Transverse Waves Worksheet
Are you teaching your students about transverse waves and looking for a way to assess their understanding? Look no further than our Transverse Waves Worksheet. Designed specifically for middle school students, this worksheet covers key concepts related to transverse waves such as amplitude, wavelength, and frequency. With a variety of practice problems and clear explanations, this worksheet is perfect for reinforcing the concept of transverse waves.
Table of Images 👆
- Sound Wave Worksheet Answer
- Sound Wave Worksheet Answer
- Labeling Waves Worksheet Answer Key
- Wave Properties Worksheet
- Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Labeling Waves Worksheet Answer Key
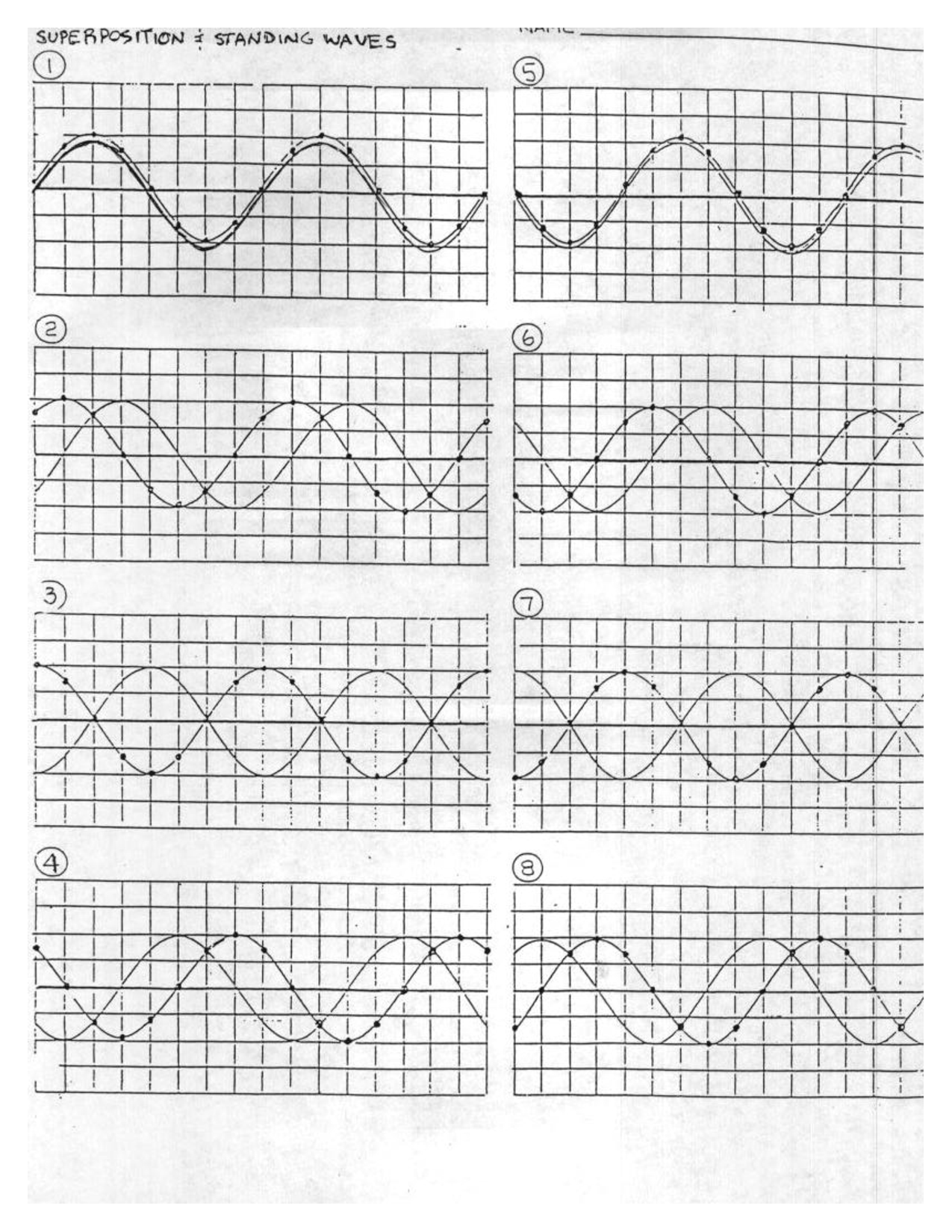
- Standing Waves Worksheet
- Transverse Wave Parts
- Light and Sound Waves Worksheets
- Wave Diagram Worksheet Answers
- Wave Frequency Diagram
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
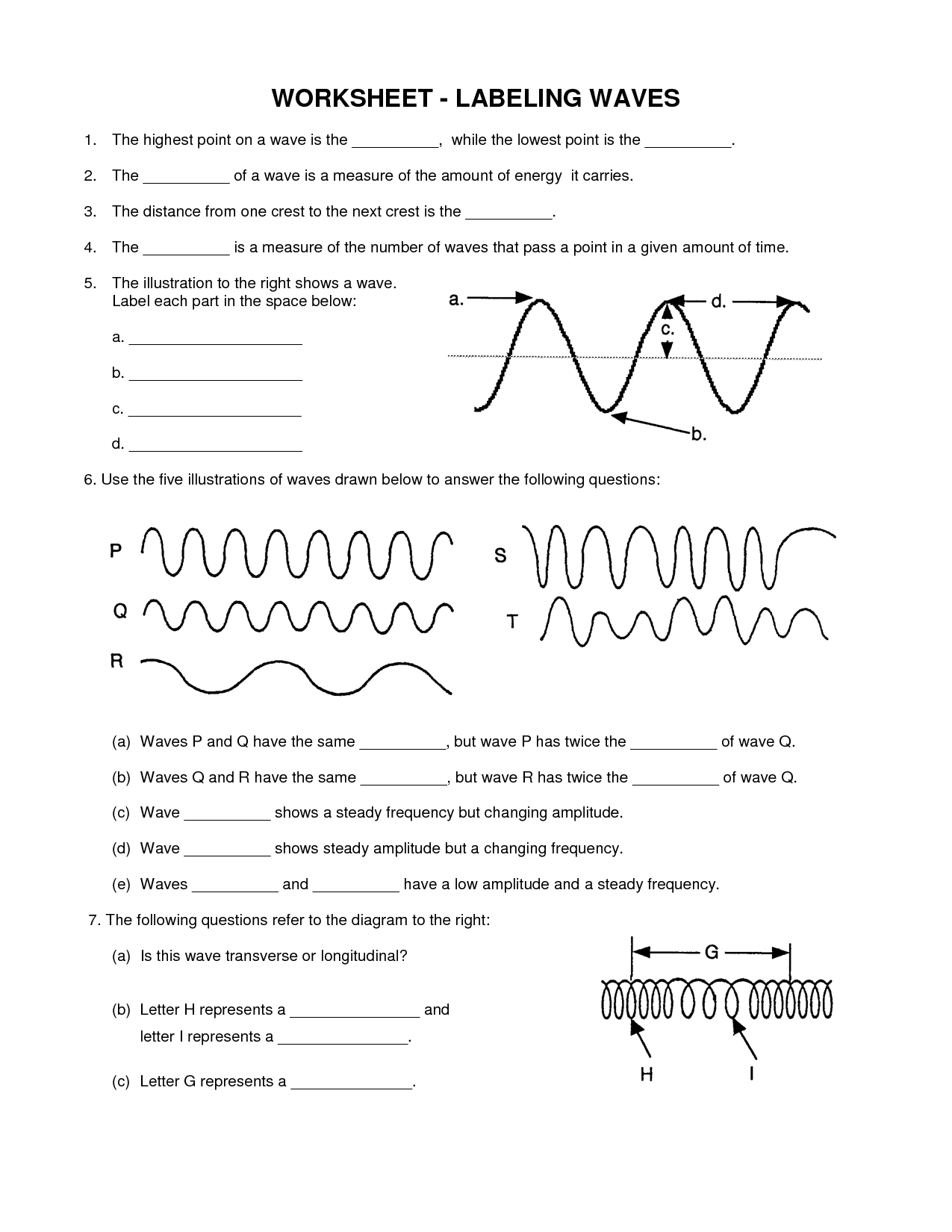
What are transverse waves?
Transverse waves refer to a type of wave motion where the medium's particles oscillate perpendicular to the direction of the wave's propagation. This means that as the wave moves from one point to another, the individual particles move up and down or side to side, creating a distinct pattern of wave motion. Examples of transverse waves include electromagnetic waves, such as light, and waves on a string or a vibrating surface.
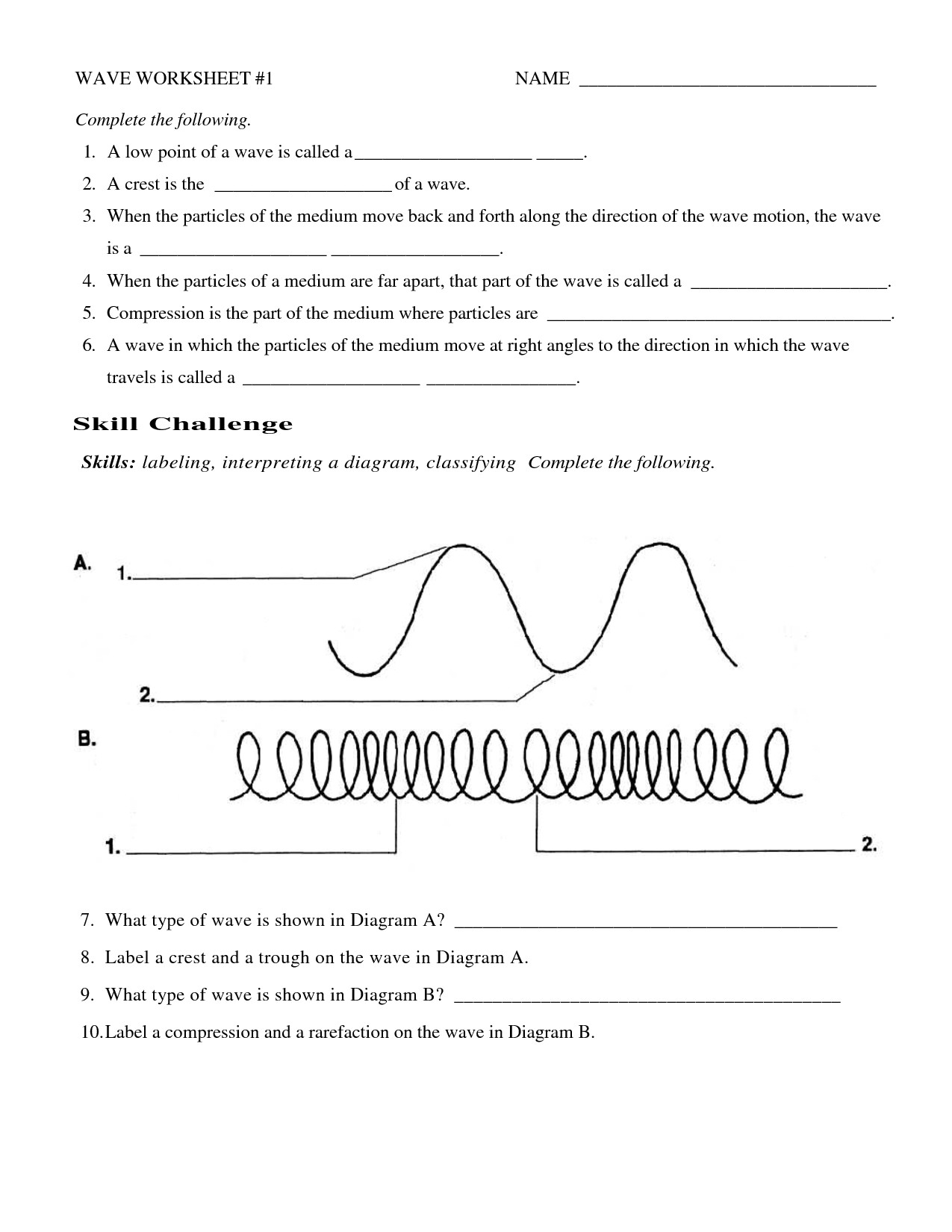
How do transverse waves differ from longitudinal waves?
Transverse waves differ from longitudinal waves in the direction of the wave oscillation. In transverse waves, the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, causing the particles to move up and down or side to side, such as in water waves or electromagnetic waves. On the other hand, in longitudinal waves, the oscillations are parallel to the direction of wave propagation, causing the particles to move back and forth along the same line, like in sound waves.
How do transverse waves propagate through a medium?
Transverse waves propagate through a medium by causing particles in the medium to vibrate perpendicular to the direction of the wave's travel. As the wave moves through the medium, energy is transferred from one particle to the next, creating a wave pattern that moves outward from the source. This type of wave motion is characteristic of light waves, seismic waves, and electromagnetic waves.
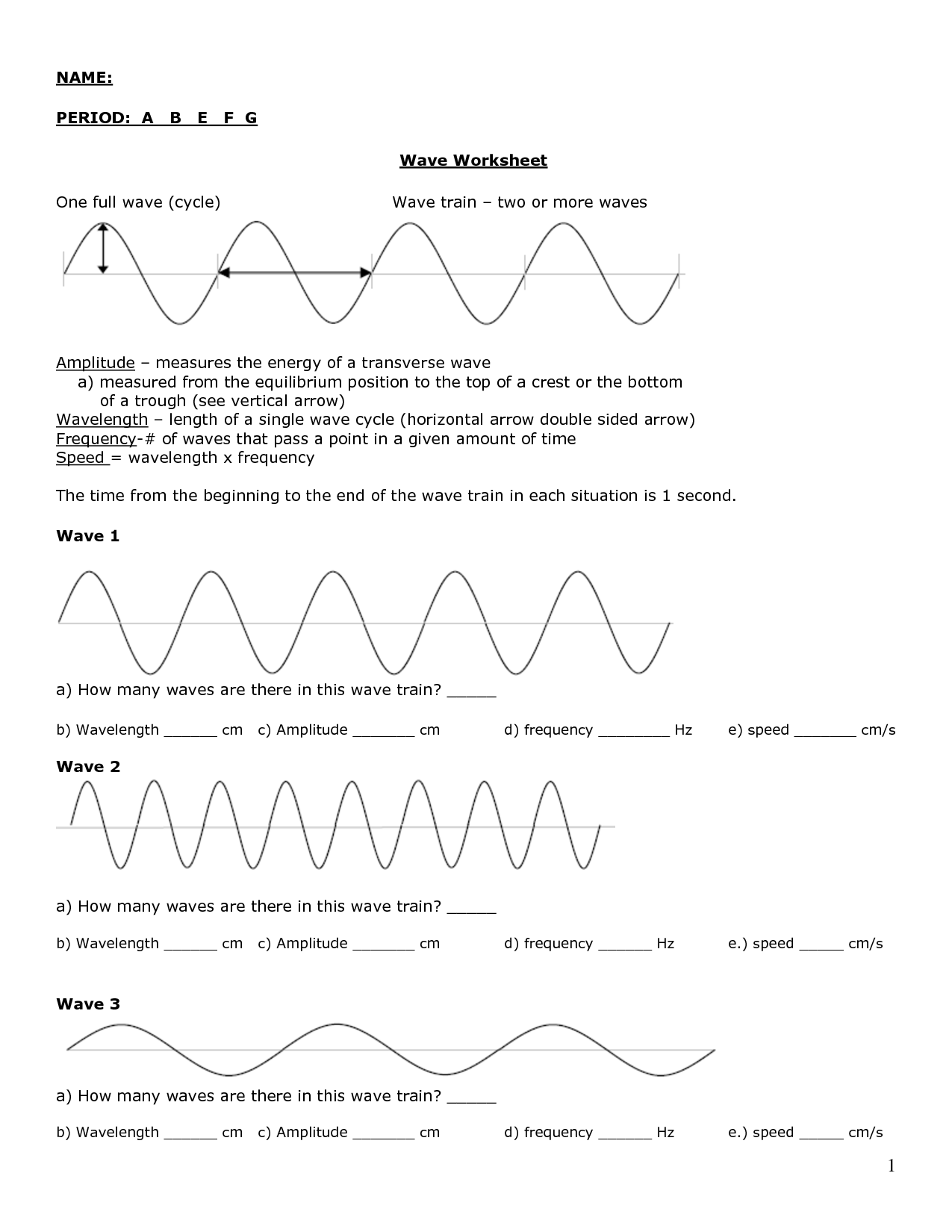
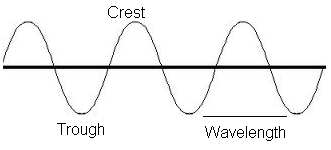
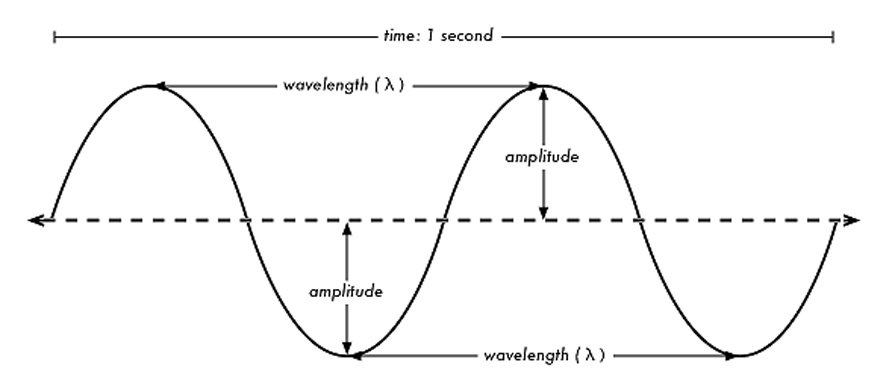
What is the amplitude of a transverse wave?
The amplitude of a transverse wave is the maximum displacement or distance from the equilibrium position to the crest (or trough) of the wave. It represents the maximum height or depth of the wave from its resting position.
How is the wavelength of a transverse wave measured?
The wavelength of a transverse wave is measured by finding the distance between two consecutive points (such as peaks or troughs) on the wave that are in phase with each other. This distance represents one complete cycle of the wave and is typically measured in meters or other units of length.
What is the frequency of a transverse wave?
The frequency of a transverse wave is the number of complete wave cycles that pass a fixed point in a given time, typically measured in Hertz (Hz). It represents how many times the particles of the medium through which the wave is traveling oscillate up and down perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation within one second.
What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength in transverse waves?
The relationship between frequency and wavelength in transverse waves is inverse - as frequency increases, wavelength decreases, and vice versa. This means that if a wave has a high frequency, it will have a shorter wavelength, and if a wave has a low frequency, it will have a longer wavelength. This relationship is described by the equation: speed of wave = frequency x wavelength.
What determines the speed of a transverse wave?
The speed of a transverse wave is determined by the tension of the medium through which the wave is propagating and the density of the medium. These two factors influence the wave speed by affecting how quickly the particles in the medium can transmit the wave energy from one point to another. Therefore, the speed of a transverse wave is directly proportional to the tension and inversely proportional to the density of the medium.
How do transverse waves transfer energy?
Transverse waves transfer energy by vibrating perpendicular to the direction of the wave's motion, causing particles in the medium to move up and down or side to side. As the wave propagates, these vibrations transfer energy from particle to particle, allowing the wave to carry energy along its path without displacing the particles permanently. This energy transfer is efficient and enables transverse waves (such as light and electromagnetic waves) to transmit information over long distances.
Give examples of transverse waves in everyday life.
Examples of transverse waves in everyday life include electromagnetic waves such as visible light, microwaves, and radio waves. Additionally, waves on a string or rope, water waves in a pond or ocean, and seismic S-waves during an earthquake are all common examples of transverse waves that can be observed in daily experiences.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments