Biology Macromolecules Worksheets
Biology macromolecules worksheets provide a comprehensive and interactive way for students to explore and understand the diverse world of macromolecules. Designed for high school and college-level biology classes, these worksheets focus on key topics such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. With clear instructions and thought-provoking questions, students can delve into the fascinating world of macromolecules and deepen their understanding of this essential subject matter.
Table of Images 👆
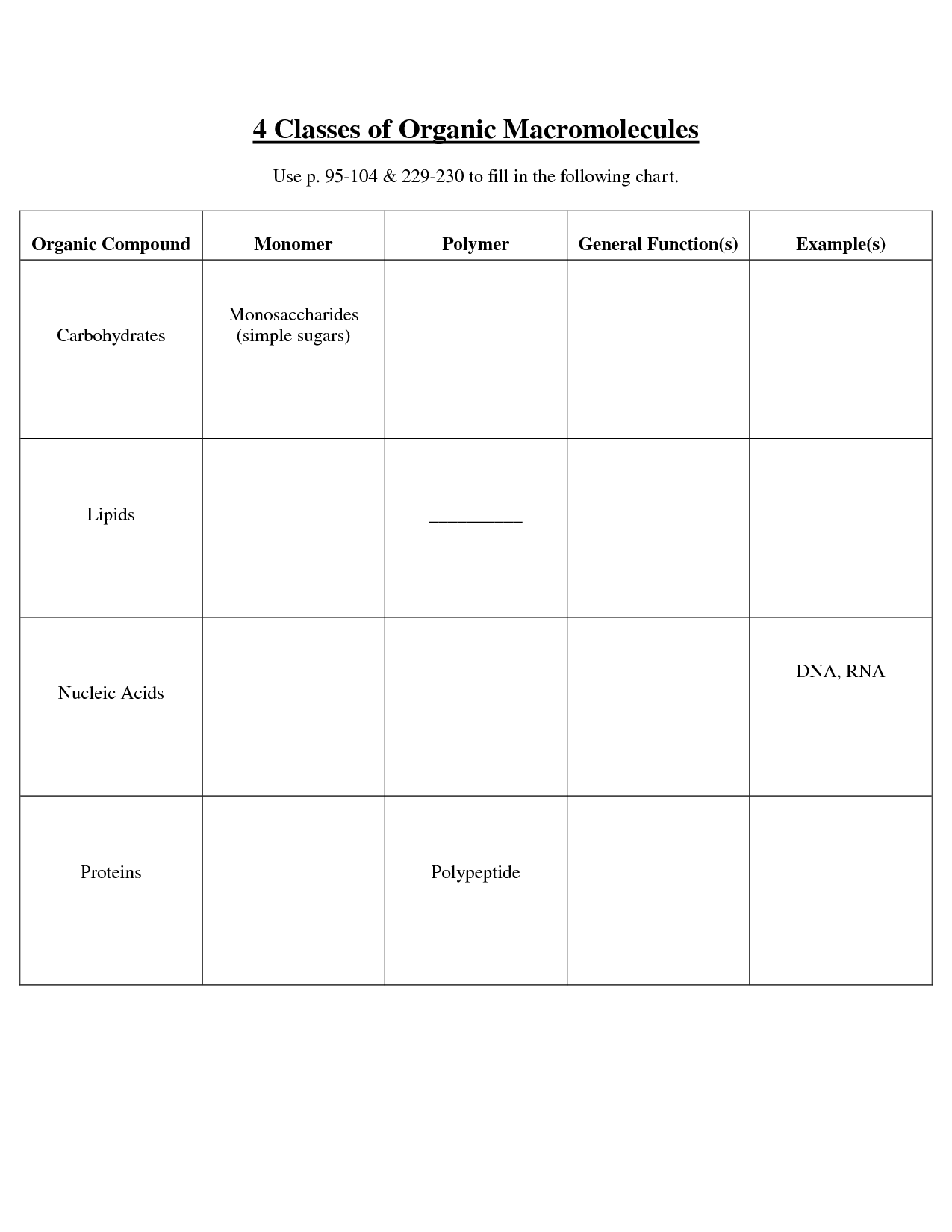
- Macromolecules Chart Worksheet
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- Macromolecules Chart Worksheet
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
- Carbohydrates Worksheet Answers
- Organic Compound Worksheet Answers Biology
- 4 Macromolecules and Their Functions
- Biology Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
- Macromolecules Chart Answers
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet
- Label and Nutrition Worksheet Macromolecules
More Biology Worksheets
Free Printable Biology WorksheetsCollege Biology Worksheets
7th Grade Biology Worksheets
Biology Macromolecules Worksheets and Answers
Karyotype Worksheet Answers Biology
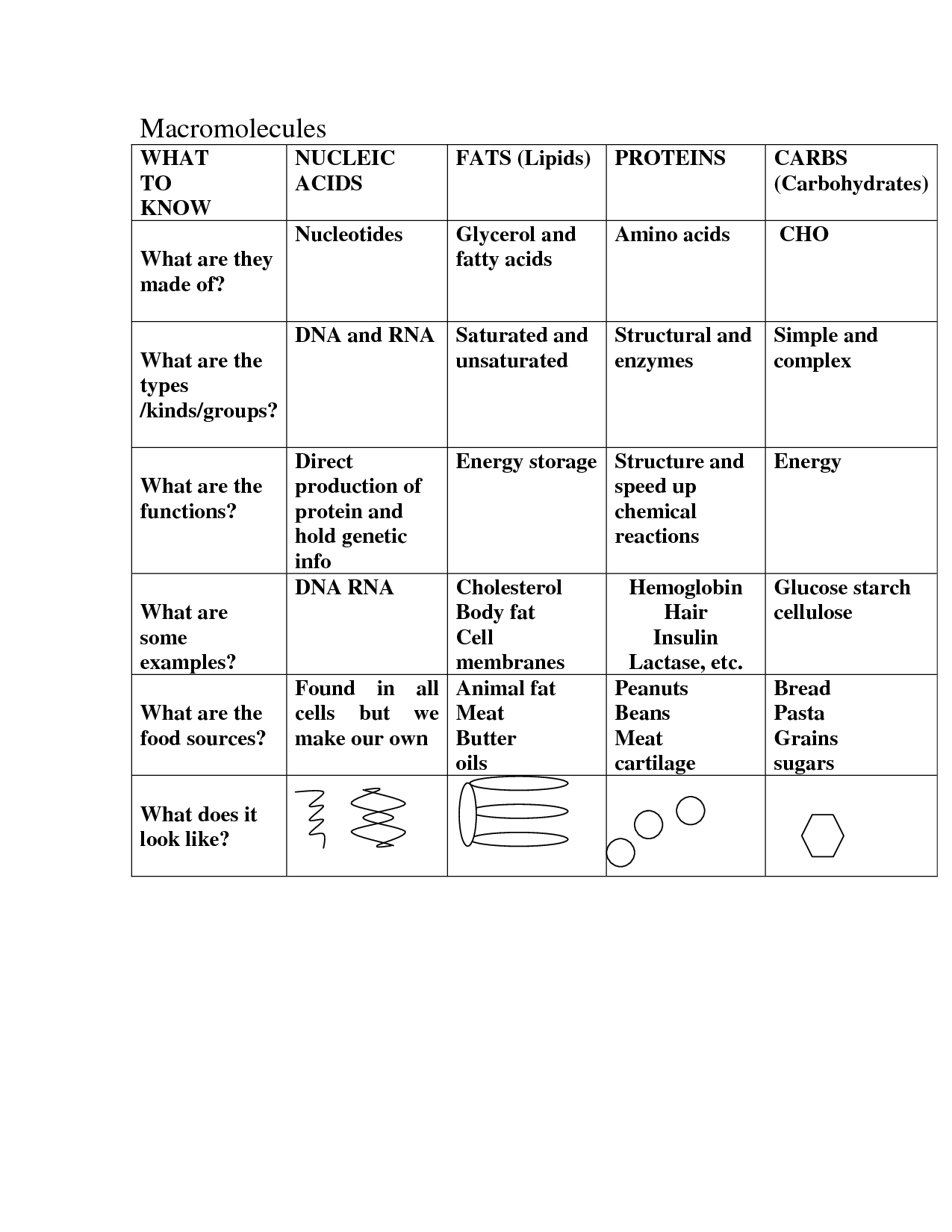
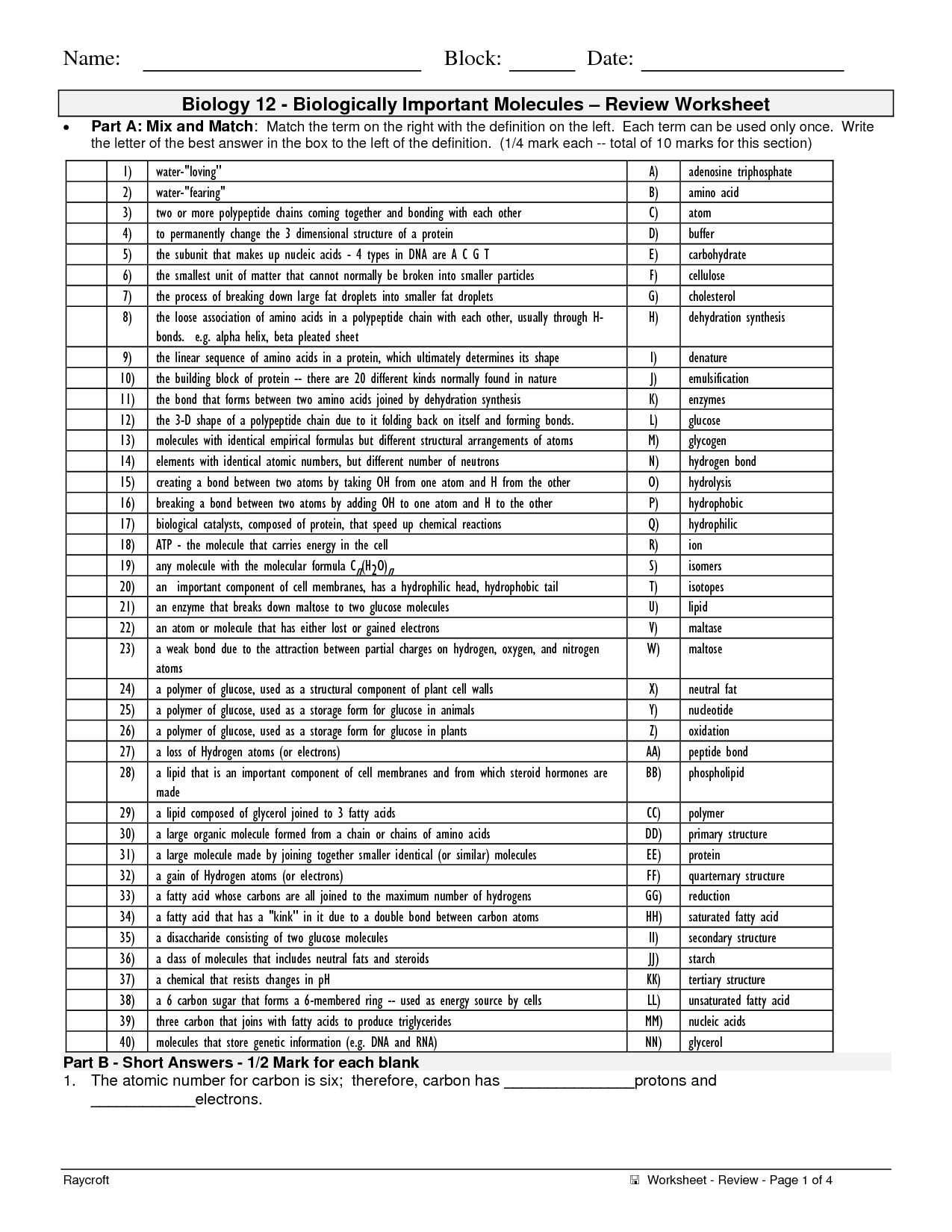
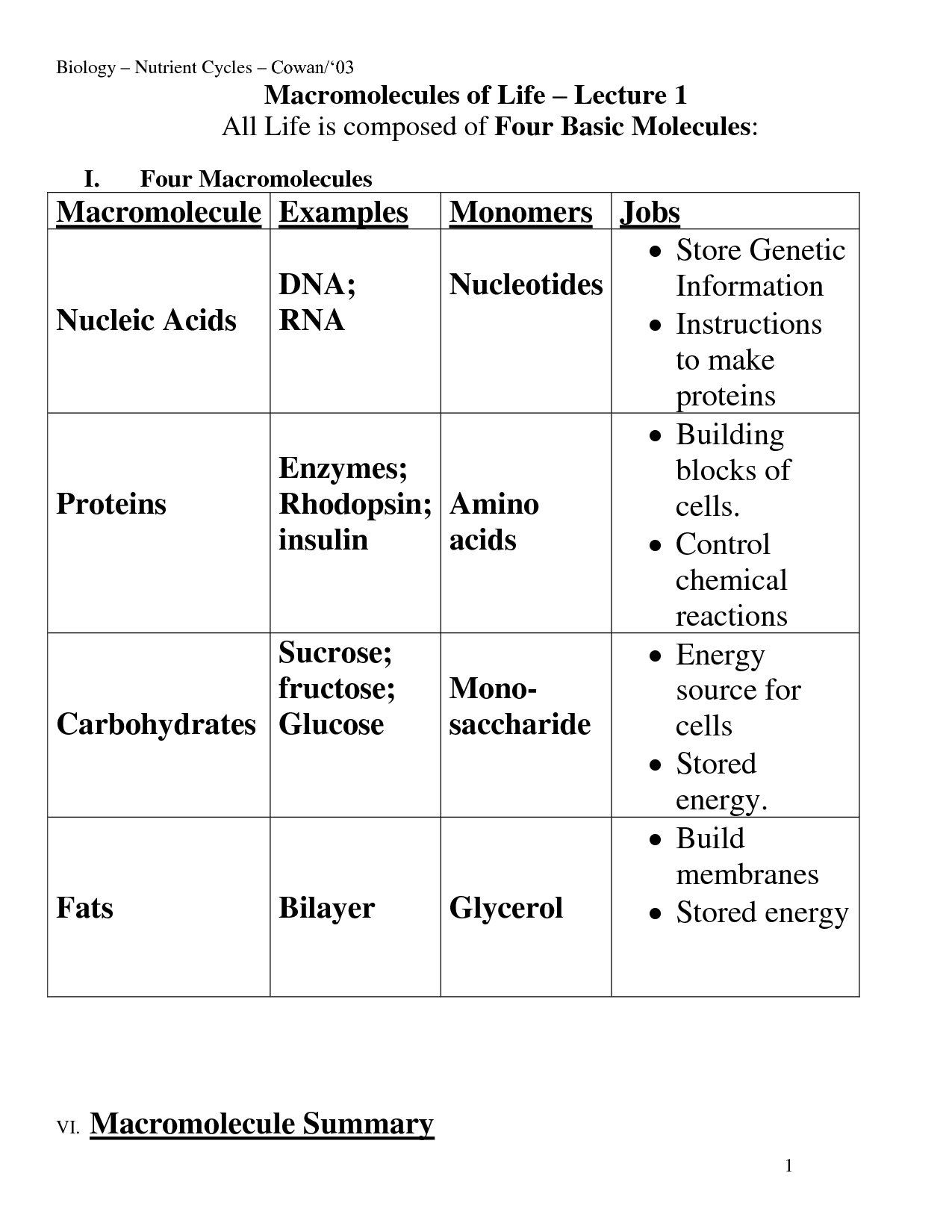
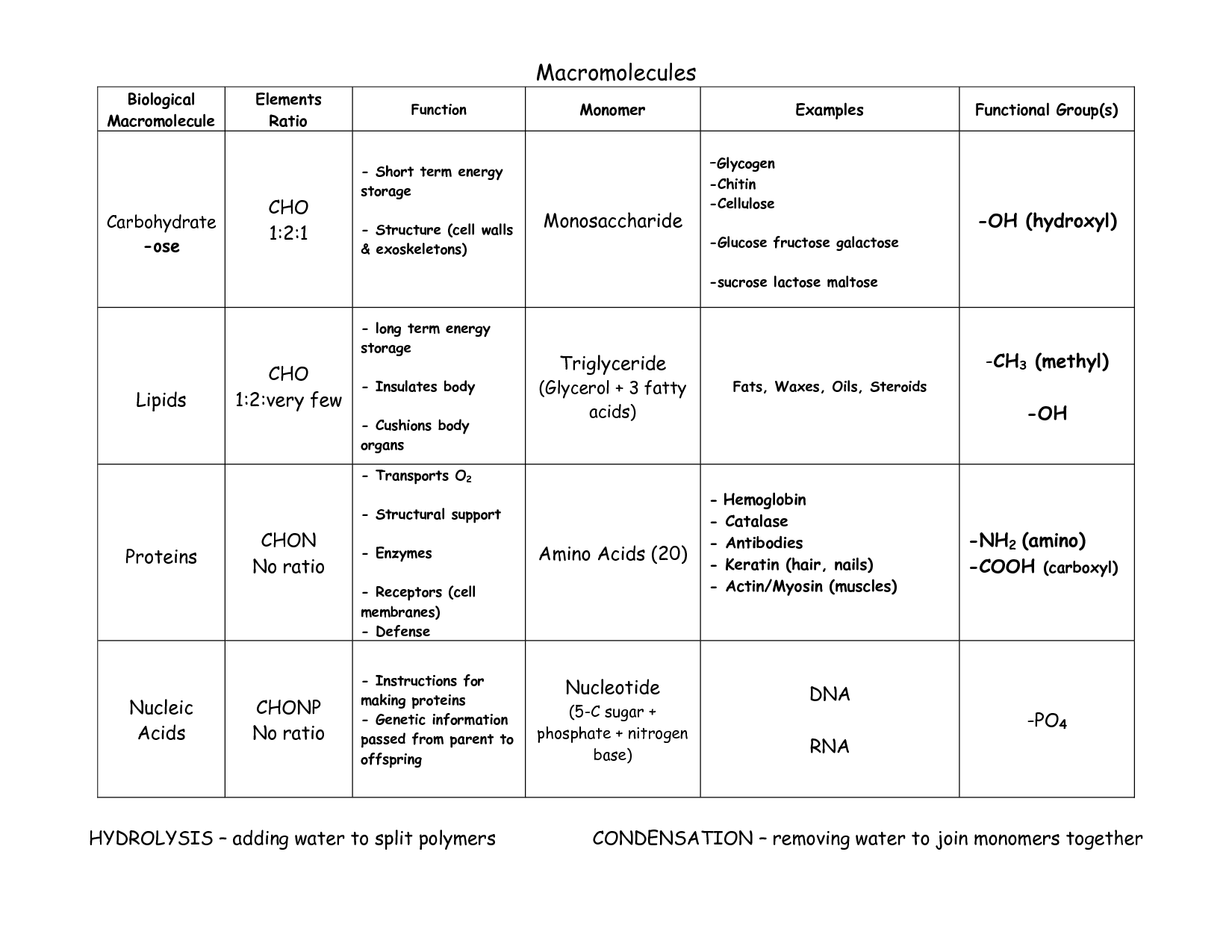
What are macromolecules?
Macromolecules are large molecules made up of smaller subunits known as monomers. These include proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids, which are essential for various biological functions in living organisms. Macromolecules play a crucial role in cell structure, energy storage, and genetic information transfer.
Name three main types of macromolecules.
The three main types of macromolecules are proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates. Proteins are composed of amino acids and play crucial roles in various biological processes. Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, store and transmit genetic information. Carbohydrates, including sugars and starches, serve as a source of energy and structural components in cells.
What is the primary function of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates serve as the body's main source of energy, providing fuel for the brain, tissues, and muscles to perform vital functions.
Give an example of a monosaccharide.
Glucose is an example of a monosaccharide.
What is the primary function of lipids?
The primary function of lipids is to store energy, provide insulation, and act as a structural component of cell membranes. Additionally, lipids play a crucial role in signaling pathways, hormone production, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins in the body.
Give an example of a saturated fat.
Butter is an example of a saturated fat.
What are proteins made up of?
Proteins are macromolecules composed of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon atom bound to a hydrogen atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain (R group) that gives each amino acid its unique properties. The sequence of amino acids in a protein dictates its structure and function.
What is the primary function of nucleic acids?
The primary function of nucleic acids is to store and transmit genetic information within a cell and between generations, playing a crucial role in the expression of traits and regulating cellular activities.
Give an example of a nucleotide.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an example of a nucleotide.
How do enzymes facilitate chemical reactions in the body?
Enzymes facilitate chemical reactions in the body by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, thus speeding up the rate of the reaction. They achieve this by binding to specific substrates, forming enzyme-substrate complexes that stabilize the transition state of the reaction. This process allows reactions to proceed more quickly and efficiently in biological systems, ultimately enabling essential processes such as digestion, metabolism, and cellular function to take place.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments