12.2 the Structure of DNA Worksheet Answers
Worksheets are versatile educational tools that offer structured exercises to reinforce learning and understanding. For students seeking comprehensive resources to delve deeper into the structure of DNA, we present the 12.2 The Structure of DNA Worksheet Answers. This informative worksheet provides a clear delineation of the entity and subject, offering suitable target audiences a reliable reference for detailed insights into the intricate nature of DNA.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answers
- DNA and Replication Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure Worksheet
- Holt Biology Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Answer Key
- DNA Replication Worksheet
- DNA Structure Worksheet
- Student Exploration Gizmo Photosynthesis Lab Answer Key
- Cell Division and DNA Replication
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answers
- DNA Model Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the structure of DNA?
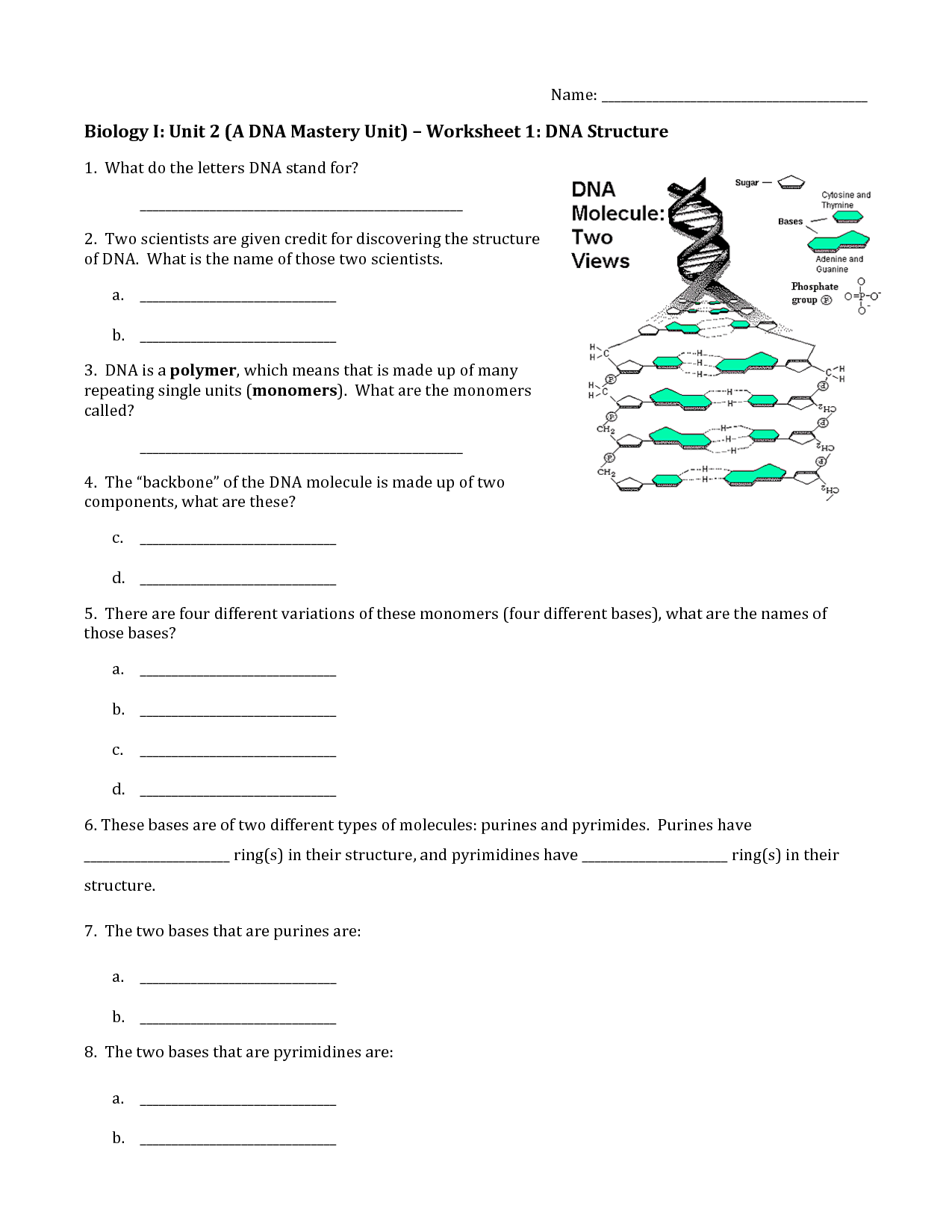
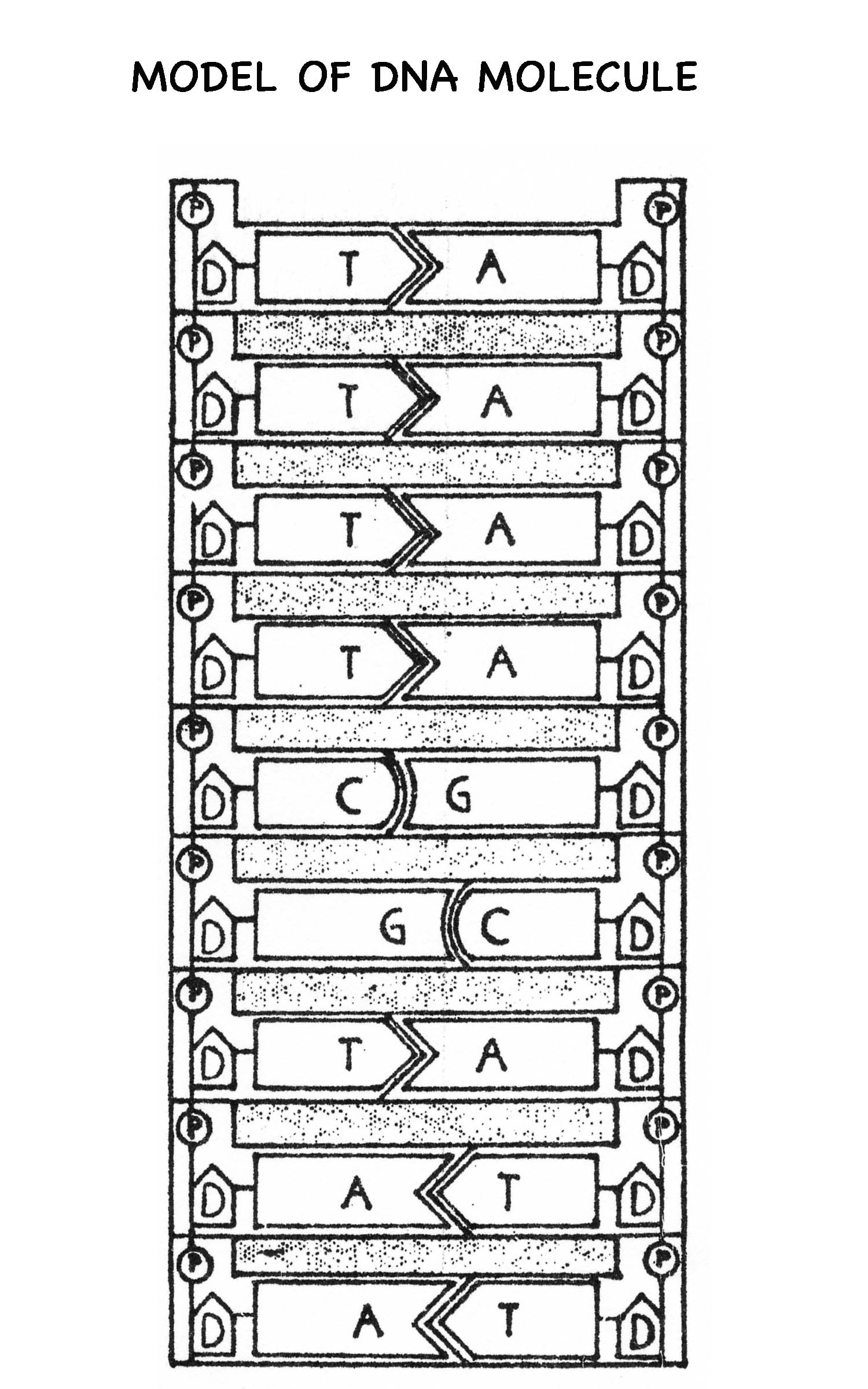
The structure of DNA consists of a double helix, comprised of two complementary strands of nucleotides that are connected by hydrogen bonds and twisted around each other. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), or thymine (T). Adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine, forming the base pairs that make up the rungs of the DNA ladder. The double helix structure of DNA allows for its replication and the transmission of genetic information.
What are the building blocks of DNA?
The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which consist of a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), or guanine (G). Each nucleotide pairs with a complementary base on the opposite strand to form the double helix structure of DNA, which carries genetic information in living organisms.
What types of nucleotides make up DNA?
There are four types of nucleotides that make up DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base (A, T, C, or G), a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), and a phosphate group. These nucleotides form the base pairs that make up the double helix structure of DNA.
What are the base pairing rules in DNA?
In DNA, the base pairing rules are adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) and cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G). This is known as complementary base pairing, where A-T and C-G form hydrogen bonds to create the double helix structure of DNA.
What holds the two strands of DNA together?
The two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary nitrogenous bases – adenine pairing with thymine and cytosine pairing with guanine. These bonds create the double-helix structure of DNA and play a crucial role in maintaining the stability and integrity of the DNA molecule.
What is the function of DNA helicase?
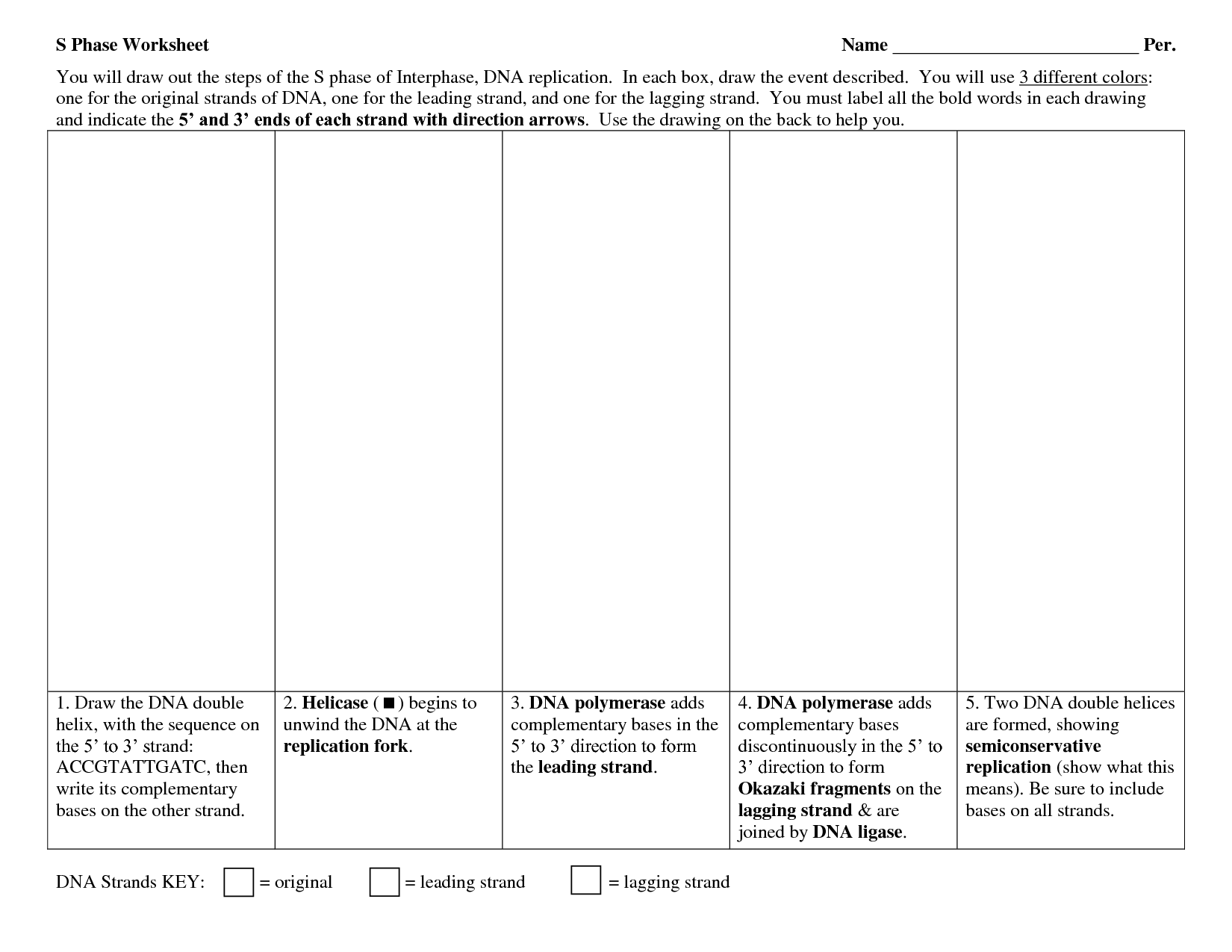
DNA helicase is responsible for unwinding the double-stranded DNA helix during processes like DNA replication, repair, and recombination. By breaking the hydrogen bonds between the two DNA strands, DNA helicase helps to separate the strands and create a replication fork where DNA polymerase and other enzymes can carry out their functions.
What is the role of DNA polymerase?
DNA polymerase plays a crucial role in DNA replication, which is the process of making an identical copy of a DNA molecule. It is responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands by adding complementary nucleotides to the existing DNA template. This enzyme ensures accurate and efficient replication of genetic material, essential for growth, development, and cell division in all living organisms.
How does DNA replication occur?
DNA replication occurs in the cell nucleus during the S phase of the cell cycle. It is a process where the double-stranded DNA molecule unwinds, and the two strands separate. Each separated strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand, resulting in two identical double-stranded DNA molecules. Enzymes such as DNA polymerase add new nucleotides to the growing strands, ensuring accurate replication of the genetic information.
What is the significance of DNA replication?
DNA replication is essential for ensuring that genetic information is accurately passed down from one generation to the next in all living organisms. This process allows cells to divide and grow, repair damaged DNA, and produce gametes for sexual reproduction. Additionally, DNA replication serves as a mechanism for genetic diversity and evolution by enabling mutations to occur during the copying process, leading to potential variations that can drive species adaptation and survival.
What is the relationship between DNA and protein synthesis?
DNA provides the instructions for protein synthesis through a process called transcription, where a segment of DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA then moves to the ribosome, where the process of translation occurs, using transfer RNA (tRNA) to decode the mRNA sequence into a specific sequence of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. In essence, DNA acts as the blueprint for proteins, and protein synthesis is the process of translating this blueprint into functional proteins.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments