowledge of blood vessels and the vital information they hold.
Table of Images 👆
- Blood Pressure Worksheet
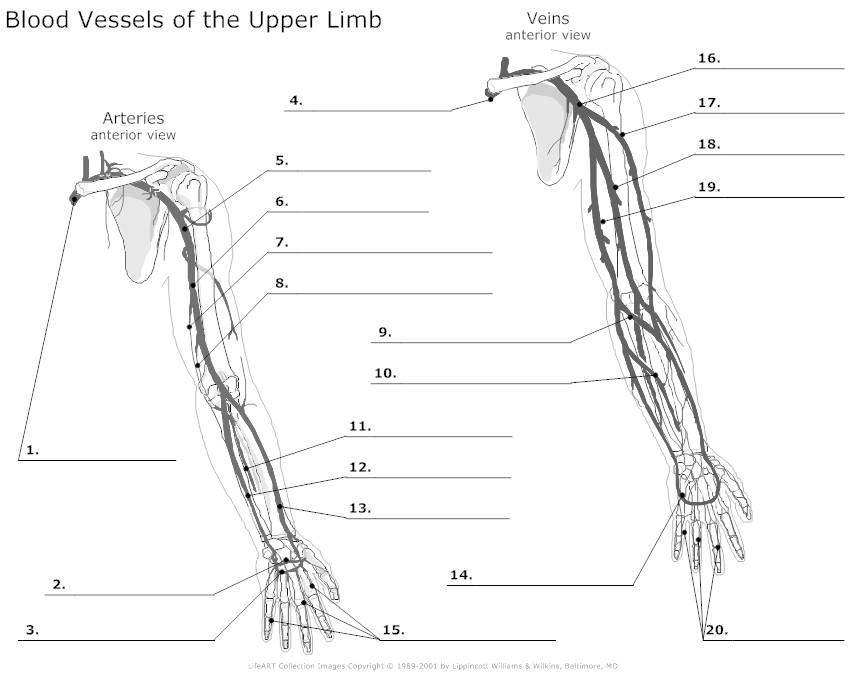
- Blood Vessel Anatomy Upper Extremity
- Major Arteries and Veins Worksheet
- Heart and Blood Vessels Worksheet
- Lower Extremity Blank Labeling Worksheet
- Blood Vessels Diagram Unlabeled
- Blood Types Worksheet Answers
- Circulatory System Coloring Worksheet
- All About My Mom Printable Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What are blood vessels?
Blood vessels are a part of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the body. They include the arteries, veins, and capillaries, which are responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells, removing waste products, and regulating body temperature. Blood vessels play a crucial role in maintaining proper circulation and overall health.
What are the three main types of blood vessels?
The three main types of blood vessels are arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the rest of the body, veins return oxygen-depleted blood back to the heart, and capillaries are tiny vessels that connect arteries and veins, allowing for the exchange of nutrients, gases, and waste products between the blood and tissues.
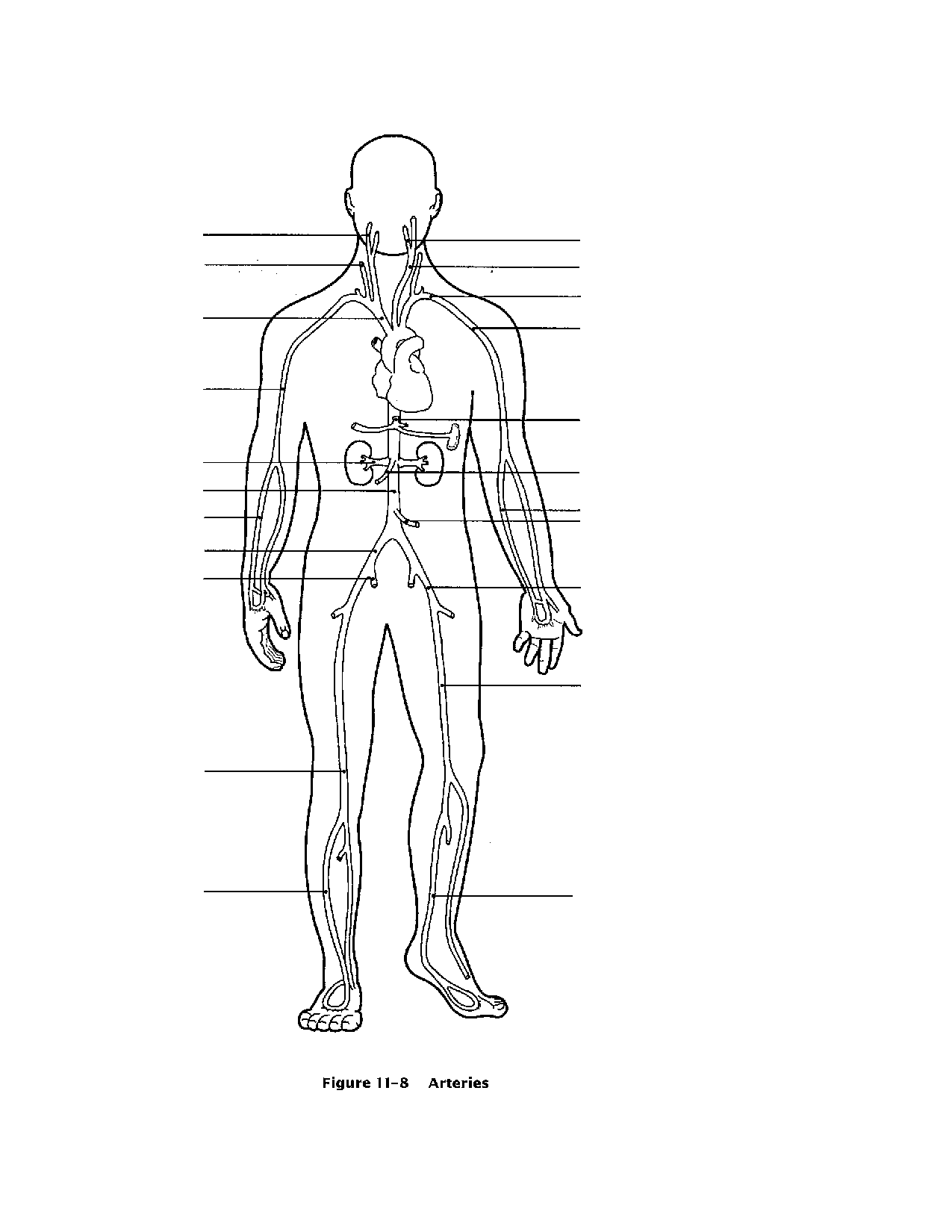
What is the function of arteries?
Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to various parts of the body, delivering nutrients and oxygen to cells, tissues, and organs. They play a vital role in the circulatory system by helping to maintain proper blood pressure and ensuring a steady flow of oxygen-rich blood throughout the body.
What is the function of veins?
Veins are blood vessels responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood from the body's tissues back to the heart. They have valves that help prevent backflow of blood and assist in returning blood to the heart against gravity. Veins also regulate blood flow and help maintain blood pressure throughout the body.
What is the function of capillaries?
Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that play a crucial role in the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between the blood and tissues. They are responsible for delivering nutrients and oxygen to cells while removing waste products like carbon dioxide. Capillaries also help regulate blood flow and blood pressure within the body.
How are arteries different from veins?
Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body, typically with thicker walls and a more elastic structure to withstand high pressure. In contrast, veins transport deoxygenated blood back to the heart, often having thinner walls and containing valves to prevent backflow. Additionally, arteries are deep within the body, closer to the center, while veins are closer to the body's surface.
How are capillaries different from arteries and veins?
Capillaries differ from arteries and veins in terms of their structure and function. Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels that connect arteries and veins, allowing for the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between the blood and surrounding tissues. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart, while veins return oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. Unlike arteries and veins, capillaries have thin walls that permit the exchange of substances with tissues and are crucial for maintaining proper blood circulation and tissue function in the body.
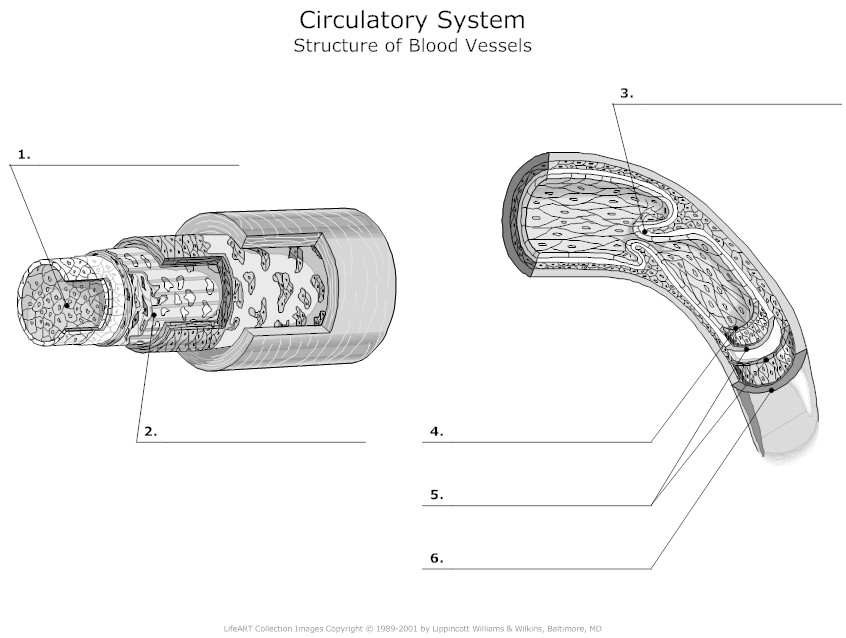
What is the structure of blood vessels?
Blood vessels are tubular structures that form a network throughout the body to transport blood. They consist of three main layers: the tunica intima (inner layer made of endothelial cells), tunica media (middle layer made of smooth muscle cells and elastic fibers), and tunica adventitia (outer layer made of connective tissue). Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Capillaries, the smallest blood vessels, allow for the exchange of nutrients and waste products between the blood and tissues.
What is the role of smooth muscle in blood vessels?
Smooth muscle in blood vessels helps regulate blood flow and blood pressure by contracting and relaxing. When smooth muscle contracts, it narrows the blood vessel, which increases blood pressure. Conversely, when smooth muscle relaxes, the blood vessel dilates, allowing more blood to flow through and decreasing blood pressure. This dynamic regulation is essential for maintaining proper blood flow to different tissues and organs in the body.
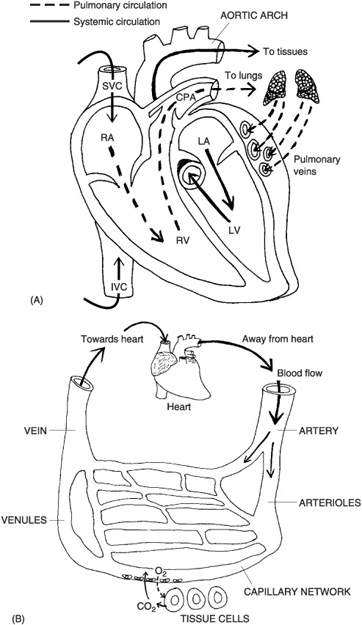
How do blood vessels contribute to blood circulation in the body?
Blood vessels play a crucial role in blood circulation by acting as a network of tubes that transport blood throughout the body. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the tissues, while veins return deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Capillaries, the smallest blood vessels, facilitate the exchange of nutrients and waste products between the blood and the surrounding tissues. The contraction and relaxation of smooth muscles in the walls of blood vessels, known as vasoconstriction and vasodilation, regulate blood flow and pressure in different parts of the body. Overall, blood vessels ensure the continuous circulation of blood, delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells and removing waste products to maintain the body's overall function.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments