Biomes and Ecosystems Worksheets
Biomes and ecosystems are fascinating subjects that help us understand the diversity and interconnectedness of the natural world. Whether you are a science teacher looking for engaging materials to supplement your lessons or a student eager to deepen your understanding, our collection of worksheets on biomes and ecosystems is here to provide you with valuable resources.
Table of Images 👆
- Printable Biome Worksheets
- Transferable Skills Worksheet
- Biome Worksheets High School
- Ecosystem Interactions Worksheet
- Printable Biome Worksheets
- Ecosystems and Biomes Worksheets
- Biomes Worksheets
- Printable Ecosystem Worksheets
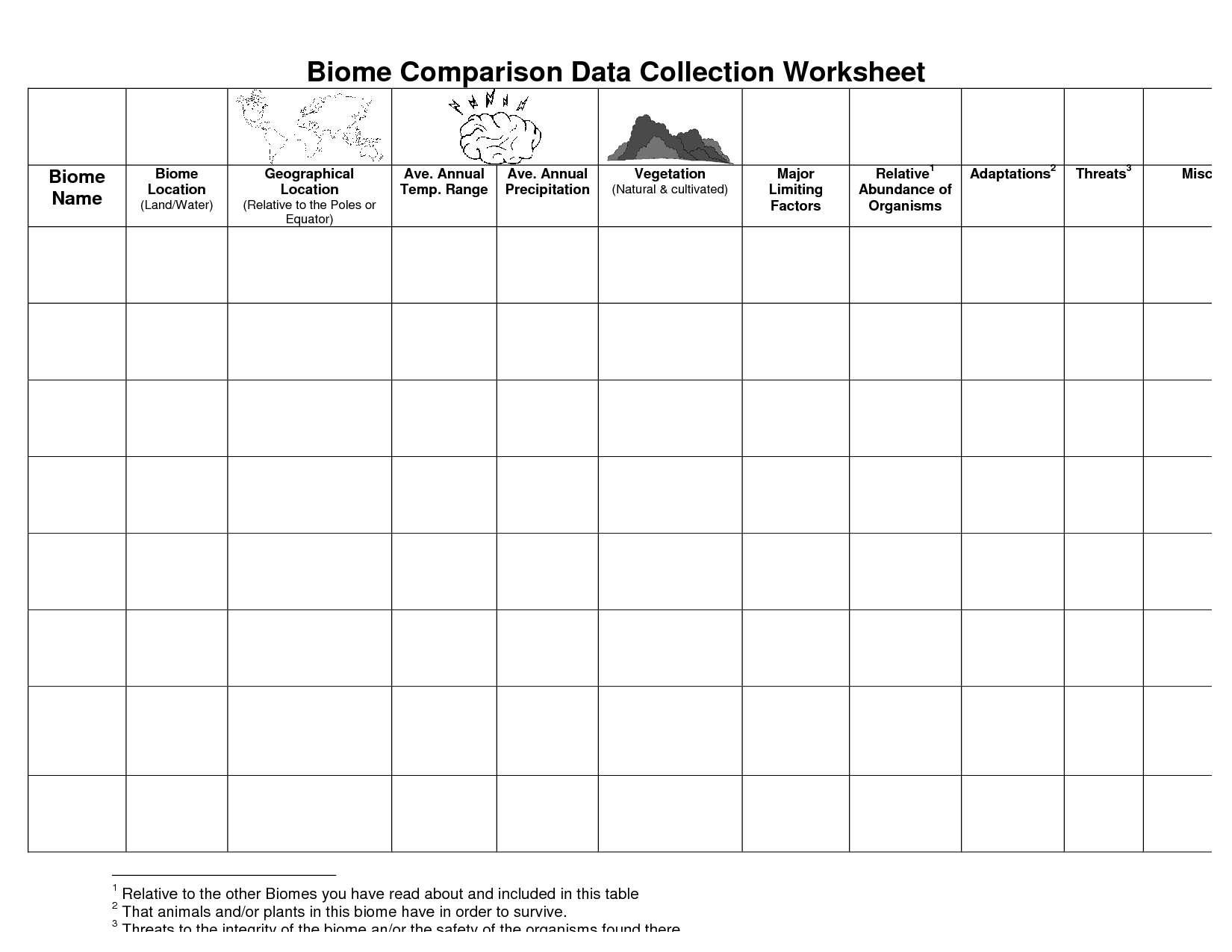
- Biome Chart Worksheet
- Printable Ecosystem Worksheets
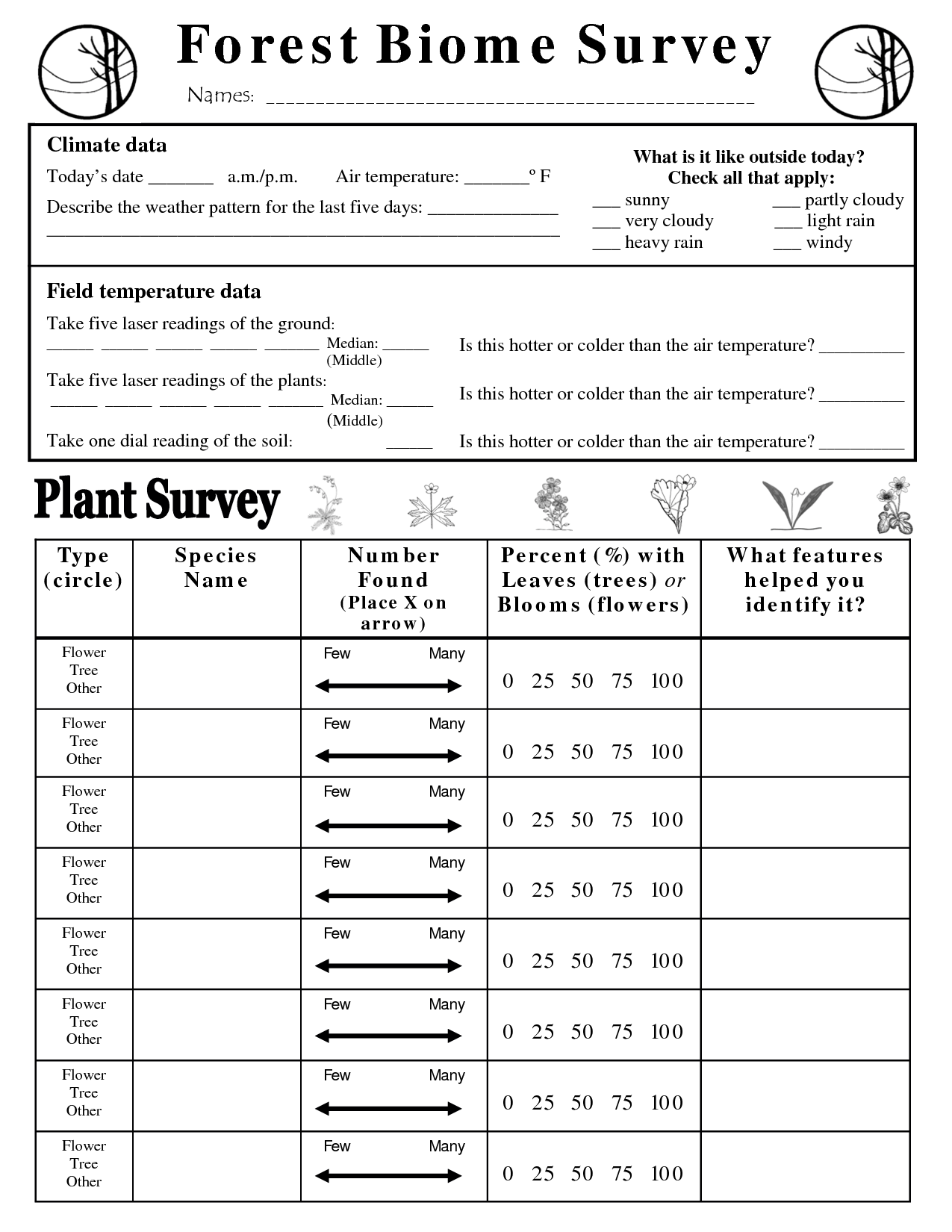
- Forest Biome Worksheets
- Population Community Ecosystem Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is a biome?
A biome is a large, naturally occurring community of plants and animals that occupy a particular habitat or environment, characterized by its distinctive climate, vegetation, and animal life. Biomes are often classified based on factors such as temperature, precipitation, and vegetation, and can include ecosystems like deserts, forests, grasslands, and tundras.
What are the major terrestrial biomes?
The major terrestrial biomes include tropical rainforest, temperate deciduous forest, coniferous forest (taiga), grassland (prairie), savanna, desert, and tundra. Each biome is characterized by unique climate, vegetation, and animal species adapted to the specific conditions found within that biome.
What factors determine the type of biome in a particular area?
The type of biome in a particular area is determined by factors such as climate (temperature and precipitation), soil type, topography, and altitude. These factors influence the dominant vegetation, which in turn shapes the characteristics and biodiversity of the biome. Temperature and precipitation play a crucial role in determining the type of biome, such as tropical rainforests in areas with high temperatures and humidity, or deserts in arid regions with low rainfall. Soil type affects water retention and nutrient availability, influencing the types of plants that can grow in an area. Topography and altitude can also impact the distribution of biomes, with mountainous regions often hosting different biomes at varying elevations.
What is an ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms interacting with each other and their physical environment. It consists of plants, animals, and microorganisms that are interconnected by food webs and nutrient cycles, sustaining a delicate balance of energy flow and matter cycling. Ecosystems can be as small as a puddle or as large as a forest, and they provide essential services such as oxygen production, waste decomposition, and water purification.
How do biomes and ecosystems differ?
Biomes refer to large geographic regions with similar climates, animals, and plants, such as deserts, grasslands, or forests. Ecosystems, on the other hand, are smaller-scale communities of living organisms interacting with each other and their physical environment within a specific biome, showcasing the intricate web of relationships among different species and their surroundings. In essence, biomes encompass broader classifications of habitats, while ecosystems focus on the specific interactions and dynamics within those habitats.
What are the main components of an ecosystem?
The main components of an ecosystem include biotic factors such as plants, animals, and microorganisms, as well as abiotic factors like soil, water, air, sunlight, and climate. These components interact and depend on each other to maintain a balanced ecosystem and support the flow of energy and nutrient cycling within it.
How do organisms interact within an ecosystem?
Organisms interact within an ecosystem in various ways, including competition for resources such as food, water, and shelter, predation where one organism hunts and consumes another, symbiosis where two or more species live closely together and either benefit or harm each other, and mutualism where both species benefit from the interaction. These interactions are essential for maintaining a balance in the ecosystem and promoting biodiversity, as they can influence population dynamics, energy flow, and nutrient cycling.
What are the primary producers in an ecosystem?
Primary producers in an ecosystem are organisms such as plants, algae, and certain types of bacteria that convert sunlight and nutrients into energy through the process of photosynthesis. They form the base of the food chain by providing energy for other organisms, making them crucial for sustaining life in the ecosystem.
How do energy and nutrients flow through an ecosystem?
Energy flows through an ecosystem in a unidirectional manner, starting with the sun as the primary source. Plants capture sunlight through photosynthesis and convert it into chemical energy, which is then consumed by herbivores and transferred through the food chain to carnivores. Nutrients, on the other hand, cycle within the ecosystem as they are absorbed by organisms, recycled through decomposition, and released back into the environment for reuse. Both energy and nutrients play crucial roles in sustaining life within an ecosystem by supporting the growth, reproduction, and overall health of organisms.
What are some examples of human impacts on biomes and ecosystems?
Examples of human impacts on biomes and ecosystems include deforestation, pollution from industrial activities and urban development, overfishing and hunting leading to loss of biodiversity, introduction of invasive species disrupting native ecosystems, and climate change causing alterations in temperature, precipitation patterns, and sea levels. These activities can lead to habitat destruction, loss of species, disruption of food chains, and overall degradation of ecosystems, ultimately threatening the balance and health of these natural environments.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments