Atomic Structure Diagram Worksheet
The Atomic Structure Diagram Worksheet is a valuable tool for students studying chemistry or physics. This worksheet provides a clear and concise layout of the essential components of an atom, including the location and charge of protons, neutrons, and electrons. With its easy-to-follow format and informative diagrams, this worksheet is designed to help students grasp the fundamental concepts of atomic structure. Whether you are a high school student embarking on your first chemistry course or a college student needing a refresher, this worksheet is an excellent resource to enhance your understanding of atomic structure.
Table of Images 👆
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemistry Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- How Do You Draw a Bohr Model
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Bohr Atomic Models Worksheet Answers
- Periodic Table Worksheet Answer Key
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Middle School
- Chemistry Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Atoms Isotopes and Ions Worksheet Answers
- Electron Orbital Diagram Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
What is the purpose of an atomic structure diagram?
An atomic structure diagram is used to visually represent the arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons within an atom. It helps illustrate the distribution of these subatomic particles in the nucleus and electron shells, providing a clear depiction of an atom's overall structure. This diagram is crucial for understanding the fundamental composition of elements and how they interact with each other in chemical reactions and bonding.
What are the different components of an atomic structure diagram?
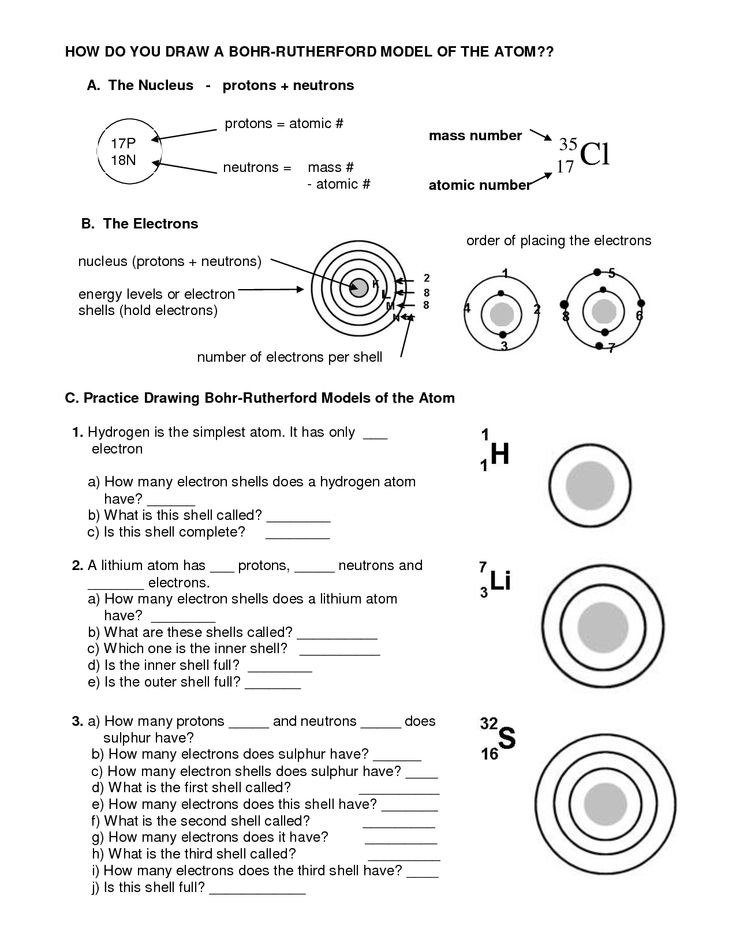
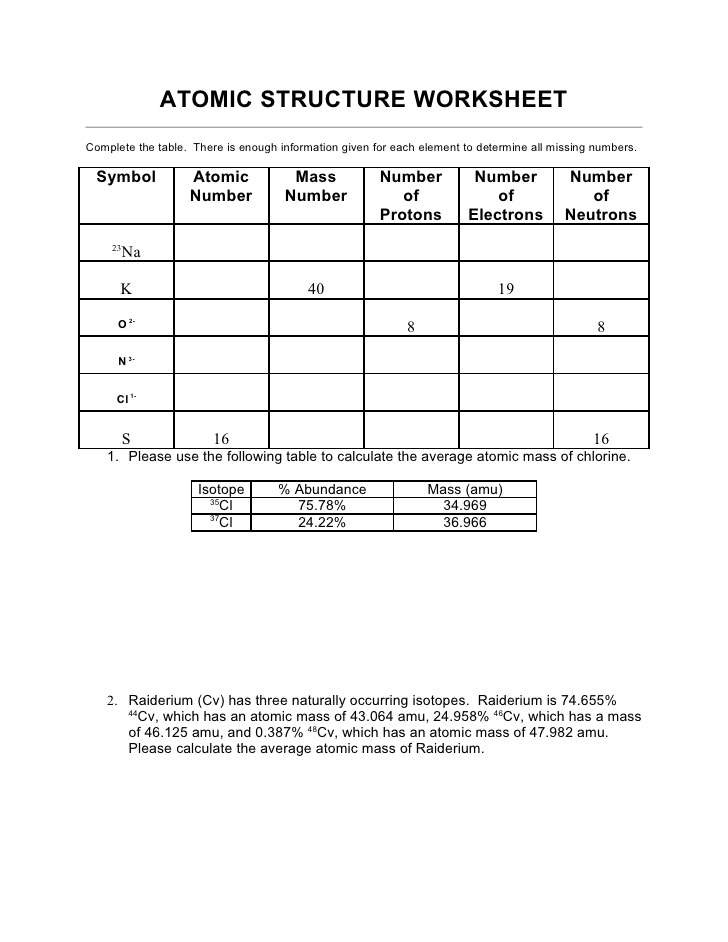
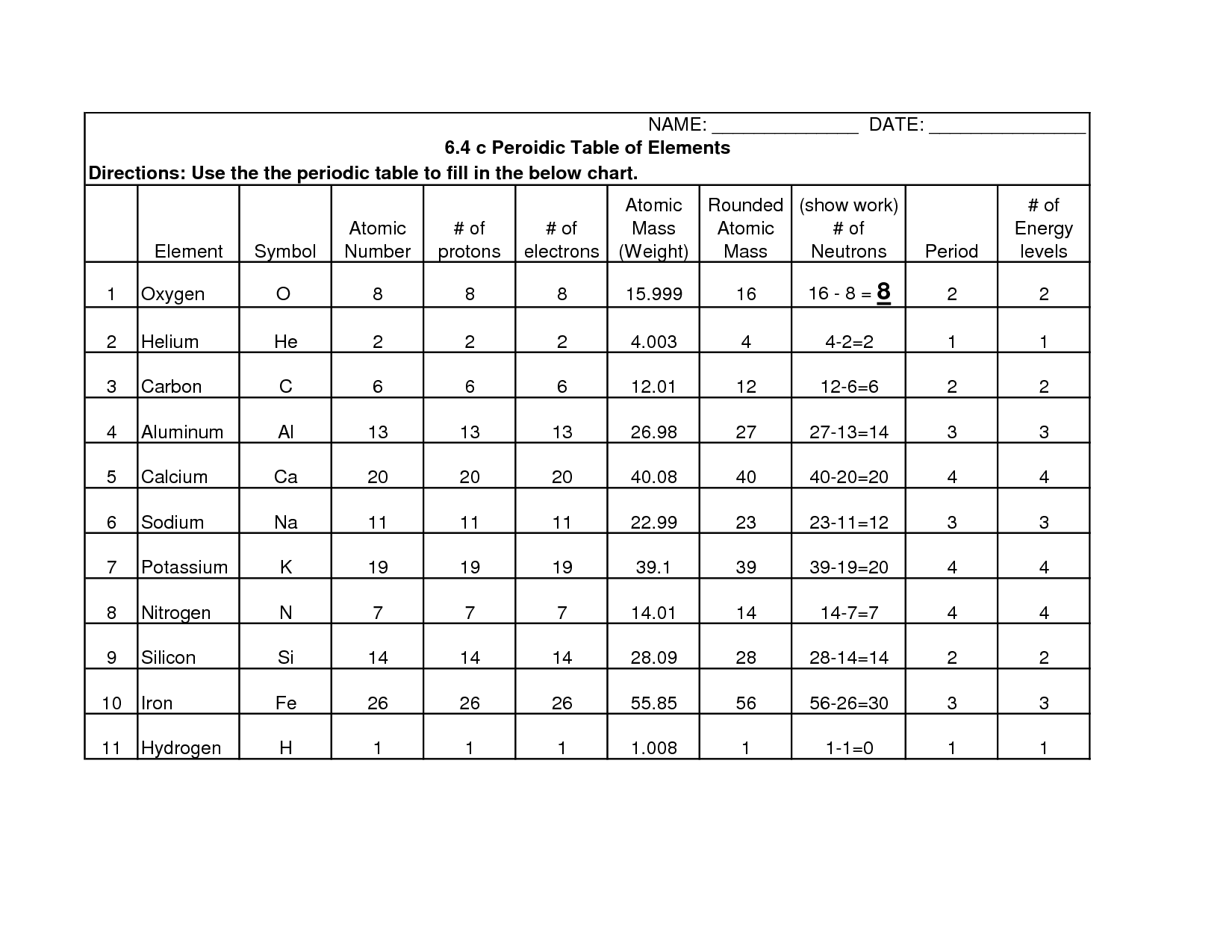
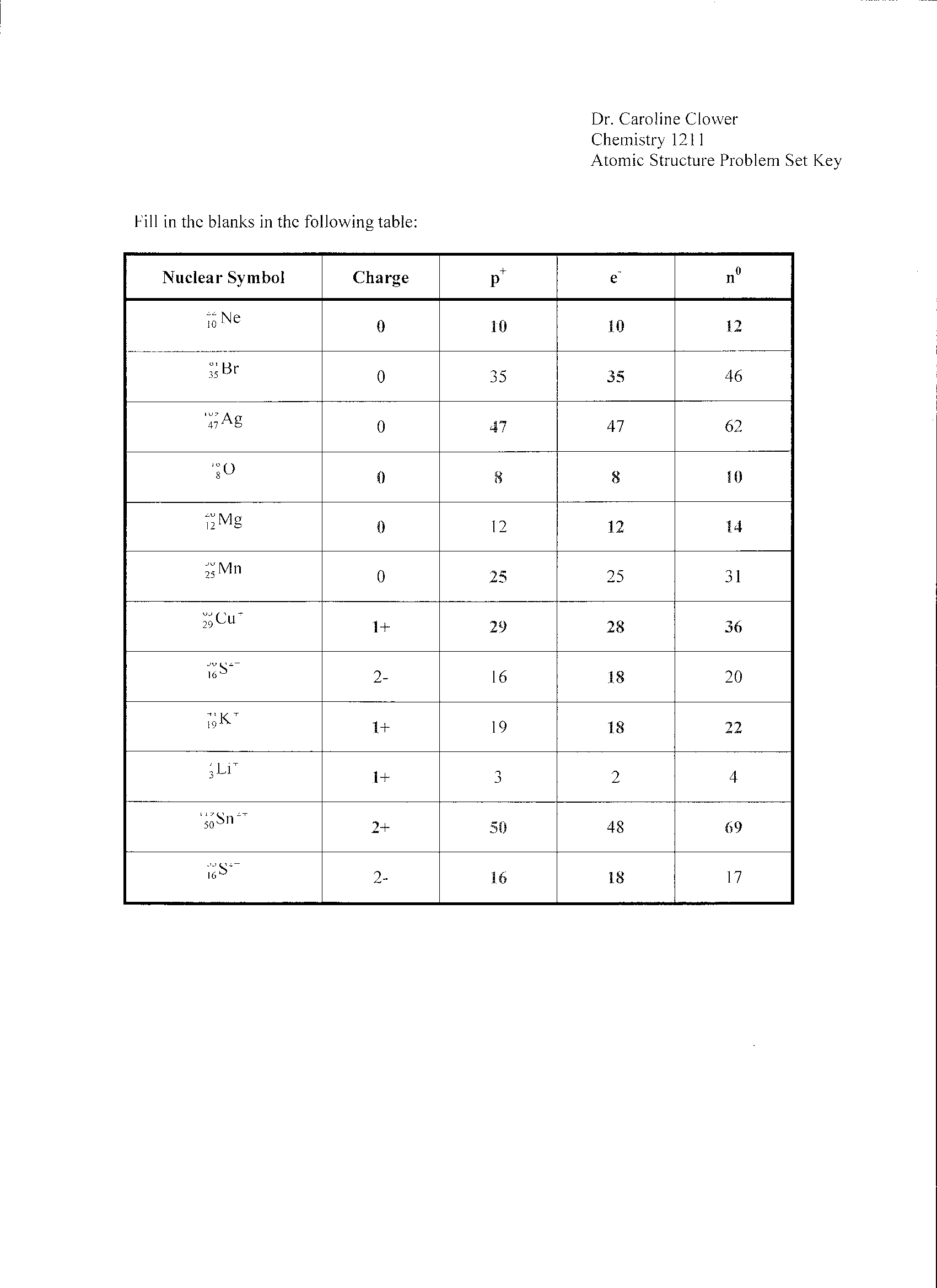
An atomic structure diagram typically includes three main components: the nucleus at the center, consisting of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electron shells representing the energy levels where electrons are located, and the electron cloud depicting the space where electrons move around the nucleus in a probabilistic manner. Each component helps illustrate the organization and behavior of particles within an atom.
How is an atom represented in an atomic structure diagram?
An atom is represented in an atomic structure diagram by a nucleus at the center, surrounded by electron orbitals or energy levels. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, while the electron orbitals depict the location of electrons. The electrons are shown orbiting the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells, with each shell capable of holding a certain number of electrons. The diagram provides a visual representation of the arrangement of particles within an atom.
What is the significance of the nucleus in an atom?
The nucleus in an atom is significant because it contains protons and neutrons, which are the building blocks of the atom. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the element's identity, while the number of neutrons affects its stability. Additionally, the nucleus holds almost all of the atom's mass and plays a crucial role in determining the atom's properties and behavior.
How are protons and neutrons represented in an atomic structure diagram?
In an atomic structure diagram, protons are represented by positively charged particles located in the nucleus of the atom, while neutrons are represented by neutral particles also found in the nucleus. Electrons, which are negatively charged, are represented by smaller particles orbiting the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, while the total number of protons and neutrons together determine the mass number of the atom.
What is the role of electrons in an atom?
Electrons in an atom play a crucial role in determining an element's chemical properties and reactivity. They orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels, creating bonds with other atoms to form molecules. The number and arrangement of electrons dictate an atom's ability to gain, lose, or share electrons, which ultimately determines how it will interact with other atoms in chemical reactions.
How are electrons represented in an atomic structure diagram?
Electrons are typically represented in an atomic structure diagram as small points or dots surrounding the nucleus of the atom. They are often depicted as moving in specific energy levels or orbitals within distinct layers around the nucleus. The number of electrons in an atom is determined by the atomic number and is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus, ensuring the atom's overall charge remains neutral.
What are energy levels or shells in an atomic structure diagram?
In an atomic structure diagram, energy levels or shells represent the regions around the nucleus where electrons are likely to be found. These shells are designated by letters such as K, L, M, etc., and each shell can hold a specific number of electrons based on its energy level. Electrons occupy the innermost shells first before moving to outer shells, with the outermost shell determining the chemical properties of the element.
How are energy levels or shells filled with electrons?
Energy levels or shells are filled with electrons based on the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons fill the lowest energy levels first before moving to higher levels. Each energy level can hold a specific number of electrons, with the first level holding a maximum of 2 electrons, the second level holding a maximum of 8 electrons, and so on. Electrons also follow the Pauli exclusion principle, with no two electrons in an atom able to have the same set of quantum numbers. Additionally, Hund's rule dictates that electrons fill orbitals of the same energy level with parallel spins before pairing up.
How does an atomic structure diagram illustrate the stability of an atom?
An atomic structure diagram illustrates the stability of an atom through the arrangement of electrons in energy levels or orbitals. A stable atom is one that has a full outermost energy level, also known as a valence shell, typically containing eight electrons. This configuration, known as the octet rule, results in stable atoms that are less likely to undergo chemical reactions. By showing the distribution of electrons in different energy levels, an atomic structure diagram can visually represent the stability of an atom based on the arrangement of its electrons.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments