Verb Forms Worksheet
Looking for a comprehensive and engaging way to teach verb forms? Look no further! In this blog post, we will delve into the world of verb forms worksheets, designed specifically for students in elementary and middle school. Whether you are a teacher searching for valuable resources or a parent wanting to supplement your child's learning, these worksheets are the perfect tool to help students grasp and practice verb forms effectively.
Table of Images 👆
- Simple Present Worksheets
- Subject Verb Agreement Worksheet Answer Key
- Future Tense Verbs Worksheet
- ING Verb Ending Worksheet
- ESL Worksheet Verb to Have
- Spanish AR ER Ir Verbs Worksheet
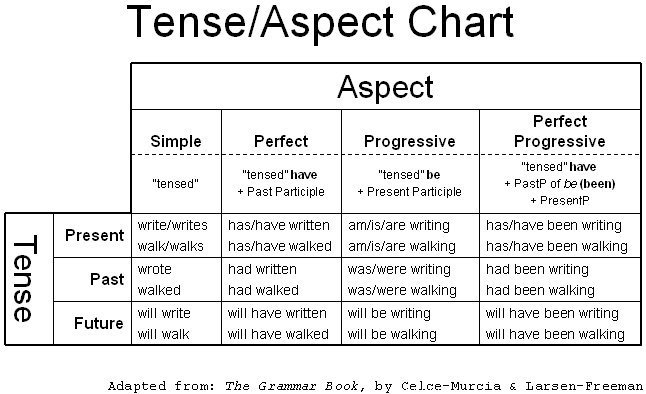
- Verb Tense and Aspect Chart
- Irregular Verb Crossword Puzzle
- Personal Subject Pronouns
- Be Do Have Worksheets
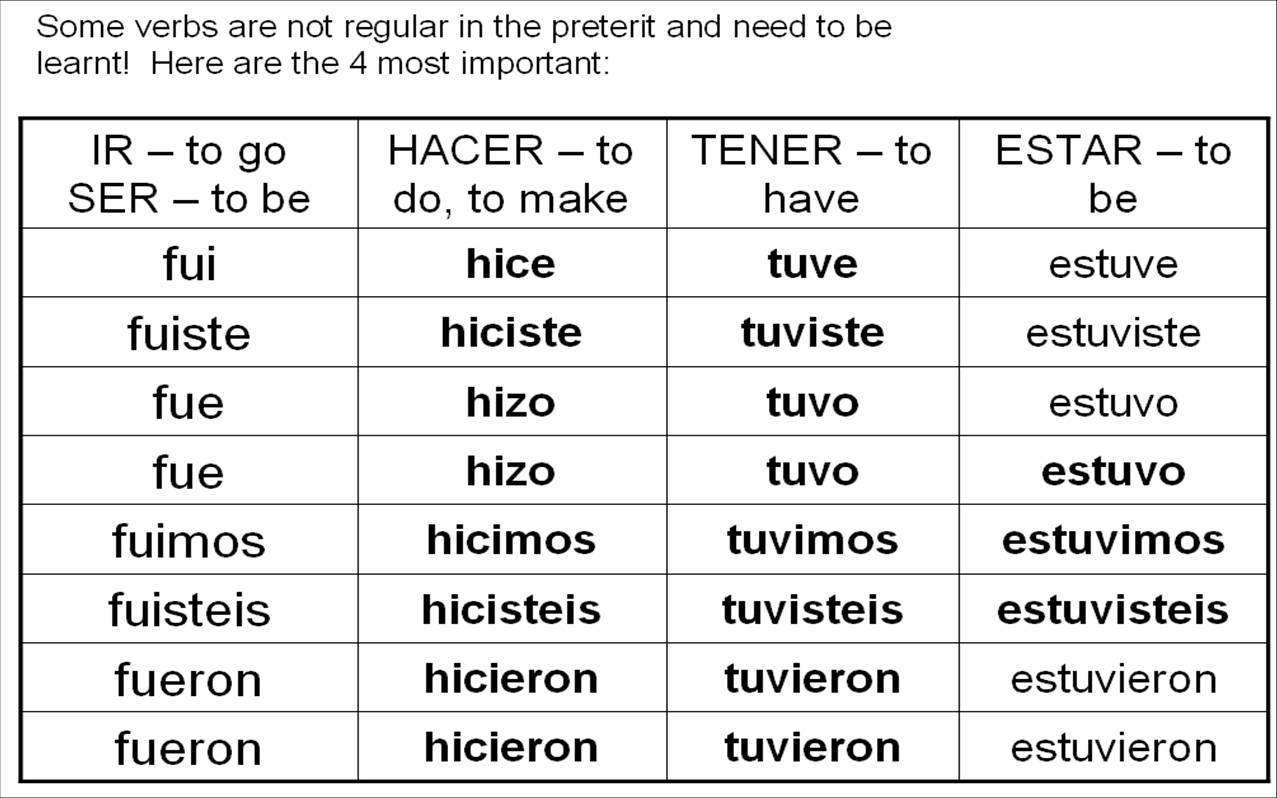
- Spanish Irregular Preterite Verb Chart
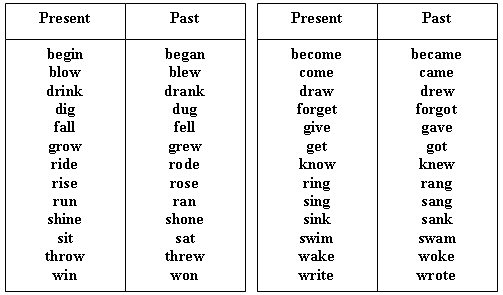
- Past and Present Tense Verbs
- French Venir Worksheet
- Verb Be Worksheets
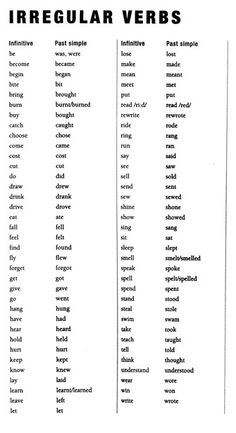
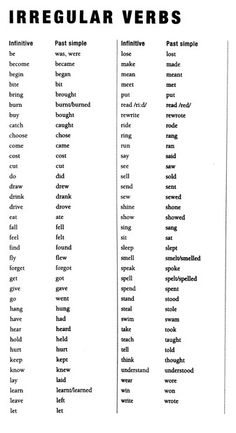
- English Irregular Verbs List
- English Irregular Verbs List
- English Irregular Verbs List
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What are the different verb forms?
The different verb forms in English include base form (infinitive), present tense, past tense, present participle, past participle, and future tense. Each form serves a specific grammatical function to indicate the time, aspect, or mood of the action being described.
How do verb forms change in the present tense?
Verb forms change in the present tense by adding specific endings or making slight modifications to the base form of the verb depending on the subject performing the action. For regular verbs, this often involves adding -s, -es, or -ies to the base form for third person singular subjects (he, she, it), while the base form remains the same for other subjects. Irregular verbs may have entirely different forms for each subject pronoun in the present tense.
How do verb forms change in the past tense?
In English, verb forms change in the past tense by adding "-ed" to regular verbs. However, irregular verbs have their own unique past tense forms that do not follow the "-ed" pattern. For example, "walk" becomes "walked" in the past tense for regular verbs, while "go" becomes "went" for irregular verbs.
What is the verb form used in the future tense?
The verb form used in the future tense is typically formed by combining the auxiliary verb "will" or "shall" with the base form of the main verb.
How are verb forms formed in the present participle?
In English, present participles are formed by adding '-ing' to the base form of the verb. This form is used to create continuous tenses or to act as an adjective. For example, the base form "talk" becomes "talking" in the present participle form.
How are verb forms formed in the past participle?
In English, past participles are formed by adding the suffix "-ed" to regular verbs. However, irregular verbs form past participles through various changes in spelling, such as "drink" becoming "drunk" or "go" becoming "gone". It is important to learn the irregular forms of past participles as they do not follow a predictable pattern like regular verbs.
What are the different forms of the verb "to be"?
The different forms of the verb "to be" in English are: am, is, are, was, were, be, being, and been.
How do verb forms change in the imperative mood?
In the imperative mood, verb forms often change from their base form. For regular verbs, the imperative form is the base form of the verb without the subject pronoun. However, irregular verbs may have unique imperative forms that do not follow a specific pattern. Additionally, some verbs may require changes in spelling or different endings in the imperative form.
How are verb forms formed in the conditional mood?
In the conditional mood, verb forms are formed by adding the conditional ending to the infinitive form of the verb. For regular verbs in Spanish, the conditional ending is -ía, -ías, -ía, -íamos, -íais, -ían. For example, the verb "hablar" (to speak) in the conditional mood would be "hablaría" (I would speak). However, there are irregular verbs in Spanish that have unique conjugations in the conditional mood and do not follow this regular pattern.
What is the difference between regular and irregular verb forms?
Regular verb forms follow a predictable pattern when conjugated in different tenses, such as adding -ed to the base form for past tense. Irregular verb forms, on the other hand, do not follow this pattern and instead change in unpredictable ways when conjugated, like "go" changing to "went" in the past tense.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments