Work Energy and Power Worksheet
Are you a student or teacher seeking a comprehensive resource for practicing work, energy, and power concepts? Look no further than this worksheet! Designed to cater to individuals studying physics or related fields, this worksheet offers a range of exercises that will help reinforce your understanding of these fundamental topics. Whether you're looking to review the equations and calculations associated with work, or explore the concept of power in depth, this worksheet has got you covered.
Table of Images 👆
- Different Forms of Energy Worksheets
- Work Energy and Power Worksheet Answers
- Potential and Kinetic Energy Worksheets
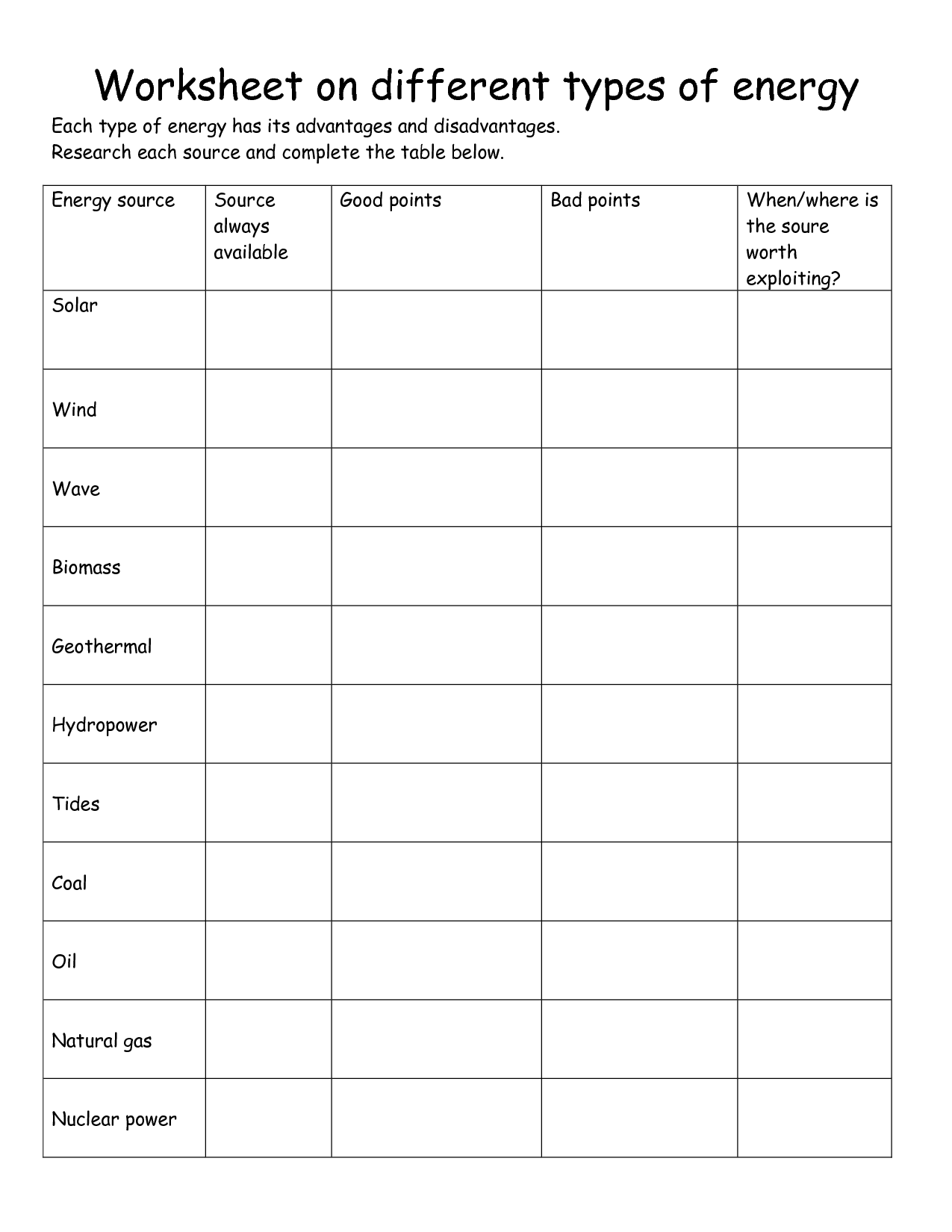
- Alternative Energy Sources Worksheet
- Electric Field Worksheet Answers
- Bill Nye Waves Worksheet Answers
- Mole Calculation Worksheet Answer Key
- 3rd Grade Energy Test
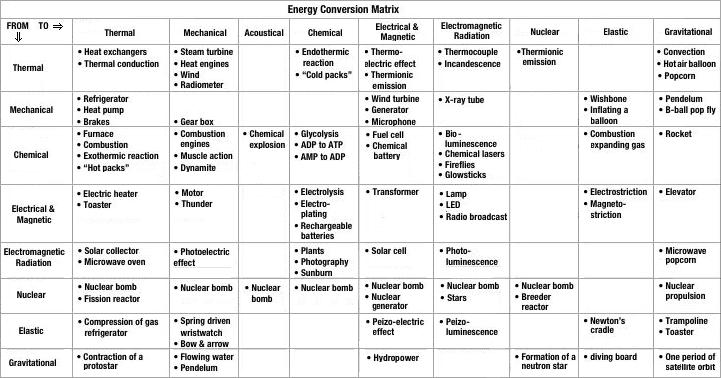
- Energy Conversion Examples
- Direct Object Worksheets
- Direct Object Worksheets
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Types of Energy Worksheet PDF
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
What is work?
In the context of physics, work is defined as the amount of energy transferred or done on an object by a force acting on the object as it is displaced in the direction of the force. It is calculated by multiplying the force applied to an object by the distance over which the force is applied. Work is a scalar quantity and is typically measured in joules.
Define energy.
Energy is a fundamental property of matter and is defined as the ability to do work or to produce a change in an object or system. It exists in various forms such as kinetic, potential, thermal, chemical, and nuclear energy, and can be transformed from one form to another. Energy plays a crucial role in all aspects of our lives, powering machines, sustaining life, and driving processes in the natural world.
What is the principle of conservation of energy?
The principle of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed but only transformed from one form to another. This fundamental law of physics maintains that the total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant over time, with energy being transferred or converted between different forms such as potential, kinetic, heat, or chemical energy.
Explain the concept of kinetic energy.
Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion. It is dependent on the mass of the object and its velocity, with the formula being KE = 0.5 * mass * velocity^2. The faster an object is moving and the more mass it has, the greater its kinetic energy. This energy enables objects to do work and is a crucial component of various physical processes and phenomena.
Define potential energy and give an example.
Potential energy is the stored energy an object possesses based on its position or configuration. An example of potential energy is a stretched rubber band - when pulled back, the rubber band has potential energy that can be released when it is let go, causing the rubber band to snap back into its original shape and releasing the stored energy.
What is the relationship between work and energy?
Work is the transfer of energy from one system to another. When work is done on an object, energy is transferred to the object which can result in changes in its motion, position, or internal energy. Conversely, when work is done by an object, such as in the case of lifting a weight against gravity, energy is transferred from the object to its surroundings. Therefore, work and energy are closely related concepts that are interdependent in the study of physics.
Define power and give its equation.
Power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred. It is calculated using the equation P = W/t, where P represents power, W represents work, and t represents time.
What is the unit of power?
Watt (W) is the unit of power, named after the Scottish engineer James Watt.
Explain the concept of mechanical advantage.
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, machine, or mechanical system to undertake a task. It is calculated by dividing the output force produced by the machine by the input force applied to it. A mechanical advantage greater than 1 indicates that the machine can multiply the input force and make it easier to lift, move, or overcome a resistance. This concept is essential in designing machines and tools to efficiently perform work by reducing the amount of force or effort needed from the user.
Discuss the relationship between work, power, and time.
Work is the amount of energy transferred by a force acting through a distance, while power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred. Time plays a crucial role as it influences the amount of work that can be done and the power output. An increase in power can allow work to be done faster, thus reducing the time taken to complete a task. Conversely, a longer period of time may be needed to complete a certain amount of work if power output is lower. Ultimately, the relationship between work, power, and time is interconnected as they all impact each other in various ways when it comes to accomplishing tasks or achieving goals efficiently.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments