Bill Nye Static Electricity Worksheet
Are you searching for an engaging and informative worksheet on static electricity? Look no further! Our Bill Nye Static Electricity Worksheet is designed to captivate learners who are eager to explore the world of science. This worksheet delves into the fascinating concepts of static electricity, providing an in-depth understanding of the subject matter.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
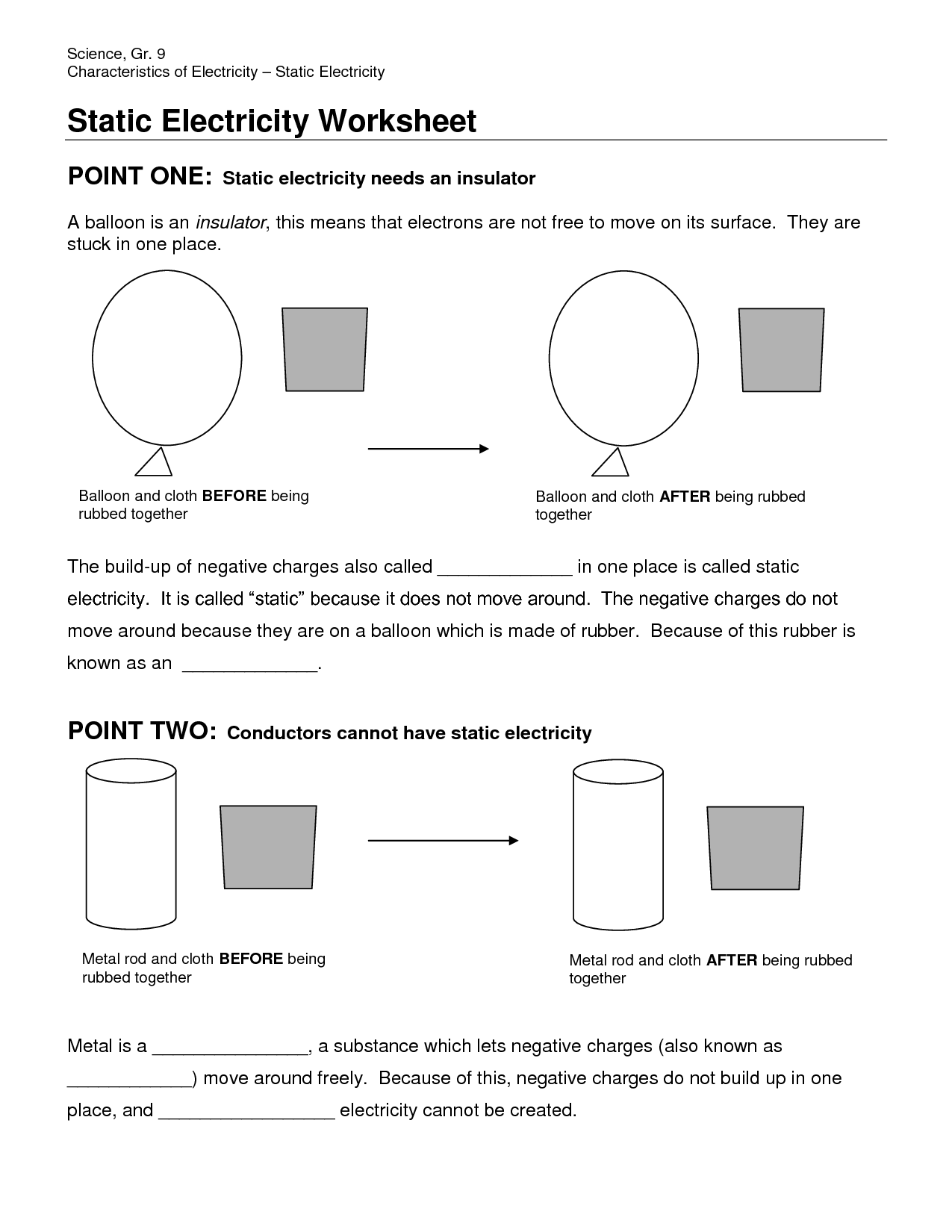
What is static electricity?
Static electricity is a build-up of electric charge on the surface of an object. It occurs when there is an imbalance of positively and negatively charged particles, such as electrons, on an object's surface, leading to the attraction or repulsion of other objects. This charge remains until it is discharged through contact with another object or by an electrical current.
How is static electricity different from current electricity?
Static electricity is the build-up of an electrical charge on the surface of an object, causing it to attract or repel other objects, while current electricity is the flow of electrical charge through a conductor, typically resulting in the generation of power or the operation of electrical devices. The key difference is that static electricity is stationary and accumulates on the surface, whereas current electricity involves the movement of charged particles in a continuous flow.
What causes static electricity to build up on objects?
Static electricity builds up on objects when there is an imbalance of negatively and positively charged particles. This imbalance occurs when electrons are transferred from one object to another through friction, contact, or separation, leaving one object with a surplus of electrons (negatively charged) and the other with a deficit (positively charged). When the charged objects come into contact with each other or with a conductor, the excess electrons can discharge, creating a spark or a shock.
How does static electricity discharge occur?
Static electricity discharge occurs when an excess of electrical charge accumulates on an object, such as due to friction or contact with another charged object. When the build-up of charge becomes too high, the electrons will seek to neutralize by moving to a more positively charged object or finding a path to the ground. This movement of electrons results in a sudden flow of current, which is the discharge of static electricity. This discharge can manifest as a visible spark, a crackling noise, or a sudden shock, depending on the circumstances.
What are some common examples of static electricity in everyday life?
Some common examples of static electricity in everyday life include when clothes cling together in the dryer, when you get a shock from touching a metal object after walking on carpet, when your hair stands up after rubbing a balloon on it, and when dust is attracted to a TV or computer screen. Static electricity can also occur when you shuffle your feet on a carpet and then touch a light switch or when you rub a balloon on your hair and it sticks to a wall.
What are conductors and insulators, and how do they relate to static electricity?
Conductors are materials that allow the flow of electric charges, while insulators are materials that prevent the flow of electric charges. In the context of static electricity, conductors facilitate the movement of excess charges, helping to dissipate static electricity and prevent the build-up of charge. On the other hand, insulators trap static charges, causing them to accumulate and potentially leading to static discharge when the insulator comes into contact with a conductor or another object.
How can static electricity be dangerous?
Static electricity can be dangerous because it can build up to levels that can cause sparks or sudden surges of electrical energy, potentially leading to fires or explosions in environments with flammable gases or materials. Additionally, static electricity can also interfere with sensitive electronic equipment, leading to malfunctions or damage. In some cases, static electricity discharge can also cause painful shocks to individuals.
How is static electricity used in everyday technology?
Static electricity is used in everyday technology in applications such as photocopying machines, air filters, and dust removal systems. For example, in photocopying machines, static electricity is used to transfer toner powder from the drum to the paper. In air filters and dust removal systems, static electricity is used to attract and trap dust particles to improve air quality. Additionally, static electricity is used in industrial processes like painting cars and applying coatings to surfaces to ensure uniform adhesion of the materials.
What are the benefits or drawbacks of static electricity?
Static electricity can have both benefits and drawbacks. Some benefits include its use in technologies like photocopiers and air purifiers. Additionally, static electricity can also help in dust removal through static cling. However, drawbacks of static electricity include its potential to damage electronic devices through electrostatic discharge and causing discomfort or even mild shocks to individuals. Additionally, static electricity can also lead to accidents in industrial settings, especially in environments with flammable materials.
How can static electricity be controlled or prevented?
Static electricity can be controlled or prevented by grounding the objects or surfaces that generate or accumulate static charges, using antistatic materials or sprays to reduce friction and static build-up, maintaining appropriate humidity levels to minimize static electricity, using ionizers to neutralize charges, avoiding wearing clothing made of materials that generate static, and using conductive flooring or mats to dissipate static charges. Regular cleaning and maintenance of equipment and surfaces can also help prevent static electricity build-up.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments