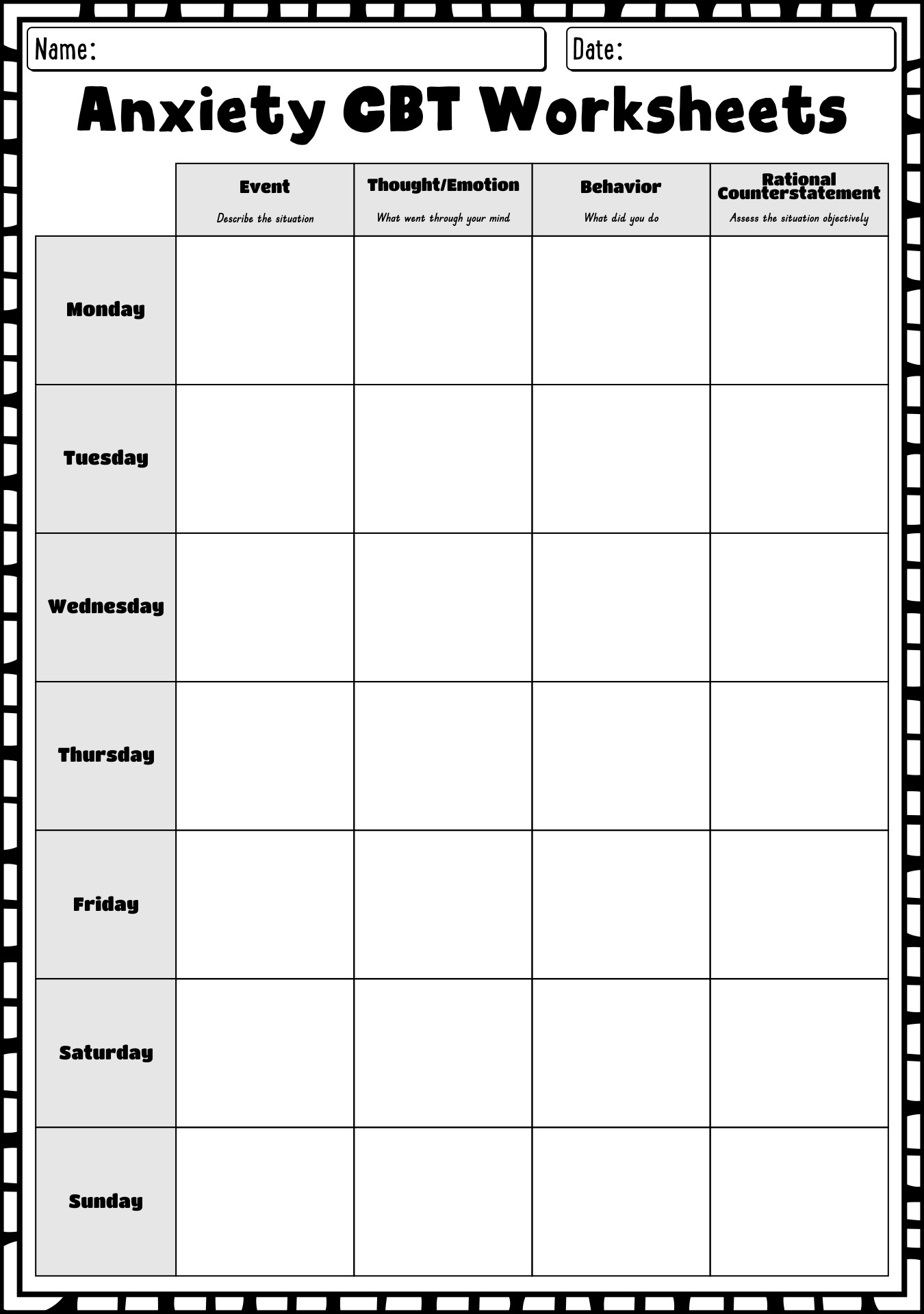
Anxiety CBT Worksheets
Anxiety CBT worksheets provide individuals struggling with anxiety a valuable tool for self-reflection and support. These worksheets focus on key concepts and exercises related to cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), empowering individuals to identify and challenge negative thought patterns and develop healthier coping strategies. Whether you are a therapist seeking additional resources for your clients or an individual looking for a practical, evidence-based approach to managing anxiety, anxiety CBT worksheets can be a useful asset.
Table of Images 👆
- Child Anxiety Worksheets CBT
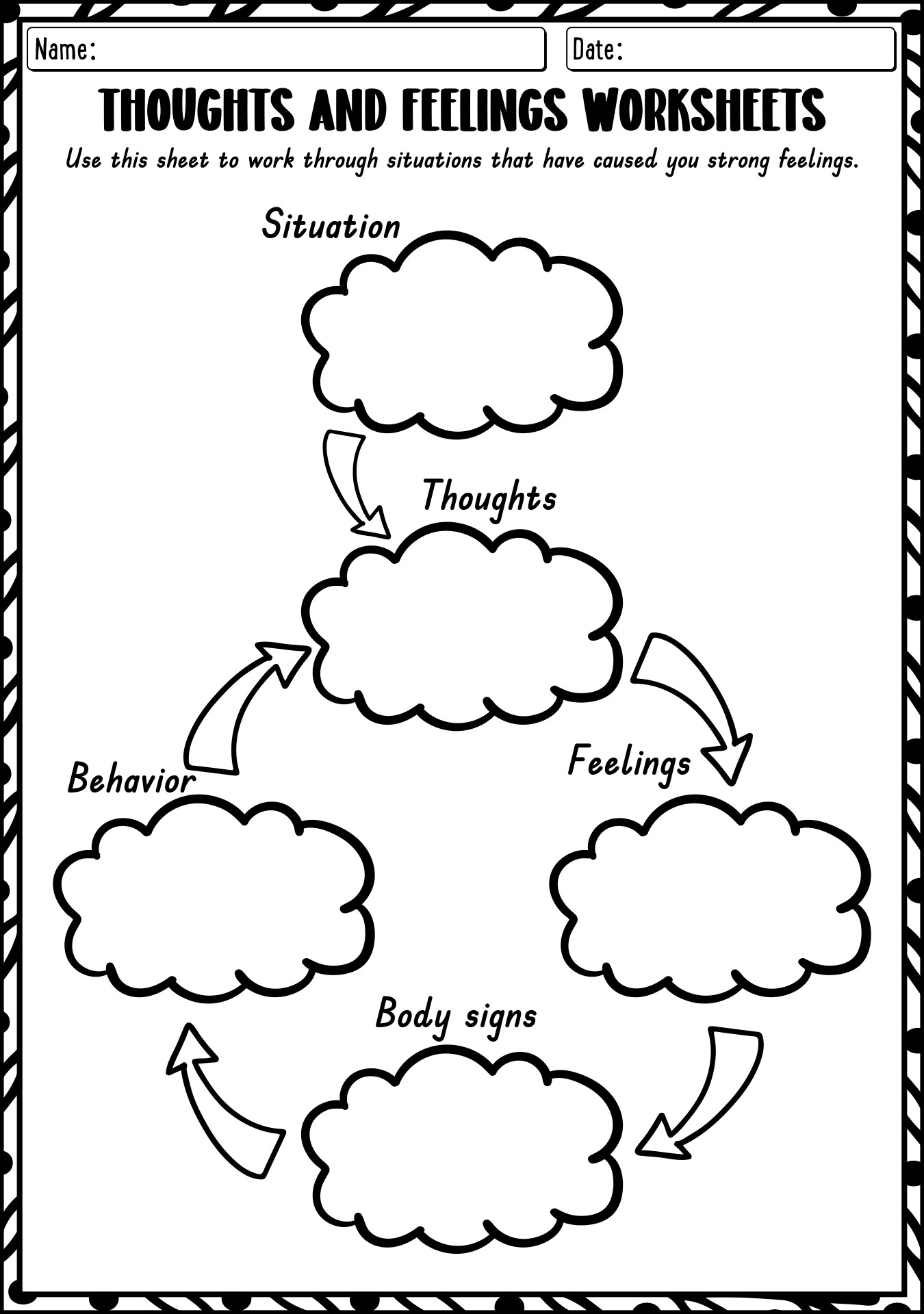
- Thoughts and Feelings Worksheets
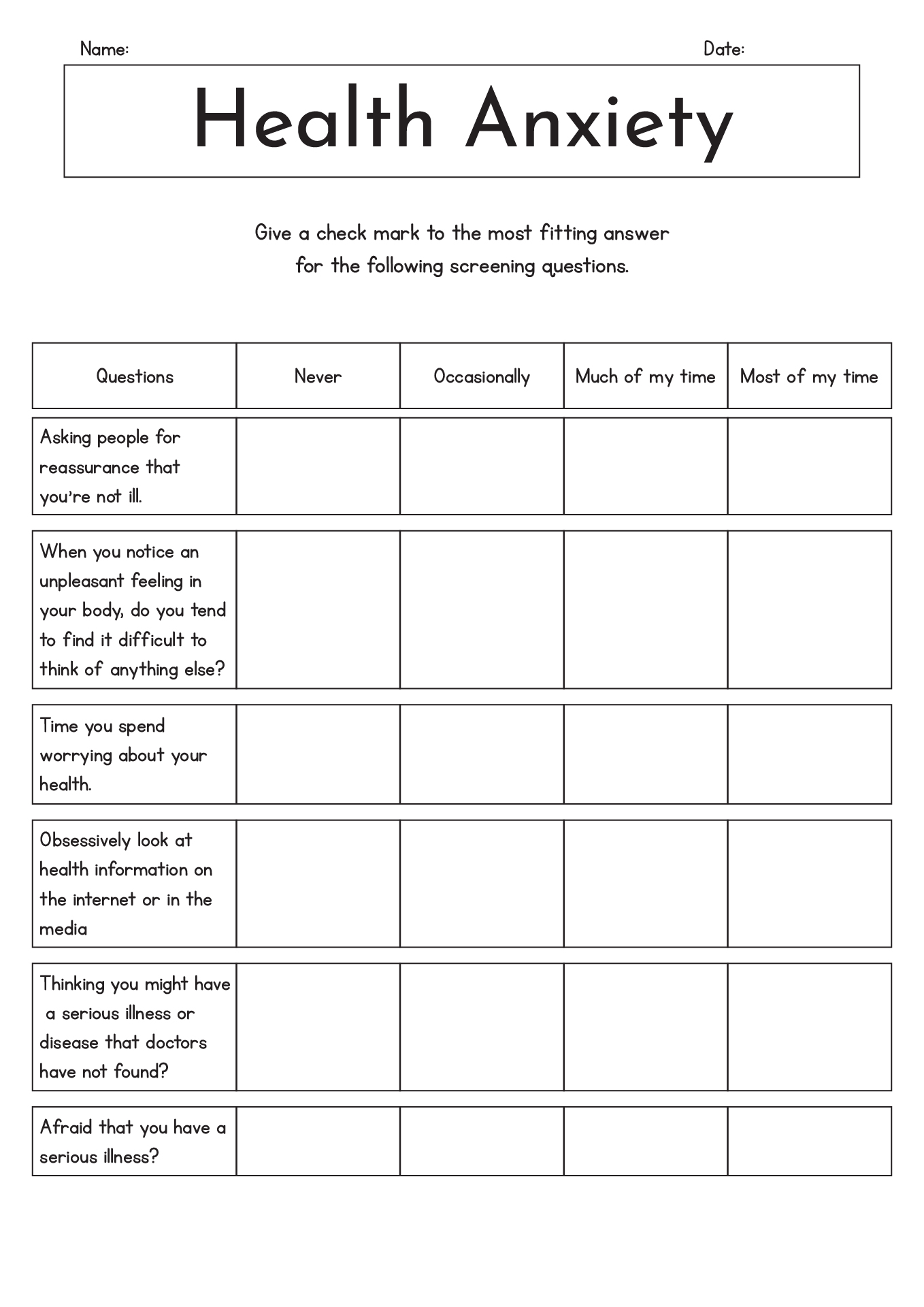
- Health Anxiety Worksheets
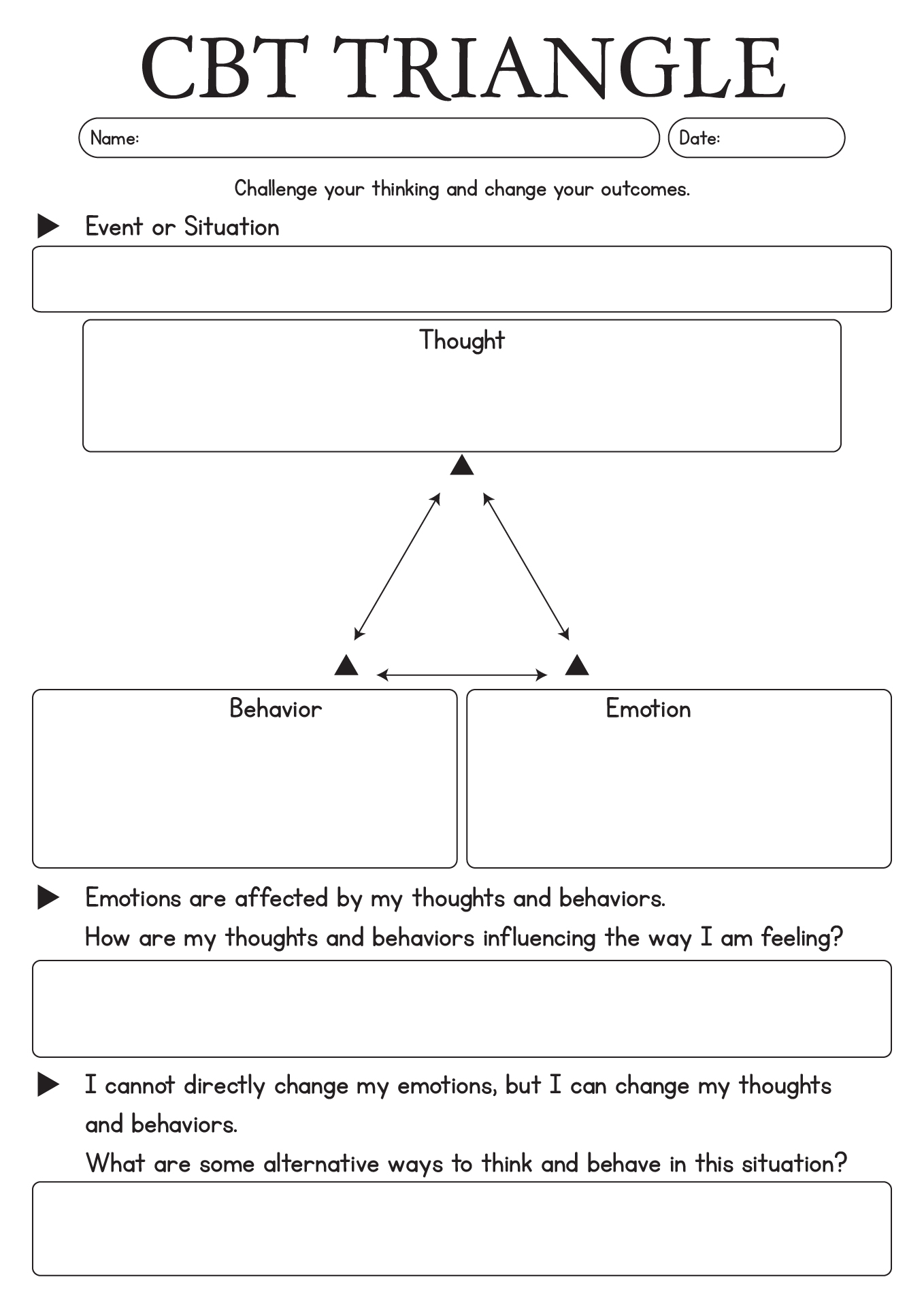
- Thought Feeling Behavior Triangle Worksheet
- Coping with Disappointment Worksheet
- Child Anxiety Worksheets CBT
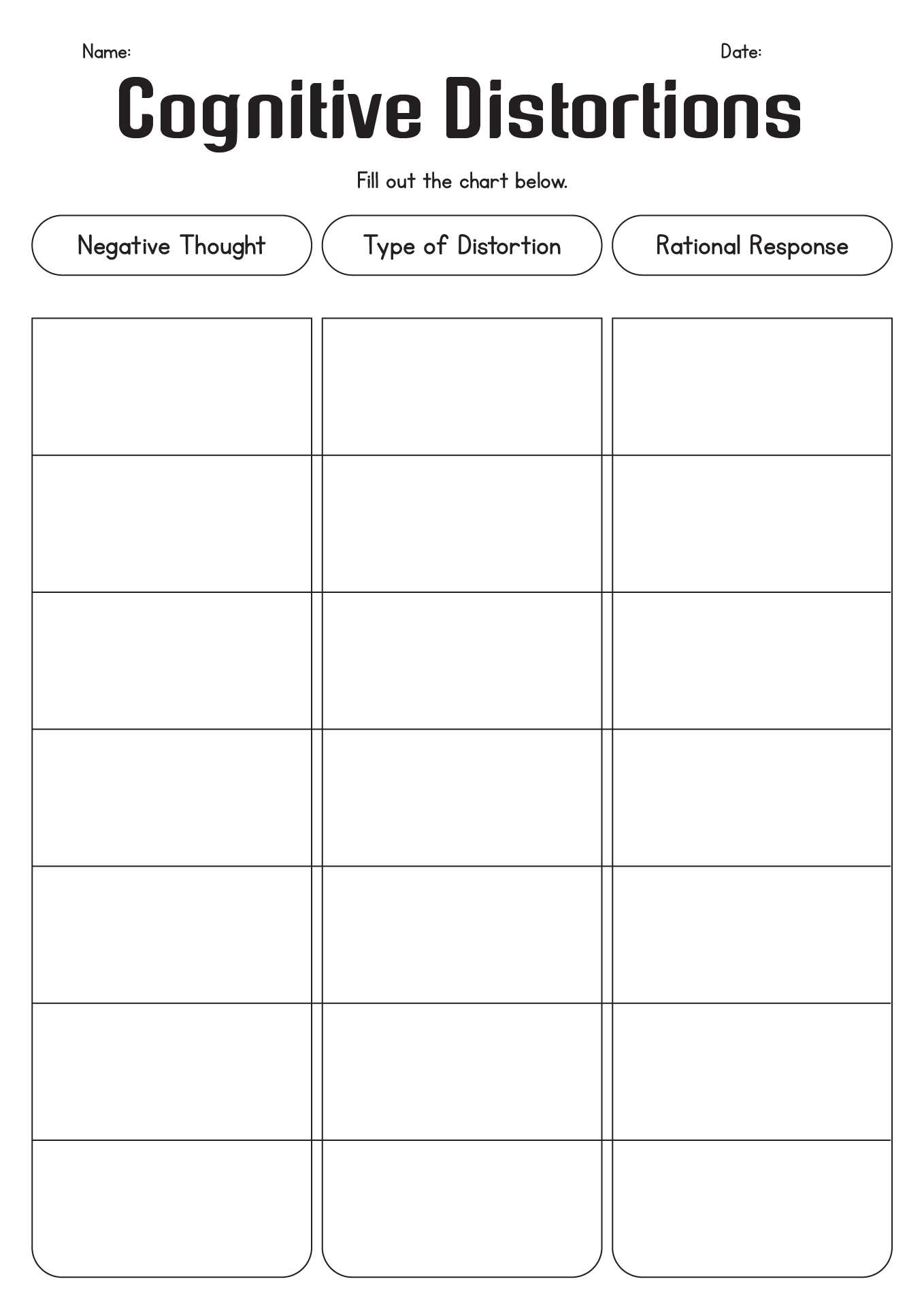
- Challenging Cognitive Distortions Worksheet
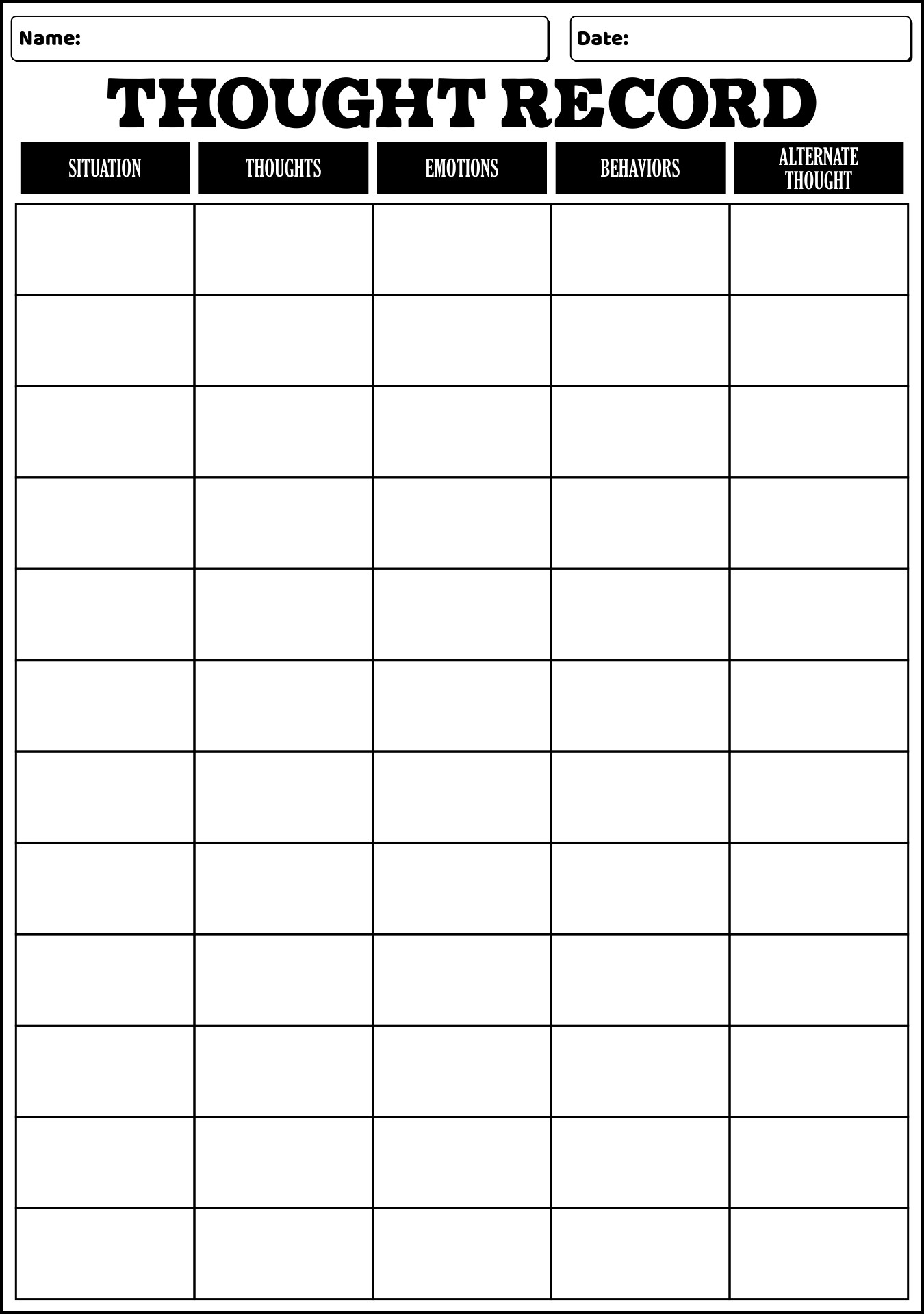
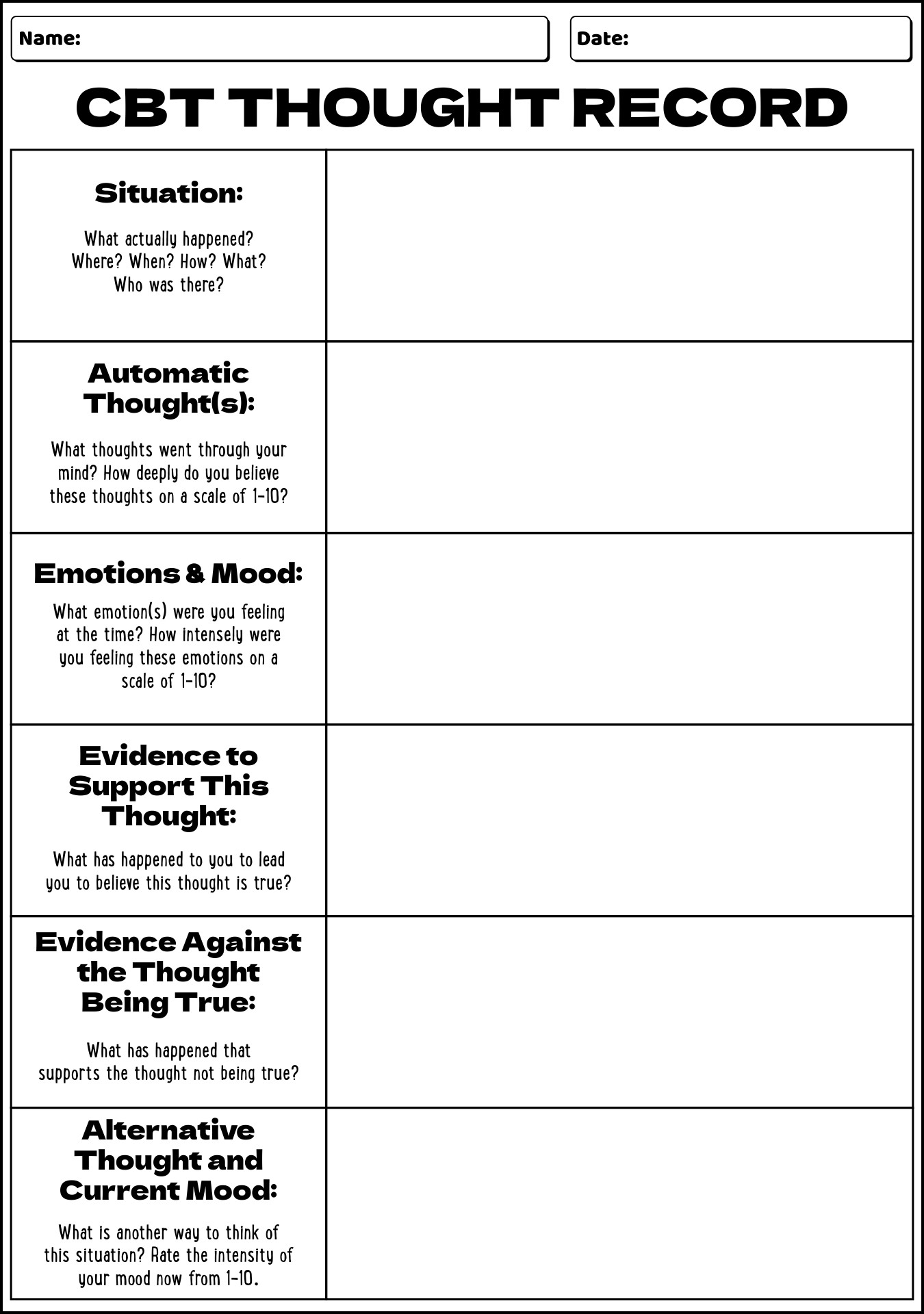
- CBT Thought Record Template
- Cognitive Behavioral Worksheets for Anxiety
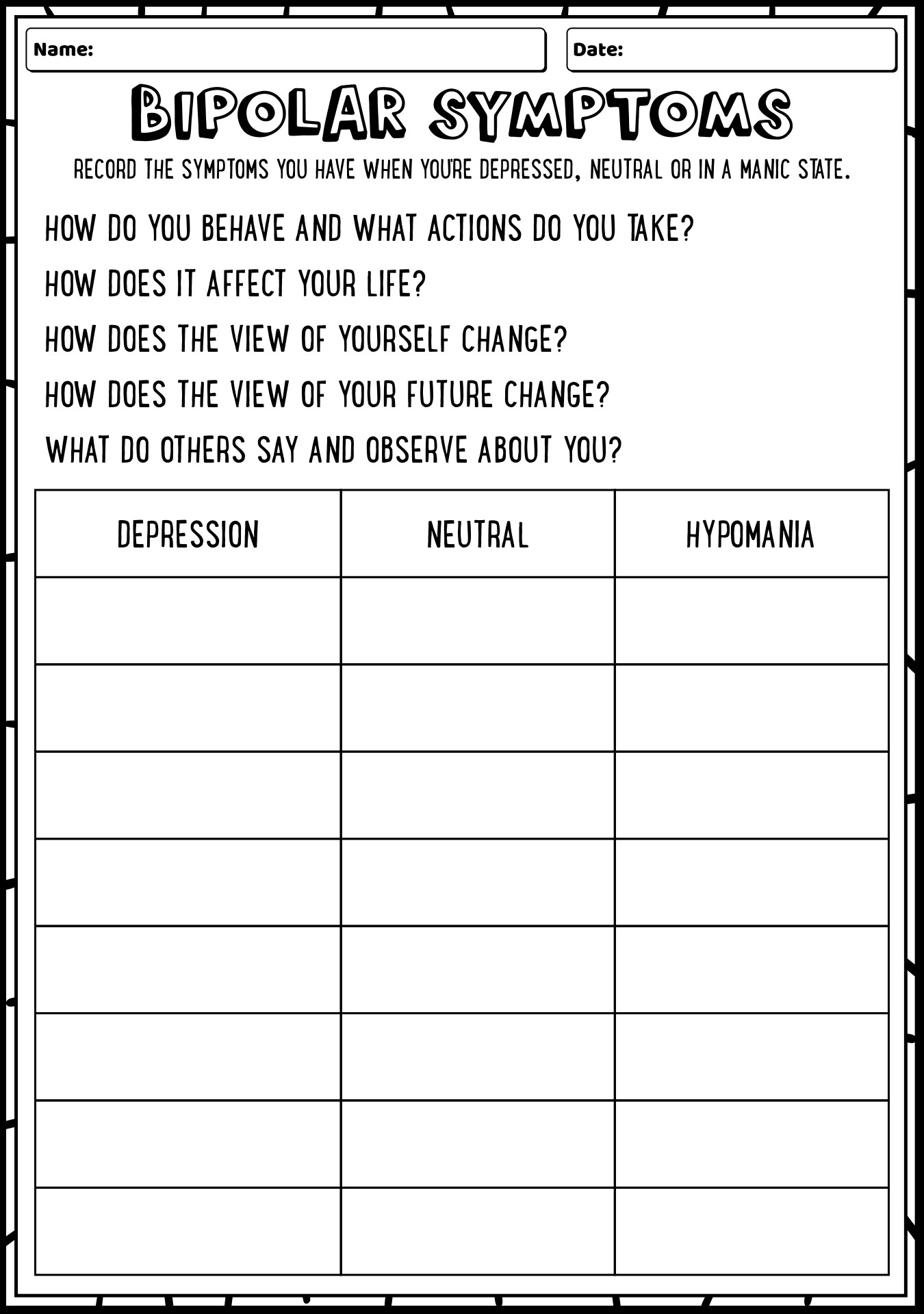
- Bipolar Disorder Worksheets
- Thoughts and Feelings Worksheets
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Worksheets
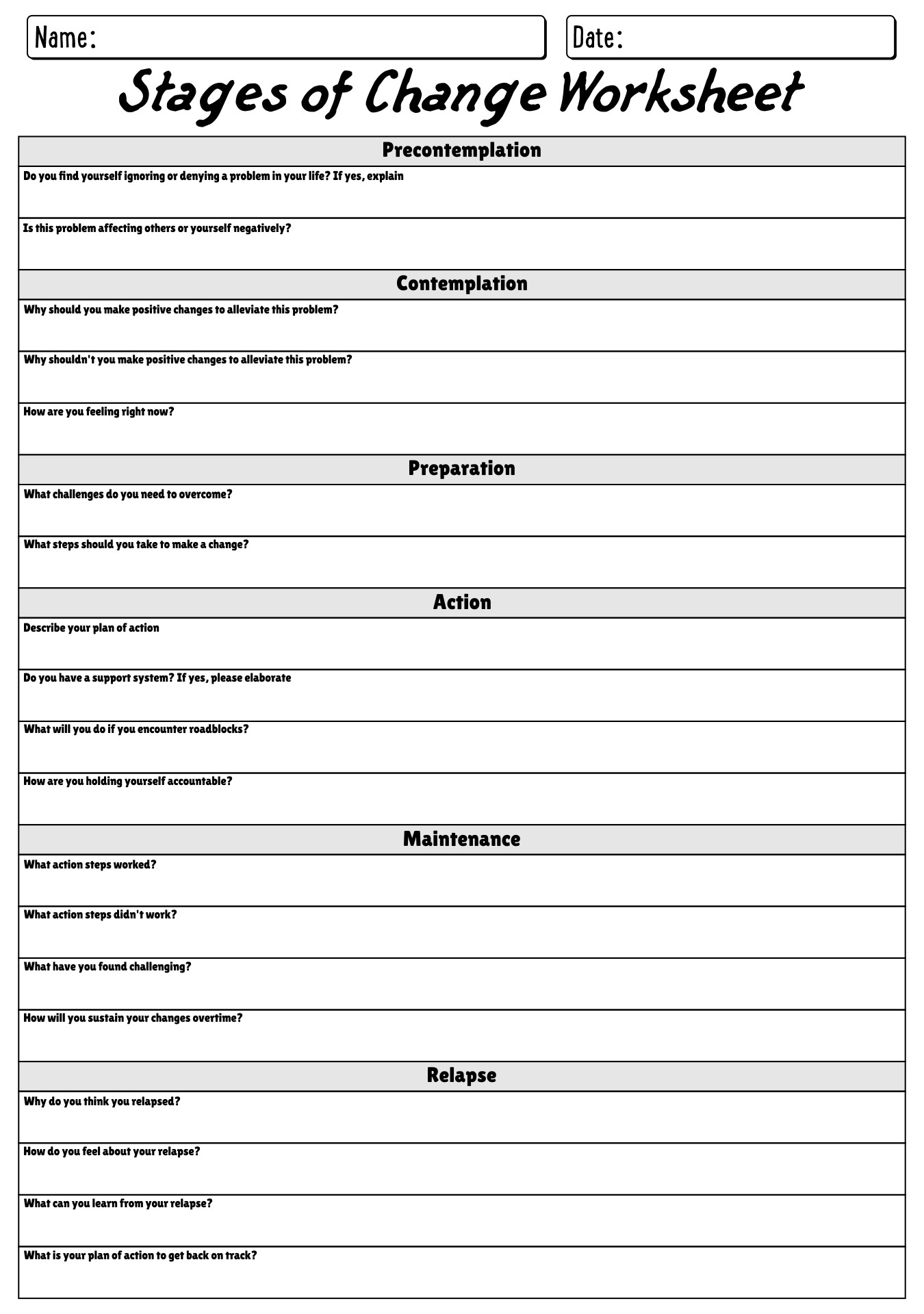
- Stages of Change Motivational Therapy
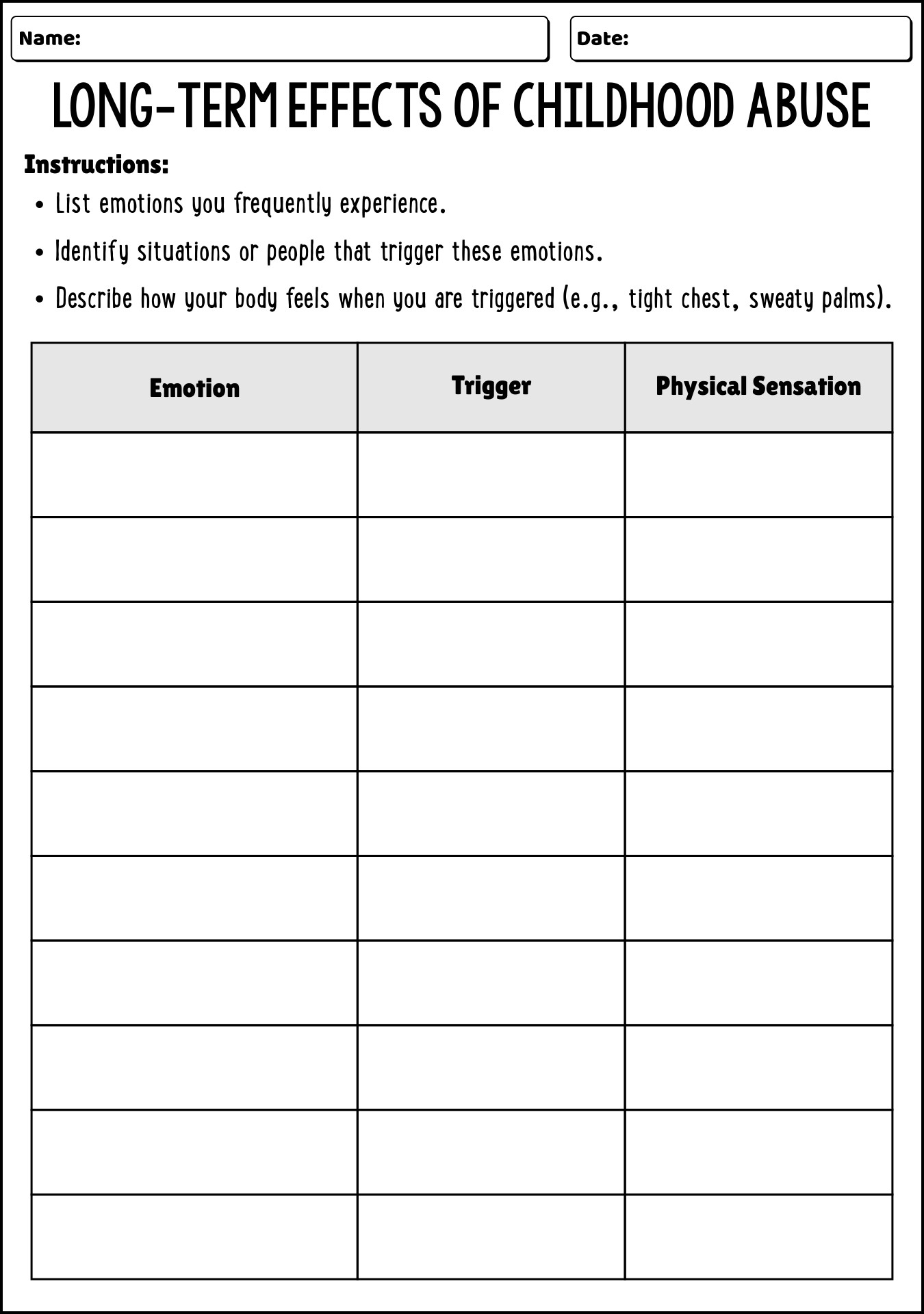
- Childhood Effects Long-Term Abuse Worksheets
- Automatic Thought Record Worksheet
- Automatic Thought Record Worksheet
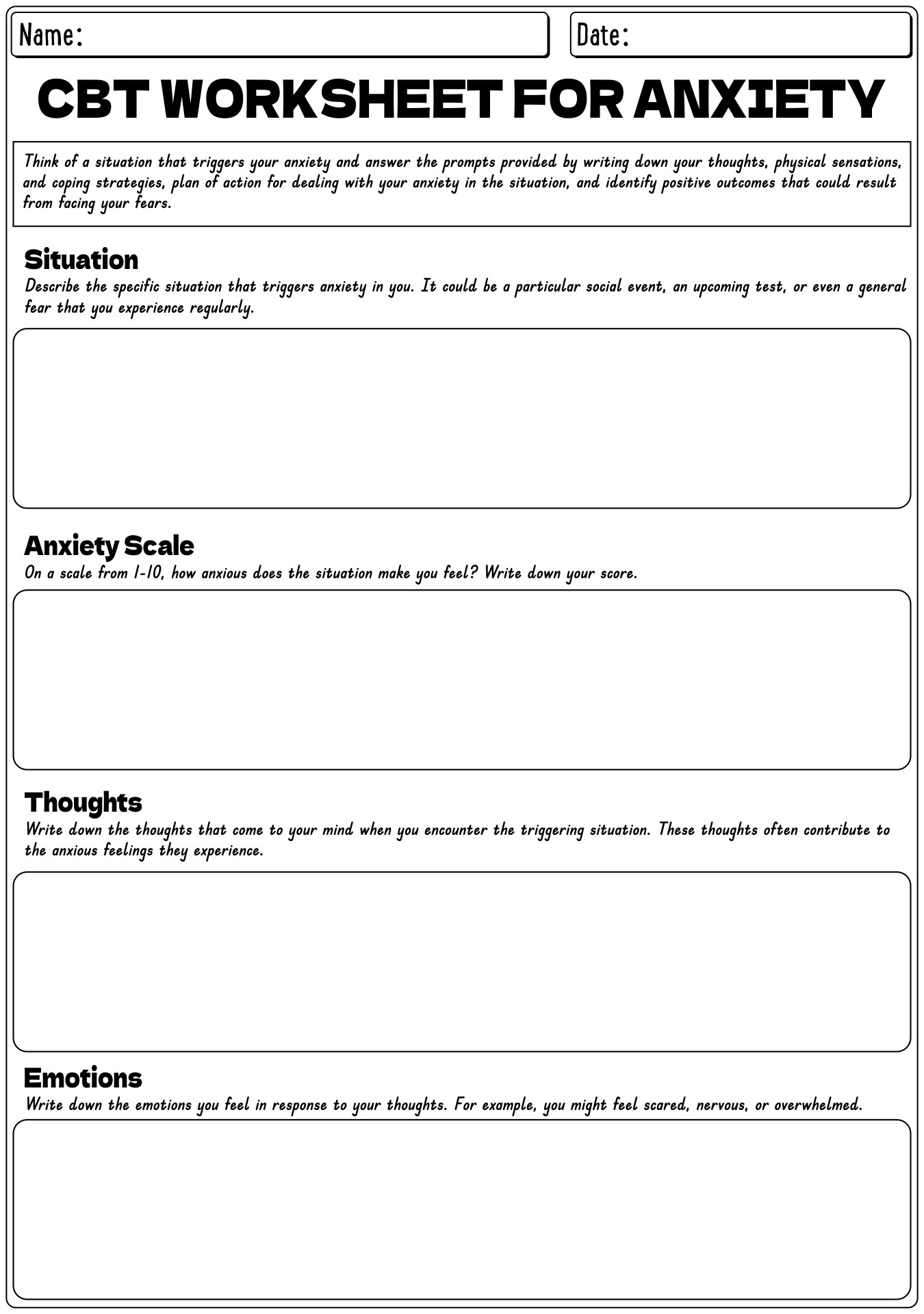
- Anxiety CBT Practice Worksheets
- CBT Task Sheets For Anxiety Reduction

Managing anxiety can be challenging, but our Anxiety CBT Worksheets provide effective tools and strategies to help you cope.
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to mental health issues. It is based on the idea that our thoughts and beliefs influence our emotions and behaviors. Through CBT, individuals learn to challenge and reframe harmful thoughts, develop coping strategies, and change unhealthy behaviors to improve their mental well-being.
How does CBT help in managing anxiety?
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps in managing anxiety by teaching individuals to identify and challenge negative thought patterns and beliefs that contribute to their anxiety. Through CBT, individuals learn coping strategies and techniques to modify their behavior and responses to anxiety-provoking situations. By addressing both the cognitive and behavioral aspects of anxiety, CBT helps individuals develop more adaptive ways of thinking and responding, ultimately reducing their anxiety symptoms and improving their overall quality of life.
What are some common anxiety CBT worksheets used in therapy?
Some common anxiety CBT worksheets used in therapy include thought records, activity schedules, exposure hierarchies, and cognitive restructuring worksheets. Thought records help individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns, while activity schedules help them track daily activities to understand patterns that may impact anxiety. Exposure hierarchies are used to gradually expose individuals to feared situations to reduce anxiety, and cognitive restructuring worksheets help challenge and reframe irrational beliefs contributing to anxiety symptoms.
How do thought records assist in identifying and challenging anxious thoughts?
Thought records assist in identifying and challenging anxious thoughts by prompting individuals to document the specific situations or triggers that lead to anxious thoughts, the automatic negative beliefs that arise, the emotions experienced, and the behavioral responses. By breaking down these components, individuals can gain insight into their thought patterns, recognize distortions or irrational beliefs, and challenge them by replacing them with more balanced and realistic interpretations. This process helps individuals develop a more accurate and rational perspective, reduce anxiety, and ultimately change their response to triggering situations.
What is the purpose of exposure hierarchies in CBT?
Exposure hierarchies in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) are used to systematically expose individuals to anxiety-provoking situations in a gradual and controlled manner. The purpose of exposure hierarchies is to help clients confront and overcome their fears by facing them in a structured way, enabling them to learn that the feared situation is not as dangerous or harmful as they initially believed. This process helps to desensitize individuals to their anxiety triggers and build confidence in their ability to manage and cope with their fears.
How do relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, aid in managing anxiety?
Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, aid in managing anxiety by activating the body's relaxation response and reducing the body's natural stress response. Deep breathing helps to slow down the heart rate, lower blood pressure, and decrease cortisol levels, all of which contribute to calming the mind and body. By focusing on controlled breathing, individuals can shift their focus away from anxious thoughts and bring their attention to the present moment, promoting a sense of calm and reducing feelings of anxiety.
What are the benefits of using activity scheduling worksheets for anxiety?
Activity scheduling worksheets can be beneficial for managing anxiety by helping individuals track and plan their daily activities, which can provide structure and routine to their day. It can help in identifying patterns or triggers that may contribute to anxiety, as well as setting goals and incorporating enjoyable and relaxing activities to reduce stress levels. By engaging in planned activities, individuals can experience a sense of accomplishment, increased self-esteem, and a distraction from anxious thoughts, ultimately promoting better mental well-being.
How do you use behavioral experiments to challenge anxious beliefs?
Behavioral experiments are used in cognitive behavioral therapy to challenge anxious beliefs by encouraging individuals to test the accuracy of their beliefs through real-life experiences. This involves designing structured activities that allow individuals to confront their fears or anxieties in a safe and controlled manner, providing an opportunity to gather evidence that may support or disconfirm their beliefs. By engaging in these experiments, individuals can often realize that their anxious beliefs are not as logical or realistic as they once thought, leading to a shift in thinking and a reduction in anxiety.
What are some strategies for dealing with avoidance behaviors in anxiety?
Some strategies for dealing with avoidance behaviors in anxiety include gradually exposing oneself to feared situations or stimuli through a process known as systematic desensitization, challenging negative thoughts and beliefs through cognitive-behavioral therapy, incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or mindfulness to manage anxiety symptoms, and seeking support from a therapist or counselor to develop coping strategies and address underlying issues contributing to avoidance behaviors. It's important to take small steps, be patient with oneself, and celebrate progress along the way.
How does CBT help in developing coping skills for long-term anxiety management?
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps in developing coping skills for long-term anxiety management by targeting negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. Through CBT, individuals learn to identify and challenge irrational thoughts, reframe negative beliefs, and develop effective coping strategies such as relaxation techniques, problem-solving skills, and gradually facing feared situations. By changing their thought patterns and behaviors, individuals can reduce anxiety symptoms and build resilience to better manage anxiety in the long term.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments