4 Major Macromolecules Worksheet
Worksheets are an essential tool for students seeking a comprehensive understanding of the four major macromolecules. These educational resources are designed to help individuals explore the entities and subjects related to carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, allowing them to grasp the fundamental concepts required for further scientific study. Whether you are a biology student or a science enthusiast, incorporating worksheets into your learning routine can greatly enhance your knowledge in this field.
Table of Images 👆
- Macromolecule Structure Worksheet
- Macromolecules Chart Worksheet
- Molecules of Life Worksheet Answers
- Biological Macromolecules Chart
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Macromolecule Structure Worksheet
- Elements and Macromolecules in Organisms Answer Key
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Macromolecules Worksheet 2 Answer Key
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Human Digestive System Worksheet Answers
- Glucose-Fructose Sucrose
- Macromolecules Graphic Organizer Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
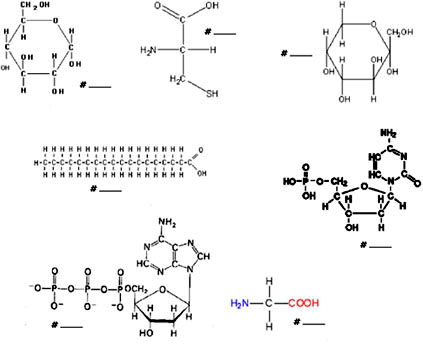
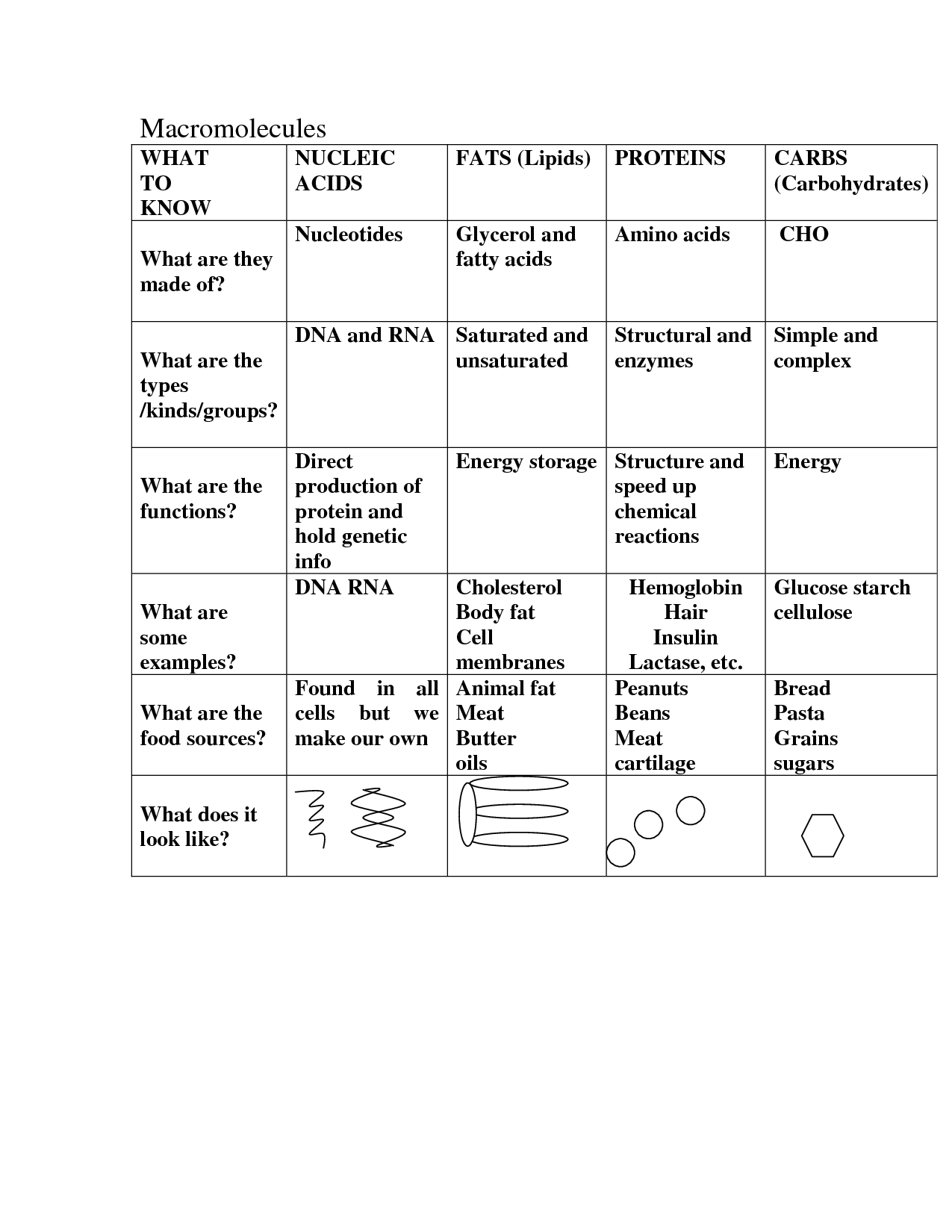
What are the four major macromolecules?
The four major macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These macromolecules are essential components of living organisms and play fundamental roles in various biological processes.
What is the primary function of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates serve as the main source of energy for the body, providing fuel for various functions and activities. They are broken down into glucose, which is then used by cells as a primary energy source for cellular processes and bodily functions. Additionally, carbohydrates play a key role in supporting brain function, maintaining muscle mass, and regulating blood sugar levels.
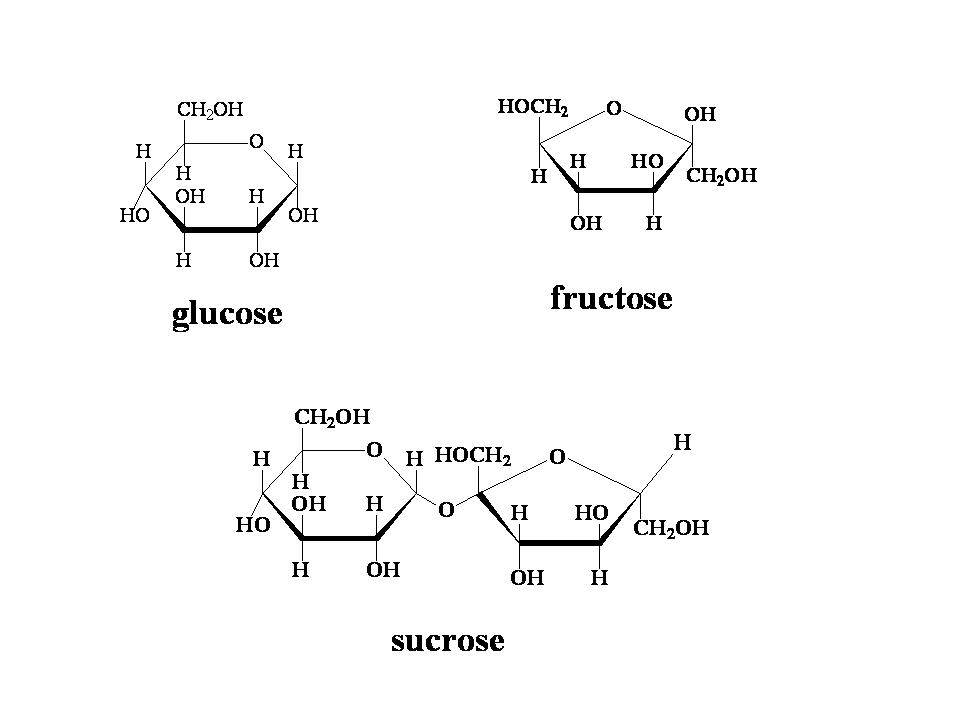
What is the structural unit of carbohydrates?
The structural unit of carbohydrates is a monosaccharide, which is a simple sugar molecule such as glucose, fructose, or galactose. These monosaccharides can combine to form more complex carbohydrates like disaccharides (two monosaccharides) or polysaccharides (many monosaccharides), which serve as important sources of energy for living organisms.
Give an example of a simple carbohydrate.
Glucose is an example of a simple carbohydrate. It is a monosaccharide that serves as a primary source of energy for the body and is found in foods like fruits, honey, and sweeteners.
What is the primary function of proteins?
The primary function of proteins is to serve as building blocks for cells, tissues, and organs in the body. Additionally, proteins play a crucial role in various physiological processes such as enzyme catalysis, immune response, transport of molecules, and structural support.
What are the building blocks of proteins?
The building blocks of proteins are amino acids. Proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids that are linked together by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain. There are 20 different amino acids that can be combined in various sequences to create the diverse range of proteins found in living organisms.
Give an example of a protein in the human body.
One example of a protein in the human body is hemoglobin, which is a protein found in red blood cells that is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body and transporting carbon dioxide back to the lungs for exhalation.
What is the primary function of lipids?
The primary function of lipids is to store energy and provide insulation in the body. Additionally, lipids play a crucial role in cell structure, hormone production, and maintaining healthy skin and hair.
What are the two types of nucleic acids?
The two types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA is the genetic material that carries hereditary information in most living organisms, while RNA is involved in various biological processes, including protein synthesis and gene expression.
What is the function of nucleic acids in cells?
Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, have crucial functions in cells including storing genetic information, transmitting genetic information during cell division and protein synthesis, regulating gene expression, and carrying out various cellular processes through their role as templates for protein synthesis. These processes are key to the growth, development, and functioning of all living organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments