The Mantle and Convection Currents Worksheet
The Mantle and Convection Currents Worksheet is a valuable educational tool designed to help students understand the role of convection currents in the Earth's mantle. Perfect for middle and high school students studying geology or earth science, this worksheet provides a comprehensive introduction to the subject. With clear instructions and thought-provoking questions, it allows students to explore the concept of convection currents and their impact on the Earth's surface in a structured and engaging way.
Table of Images 👆
- Plate Tectonics Coloring Page
- Tsunami Worksheets High School
- Convection Currents Worksheet
- Convection Currents Worksheet
- Convection Currents Worksheet
- Convection Currents Worksheet
- Convection Currents Worksheet
- Convection Currents Worksheet
- Convection Currents Worksheet
- Convection Currents Worksheet
- Convection Currents Worksheet
- Convection Currents Worksheet
- Convection Currents Worksheet
- Convection Currents Worksheet
- Convection Currents Worksheet
- Convection Currents Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
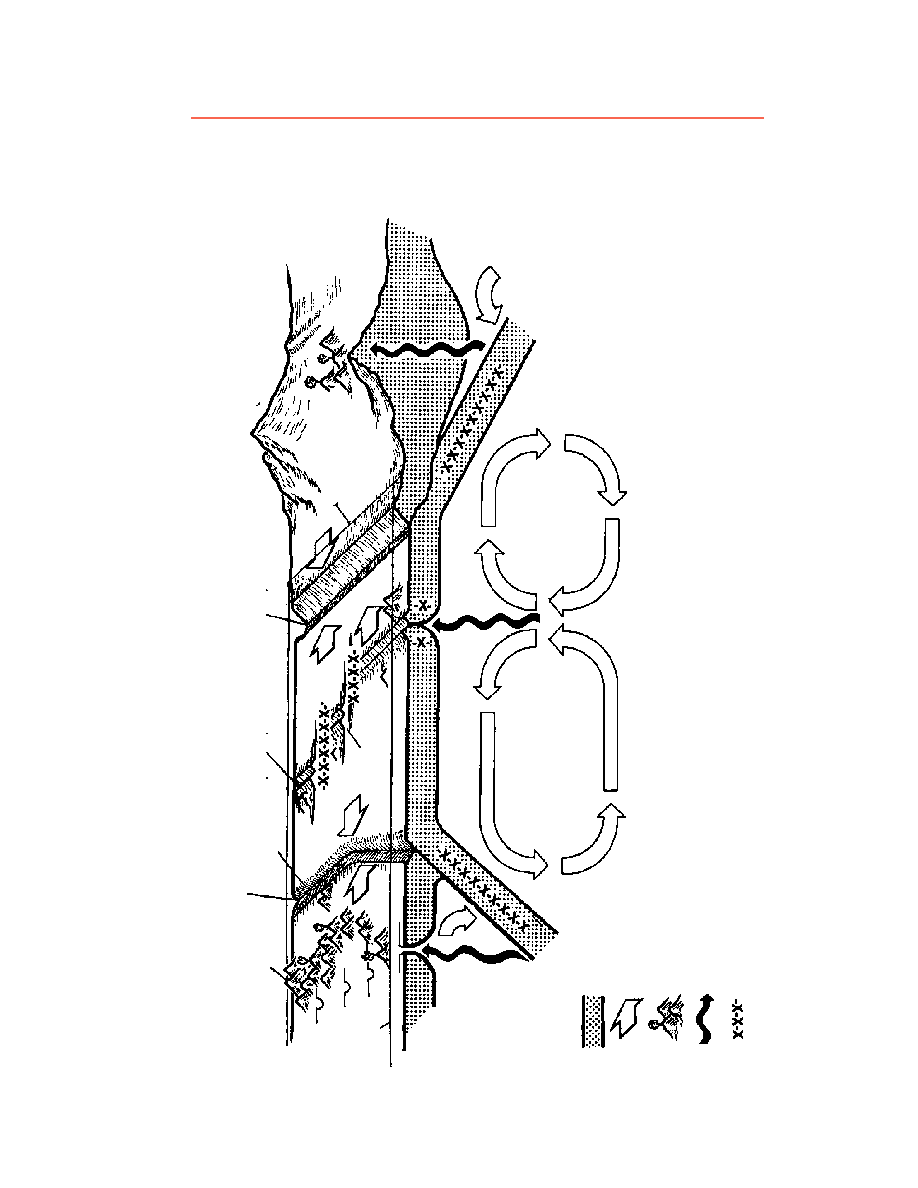
What is the mantle?
The mantle is a layer of the Earth located between the crust and the core. It is primarily made up of solid rock material and is responsible for generating convection currents that drive the movement of tectonic plates. The mantle plays a crucial role in the Earth's geology and the various processes that shape the planet's surface.
What are convection currents?
Convection currents are the movement of fluids, such as air or water, due to differences in temperature and density. As a fluid is heated, it becomes less dense and rises, while cooler, denser fluid sinks. This creates a circular flow pattern, transferring heat energy and leading to the circulation of the fluid. Convection currents play a crucial role in various natural phenomena, such as the formation of weather patterns and ocean currents.
How do convection currents in the mantle work?
Convection currents in the mantle occur due to the heat generated by the Earth's core. Hot material near the core rises, cools as it reaches the top of the mantle, then sinks back down, creating a circular motion. This movement of hot and cold material drives the tectonic plates above, causing them to move and resulting in phenomena like earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the formation of mountain ranges.
What causes convection currents in the mantle?
Convection currents in the mantle are primarily caused by the heat generated from the Earth's core. Radioactive decay and residual heat from the Earth's formation create a temperature difference within the mantle. As the hotter material rises and the cooler material sinks, it sets up a continuous cycle of motion, driving convection currents in the mantle. This movement plays a crucial role in driving plate tectonics and shaping the Earth's surface.
What role do convection currents play in plate tectonics?
Convection currents in the mantle play a crucial role in driving the movement of tectonic plates. As mantle material near the Earth's core heats up, it becomes less dense and rises towards the surface, then cools and sinks back down. This continuous cycle of rising and sinking creates horizontal movement that pushes and drags the overlying tectonic plates, causing them to move and interact with each other. This process, known as mantle convection, is a major driving force behind plate tectonics and leads to phenomena such as seafloor spreading, subduction zones, and the formation of mountains and earthquakes.
How do convection currents affect Earth's crust?
Convection currents play a significant role in shaping Earth's crust by driving the movement of tectonic plates. The heat generated from the Earth's interior causes convection currents in the mantle, which in turn leads to the movement of the rigid outer layer or lithosphere. This movement results in the shifting of tectonic plates, leading to processes like seafloor spreading, subduction, and mountain formation, ultimately influencing the Earth's crust morphology and geological features.
What happens when plates collide due to convection currents?
When plates collide due to convection currents, they can either crumple and push upwards to form mountain ranges, or one plate may slide beneath the other in a process called subduction. Subduction can lead to the formation of deep ocean trenches and volcanic arcs. Collision between plates can also result in the creation of faults and earthquakes due to the immense pressure and stress that builds up at the plate boundaries. Overall, these collisions and interactions between plates are instrumental in shaping the Earth's surface and driving geological processes.
How do convection currents contribute to the formation of volcanoes?
Convection currents play a critical role in the formation of volcanoes by creating movement in the Earth's mantle, causing magma to rise towards the surface. As the magma reaches the crust, it can build up pressure and eventually erupt, forming volcanic mountains and landforms. The continuous movement of convection currents maintains the heat and pressure necessary for volcanic activity, shaping the Earth's surface over time.
What role do convection currents play in the formation of mountain ranges?
Convection currents play a significant role in the formation of mountain ranges by driving the movement of tectonic plates. As hot magma rises and cools beneath the Earth's crust, it creates convection currents that push the tectonic plates apart at divergent boundaries or pull them together at convergent boundaries. This movement can result in the uplifting of land and the formation of mountain ranges through processes like subduction, collision, and crustal thickening.
How do scientists study convection currents in the mantle?
Scientists study convection currents in the mantle through various methods, including seismic imaging, mapping of hotspots, and analyzing the magnetic properties of rocks. Seismic waves generated by earthquakes travel through the Earth's interior and provide information about temperature variations and movement of materials within the mantle. Hotspots on the Earth's surface indicate areas of upwelling magma due to mantle convection, while magnetic properties of rocks reveal past movements and changes in the Earth's magnetic field associated with convection currents. By combining these methods, scientists gain a better understanding of the complex dynamics of convection in the mantle.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


















Comments