Atoms and Molecules Worksheet
Are you a science teacher or a student studying atoms and molecules? If so, you're in luck! In this blog post, we will discuss how worksheets can be a valuable tool for both educators and learners when it comes to understanding this complex subject. Worksheets provide a structured way to explore the concept of atoms and molecules, enabling individuals to grasp their properties and relationships in a clear and organized manner.
Table of Images 👆
- Atoms and Molecules in Chemical Formulas Worksheet
- Atomic Structure of Atoms Worksheets
- Worksheet Atoms Molecules Compounds
- How to Draw a Helium Atom
- Mole Conversion Problems Worksheet Answers
- Carbon-14 Atom
- Solid Liquid and Gas Worksheets
- Matter Solid-Liquid Gas Worksheet
- Electron Distribution Worksheet Answers
- Moles Molecules Grams Worksheet
- Chemical Reaction Worksheet Answer Key
- Super Scientists Worksheet Answers
- Super Scientists Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
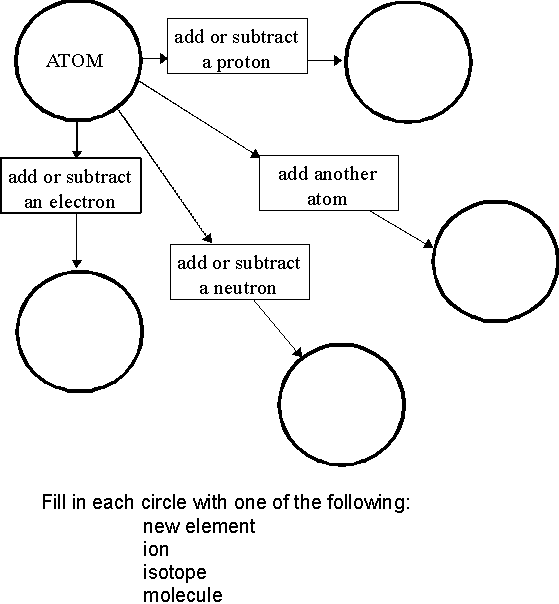
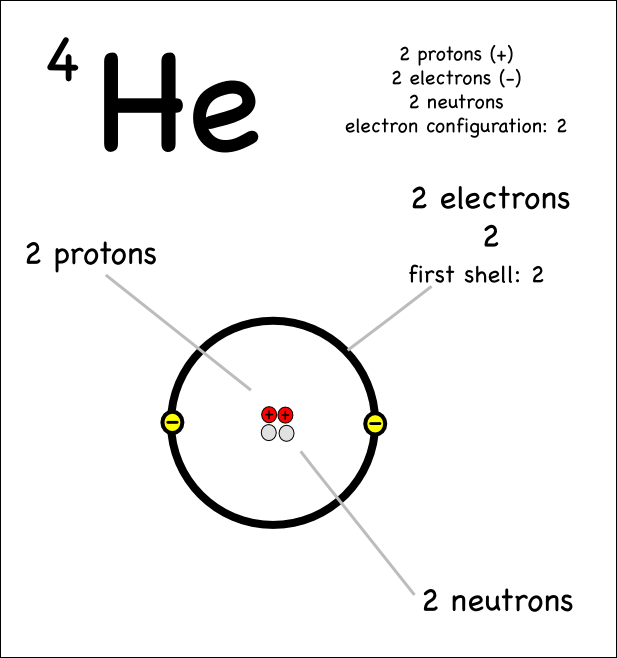
What is an atom?
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element. It consists of a nucleus made up of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons orbiting in energy levels. Atoms combine to form molecules, which are the building blocks of all substances.
What are the three subatomic particles?
The three subatomic particles are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons have no charge, and electrons have a negative charge. Together, they make up the building blocks of atoms.
How are protons different from electrons?
Protons are positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom, while electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus. Protons have a much larger mass than electrons, and they contribute to the overall positive charge of an atom, whereas electrons contribute to the negative charge. Protons determine the element of an atom, while electrons are involved in chemical bonding and determining the atom's reactivity.
What is an atomic nucleus?
An atomic nucleus is the central core of an atom that contains protons and neutrons, held together by strong nuclear forces. It accounts for almost all of the atom's mass and has a positive charge due to the presence of protons. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the element's identity, while the number of neutrons can vary, leading to different isotopes of the same element.
What is an element?
An element is a substance that consists of only one type of atom, characterized by its unique atomic number on the periodic table. Elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances through chemical reactions and retain their unique properties. Each element has distinct physical and chemical characteristics, making up the building blocks of all matter in the universe.
How are molecules different from atoms?
Molecules are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together, while atoms are the basic building blocks of matter. Atoms cannot exist independently in a stable state and typically combine with other atoms to form molecules. Molecules have unique properties based on the arrangement and types of atoms they are composed of, whereas atoms are the smallest unit of an element and retain its chemical properties.
What is a covalent bond?
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond formed between two atoms when they share one or more pairs of electrons. This sharing of electrons creates a stable arrangement of electrons in the outer energy levels of the atoms involved, leading to the formation of molecules.
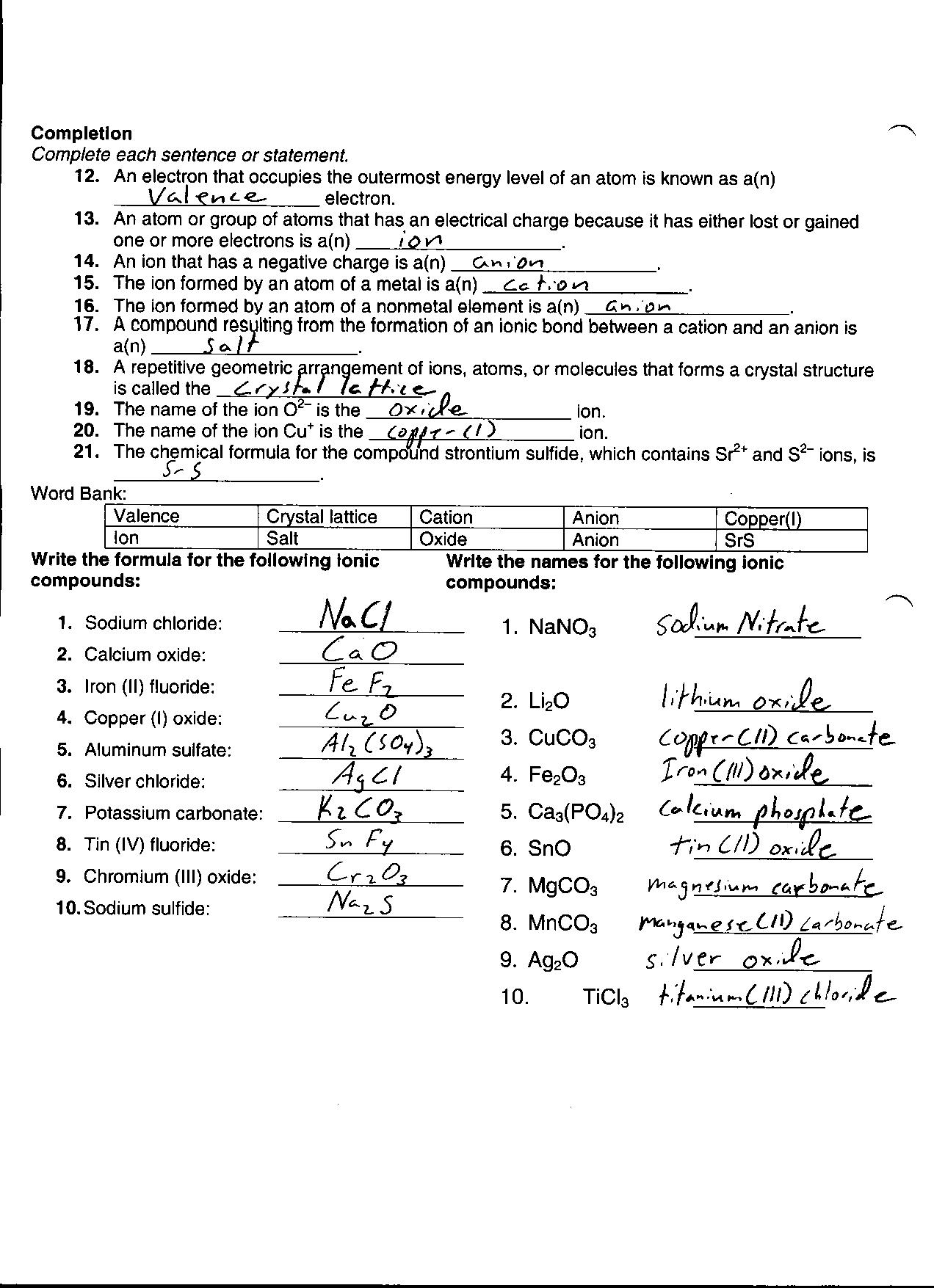
What is an ionic bond?
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that forms between two atoms when one atom donates an electron to another atom, resulting in the formation of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). These oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, leading to the creation of a strong bond between the two atoms.
How are ionic and covalent bonds different?
Ionic bonds are formed when electrons are transferred between atoms, resulting in the attraction between oppositely charged ions. Covalent bonds, on the other hand, are formed when atoms share electrons to achieve a full outer shell, creating a strong bond based on shared electrons. The key difference is that ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons while covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons.
How do atoms and molecules contribute to the properties of matter?
Atoms and molecules contribute to the properties of matter through their composition and arrangement. The type and number of atoms in a molecule determine its chemical properties, such as reactivity and bonding. The arrangement of molecules in a substance influences its physical properties, such as density, melting point, and conductivity. Overall, the interactions between atoms and molecules dictate the observable characteristics of different types of matter.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments