Biochemistry Review Worksheet Answers
Are you a biochemistry student struggling to grasp complex concepts? Look no further! In this blog post, we will provide you with the answers to a biochemistry review worksheet, helping you gain a better understanding of the subject matter. By having access to these answers, you can check your work, identify areas that need improvement, and reinforce your understanding of core biochemistry principles. So, let's dive in and unlock the solutions to your biochemistry review worksheet!
Table of Images 👆
- Evolution Review Worksheet Answer Key
- Synthesis Reaction Worksheet
- Chemistry Unit 1 Worksheet 6 Answers
- Unit 2 Chemistry Review Sheet Answer Key
- Unit 9 Assignment 1 Social Communication Model
- Photosynthesis Diagrams Worksheet Answer Key
- Enzymes Worksheet Answer Key
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- Classification of Living Things Worksheets Answer
- Protein Synthesis Crossword Puzzle Answer Key
More Chemistry Worksheets
Chemistry Lab Equipment WorksheetChemistry Stoichiometry Worksheet Answer Key
Chemistry Conversion Factors Worksheet
Fun Chemistry Worksheets
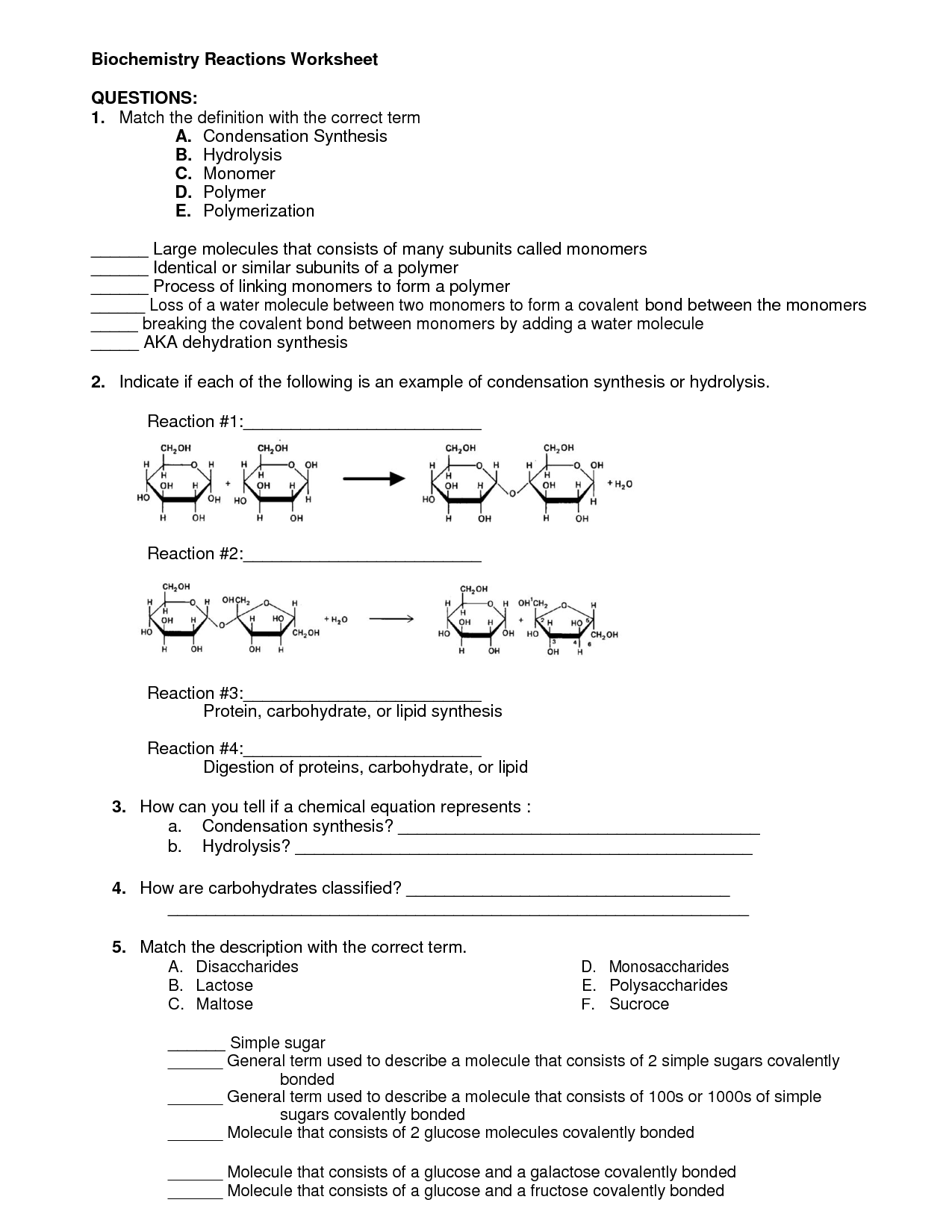
What is a carbohydrate?
Carbohydrates are macronutrients consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, serving as a primary source of energy for the human body. They can be categorized as simple carbohydrates, like sugars, or complex carbohydrates, such as starches and fiber. Sources of carbohydrates include fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes, playing a crucial role in providing fuel for the brain and muscles to function optimally.
A type of biomolecule that serves as a major source of energy and provides structural support in cells.
Carbohydrates are a type of biomolecule that serves as a major source of energy and provides structural support in cells.
What is an enzyme?
An enzyme is a type of protein that acts as a catalyst in biochemical reactions, speeding up the rate of the reaction without being consumed in the process. Enzymes play a crucial role in various biological functions, such as metabolism, digestion, and cell signaling, by lowering the activation energy required for chemical reactions to occur.
A biological catalyst that speeds up chemical reactions in cells.
The biological catalyst that speeds up chemical reactions in cells is called an enzyme.
What is DNA?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that carries the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all living organisms. It is a double-helix structure made up of nucleotides containing the genetic information that is passed down from generation to generation. DNA is found in the nucleus of cells and is essential for the inheritance of traits and characteristics in all living organisms.
The genetic material that carries the hereditary information of organisms.
The genetic material that carries the hereditary information of organisms is known as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA contains the blueprint for an organism's growth, development, and functioning, and it is passed on from one generation to the next through the process of reproduction. DNA is composed of genes, which contain specific sequences of nucleotides that encode for proteins and ultimately determine an organism's traits and characteristics.
What is a protein?
A protein is a large biological molecule made up of amino acids that play a crucial role in various biological processes in living organisms, such as enzyme catalysis, structural support, cell signaling, and immune responses. Proteins are essential for the growth, development, and maintenance of cells and tissues in the body.
A large biomolecule composed of amino acids, involved in various cellular functions such as structure, enzymes, and signaling.
The large biomolecule composed of amino acids that you are referring to is a protein. Proteins play crucial roles in the functioning of cells, acting as enzymes for chemical reactions, providing structural support, and participating in signaling pathways. These versatile molecules are essential for the growth, development, and maintenance of living organisms.
What is the role of lipids in cells?
Lipids play a crucial role in cells by serving as components of cell membranes, providing structure and support to cells, as well as regulating various cellular processes. They act as energy storage molecules, insulate and protect organs, and play a role in cell signaling. Lipids are also involved in the transport of fat-soluble vitamins and hormones.
They serve as a source of energy, insulation, and protection in cell membranes.
Lipids play crucial roles in cells by serving as a source of energy through lipid metabolism, providing insulation to maintain body temperature, and offering protection by forming cell membranes that regulate the passage of molecules in and out of cells.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments