Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
Worksheets are a valuable educational tool that provides a structured format for practicing and reinforcing concepts taught in the classroom. Whether you are a teacher in need of engaging materials for your students or a student seeking additional practice, worksheets offer a practical solution to aid in understanding and retention of subject matter.
Table of Images 👆
- Transcription and Translation Practice Worksheet
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Replication Transcription Translation Worksheet
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Transcription and RNA Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Biology EOC Review Packet Answer Key
- DNA RNA Transcription Translation Worksheets
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
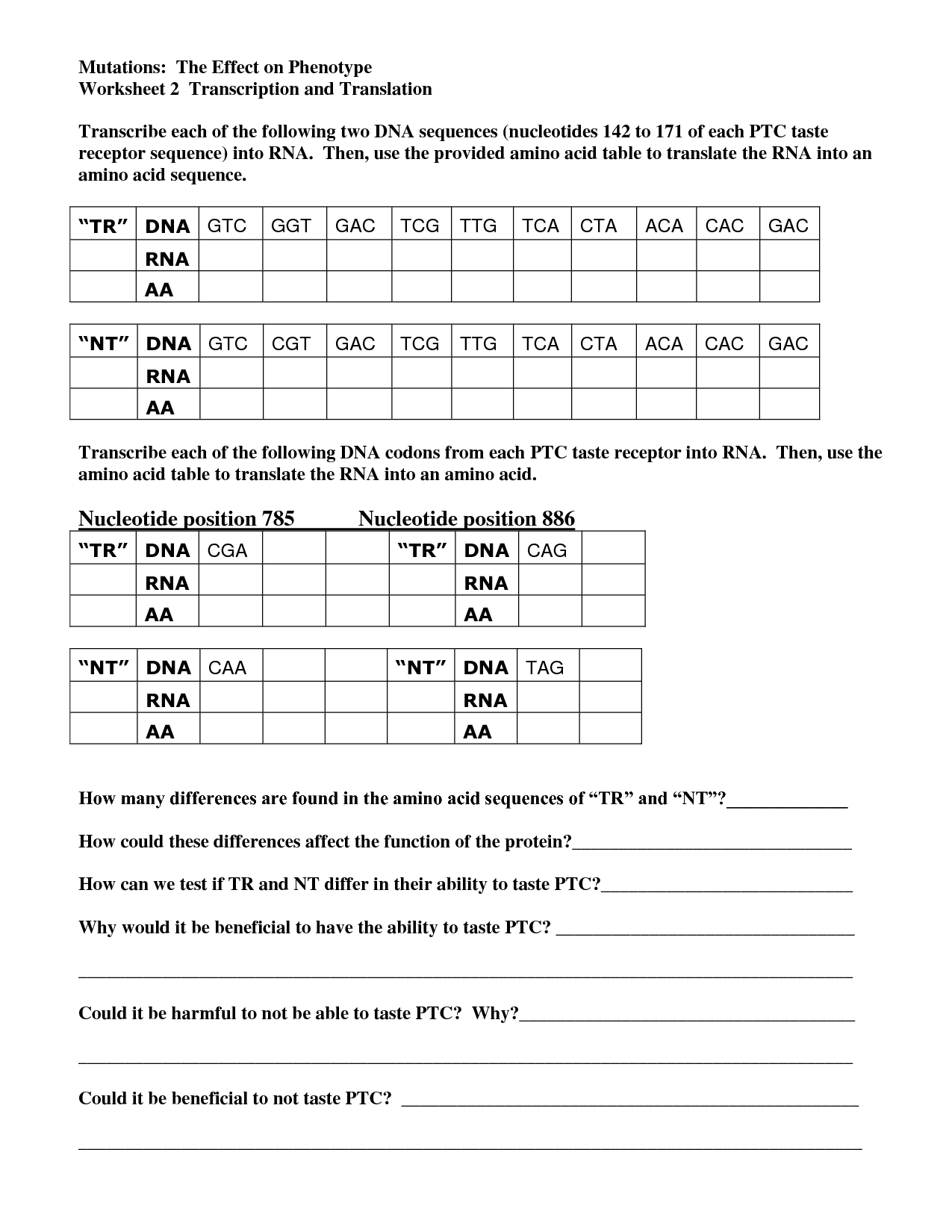
What is the purpose of transcription?
The purpose of transcription is to convert spoken words into written or typed format, allowing for easier documentation, reference, and dissemination of information. Transcription is commonly used in various fields such as research, legal proceedings, medical records, and media production to ensure accurate records are maintained and communication is effectively conveyed.
What are the two main enzyme types involved in transcription?
The two main enzyme types involved in transcription are RNA polymerase and transcription factors. RNA polymerase is responsible for synthesizing the RNA molecule by reading the DNA template, whereas transcription factors help RNA polymerase bind to the promoter region of the DNA and regulate the initiation and rate of transcription.
Describe the process of transcription.
Transcription is the process in which the genetic information stored in DNA is copied into a complementary RNA molecule. It occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and involves three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, RNA polymerase binds to the DNA at the specific site called the promoter. Then, the enzyme unwinds and separates the DNA strands, allowing RNA synthesis to begin. In the elongation phase, RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template, synthesizing a complementary RNA strand. Finally, termination occurs when the RNA polymerase reaches a specific sequence in the DNA called the terminator, causing the RNA polymerase to detach and release the newly formed RNA molecule.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase is an enzyme responsible for synthesizing RNA from a DNA template during transcription. It binds to the promoter region of a gene on the DNA molecule and unwinds the DNA helix to begin transcribing the information from the gene into messenger RNA (mRNA). RNA polymerase moves along the DNA strand, adding nucleotides to the growing mRNA chain based on the complementary base pairing with the DNA template. Ultimately, RNA polymerase plays a crucial role in the process of gene expression by transcribing the genetic information stored in DNA into a form that can be used by the cell to produce proteins.
What happens during RNA splicing?
During RNA splicing, introns (non-coding regions) are removed from the pre-mRNA molecule, and exons (coding regions) are connected together to form the mature messenger RNA (mRNA). This process is essential for generating a functional mRNA that can be translated into a protein by the ribosome. RNA splicing is carried out by a molecular complex called the spliceosome, which accurately recognizes splice sites and catalyzes the removal of introns and joining of exons.
What is the function of the 5' cap and poly-A tail in mRNA?
The 5' cap and poly-A tail in mRNA serve important functions in mRNA stability, processing, and translation. The 5' cap protects the mRNA from degradation and facilitates mRNA export from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, while also aiding in ribosome binding during translation. The poly-A tail helps protect the mRNA from degradation, aids in mRNA stability, and acts as a signal for the termination of translation. Together, these structures play crucial roles in regulating gene expression and ensuring proper mRNA function within the cell.
What is the genetic code and how is it used in translation?
The genetic code is a set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA) is translated into proteins. For translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic code from the DNA to the ribosome, where transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules recognize specific codons on the mRNA and deliver the corresponding amino acids. The genetic code dictates the specific relationship between a sequence of three nucleotides (codon) and the amino acid it codes for, allowing the ribosome to link amino acids together in the correct sequence to form a protein during translation.
Explain the process of translation.
Translation is the process of converting the meaning of text from one language (the source language) to another language (the target language). It involves understanding the original text, capturing its intended message and nuances, and then expressing it in the target language while maintaining accuracy and cultural relevance. A translator must have a deep understanding of both languages, as well as cultural nuances, idiomatic expressions, and context to ensure a high-quality and faithful translation. The process may also involve editing, proofreading, and revision to ensure the final translation is accurate and effective.
What is the role of tRNA in translation?
tRNA, or transfer RNA, plays a crucial role in translation by carrying specific amino acids to the ribosome and matching them to the codons on the mRNA strand during the protein synthesis process. Each tRNA molecule is specific to a particular amino acid and contains an anticodon that recognizes and binds to the corresponding mRNA codon through base pairing. This process ensures that the correct amino acids are brought to the ribosome in the correct sequence to assemble a protein according to the genetic code.
What is the significance of post-translational modifications?
Post-translational modifications play a crucial role in regulating protein structure, function, and localization within cells. These modifications can affect protein activity, stability, interactions with other molecules, and subcellular trafficking. They also contribute to a wide range of cellular processes including signal transduction, gene expression, and cell division. Overall, post-translational modifications are essential for the proper functioning of proteins and maintain cellular homeostasis.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments