8th Grade Science Vocabulary Worksheets
Science students in 8th grade can enhance their understanding of key concepts with the help of carefully designed vocabulary worksheets. These worksheets focus on scientific terminology and offer a comprehensive review of important terms and their definitions. By reinforcing their knowledge of science vocabulary, students will become more confident in their grasp of subject matter and better prepared for quizzes, tests, and classroom discussions.
Table of Images 👆
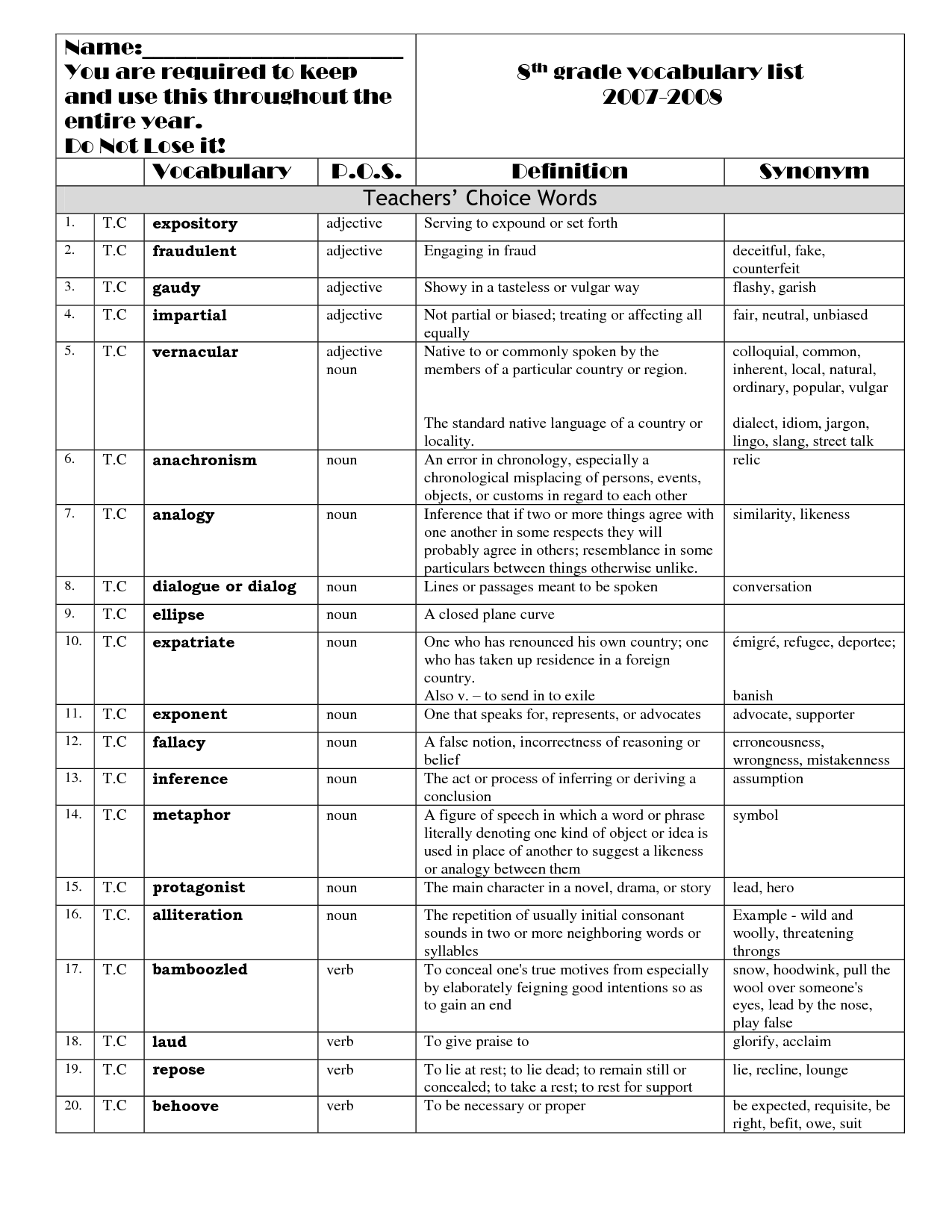
- 8th Grade Science Vocabulary Words
- 8th Grade Vocabulary Words Worksheet
- 8th Grade Science Worksheets
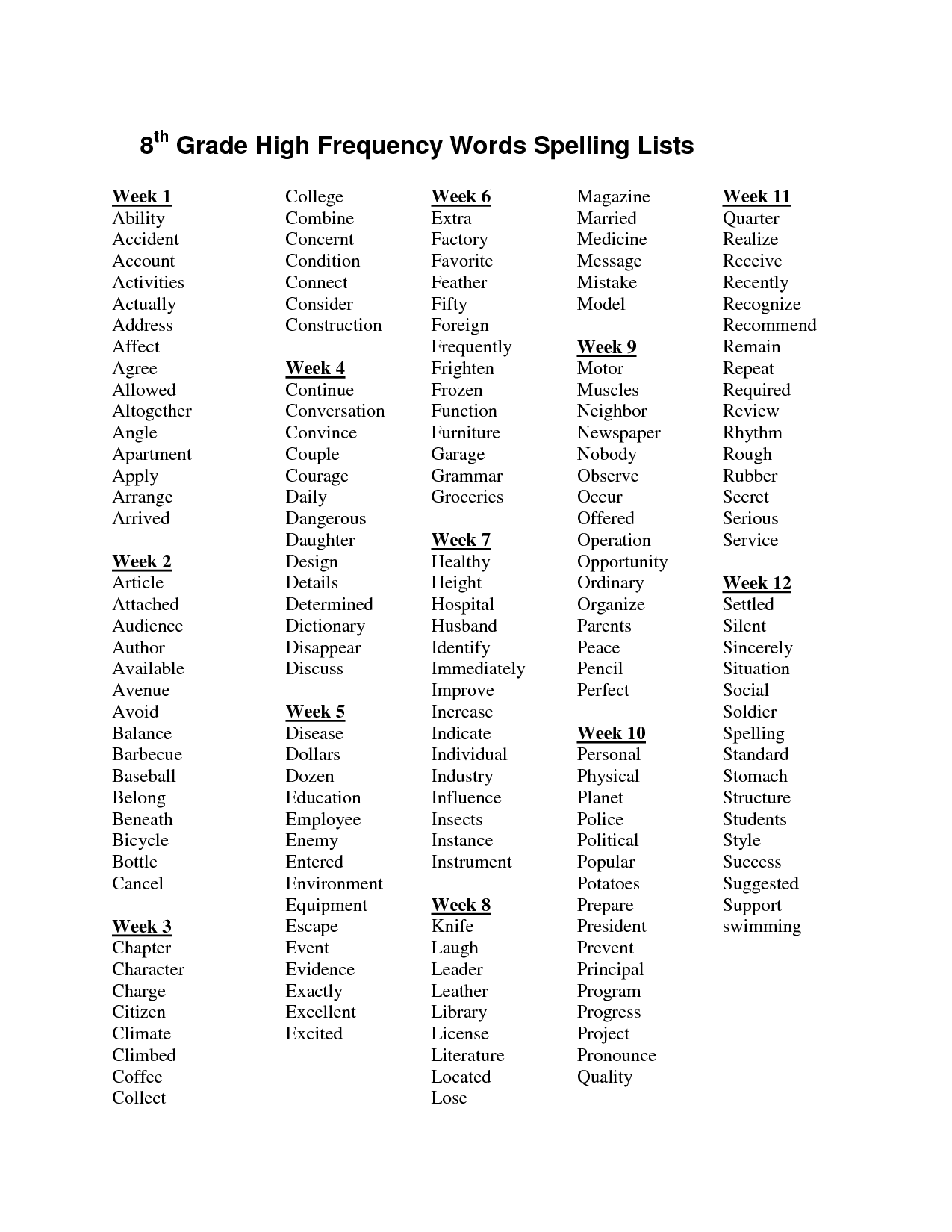
- 8th Grade High Frequency Words
- 8th Grade Vocabulary Word List
- 8th Grade Science Vocabulary Words
- Science Matter Worksheets for 8th Grade
- 8th Grade Science Vocabulary Words
- 8th Grade Science Worksheets
- Free Worksheets for 8th Grade Science Solar System
More 8th Grade Worksheets
8th Grade Spelling Worksheets8th Grade Worksheets Homeschooling
8th Grade Vocabulary Worksheets
Rotations Worksheet 8th Grade
What is the definition of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy, usually from the sun, into chemical energy stored in glucose or other organic compounds. This process involves the absorption of carbon dioxide and water, facilitated by chlorophyll and other pigments, to produce oxygen as a byproduct.
What are the three states of matter?
The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
Explain the concept of Newton's first law of motion.
Newton's first law of motion, also known as the law of inertia, states that an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion with a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force. In other words, an object will not change its state of motion unless a force is applied to it. This law highlights the concept of inertia, which is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its velocity.
What is the difference between potential and kinetic energy?
Potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position or configuration, such as when an object is lifted off the ground, while kinetic energy is the energy of motion, such as when an object is moving. In essence, potential energy is stored energy that has the potential to do work, while kinetic energy is the energy of an object in motion.
Describe the water cycle.
The water cycle is a continuous process through which water circulates on Earth. It begins with evaporation of water from oceans, lakes, and rivers due to heat from the sun, turning it into water vapor that rises into the atmosphere. As the vapor cools, it condenses into clouds. When the clouds become heavy with water droplets, precipitation occurs in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail, returning water to Earth's surface. This water then flows into rivers, lakes, or oceans, where the cycle begins again.
What is the structure and function of a cell membrane?
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell and separates its internal environment from the external environment. It is composed of a double layer of phospholipids with embedded proteins, forming a fluid mosaic structure. The main function of the cell membrane is to regulate the passage of substances in and out of the cell, allowing necessary molecules to enter while keeping unwanted molecules out. It also helps maintain cell shape and integrity, as well as facilitating cell-to-cell communication and signaling.
Explain the process of mitosis.
Mitosis is a type of cell division where a single cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells. The process involves several stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down. In metaphase, chromosomes align at the cell's equator. Anaphase sees the separated sister chromatids move to opposite ends of the cell. Finally, in telophase, new nuclear envelopes form around the separated chromosomes. Cytokinesis involves the division of the cell's cytoplasm to create two new daughter cells, each with a complete set of chromosomes.
Define density and how it is calculated.
Density is a physical property of a substance that is defined as the mass of an object per unit volume. It is calculated by dividing the mass of an object by its volume. The formula for density is: Density = Mass / Volume. The units of density are typically expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) for solids and liquids, and in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) for gases.
What is the role of enzymes in biological reactions?
Enzymes serve as biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms by lowering the activation energy required for the reactions to occur. They are specific to particular substrates and help convert them into products efficiently. Enzymes play a crucial role in various biological processes, such as digestion, metabolism, and cell signaling, by facilitating reactions without being consumed in the process.
Describe the process of digestion in the human body.
Digestion in the human body begins in the mouth, where food is physically broken down by chewing and mixed with saliva containing enzymes that start the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates. The food then moves down the esophagus to the stomach, where it is further broken down by stomach acid and enzymes. From the stomach, partially digested food enters the small intestine where additional enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver further break down nutrients. Nutrients are absorbed through the small intestine wall into the bloodstream, while waste products pass into the large intestine for further processing before being eliminated from the body.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments