Biological Molecules Worksheet
A biological molecules worksheet is a valuable resource for students studying biology or chemistry. This worksheet focuses on the essential entities and subjects related to biological molecules, providing a comprehensive overview of their structures, functions, and interactions. By engaging with this worksheet, students can deepen their understanding of the molecular components that make up living organisms, such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Table of Images 👆
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
- Biology Macromolecules Worksheets
- Molecules of Life Worksheet Answers
- Organic Molecules Worksheet
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- Building Blocks of Life Worksheet Answers
- Macromolecules Chart Answers
- Biology Macromolecules Worksheets and Answers
- Identifying Macromolecules Worksheet
- 4 Macromolecules and Their Functions
- Atoms and Molecules Worksheet
- Molecules of Life Worksheet Answers Key
- DNA Structure and Replication Answer Key POGIL
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is a biological molecule?
A biological molecule is a type of molecule that is involved in the structure, function, and regulation of living organisms. These molecules include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, which play crucial roles in various processes such as energy storage, cell communication, and genetic information transmission within cells.
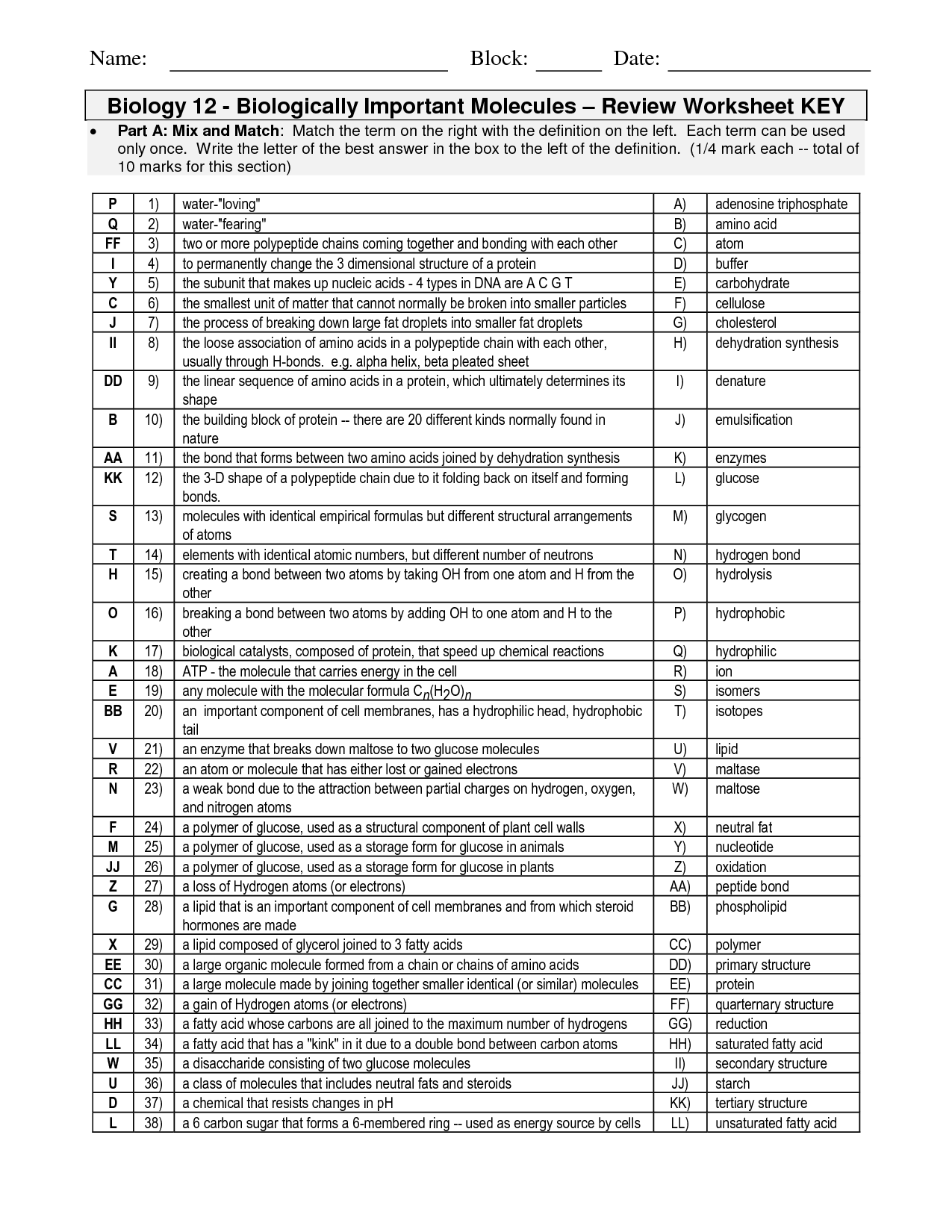
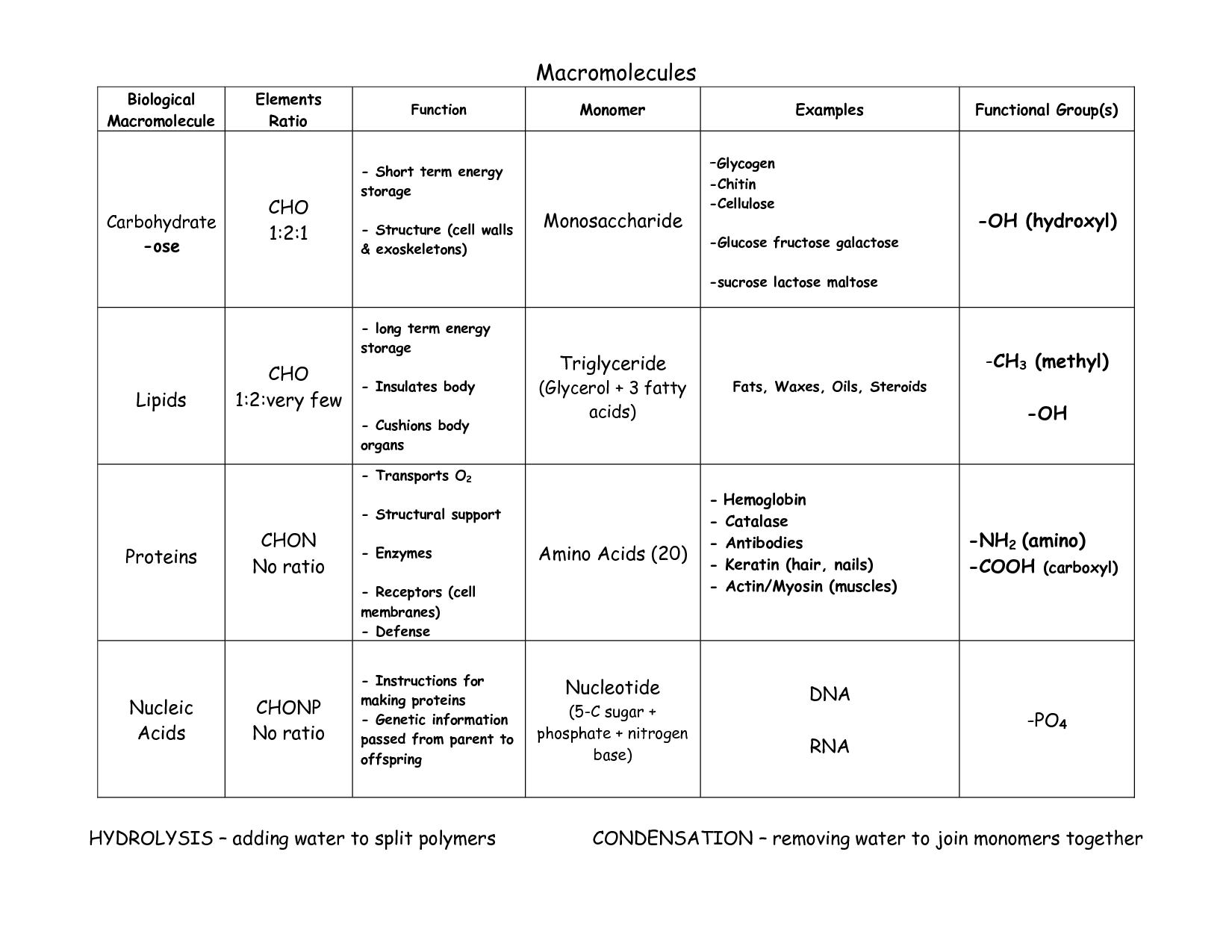
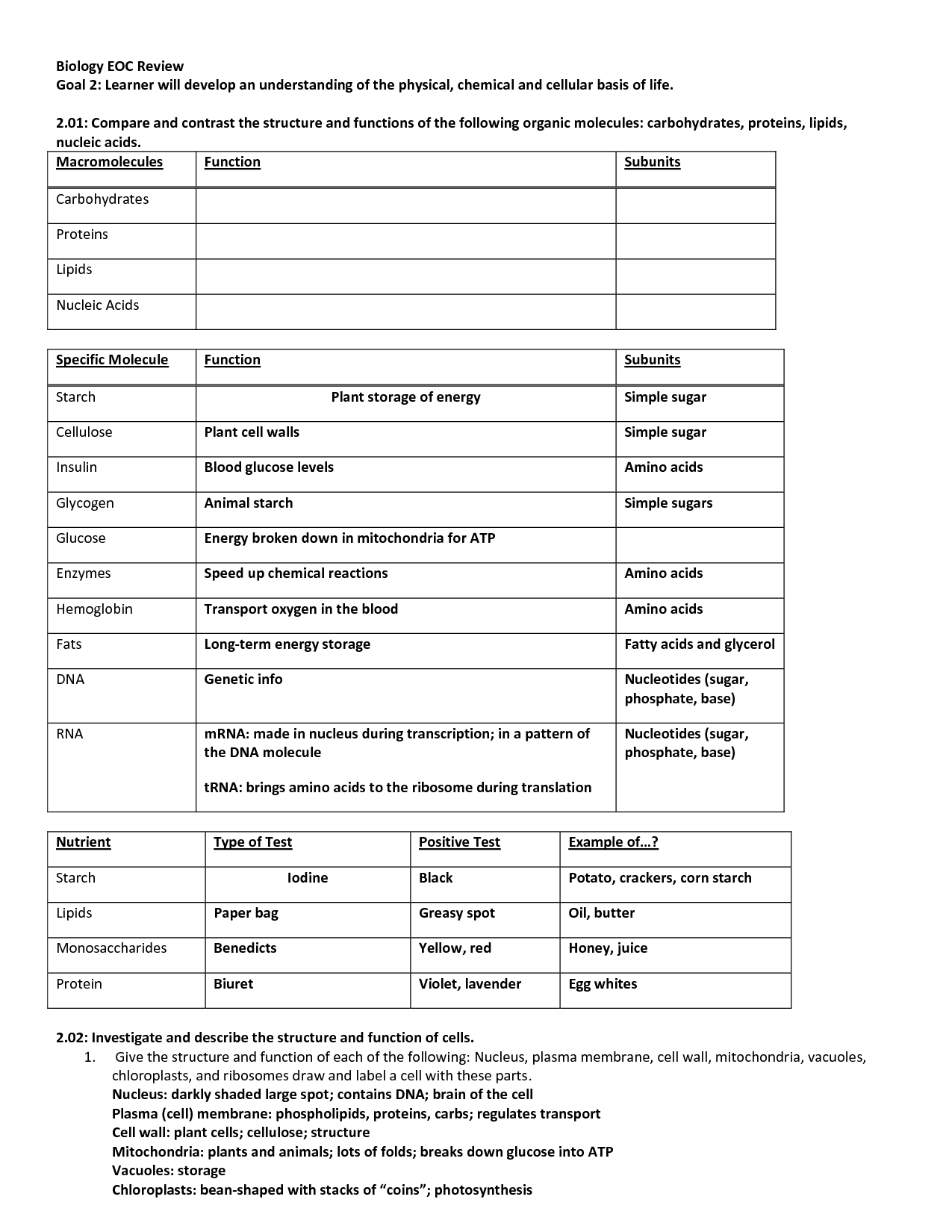
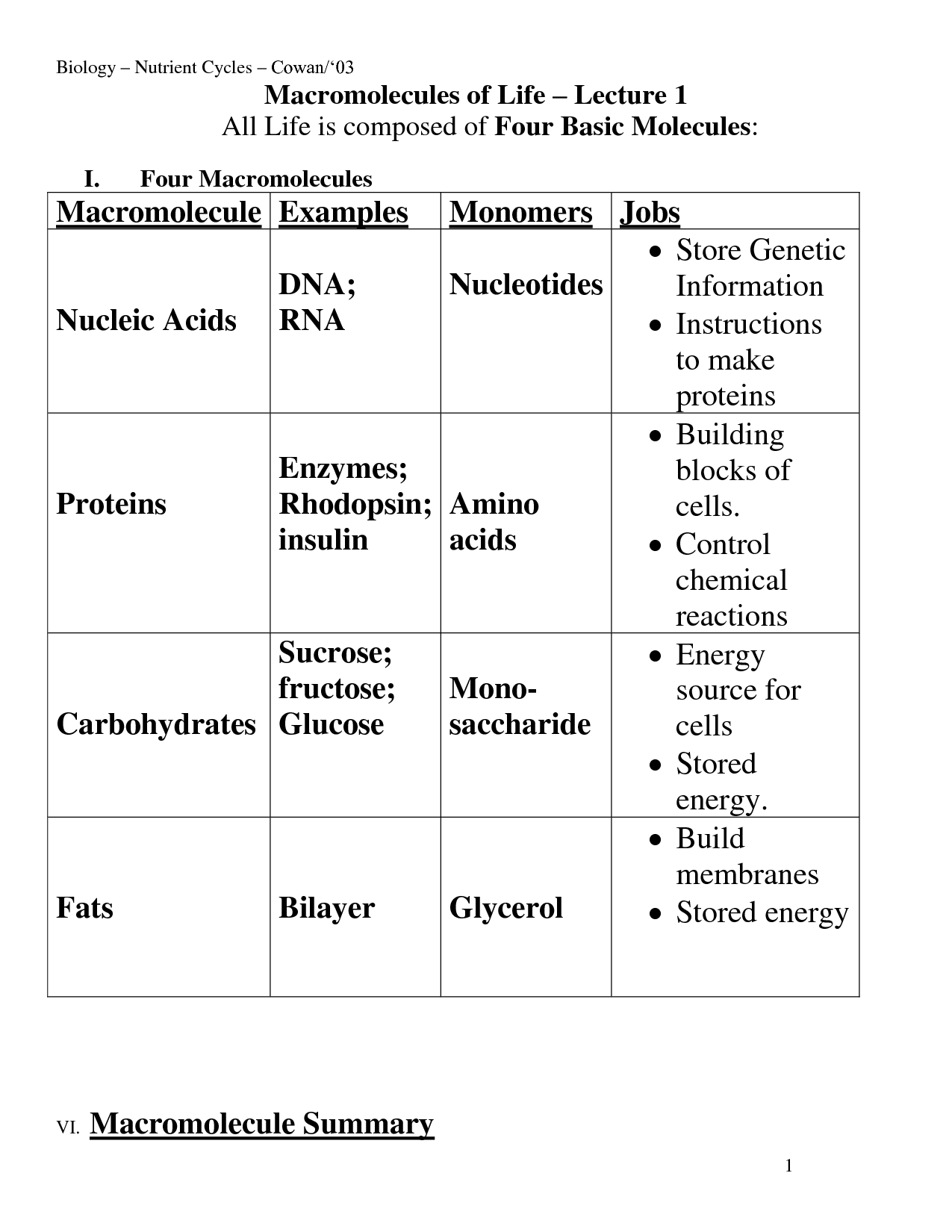
What are the four major classes of biological macromolecules?
The four major classes of biological macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates serve as a primary source of energy for cells, lipids are involved in energy storage and cell membrane structure, proteins are responsible for various functions in the body including enzyme activity and cell signaling, and nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information.
What is the primary function of carbohydrates in living organisms?
Carbohydrates primarily serve as a source of energy for living organisms. When broken down through cellular respiration, carbohydrates provide the necessary fuel for various cellular processes, including growth, repair, and maintenance of the body.
What are lipids and what are their main roles in cellular processes?
Lipids are a diverse group of molecules that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. They serve various critical functions in cellular processes, such as being the main component of cell membranes, providing energy storage, and acting as signaling molecules. Lipids also play roles in cellular communication, insulation, and protection of internal organs. Overall, lipids are essential for maintaining the structure and function of cells, tissues, and organs in living organisms.
Describe the structure and function of proteins.
Proteins are large, complex molecules made up of long chains of amino acids. The structure of a protein is crucial to its function, which can range from providing structural support to catalyzing chemical reactions in the body. Proteins have a specific three-dimensional shape that is determined by the sequence of amino acids in their chain. This shape allows proteins to interact with other molecules and perform their specific roles in the body, such as enzymes that speed up chemical reactions, antibodies that help fight infections, and hormones that regulate various processes. Overall, proteins play a vital role in almost every biological process in living organisms.
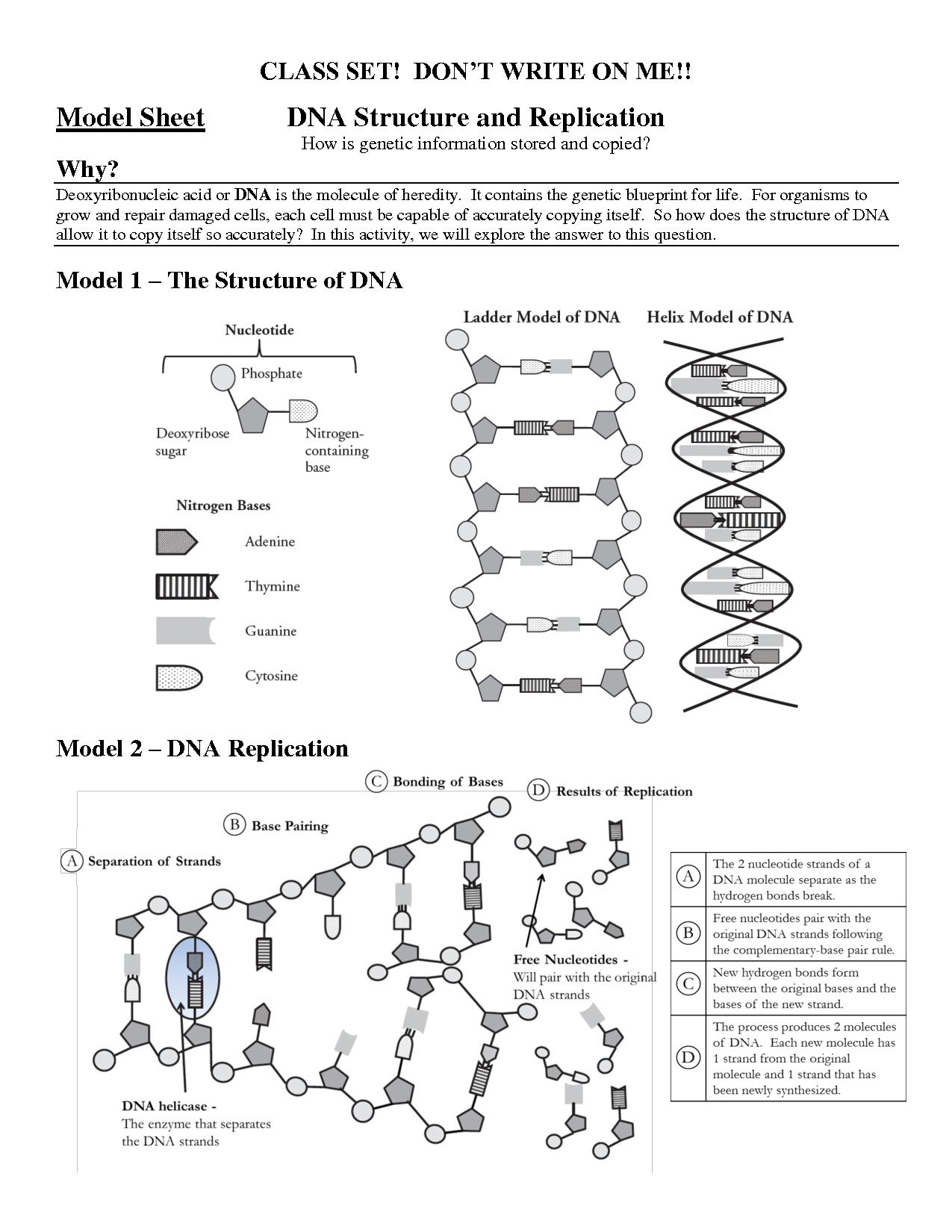
What is the importance of nucleic acids in storing and transmitting genetic information?
Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are crucial in storing and transmitting genetic information because they contain the genetic code that determines an organism's characteristics. Through the process of replication, DNA makes copies of itself to pass on genetic information to daughter cells during cell division. Additionally, RNA plays a key role in translating this genetic information into proteins through the process of transcription and translation. Overall, nucleic acids are indispensable in the inheritance and expression of genetic traits, making them essential for the survival and functioning of living organisms.
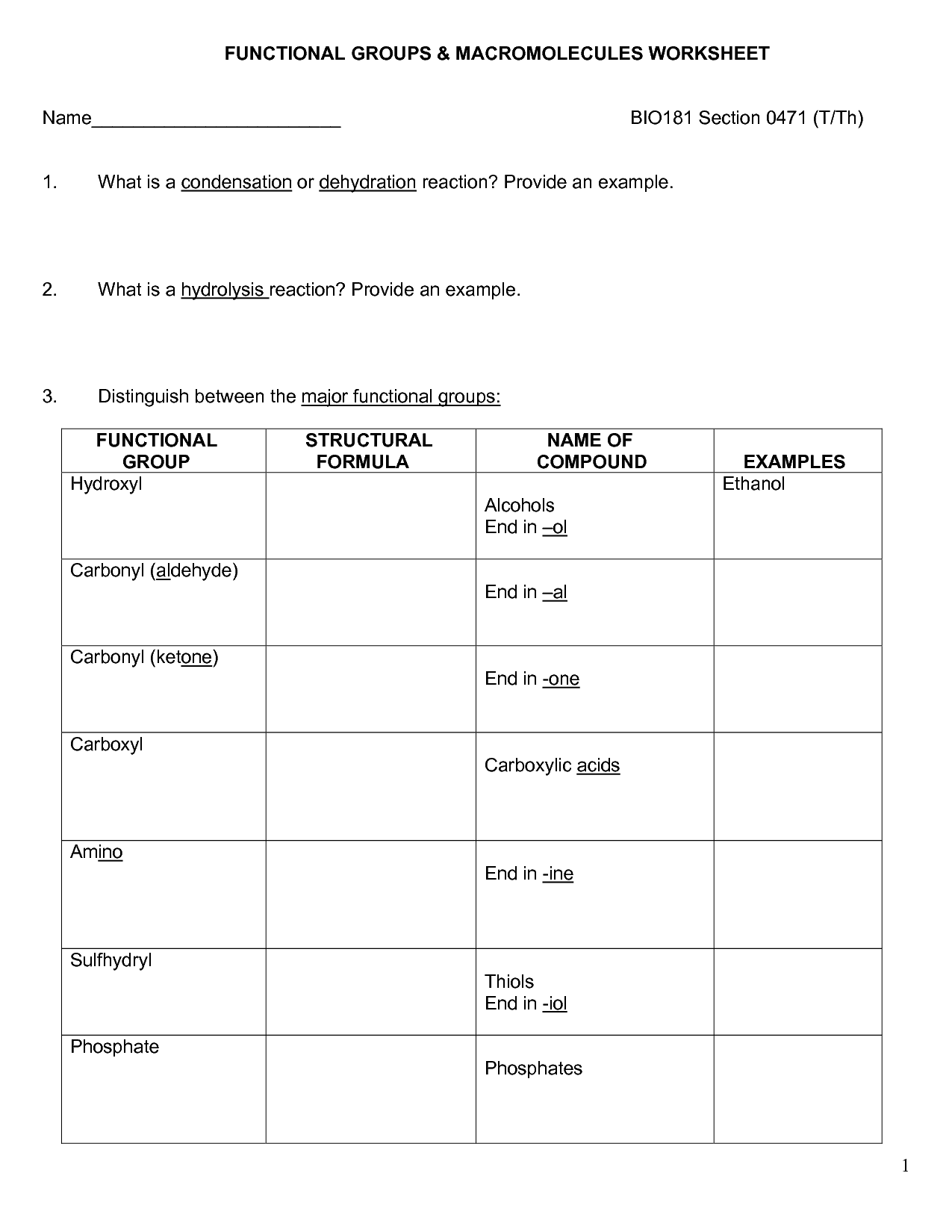
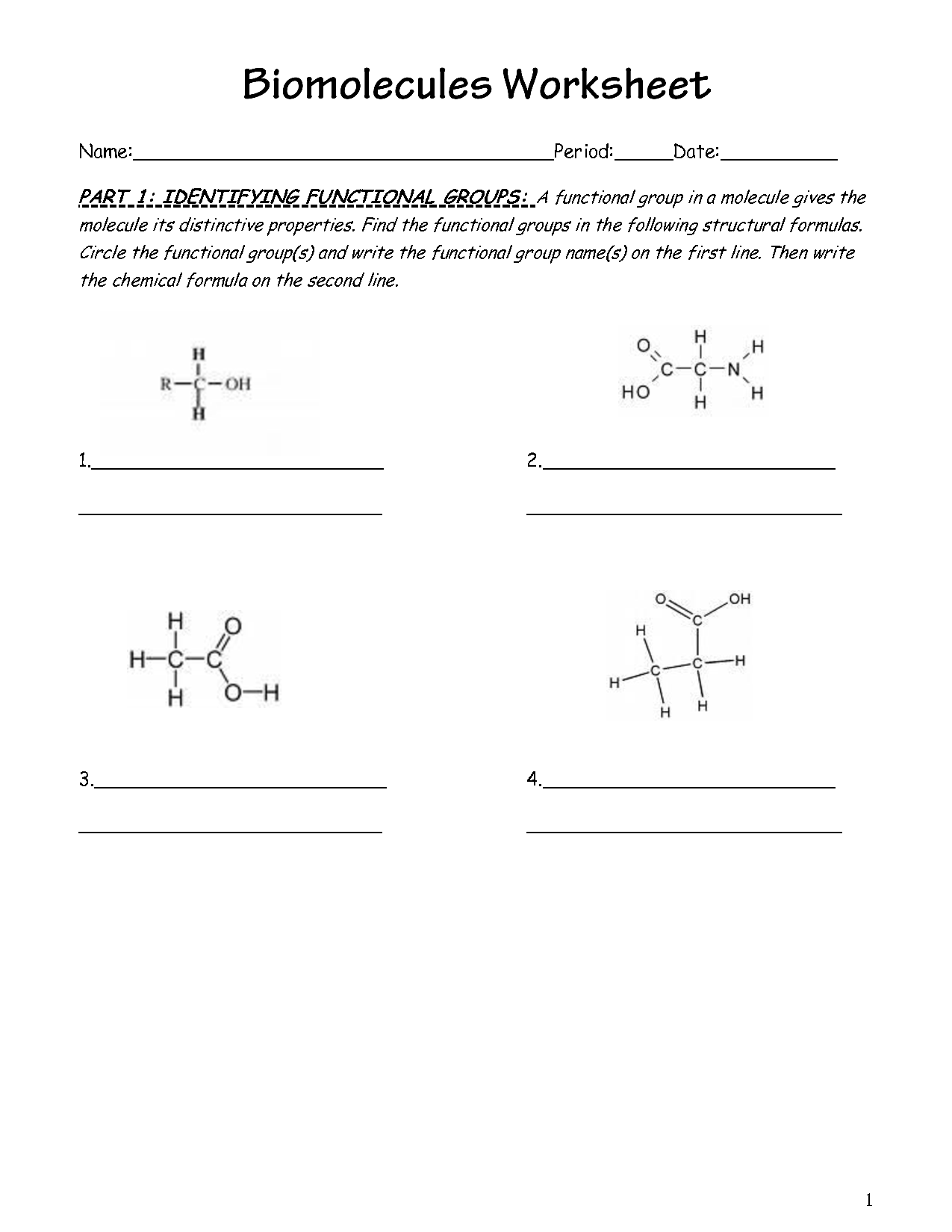
What are the building blocks of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids?
Carbohydrates are made of simple sugars such as glucose and fructose, lipids are composed of fatty acids and glycerol, proteins are made of amino acids, and nucleic acids consist of nucleotides such as adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil.
How are carbohydrates broken down and used for energy in the body?
Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose through the process of digestion. Glucose is then absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to cells where it is converted into ATP, the body's main source of energy. This energy is utilized by cells for various functions such as muscle contraction, metabolism, and overall bodily functions. Any excess glucose is stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen for later use.
Explain the process of protein synthesis in cells.
Protein synthesis in cells begins with transcription, where a segment of DNA is copied into a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). This mRNA moves from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where translation takes place. During translation, ribosomes read the mRNA sequence in groups of three nucleotides called codons, and match each codon with a specific transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule carrying the corresponding amino acid. These amino acids are then linked together in a specific sequence to form a polypeptide chain, which folds into a functional protein that can perform various roles in the cell.
How do enzymes contribute to biochemical reactions in living organisms?
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. Enzymes do this by providing an alternative pathway for the reaction to proceed, allowing it to occur more rapidly and efficiently. They accomplish this by binding to specific substrates and facilitating the formation of new chemical bonds or the breaking of existing ones. Additionally, enzymes are highly selective and can regulate specific reactions in a cell, thus playing a crucial role in maintaining the proper functioning of biochemical pathways within living organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments