7th Grade Science Worksheets On Cells
Are you a 7th-grade student learning about cells in your science class? If so, you may be on the lookout for some helpful worksheets to reinforce your understanding of this important topic. Look no further! In this blog post, we will explore a variety of 7th-grade science worksheets specifically focusing on cells, designed to aid in your learning journey.
Table of Images 👆
- 7th Grade Life Science Cells Worksheet
- Free 7th Grade Science Worksheets
- 7th Grade Science Worksheets
- 7th Grade Life Science Worksheets
- 7th Grade Science Worksheets
- Cell Organelles 7th Grade Worksheets
- 7th Grade Life Science Test
- 5th Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
- Cell Organelles and Functions Worksheet
- Plant and Animal Cell Worksheets 7th Grade
- 7th Grade Life Science Worksheets
- Cell Organelles and Functions Worksheet
- Photosynthesis 7th Grade Science Worksheet Answers
- 7th Grade Cell Worksheets
- 7th Grade Physical Science Worksheets
- 7th Grade Science Chart
- 7th Grade Life Science Cells Worksheet
More 7th Grade Worksheets
7th Grade Math Worksheets with Answer Key7th Grade Vocabulary Worksheets
Pre-Algebra 7th Grade Math Worksheets
7th Grade Math Worksheets Proportions
Complex Sentence Worksheets 7th Grade
Geometry Angles Worksheet 7th Grade Math
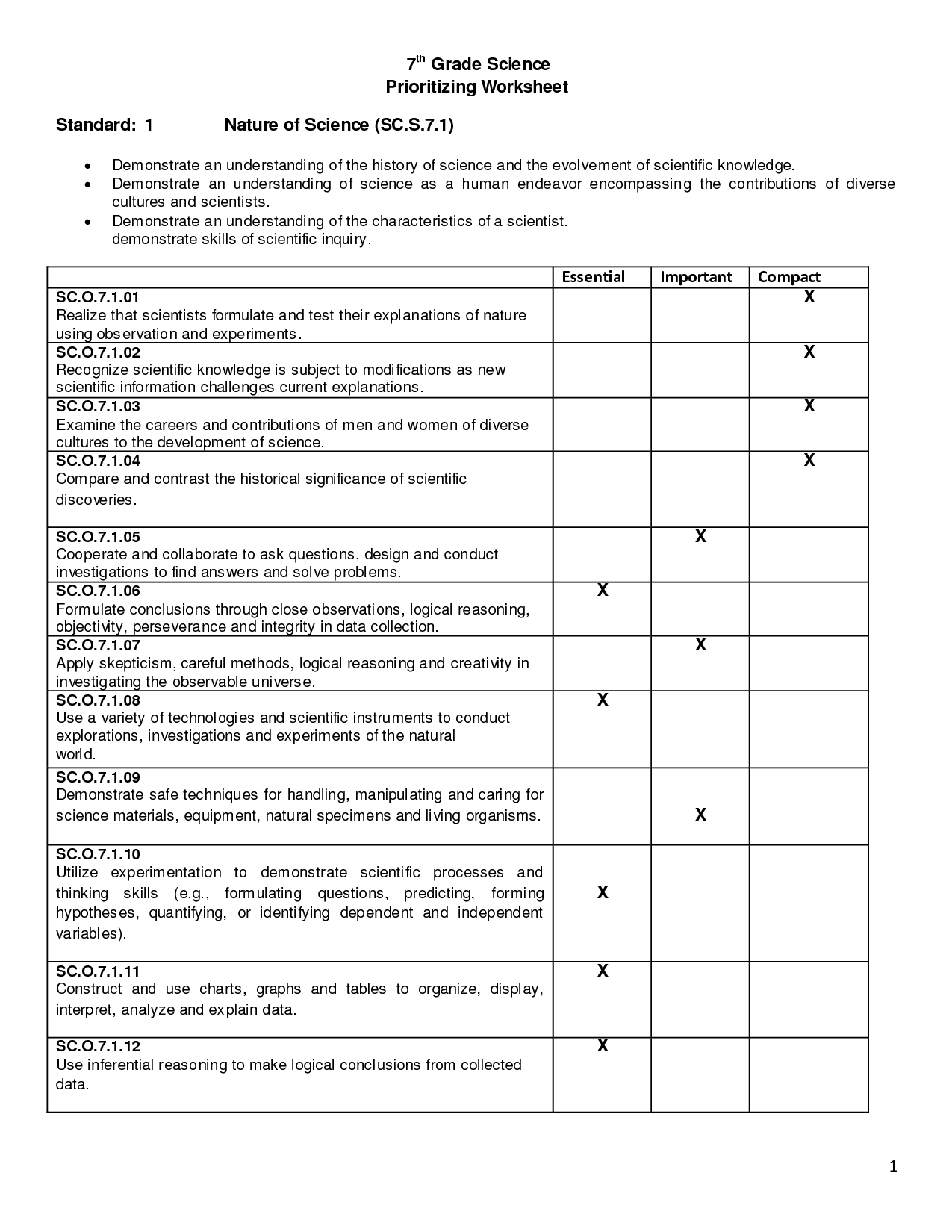
What are cells?
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of all living organisms. They contain genetic material, proteins, and other molecules that allow them to perform various biological functions, such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism. Cells can be simple, like bacteria, or complex, like human cells that are specialized to perform specific tasks in different tissues and organs.
What is the basic unit of life?
The basic unit of life is the cell. Cells are the smallest functional units of living organisms that carry out essential functions to sustain life, such as obtaining nutrients, replicating genetic material, and producing energy. These building blocks of life have different structures and functions depending on the type of organism they belong to.
What are the two main types of cells?
The two main types of cells are prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, and eukaryotic cells, which have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
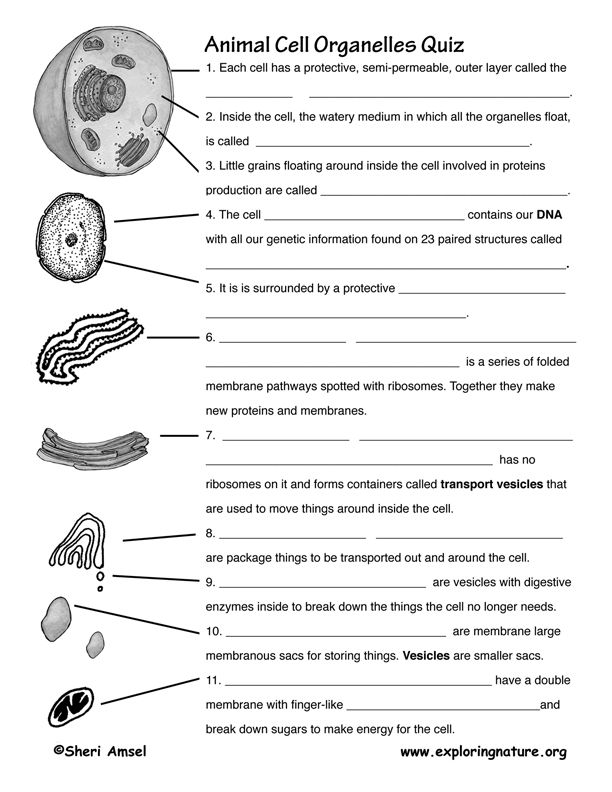
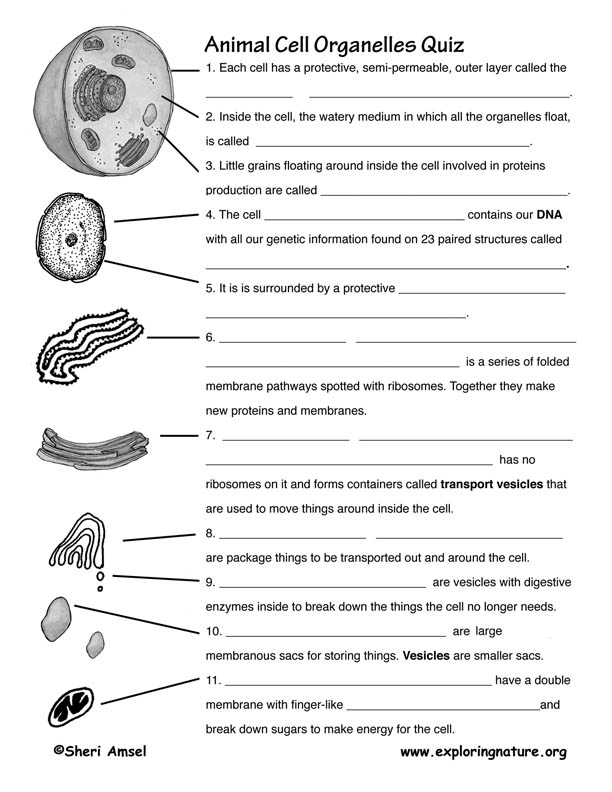
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane acts as a semi-permeable barrier that surrounds and protects the cell, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell. It allows for the transportation of essential nutrients into the cell, the removal of waste products, and the maintenance of the cell's internal environment. Additionally, the cell membrane plays a role in cell communication and signal transduction, allowing cells to interact with their environment and other cells.
What is the role of the nucleus in a cell?
The nucleus is a key organelle in a cell that serves as the control center, housing the cell's genetic material in the form of DNA. It regulates gene expression, controls cellular functions, and is responsible for the replication and transmission of genetic information during cell division. Additionally, the nucleus is essential for synthesizing important molecules like RNA and regulating the overall growth and metabolism of the cell.
What are mitochondria and why are they important in cells?
Mitochondria are membrane-bound organelles found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's main energy source, through cellular respiration. They play a crucial role in producing energy for various cellular activities, such as metabolism, growth, and cell division. Additionally, mitochondria are involved in regulating cell signaling, controlling cell cycle, and triggering apoptosis, making them essential for the overall functioning and survival of the cell.
How do cells obtain energy?
Cells obtain energy through a process called cellular respiration, where they break down nutrients such as glucose to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy currency of cells. This process involves three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, which occur in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the cell. The ATP produced is used to power various cellular activities and processes essential for cell function and survival.
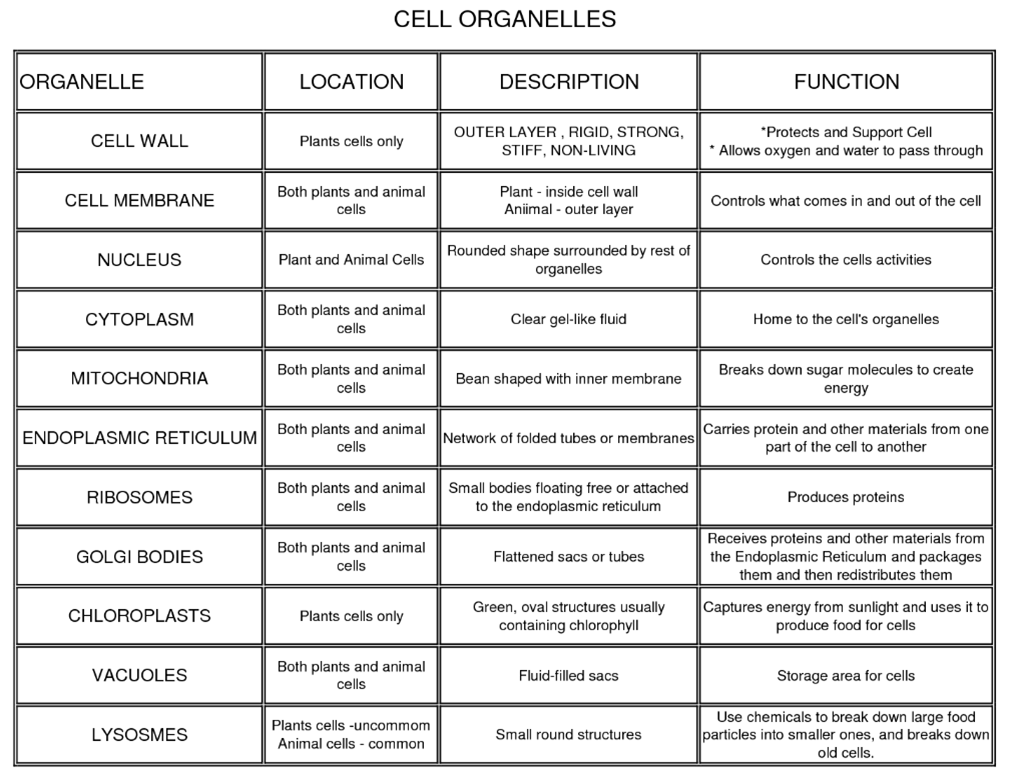
What is the difference between plant and animal cells?
Plant cells have cell walls composed of cellulose, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and large central vacuoles for storage, while animal cells lack cell walls and chloroplasts, and have smaller vacuoles. Plant cells also typically have a rectangular shape, while animal cells are more rounded. Additionally, plant cells can produce their own food through photosynthesis, whereas animal cells rely on external sources of food.
What are the three main parts of a plant cell?
The three main parts of a plant cell are the cell wall, the cell membrane, and the nucleus. The cell wall provides structure and support, the cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, and the nucleus contains the cell's genetic material and controls its activities.
How do cells communicate with each other?
Cells can communicate with each other through a variety of methods, such as direct cell-to-cell contact, secretion of signaling molecules like hormones or neurotransmitters, and through receptor-mediated signaling pathways. These signals can trigger a variety of responses within the receiving cell, influencing processes such as growth, differentiation, and immune responses. Overall, cell communication plays a crucial role in coordinating the activities of different cells within the body to maintain homeostasis and respond to changing environments.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments