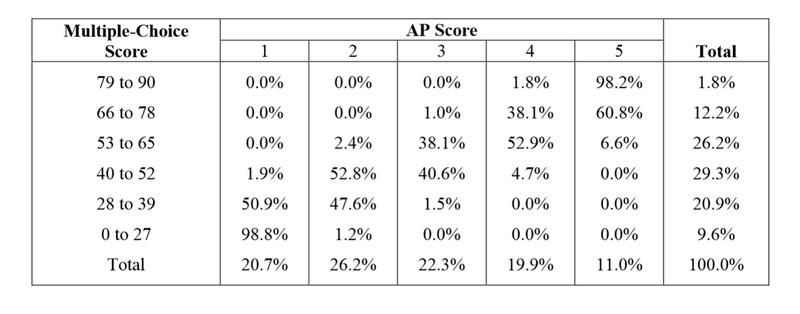
World History AP Scoring Worksheet
The World History AP Scoring Worksheet is a valuable resource designed to assist students in their preparation for the AP World History exam. This comprehensive tool provides a clear and organized outline of the scoring criteria used by the examiners, enabling students to confidently approach their studying and be well-prepared for the exam. Whether you are a high school student looking to boost your score on the AP World History exam or a teacher seeking a helpful resource for your students, the World History AP Scoring Worksheet is an essential asset.
Table of Images 👆
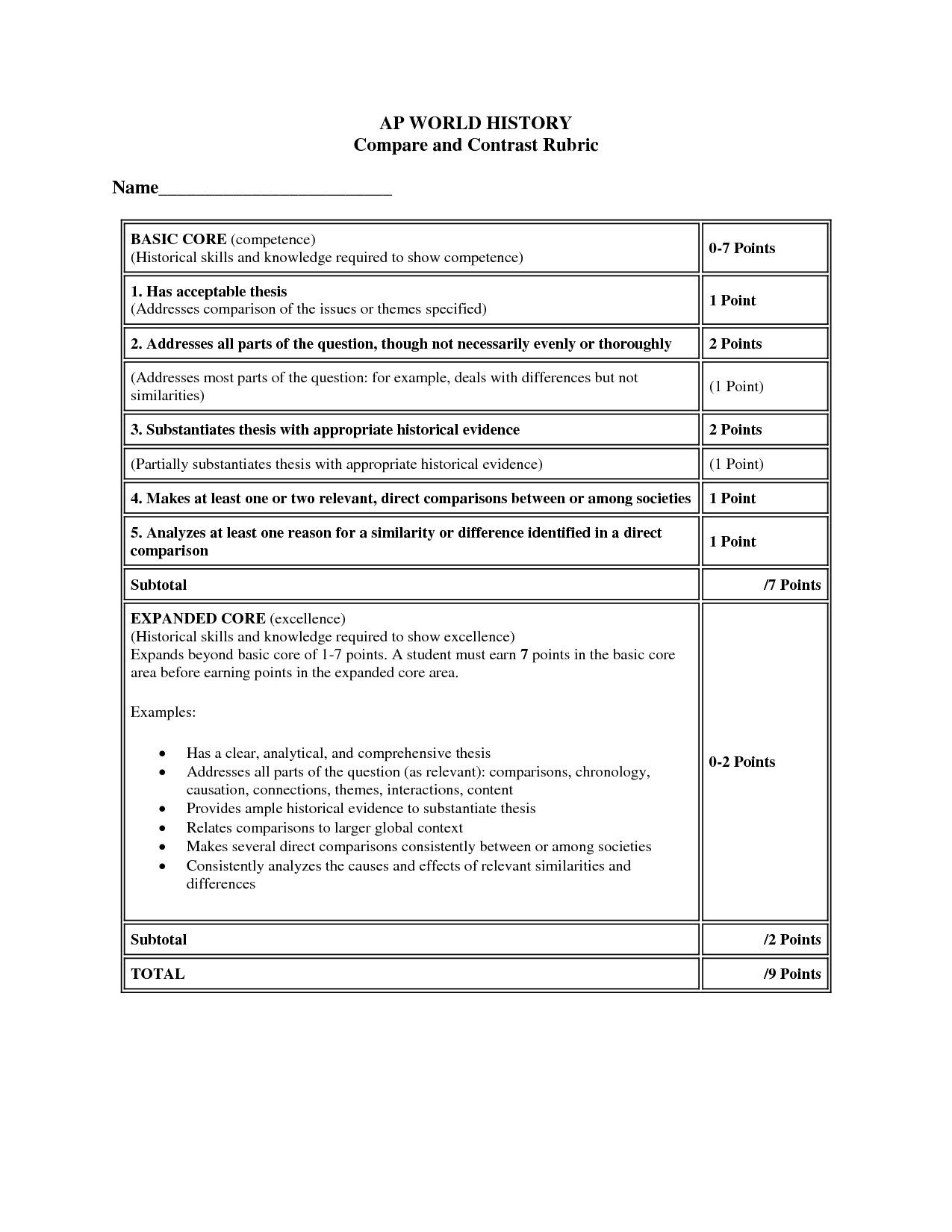
- Compare and Contrast Essay Rubric AP World History
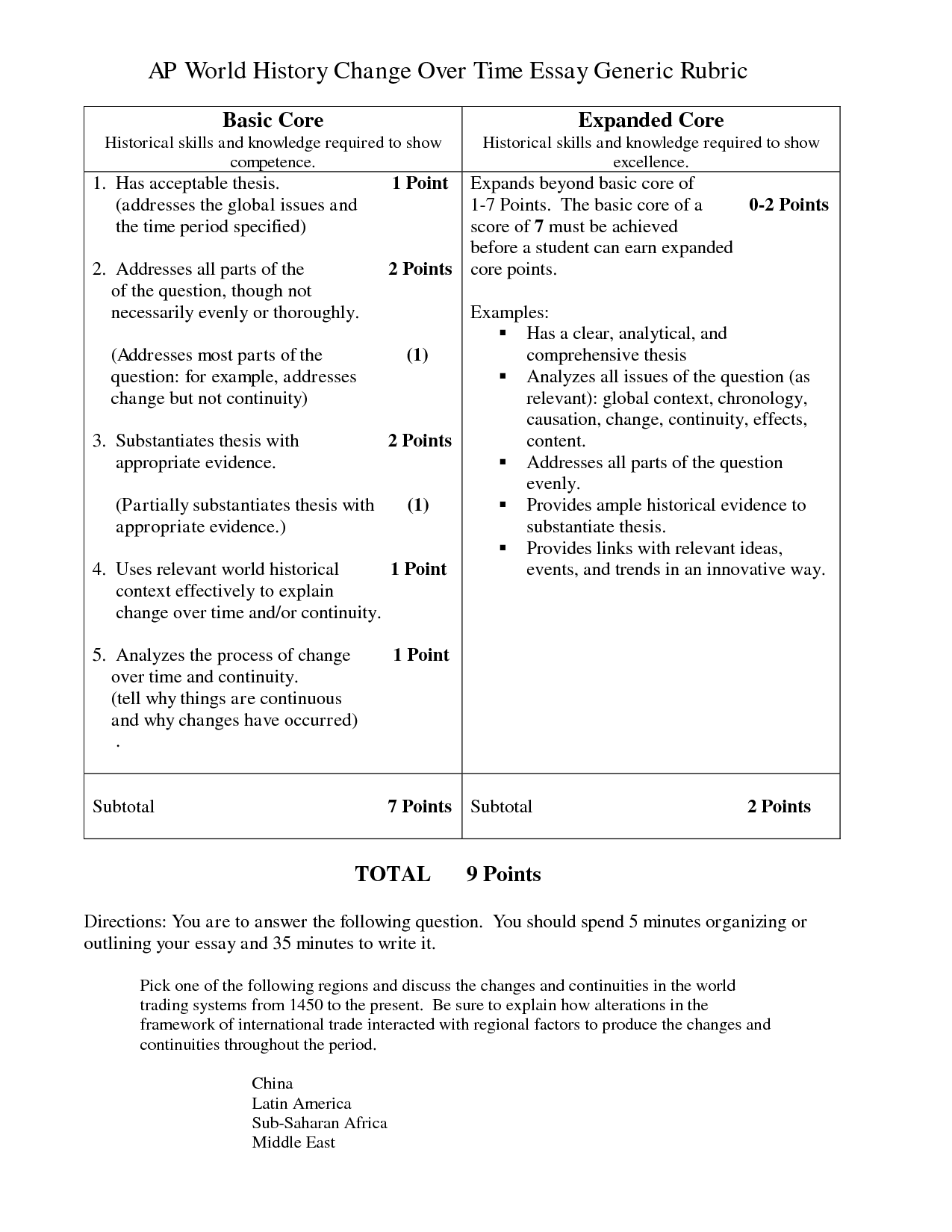
- Essay Rubric AP World History Change
- Nervous System Worksheets Answer Key
- AP World History DBQ
- AP World History Study Guide Answers Chapter 3
- AP US History DBQ Essay Format
- Ccot Essay AP World History Rubrics
- Social Studies Current Event Worksheet
- Sample DBQ Essay
- Debate Grading Rubric Template
- The People Paradox Worksheet Answers
- AP World History Essay Questions
More History Worksheets
Reading Worksheets High School HistoryFree Printable History Worksheets
U.S. History Worksheets
Black History Worksheets for Kindergarten
Black History Month Reading Comprehension Worksheets
Who was the ruler of the Roman Empire during its peak in the 2nd century AD?
The ruler of the Roman Empire during its peak in the 2nd century AD was Emperor Trajan.
What was the major cause of the French Revolution in 1789?
The major cause of the French Revolution in 1789 was widespread social inequality and economic hardship, which was exacerbated by the extravagant spending of the French monarchy, high taxes on the common people, and a deeply divided society based on class privileges. These grievances fueled discontent among the French population, leading to calls for political reform and eventually to the outbreak of the Revolution.
Which scientist formulated the laws of gravity and motion in the late 17th century?
The scientist who formulated the laws of gravity and motion in the late 17th century was Sir Isaac Newton.
What event sparked World War I in 1914?
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary and his wife Sophie in Sarajevo on June 28, 1914 by a Bosnian-Serb nationalist named Gavrilo Princip sparked World War I.
Who were the primary negotiators of the Treaty of Versailles after World War I?
The primary negotiators of the Treaty of Versailles after World War I were the "Big Four" leaders: Georges Clemenceau of France, Woodrow Wilson of the United States, David Lloyd George of Great Britain, and Vittorio Orlando of Italy. They were instrumental in drafting the terms of the treaty that aimed to maintain peace and punish Germany for its role in the war.
What was the significance of the Berlin Wall, which stood from 1961 to 1989?
The Berlin Wall, which stood from 1961 to 1989, was a physical and symbolic division between East and West Berlin, representing the larger ideological and political divide of the Cold War. It was a physical barrier erected by the East German government to prevent East Berliners from defecting to West Berlin. The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 symbolized the end of the Cold War and the reunification of East and West Germany, leading to significant geopolitical changes in Europe and marking the beginning of the end of the Soviet Union.
What were the main causes of the Great Depression in the 1930s?
The main causes of the Great Depression in the 1930s were the stock market crash of 1929, which led to a collapse in consumer confidence and investment, high levels of speculation and excessive borrowing, a decrease in international trade due to protectionist policies and tariffs, a decline in agricultural prices and overproduction in the farming sector, and a lack of government intervention to stabilize the economy. These factors combined to create a severe economic downturn that lasted for a decade.
Who was the leader of the Soviet Union during the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962?
The leader of the Soviet Union during the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962 was Nikita Khrushchev.
What was the impact of the Industrial Revolution on society and the economy?
The Industrial Revolution had a significant impact on both society and the economy. It led to urbanization as people moved from rural areas to cities for job opportunities in factories, resulting in the growth of urban centers and changes in social structures. Economically, the Industrial Revolution brought about mass production, technological advancements, and increased trade, leading to economic growth and the emergence of capitalism. However, it also gave rise to poor working conditions, child labor, and income inequality, sparking social movements and labor reforms to address these challenges.
What was the long-term consequence of the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand in 1914?
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand in 1914 was a catalyst for the outbreak of World War I, which had far-reaching consequences on a global scale. It led to the mobilization of European powers, escalating tensions, and ultimately resulting in one of the deadliest conflicts in history. The war reshaped international relations, led to the collapse of empires, and set the stage for future conflicts, including World War II.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments