AP Biology Mitosis Worksheets
Mitosis is a fundamental concept in AP Biology, and what better way to reinforce your understanding than with worksheets specifically designed to enhance your learning experience? Whether you are a student preparing for an exam, a teacher looking for engaging classroom materials, or a homeschooling parent seeking supplementary resources, these AP Biology Mitosis Worksheets are the perfect tool to solidify your comprehension of this important biological process.
Table of Images 👆
- Onion Cell Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Mitosis Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle Review Worksheet Answers
- Onion Cell Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Biology Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis versus Meiosis Worksheet Answers
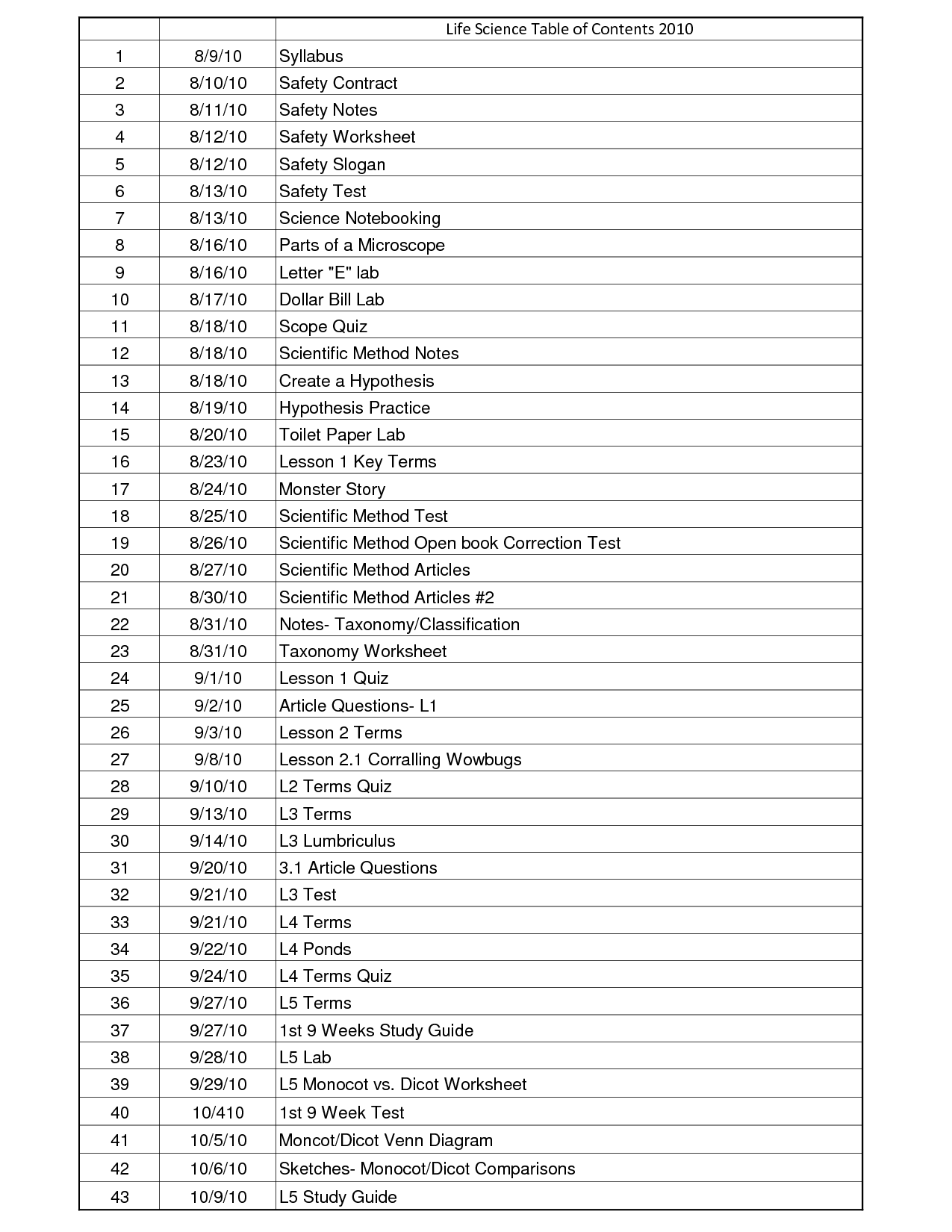
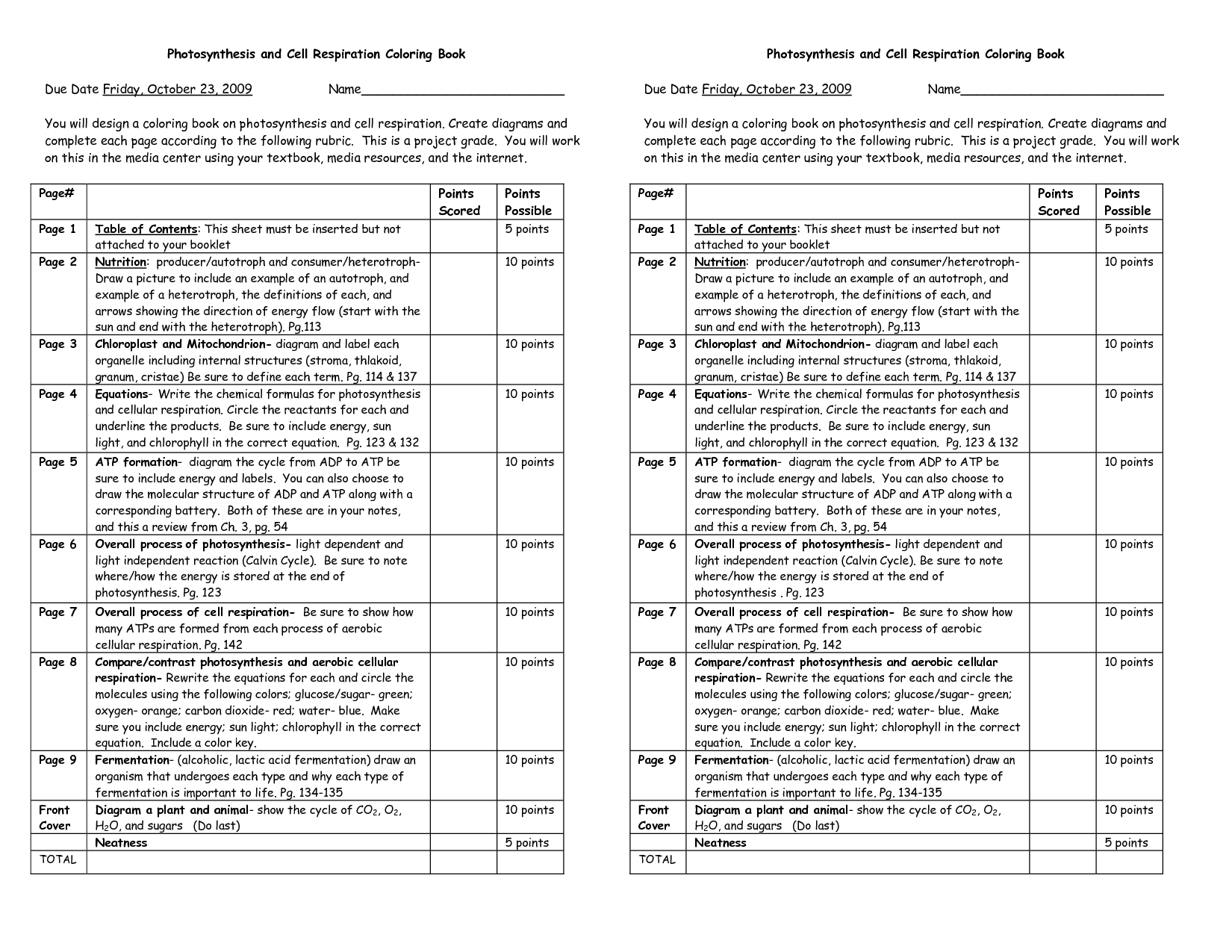
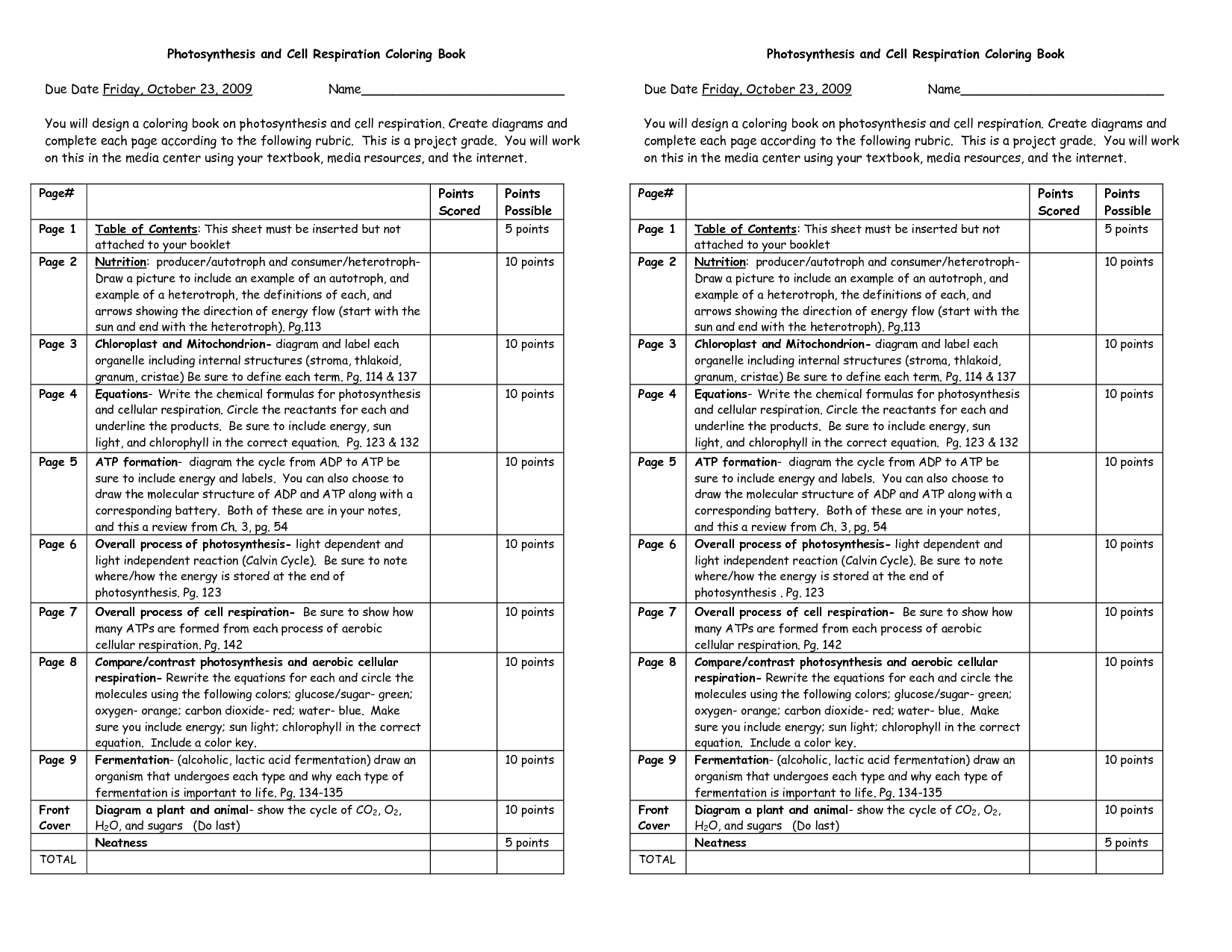
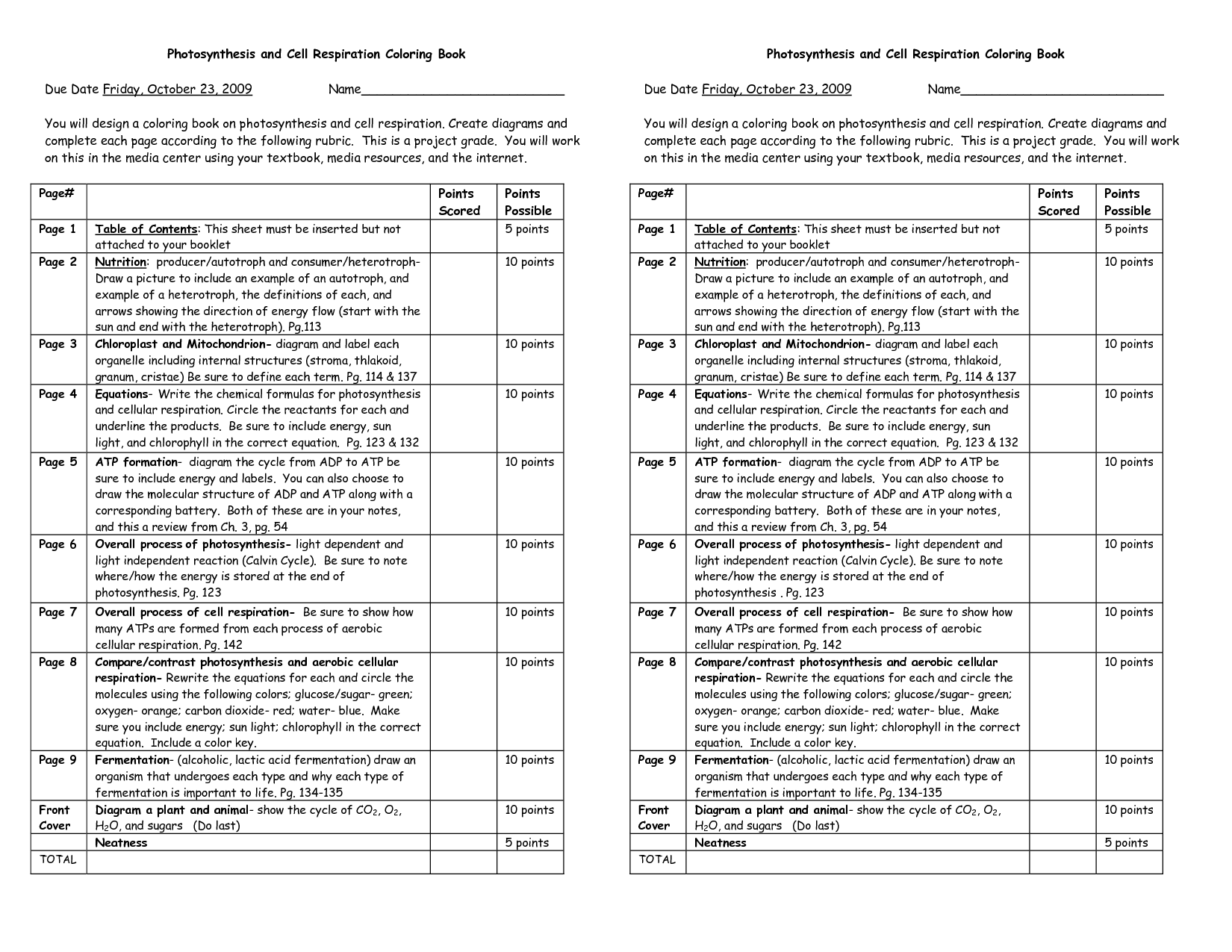
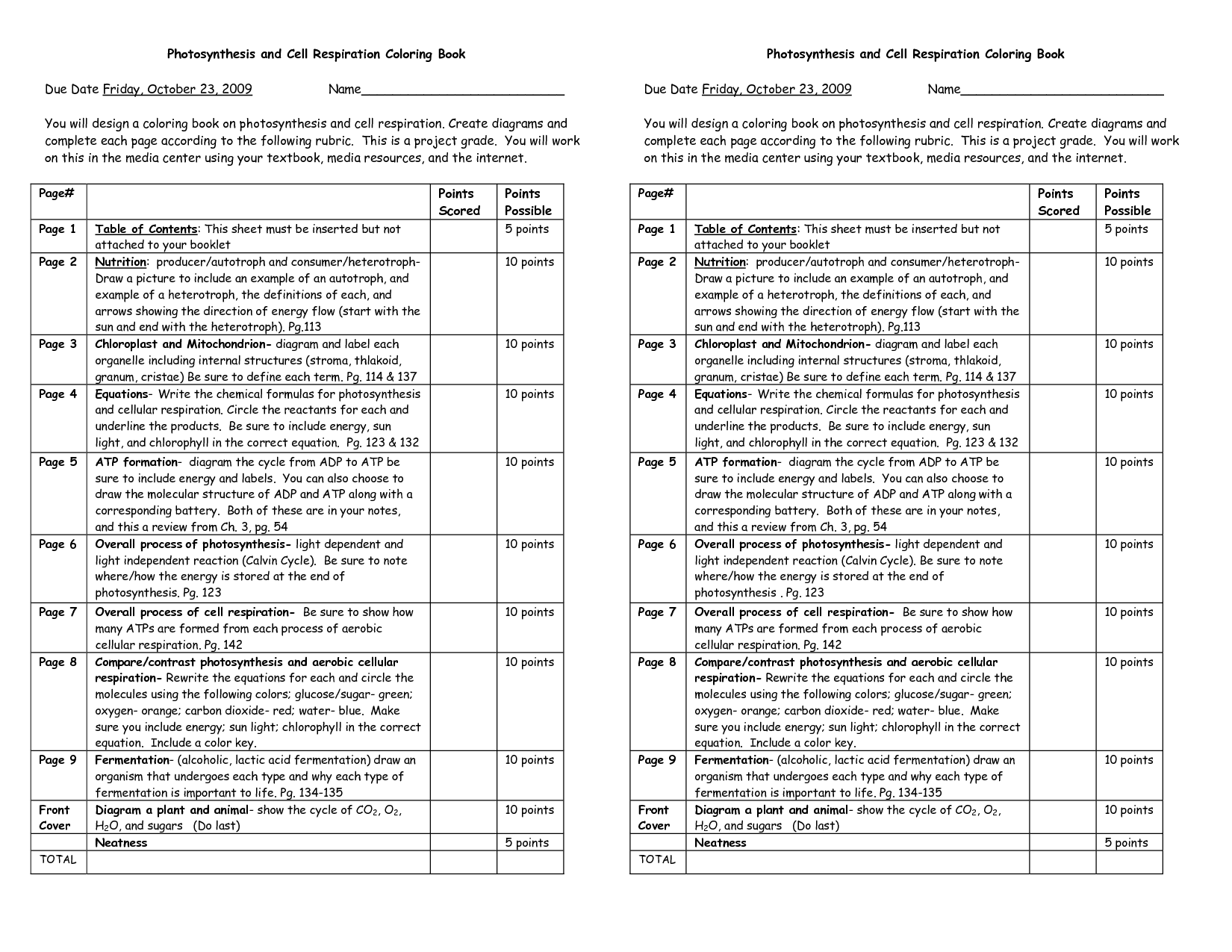
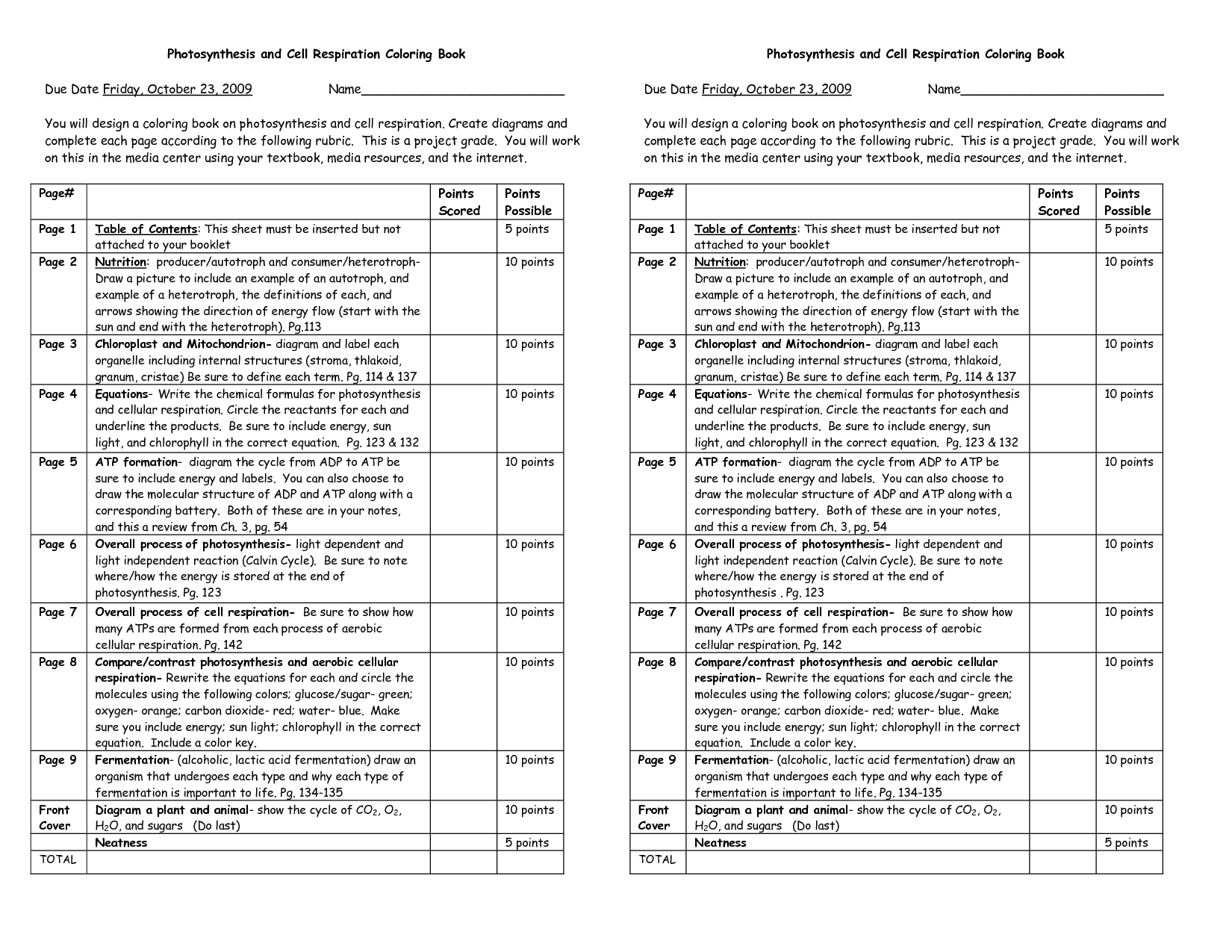
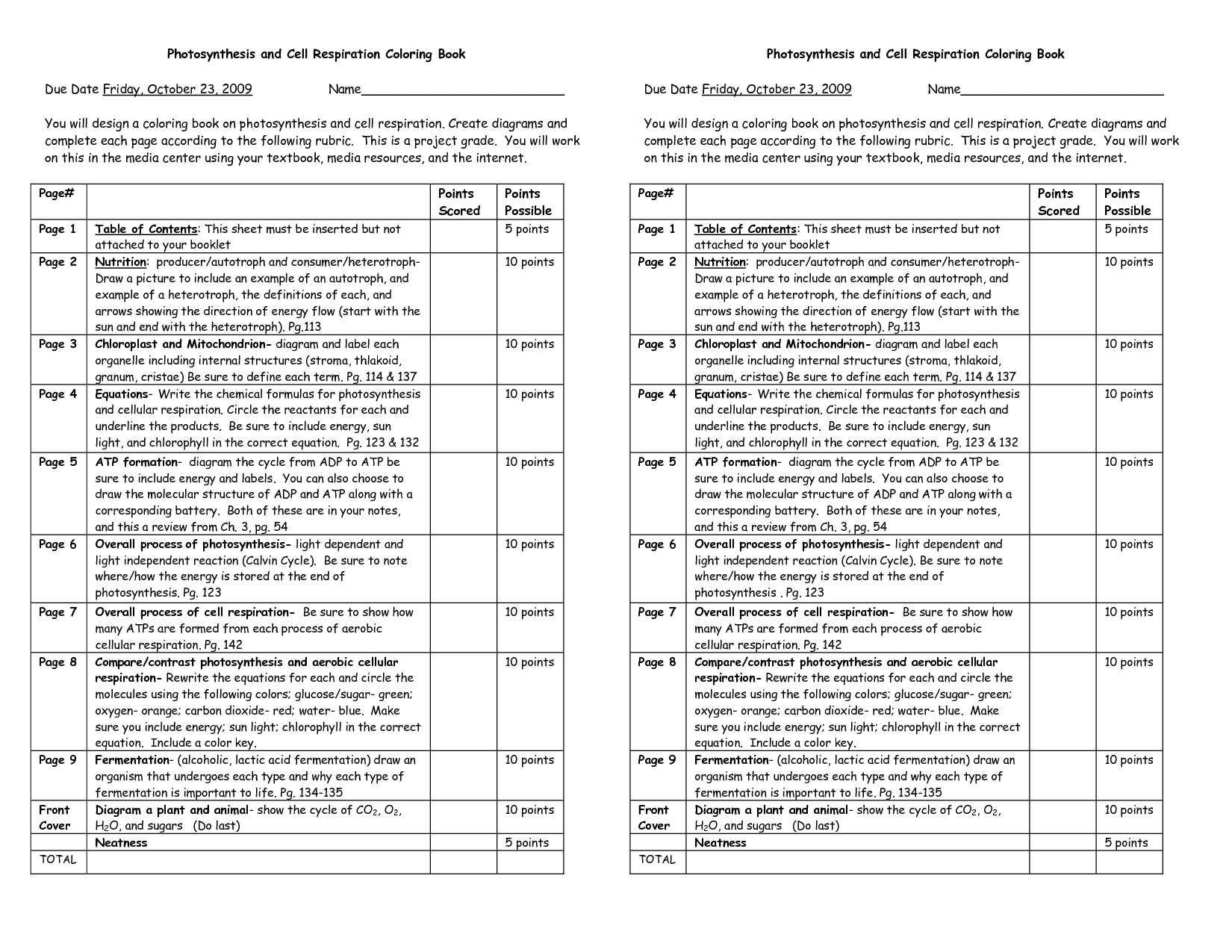
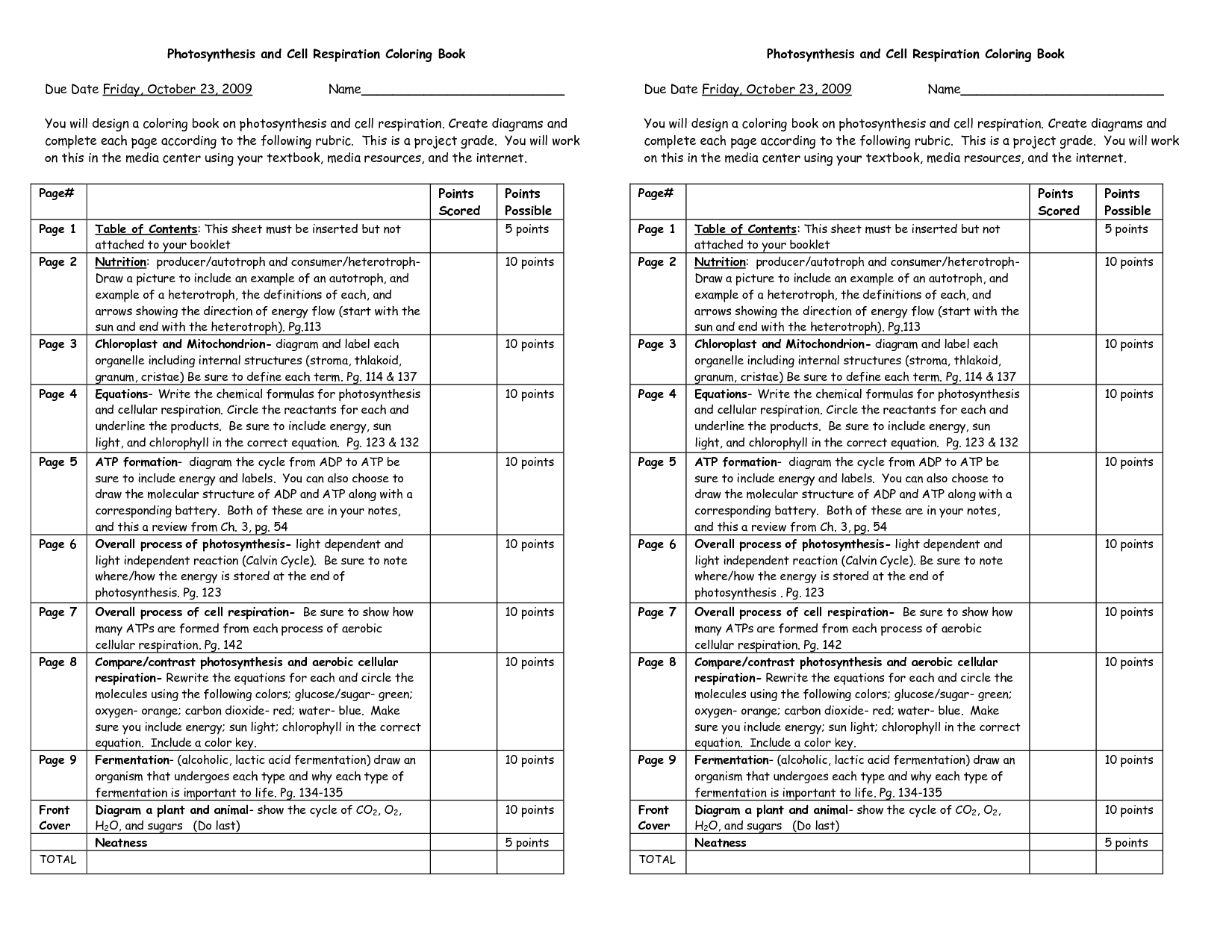
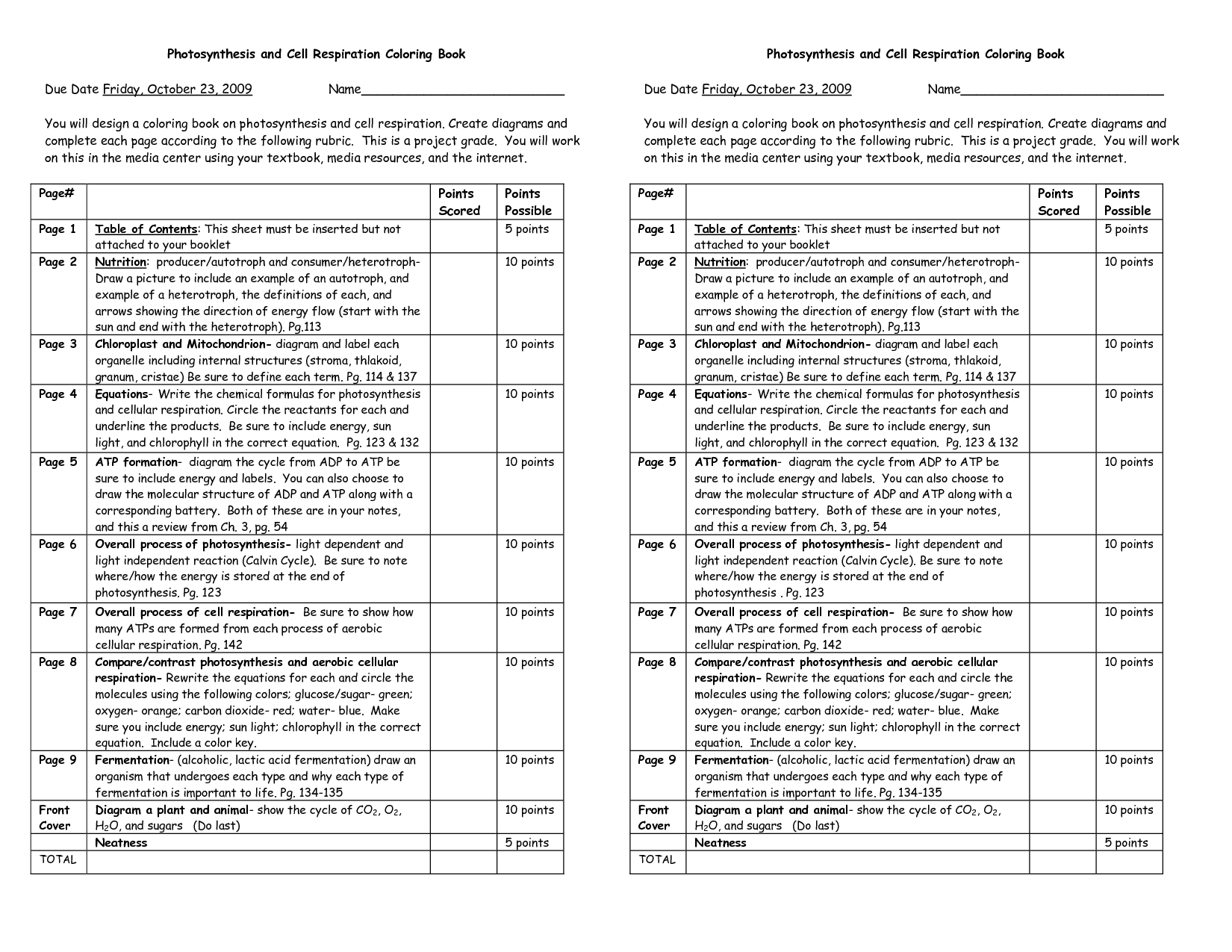
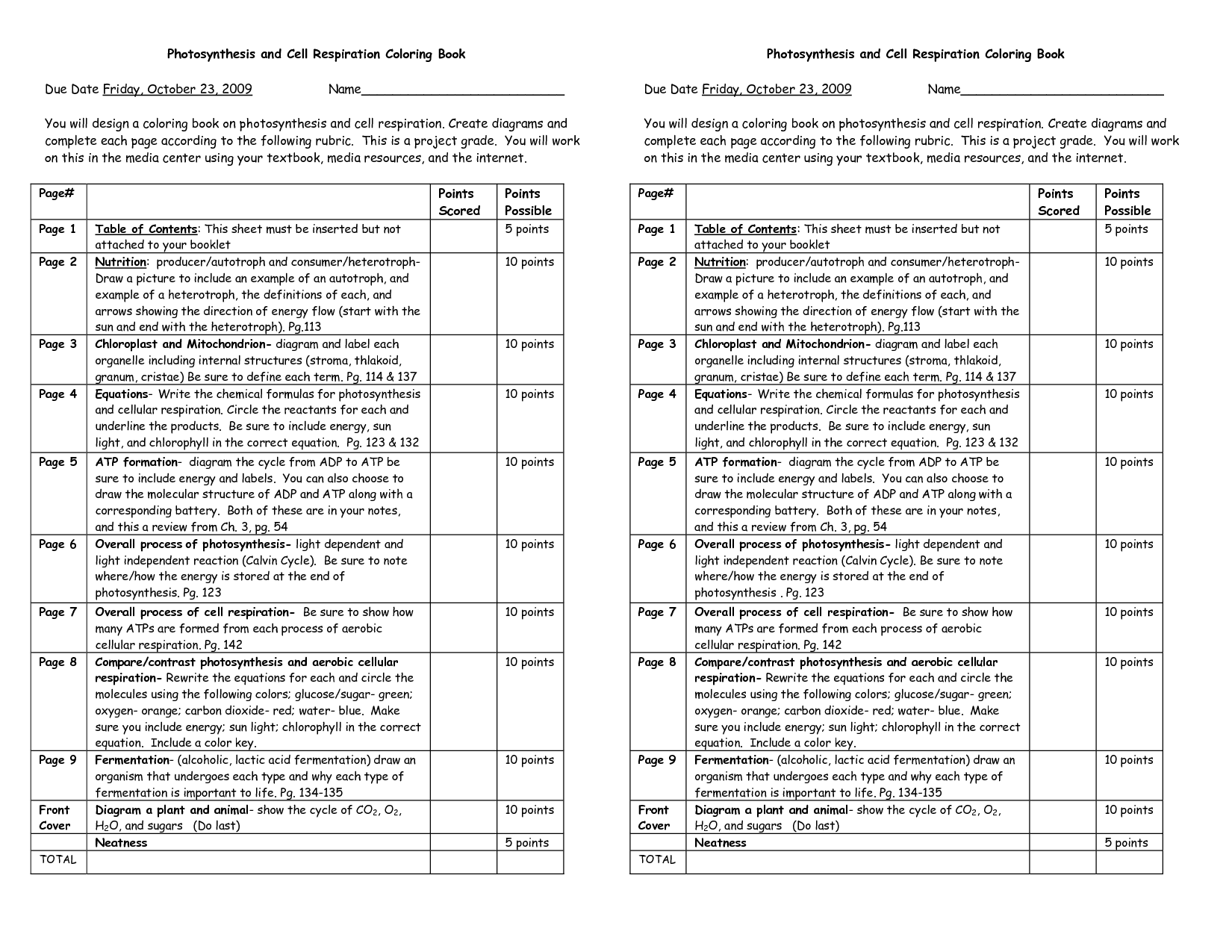
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Coloring Sheet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Coloring Sheet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Coloring Sheet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Coloring Sheet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Coloring Sheet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Coloring Sheet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Coloring Sheet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Coloring Sheet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Coloring Sheet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Coloring Sheet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Coloring Sheet
More Biology Worksheets
Free Printable Biology WorksheetsCollege Biology Worksheets
7th Grade Biology Worksheets
Biology Macromolecules Worksheets and Answers
Karyotype Worksheet Answers Biology
What is the purpose of mitosis?
The primary purpose of mitosis is to enable cell division, allowing for growth, development, and repair of tissues in multicellular organisms. Mitosis ensures that each new cell receives an identical set of chromosomes to the parent cell, maintaining genetic stability and promoting the overall health and function of the organism.
What are the phases of mitosis in order?
The phases of mitosis in order are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Describe the events that occur during prophase.
During prophase, the first stage of mitosis in cell division, the nuclear envelope breaks down, allowing the genetic material to be exposed in the form of chromosomes. The chromosomes condense and become visible under a microscope. Spindle fibers form and stretch across the cell, connecting to the centromeres of the chromosomes. Additionally, the centrioles migrate to opposite ends of the cell, organizing the spindle fibers and preparing for chromosome movement. Overall, prophase is characterized by the preparation and organization of the cell's genetic material for division.
Explain the significance of the metaphase plate.
The metaphase plate is a significant structure in mitosis and meiosis where chromosomes align along the equatorial plane of the cell. This alignment ensures that chromosomes are evenly distributed between daughter cells during cell division, contributing to the accurate segregation of genetic material. The metaphase plate also facilitates the attachment of spindle fibers to the centromeres of chromosomes, allowing for the equal separation of sister chromatids to opposite poles of the cell. This precise alignment and separation are crucial for maintaining genetic stability and ensuring the proper distribution of chromosomes in daughter cells.
What happens during anaphase?
During anaphase of mitosis or meiosis, the sister chromatids separate and are pulled apart towards opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers. This ensures that each daughter cell will receive an identical set of chromosomes. The cell elongates as the chromatids move apart, preparing for the subsequent telophase and cytokinesis stages of cell division.
How is telophase different from prophase?
Telophase and prophase are both stages of mitosis, but they have distinct characteristics. Telophase is the final stage of mitosis where the chromosomes reach the opposite poles of the cell, the nuclear membrane reforms around each set of chromosomes, and the chromosomes begin to decondense. In contrast, prophase is the initial stage of mitosis marked by the condensation of chromatin into visible chromosomes, the breakdown of the nuclear envelope, and the formation of the mitotic spindle fibers to move the chromosomes. The key difference between telophase and prophase is that telophase is the end of mitosis when the cell prepares to divide, while prophase is the beginning stage when the cell's components get ready for chromosome alignment and separation.
Describe the process of cytokinesis.
Cytokinesis is the final stage of cell division and involves the physical separation of the two daughter cells that have been formed during mitosis. In animal cells, a structure called the cleavage furrow forms at the equator of the cell and gradually deepens, ultimately pinching the cell into two daughter cells. In plant cells, a cell plate forms at the equator of the cell, gradually expanding outward to divide the cell into two daughter cells. This process ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes and necessary organelles before they fully separate and become independent cells.
What is the role of the cell cycle checkpoints?
Cell cycle checkpoints play a crucial role in ensuring the accurate division of cells by monitoring the progression of the cell cycle and detecting any errors or abnormalities. They help to regulate key events, such as DNA replication and chromosome segregation, by either halting the cell cycle to allow for repair of DNA damage or triggering cell death if the damage is irreparable. This quality control mechanism helps to maintain genomic stability and prevent the propagation of mutations that could lead to diseases like cancer.
How does mitosis differ in plant and animal cells?
Mitosis in plant and animal cells is similar in most aspects, such as the phases of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. However, one key difference is that plant cells form a cell plate during cytokinesis to divide the cytoplasm and create two separate daughter cells, while animal cells form a cleavage furrow to pinch the cell in two. Additionally, plant cells do not have centrioles like animal cells do, so they rely on structures called microtubule organizing centers to help with spindle formation during mitosis.
What are the consequences of errors in mitosis?
Errors in mitosis can lead to a variety of consequences, such as genetic mutations, chromosomal abnormalities, and cell death. Genetic mutations can result in changes to an organism's DNA, potentially leading to the development of diseases such as cancer. Chromosomal abnormalities, such as having too many or too few chromosomes, can cause developmental disorders and prevent the cell from functioning properly. Additionally, errors in mitosis can lead to cell death, which can impact tissue and organ function. Overall, errors in mitosis can have serious consequences for the health and development of an organism.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments