Volcano Worksheets Grade 3
Are you a third-grade teacher searching for engaging and educational activities about volcanoes for your students? Look no further! Our volcano worksheets are designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of this natural phenomenon. With clear and concise instructions, these worksheets are perfect for incorporating into your science curriculum. From identifying different parts of a volcano to understanding the eruption process, these worksheets are tailored to cater to the specific needs of third-grade students.
Table of Images 👆
- Types of Volcanoes Worksheet
- Volcano Mini Book Coloring Page
- Easy Labeled Picture Of A Volcano
- 3rd Grade Volcano Worksheets
- Volcano Crossword Puzzles Worksheets
- Third Grade Science Worksheets
- Second Grade Writing Prompts Worksheets
- Printable Rock Cycle Worksheets
- 4th Grade Science Worksheets
- Essay Grade Social Studies
- Volcano Worksheets and Answer Key
- Spanish Family Tree Worksheet
- Adjective Practice Worksheets
- Adjective Practice Worksheets
- Adjective Practice Worksheets
- Adjective Practice Worksheets
- Adjective Practice Worksheets
- Adjective Practice Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
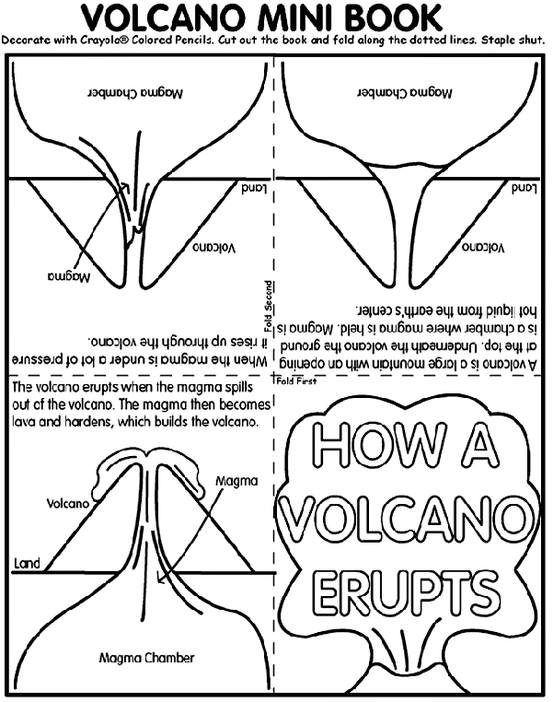
What is a volcano and how is it formed?
A volcano is a mountain that opens downward to a pool of molten rock below the surface of the Earth. It is formed when molten rock, ash, and gases escape through a crack in the Earth's crust and erupt onto the surface. This eruption can be explosive, sending ash, rocks, and lava flowing down the sides of the volcano, or it can be more gentle, with lava slowly oozing out. Over time, repeated eruptions build up layers of hardened lava and ash, creating the cone-shaped structure we recognize as a volcano.
What are the different parts of a volcano?
A volcano consists of three main parts: the magma chamber, where molten rock is stored beneath the Earth's surface; the main vent, which is the main opening through which magma and gases erupt onto the surface; and the crater, which is the bowl-shaped depression at the summit of the volcano where eruptions occur. Additionally, secondary vents, lava flows, and ash clouds are other important components that form during volcanic activity.
What happens during a volcanic eruption?
During a volcanic eruption, molten rock, ash, and gases are expelled from a volcano's vent or fissure. This process can result in various hazardous phenomena such as lava flows, pyroclastic flows, ashfall, explosions, and volcanic gases being released into the atmosphere. The severity and type of eruption depend on various factors such as the composition of the magma, gas content, and the shape of the volcano. Volcanic eruptions can have significant impacts on the surrounding environment, including causing destruction of property, loss of life, and disruption of air travel and infrastructure.
How do volcanoes affect the Earth's surface?
Volcanoes affect the Earth's surface in various ways including shaping the landscape through the deposition of lava, ash, and other volcanic materials, creating new land formations such as volcanic mountains and islands. They also contribute to the replenishment of nutrients in the soil, supporting ecosystems and promoting biodiversity. Additionally, volcanic eruptions can lead to temporary climate changes by releasing ash and gases into the atmosphere, affecting weather patterns and air quality.
What are some common types of volcanoes?
Some common types of volcanoes include stratovolcanoes (composite volcanoes), shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, and calderas. Stratovolcanoes are tall, steep-sided cones built by alternating layers of lava flows, volcanic ash, and debris. Shield volcanoes have gentle slopes and are formed by the eruption of low-viscosity lava. Cinder cone volcanoes are small, steep-sided cones made up of pyroclastic materials such as volcanic ash and cinders. Calderas are large, crater-like depressions formed when the summit of a volcano collapses after a massive eruption.
What are the dangers associated with living near a volcano?
Living near a volcano poses several dangers, including the risk of lava flows, ash clouds causing respiratory issues and air traffic disruptions, pyroclastic flows that move at high speeds and temperatures destroying everything in their path, lahars (mudflows) triggered by rainfall mixing with volcanic debris, and volcanic gases that can be harmful or even fatal if inhaled. Additionally, spontaneous volcanic activity can result in sudden evacuations and infrastructure damage, making it crucial for people in close proximity to be prepared and aware of the potential risks.
How are scientists able to predict volcanic eruptions?
Scientists can predict volcanic eruptions by monitoring various geophysical and geochemical signals from the volcano, such as seismic activity, ground deformation, gas emissions, and thermal changes. By analyzing these data, scientists can identify patterns that indicate increased volcanic activity and potential eruption. Additionally, historical data and knowledge of a volcano's behavior can also inform predictions. While not always precise, these monitoring techniques help scientists issue early warnings to mitigate risks and protect communities near active volcanoes.
What are some famous volcanic eruptions in history?
Some famous volcanic eruptions in history include the 1883 eruption of Krakatoa in Indonesia, the 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora in Indonesia, which led to the "Year Without a Summer," and the 79 AD eruption of Mount Vesuvius in Italy that buried the city of Pompeii. Additionally, the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens in the United States and the ongoing eruptions of Kilauea in Hawaii are also well-known volcanic events.
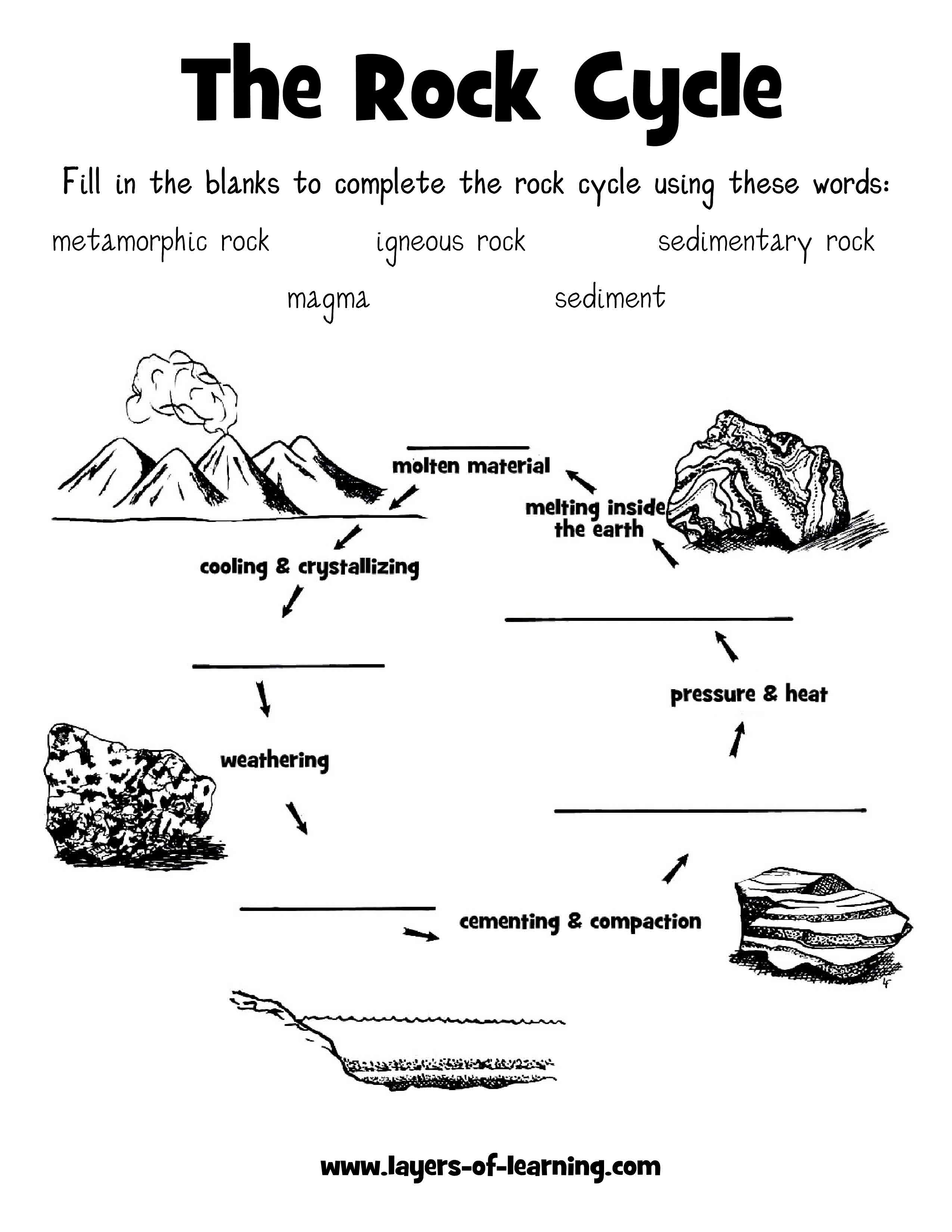
How do volcanoes contribute to the formation of new land?
Volcanoes contribute to the formation of new land through volcanic eruptions, where molten rock (magma) rises to the surface and solidifies into solid rock, known as igneous rock. Over time, repeated eruptions build up layers of solidified lava and ash, creating new landmasses on the Earth's surface. This process, called volcanic activity, can lead to the formation of volcanic islands, mountains, and other landforms, ultimately contributing to the Earth's constantly changing geography.
How are volcanoes used for geothermal energy?
Volcanoes are used for geothermal energy by harnessing the heat from magma chambers deep underground. Water is injected into boreholes drilled into the Earth's crust, where it is heated by the surrounding rocks and magma. The heated water turns into steam, which is then used to power turbines and generate electricity. This process takes advantage of the natural heat source created by volcanic activity, making geothermal energy a renewable and reliable source of power.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

































Comments