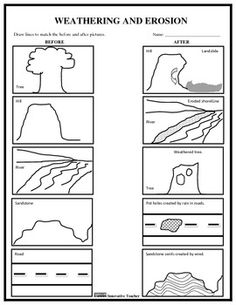
Weathering Erosion and Deposition Worksheets
Weathering, erosion, and deposition are crucial topics for students learning about the Earth's surface processes. These worksheets provide a comprehensive and interactive way for young learners to understand and engage with these natural phenomena. Through carefully crafted questions and activities, students will be able to develop a strong understanding of the entity and subject of weathering, erosion, and deposition.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
How does weathering change the appearance of rocks?
Weathering can change the appearance of rocks by physically breaking them down or chemically altering their composition. Over time, exposure to elements like wind, water, and ice can cause rocks to erode, creating smoother surfaces, rounded edges, and fractures. Chemical weathering can lead to the formation of new minerals, discoloration, or the breakdown of rock into smaller particles, ultimately changing the overall color, texture, and shape of the rock.
What are the main factors that contribute to physical weathering?
The main factors that contribute to physical weathering are thermal fluctuations, such as freeze-thaw cycles that cause rocks to expand and contract, leading to cracking and disintegration; abrasion by wind, water, ice, or other particles that wear down rocks over time; biological activity, such as plant roots growing into cracks and causing rocks to break apart; and pressure changes, such as when rocks are uplifted to the Earth's surface or exposed to lower pressure underground, leading to fracturing and erosion.
Describe the process of chemical weathering.
Chemical weathering is the process where rocks and minerals are broken down by chemical reactions, leading to their decomposition and alteration. This occurs through various processes such as oxidation, hydration, hydrolysis, and dissolution. These reactions can weaken the structure of the rocks, causing them to disintegrate over time. For example, carbonic acid can dissolve limestone, turning it into calcium bicarbonate and water. Chemical weathering can also change the mineral composition of the rocks, ultimately transforming them into different materials.
How do plants contribute to weathering?
Plants contribute to weathering by releasing organic acids and gases through their roots and leaves. The organic acids released by plant roots can break down minerals in the soil, slowly weakening rocks and facilitating physical weathering. Additionally, plant roots can physically break apart rocks as they grow and expand. Furthermore, the gases released by plants, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, can react with minerals on the Earth's surface, leading to chemical weathering processes. Overall, the presence of plants can play a significant role in accelerating the weathering of rocks and minerals.
Explain how erosion occurs and what factors can impact its rate.
Erosion occurs when soil, rock, or sediment is moved from one location to another by natural forces such as water, wind, or ice. Factors that can impact the rate of erosion include the type of soil or rock present, the steepness of the slope, the amount and intensity of precipitation, the presence of vegetation or protective land cover, and human activities such as deforestation or construction that can disrupt natural erosion processes. Ultimately, erosion rates are influenced by a combination of these factors working together to shape the landscape over time.
What are the different agents of erosion?
The different agents of erosion include water, wind, ice, and gravity. Water erosion is caused by rainfall, rivers, and waves, while wind erosion is primarily caused by the force of wind carrying and depositing sediment. Ice erosion, or glacial erosion, occurs from the movement of glaciers scouring and shaping the land. Gravity erosion, also known as mass wasting, involves the downhill movement of rock and soil due to gravity's pull. These agents work continuously to reshape the Earth's surface over time.
Describe the role of gravity in erosion.
Gravity plays a crucial role in erosion by constantly pulling materials downhill. Gravity causes loose rocks, soil, and sediments to move down slopes, contributing to processes such as mass wasting, landslides, and rockfalls. The force of gravity also influences the flow of water in rivers and streams, allowing them to carry sediment downstream and gradually wear away the land. Overall, gravity accelerates the movement of materials on Earth's surface, aiding in the erosion of landscapes over time.
What are the main types of deposition?
The main types of deposition include erosion, sedimentation, and precipitation. Erosion involves the movement of sediments or rocks by natural processes like wind, water, or ice. Sedimentation occurs when eroded materials settle down due to a loss of energy in the transporting medium. Precipitation refers to the process where dissolved minerals come out of a solution and collect as solid particles, such as when minerals in water solidify to form sedimentary rock. These processes play a crucial role in shaping the Earth's surface and creating various landforms.
How does deposition contribute to the formation of landforms?
Deposition contributes to the formation of landforms by depositing sediment, rocks, and other material in specific areas. Over time, these deposited materials accumulate and can create various landforms such as deltas, beaches, sand dunes, and floodplains. Deposition also plays a crucial role in shaping coastlines and riverbanks by building up sediment and altering the land's topography. The process of deposition is driven by the movement of wind, water, ice, and gravity, which all work together to shape the Earth's surface.
Explain the relationship between weathering, erosion, and deposition in shaping the Earth's surface.
Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks into smaller pieces, erosion is the movement of these pieces by wind, water, or ice, and deposition is the settling of these sediments in a new location. Together, these three processes work hand in hand to shape the Earth's surface by wearing down mountains, carving out valleys, and creating landscapes such as canyons and deltas. Weathering weakens rocks, erosion transports the sediments, and deposition builds up new landforms, ultimately reshaping the Earth's surface over time.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments