Aerobic Respiration Worksheet Answer Key
Are you a biology teacher or student searching for the answer key to an aerobic respiration worksheet? Look no further! We have compiled a comprehensive and accurate answer key specifically tailored to help you understand the complexities of aerobic respiration. This worksheet will enhance your understanding of the topic and assist you in assessing your knowledge and progress.
Table of Images 👆
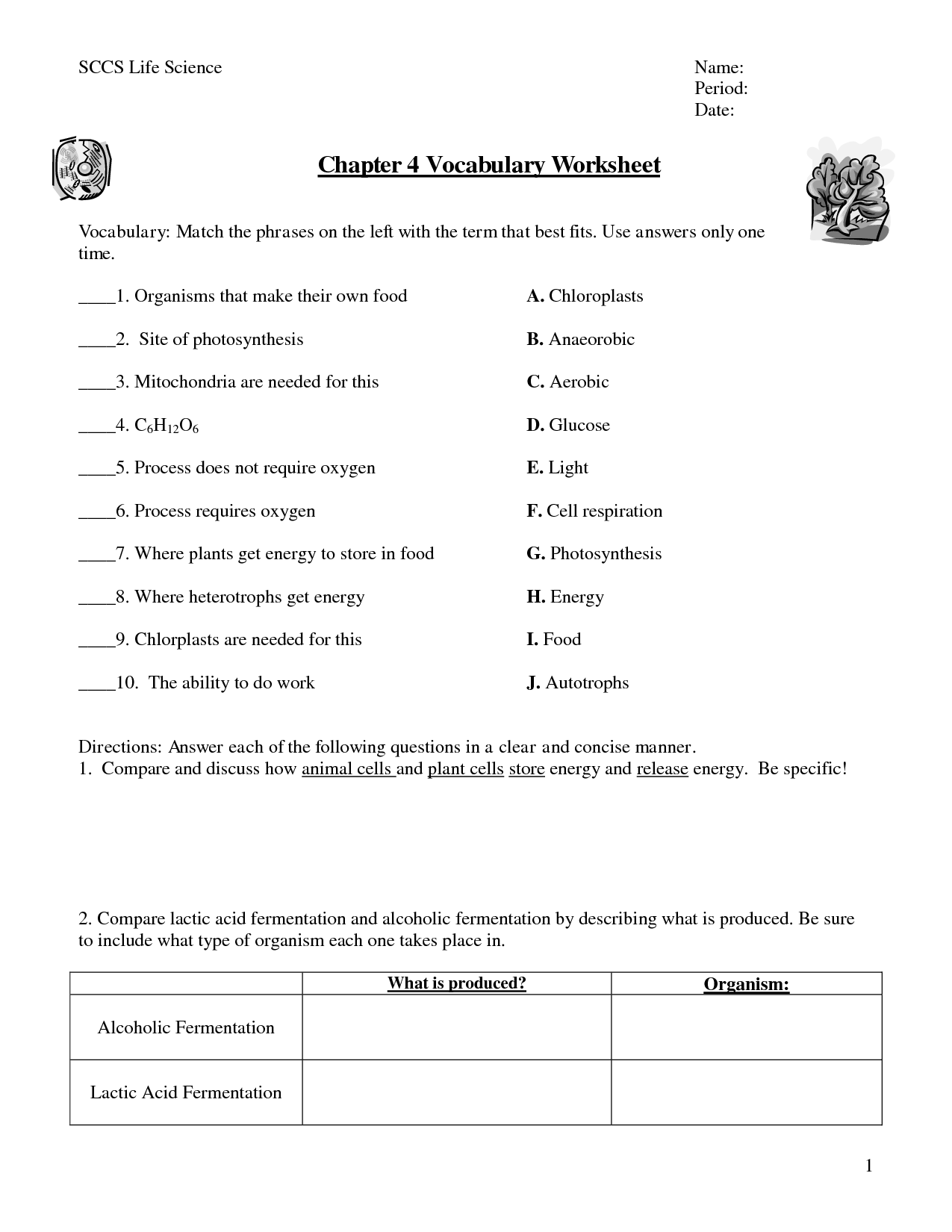
- Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answer Key
- Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Circulatory System Worksheet Answer Key
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Section 8 1 Review Answer Key
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers Crossword Puzzle
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Fill in the Blank Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Cellular Respiration Worksheets and Answers
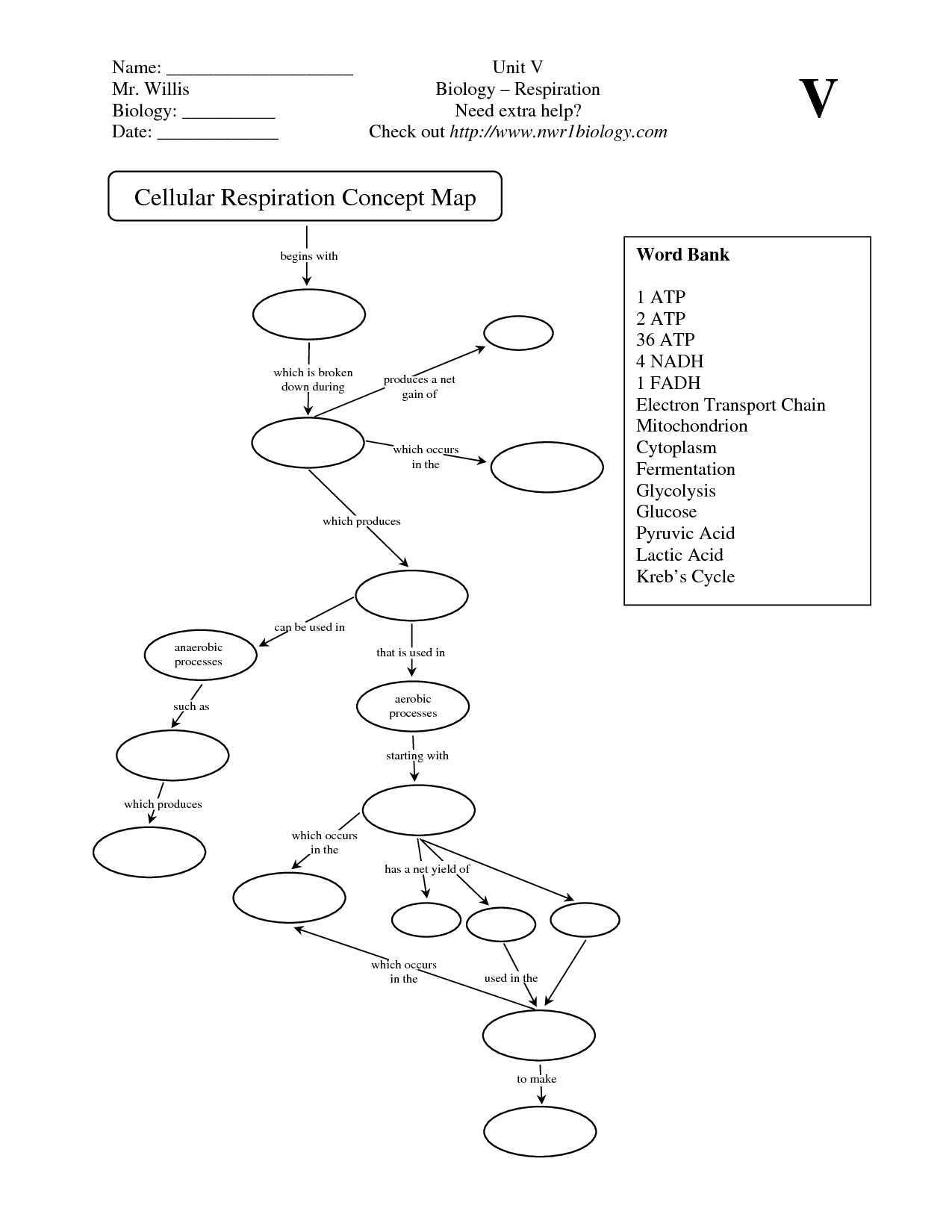
- Cellular Respiration Concept Map Worksheet
- Cellular Respiration Flow Chart
- Metabolism Worksheet Answers
- Cellular Respiration WebQuest Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is the process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy, carbon dioxide, and water. This process involves the series of biochemical reactions that take place in the mitochondria of cells and is the most efficient way for organisms to harvest energy from the food they consume.
What is the main purpose of aerobic respiration?
The main purpose of aerobic respiration is to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the process of breaking down glucose in the presence of oxygen. This process occurs in the mitochondria of cells and is essential for providing the energy needed for various cellular functions and activities.
Which organelle is primarily responsible for aerobic respiration in eukaryotic cells?
The mitochondria is primarily responsible for aerobic respiration in eukaryotic cells.
How many ATP molecules are produced during aerobic respiration?
During aerobic respiration, a total of 36-38 ATP molecules are produced from one molecule of glucose through the processes of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation in the presence of oxygen.
What are the three main stages of aerobic respiration?
The three main stages of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation (or electron transport chain). Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and breaks down glucose to produce pyruvate and a small amount of ATP. Pyruvate then enters the mitochondria where it is further oxidized in the citric acid cycle to generate more ATP and electron carriers. Finally, in oxidative phosphorylation, the majority of ATP is produced through the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis, utilizing the electron carriers produced in the previous stages.
Describe glycolysis and its role in aerobic respiration.
Glycolysis is the initial step in cellular respiration, where a molecule of glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate. This process occurs in the cytoplasm of cells and does not require oxygen. The pyruvate generated from glycolysis can then enter the citric acid cycle in aerobic respiration, where it is further broken down to release energy in the form of ATP. Overall, glycolysis plays a crucial role in producing energy for the cell by converting glucose into usable energy molecules.
What happens during the Krebs cycle?
During the Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, acetyl-CoA derived from pyruvate is oxidized to produce ATP, NADH, and FADH2. This process involves a series of enzymatic reactions that result in the release of carbon dioxide as a waste product. The cycle takes place in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and plays a key role in the production of energy through the oxidation of glucose and fatty acids.
Where does the majority of ATP synthesis occur during aerobic respiration?
The majority of ATP synthesis during aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondria, specifically within the inner mitochondrial membrane through a process called oxidative phosphorylation. This involves the electron transport chain, where electrons generated from the breakdown of glucose are passed along a series of protein complexes to create a proton gradient, ultimately driving the production of ATP by ATP synthase.
How is oxygen involved in aerobic respiration?
Oxygen is essential for aerobic respiration as it serves as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. During aerobic respiration, glucose is broken down in the presence of oxygen to produce energy in the form of ATP. Oxygen plays a crucial role in this process by accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain, allowing for the production of a significant amount of ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Without oxygen, aerobic respiration cannot occur efficiently, resulting in a much lower yield of ATP production.
What are some examples of organisms that rely on aerobic respiration for energy production?
Examples of organisms that rely on aerobic respiration for energy production include humans, plants, most animals, and fungi. These organisms use oxygen to break down glucose into carbon dioxide, water, and ATP, which is then used as the primary source of energy for cellular functions and processes.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments